B2.3 Cell Specialisation
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Zygote
Fertilised egg cell
Morula
Solid ball of cells formed from divisions.
The cell continues to divide and after 5-6 days, it will start to differentiate into a hallow ball of cells called _______ . This contains an outer layer of cells called ________
blastocyst, trophoblast
Alleles
A variant/version of a gene
Differentiation
Cells are specialised to carry out specific functions
Morphogens
Chemical in the cell governing the pattern of tissue development
Totipotent Cells
Cells that can divide and generate an entire organism
Pluripotent
Cells that can generate multiple types of cells of an organism.
Multipotent
Cells that can generate many cells of an organism.
Stem Cell Niche
Microenvironment in which the stem cells exist and receive instructions.
Haemoglobin
Iron-containing proteins within red blood cells (helps give blood the red pigment as well)
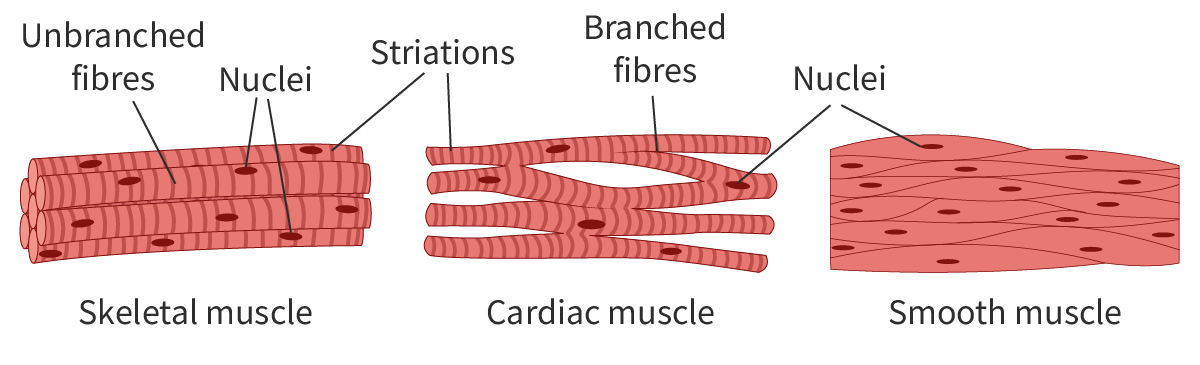
Types of muscles
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth
Compare and Contrast toti, multi and pluripotent
Toti. | Multi. | Pluri. | |
|---|---|---|---|
Similarities | unspecialised cell | unspecialised cell | unspecialised cell |
Differences | can give rise to both embryonic and extraembryonic tissues | typically found in adult tissues | differentiated in only embryonic tissues |
Feature of surfactant
(is a lipoprotein complex) reduces surface tension in alveoli
Size of sperm
3–5 μm length
Size of female egg
0.12 mm in diameter
Size of red and white blood cells
Red: 7.5 µm diametre, 2 µm thick
White: 10 to 20 µm
Size of neurons and striated muscle fibres
Neuron: <1mm
Striated muscle fibres: 1-40mm long, 10-100 µm in diametre
Length of sciatic nerve
> 1m
Explain the adaptations of flattening of cells to increase SA:V ratios in cells
