DMUT2020- quality assurance and bioeffects/safety
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is quality assurance?
routine, periodic evaluation of an ultrasound system to guarantee optimal image quality and ensure excellence in healthcare
What is quality control?
Part of a quality assurance program that deals with instrumentation and equipment
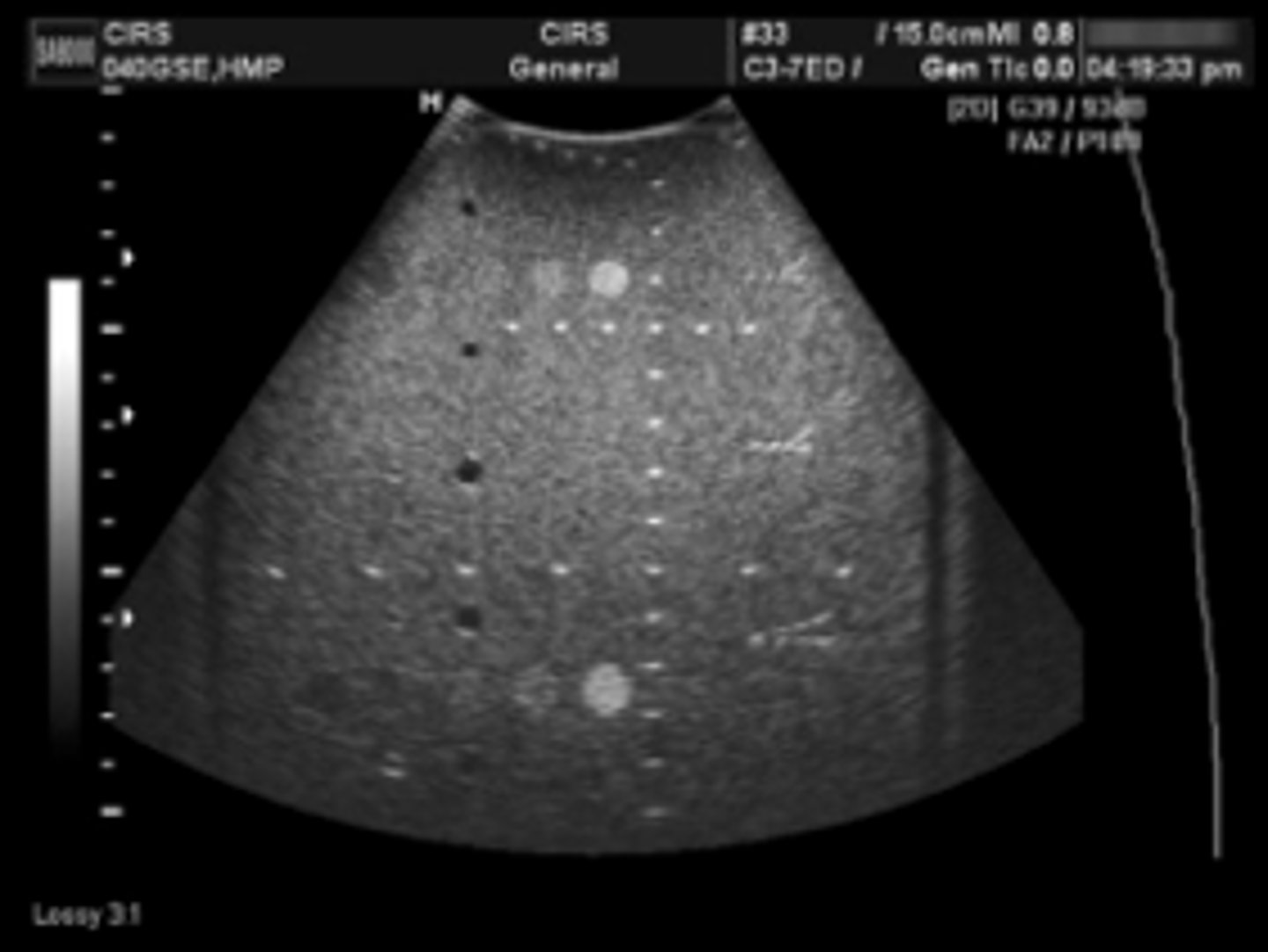
How are ultrasound systems tested?
Using a tissue equivalent phantom
What is a hydrophone?
A small transducer element on a hollow needle is used to measure the acoustic output

What material is used for a hydrophone? Why?
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) because of its wide bandwidth
List the imaging systems from lowest acoustic output to highest
B-mode (2D), M-mode, colour doppler, pulsed wave doppler
What is a tissue equivalent phantom made of?
Water-based gelatin with graphite and nylon-line targets throughout to mimic tissue with a propagation speed of 1540 m/s
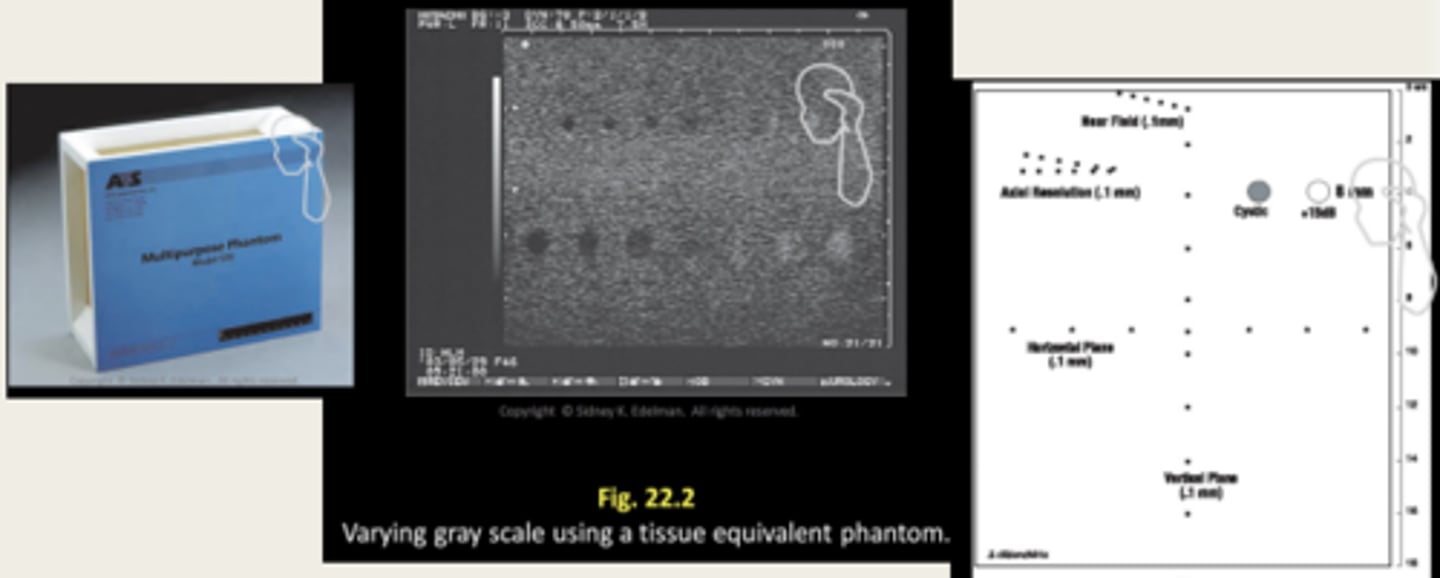