Squamous epithelial cells are thin, flat, and horizontal or elliptical in shape
Found in locations such as alveoli of the lungs, kidney tubules, and capillaries
Facilitate diffusion of molecules, including gas exchange and nutrient transfer
Explain the adaptations of invaginations to increase SA:V ratios in cells
Mitochondria, generate ATP
They contain numerous invaginations of the inner membrane (cristae) enabling increased metabolic reactions to take place
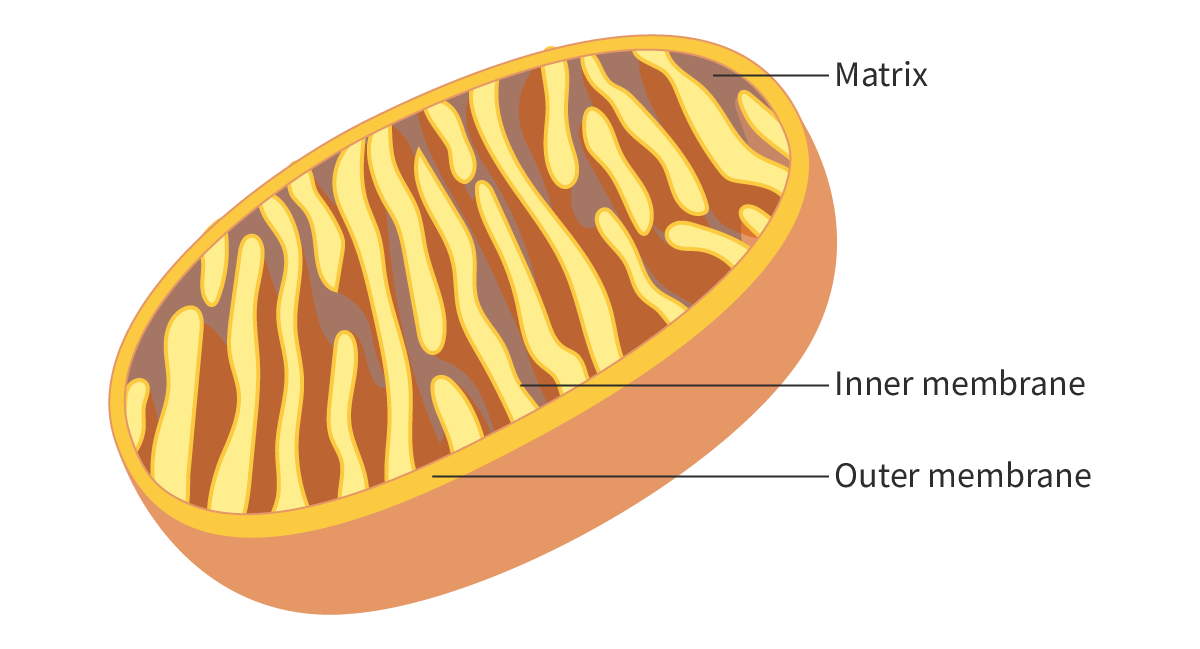
Invagination
Process of folding in on itself to form a cavity, pouch or tube
Explain the adaptations of chloroplasts to increase SA:V ratios in cells
Have multiple membranes, enabling more reactions to occur
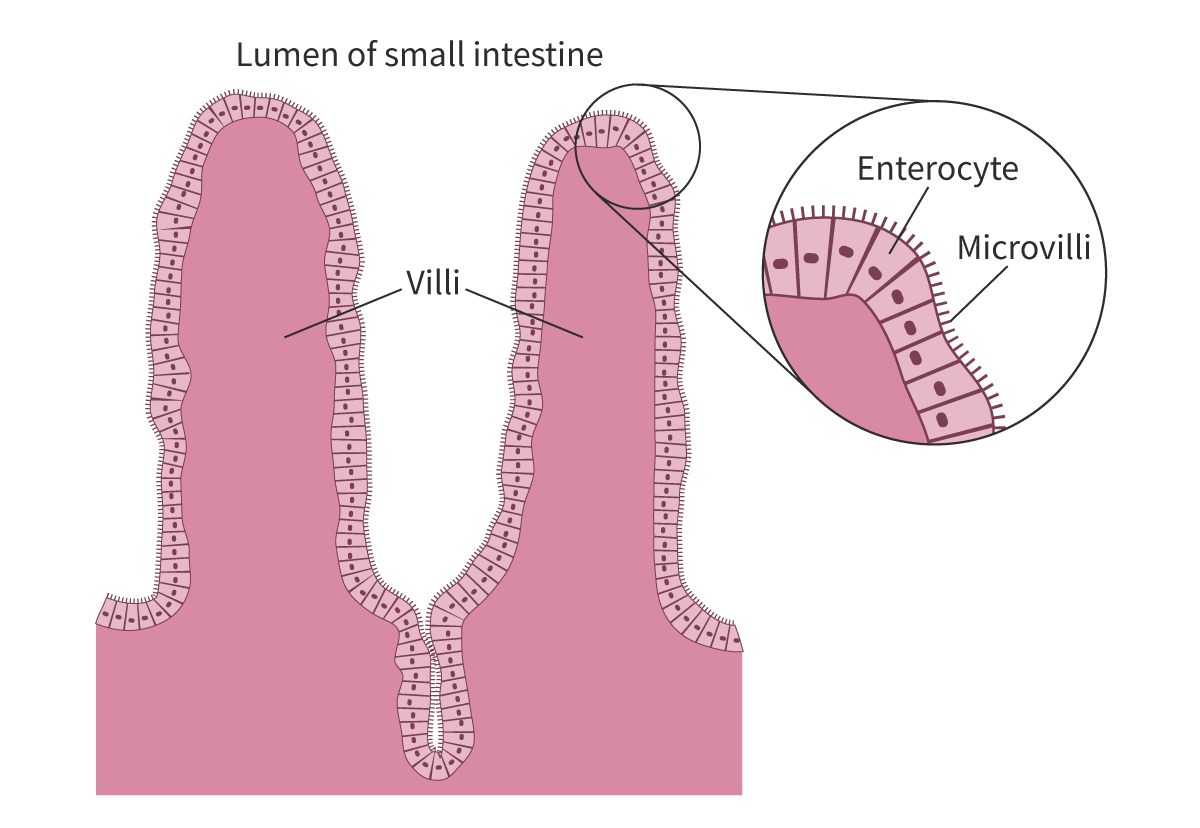
Explain the adaptations of microvilli to increase SA:V ratios in cells
Columnar cell has these
Forms a brush border of the small intestine
Facilitate max absorption possible in intestine