Tissue equivalent phantom: System sensitivity
The maximum depth that an echo signal can be detected and clearly displayed (maximum depth of visualization)
Tissue equivalent phantom: Image uniformity
Uniform brightness throughout when the system's gain settings are set properly
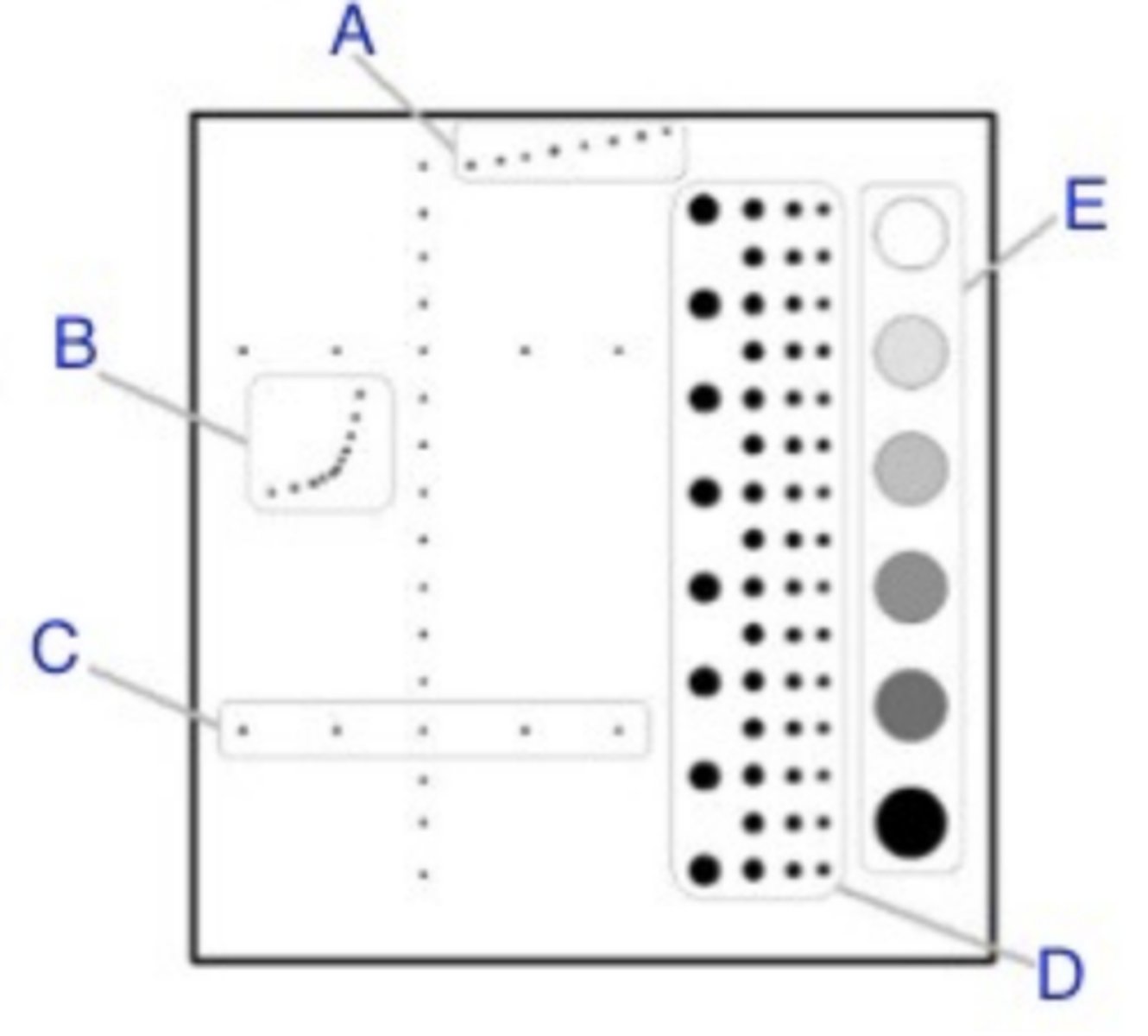
Tissue equivalent phantom: Dead zone
A. The distance from the front face of the transducer to the first identifiable echo at the phantom interface, no clinical data can be collected from this region. If the depth is too large, corrective action has to be considered.
How can dead zone be prevented?
By using an acoustic standoff
Tissue equivalent phantom: Resolution
The minimum reflector separation between two closely spaced objects which can be imaged separately. Poor resolution= small structures will appear as one
Tissue equivalent phantom: Axial resolution
The minimum VERTICAL reflector separation which can be distinguished
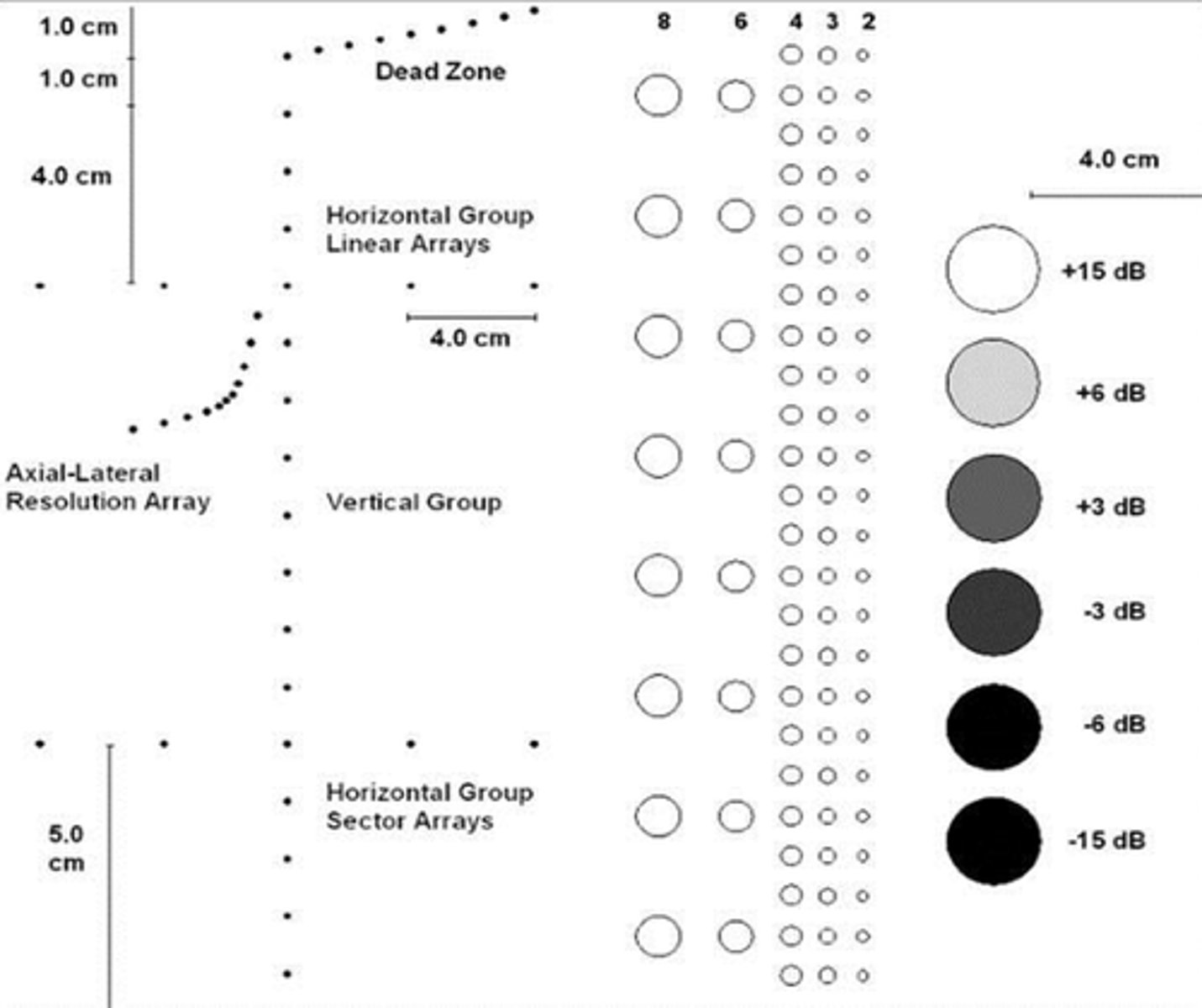