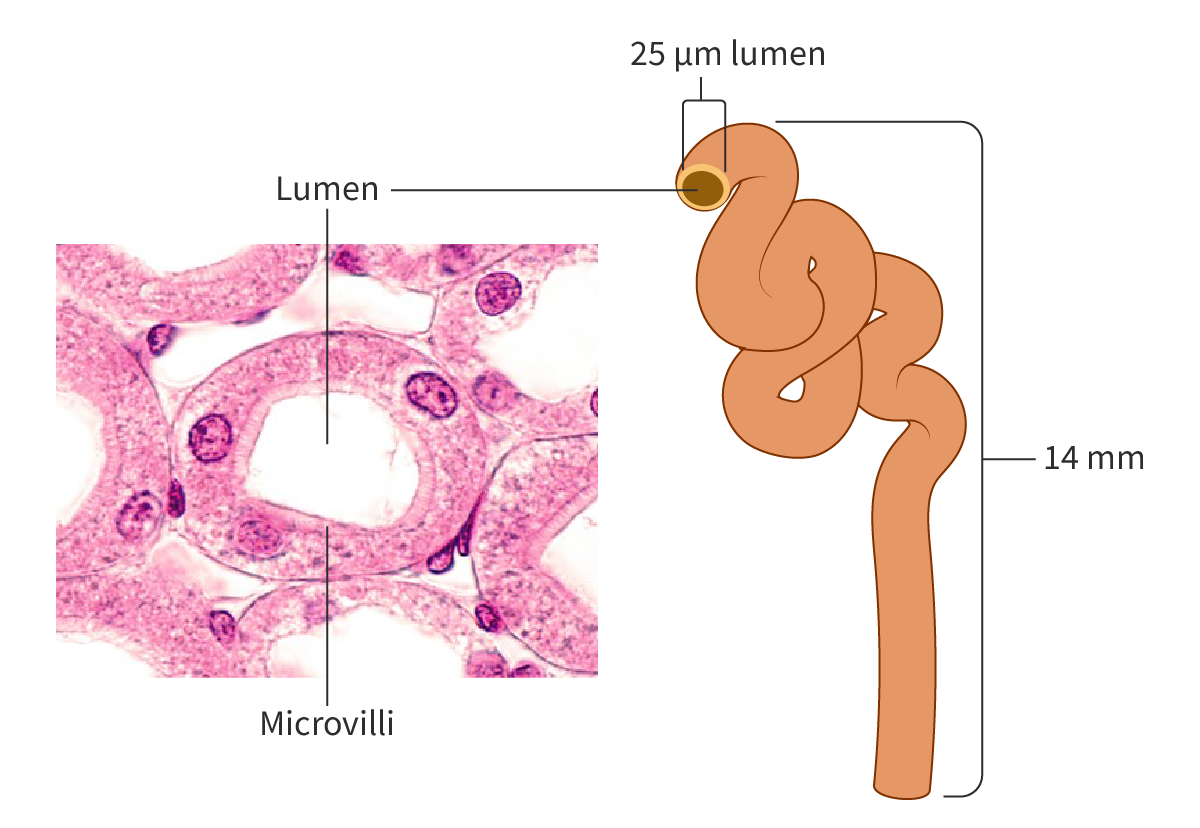
Explain the adaptations of proximal convuluted tubule to increase SA:V ratios in cells
Lining has cuboidal-shaped cells with microvilli to increase absorption of substances
Type I pneumocytes
Extreme thinness of cells in lungs to reduce distances for diffusion for gas exchange
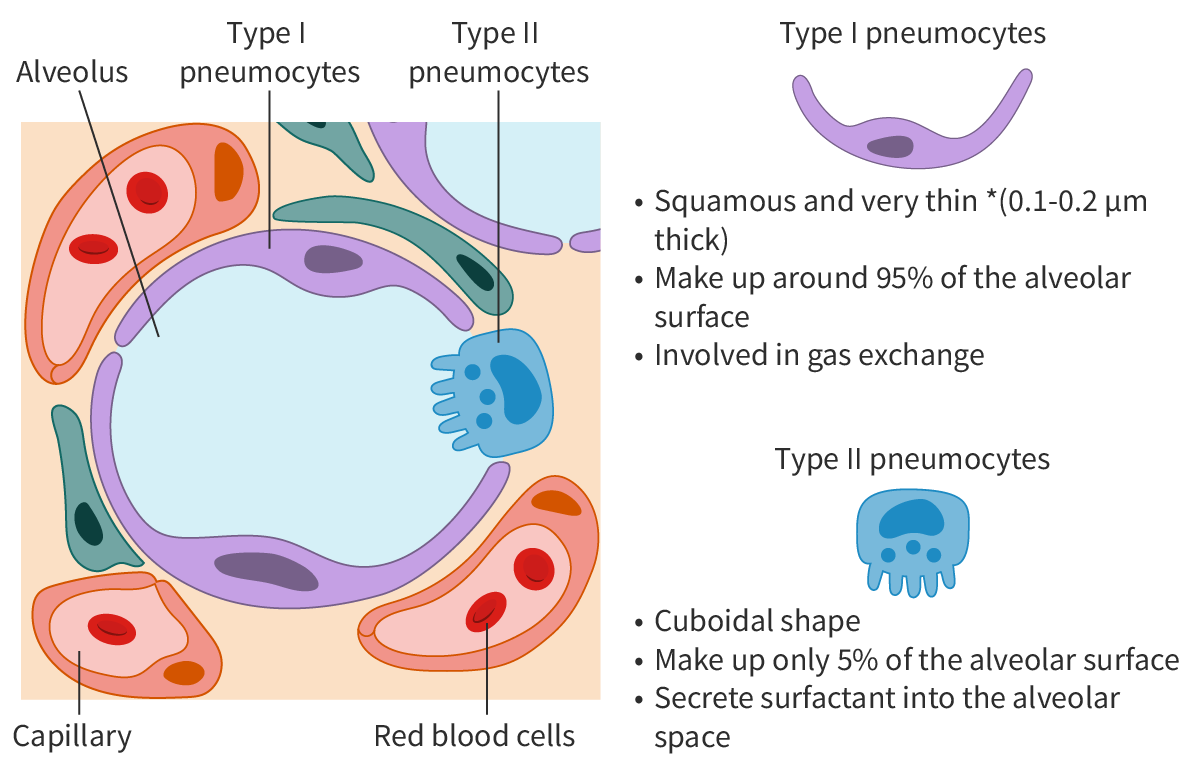
Type II pneumocytes
Presence of many lamellar bodies (secretory vesicles) in cytoplasm
Cuboidal cells of the lung that secrete surfactant
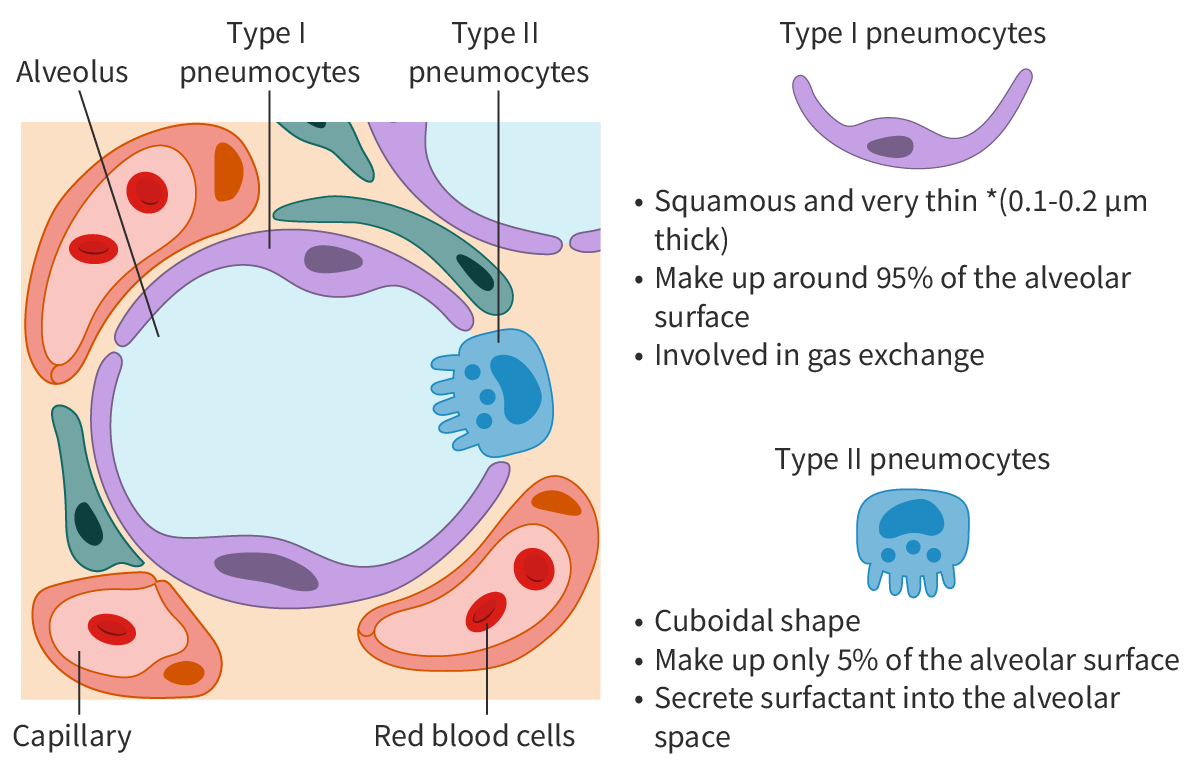
Alveolar epithelieum
A tissue that has more than one cell type because different adaptaitions are required for the overall function of tissue
Sacromeres
Unit of a muscle containing actin and myosin
Striated
Shapes that are long, thin streaks
Cardiac cells
Form the contractile walls in the heart
Have a single nucleus, contain many mitochondria and have branched fibres
Skeletal cells
up to 12cm
Attached to bones, and is responsible for moving the skeleton as the muscle contracts and relaxes
Branches of the muscle types
Skeletal: UNbranch
Cardiac: Branched
Compare and contrast cardiac and striated muscles
SIMILARITIES
both contain myofibrils
DIFFERENCES
cardiac muscle cells are branched whereas striated muscle cells unbranched
cardiac muscle cells are shorter than striated muscle cells;
cardiac muscle cells have one nucleus but striated muscle cells have many nuclei/ are multinucleated;
Adaptations of sperm and egg cells
SPERM
Being motile
Contain mitochondria for energy
EGG
Has several specialised layers of cells covering the outside, prevents polyspermy
State why cell length and volume ratios are not constant for all cell types
Cell shape is not constant
Cell shape is related to function
Role of stem cells
Retain the ability to divide
Divide by mitosis
Division produces new tissue
Can replace stem cells