Tissue equivalent phantom: Lateral resolution
Resolution perpendicular to the sound beam (across). Dependent on the beam width: increased beam width=reduced lateral resolution
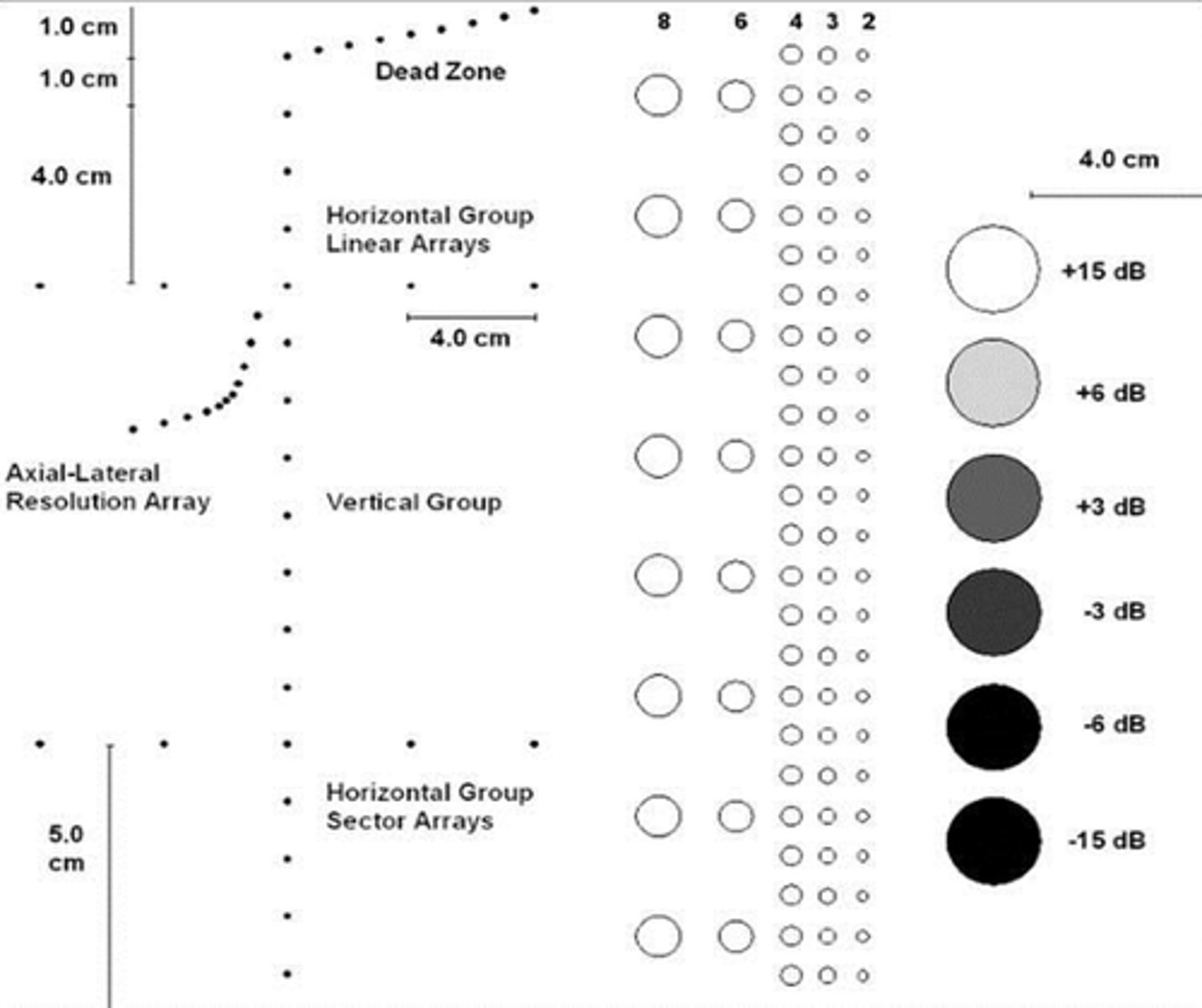
Tissue equivalent phantom: Vertical measurement accuracy
Used to measure depth calibration accuracy. The distance between several (vertically placed) rods are measured and compared with the actual distance given by the manufacturer. Difference >1mm warrants correction
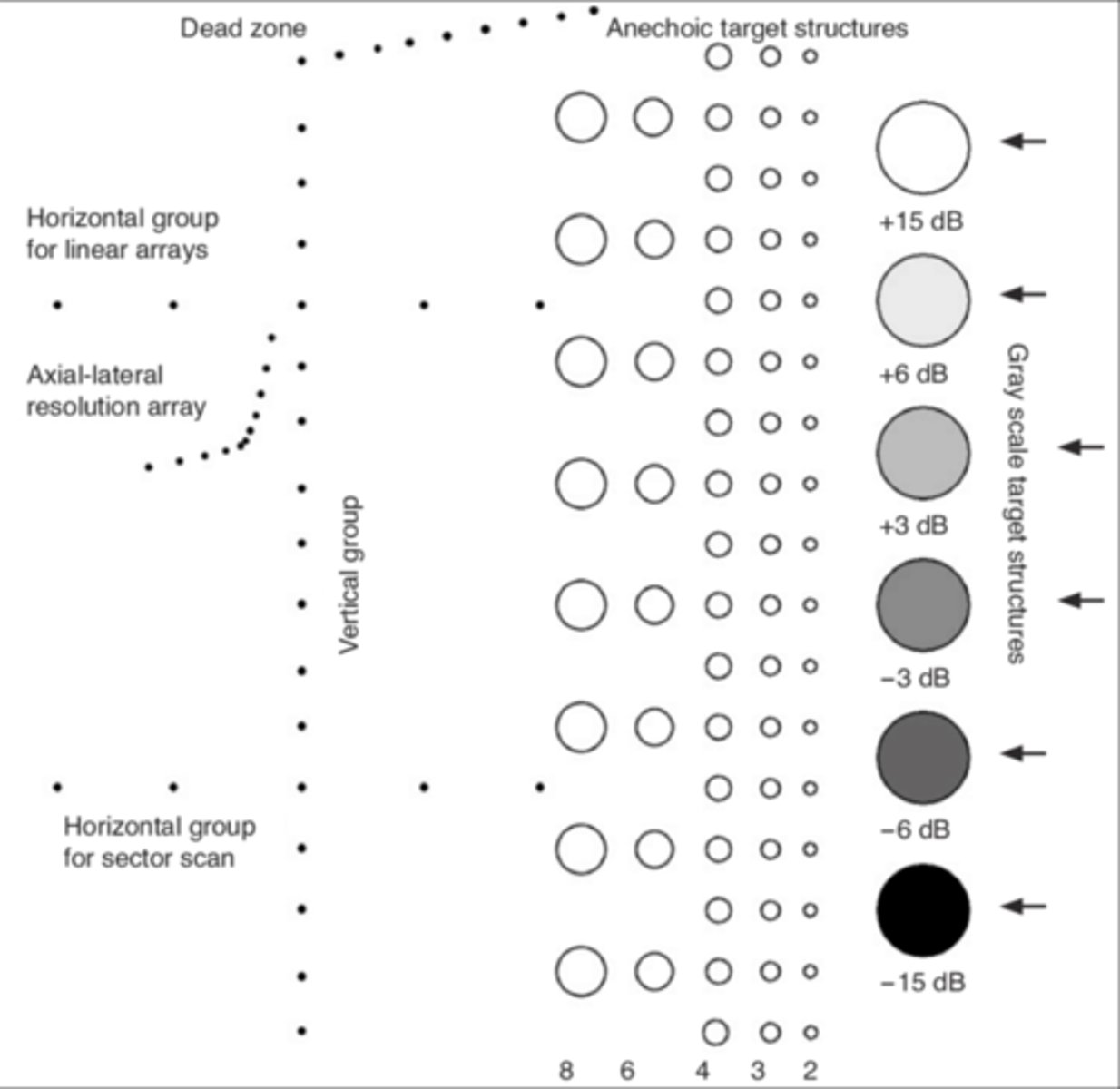
Tissue equivalent phantom: Horizontal measurement accuracy
The distance between several rods (lined perpendicular to the sound beam: horizontal) are measured and compared with the actual distance given by the manufacturer. Difference >2mm warrants correction
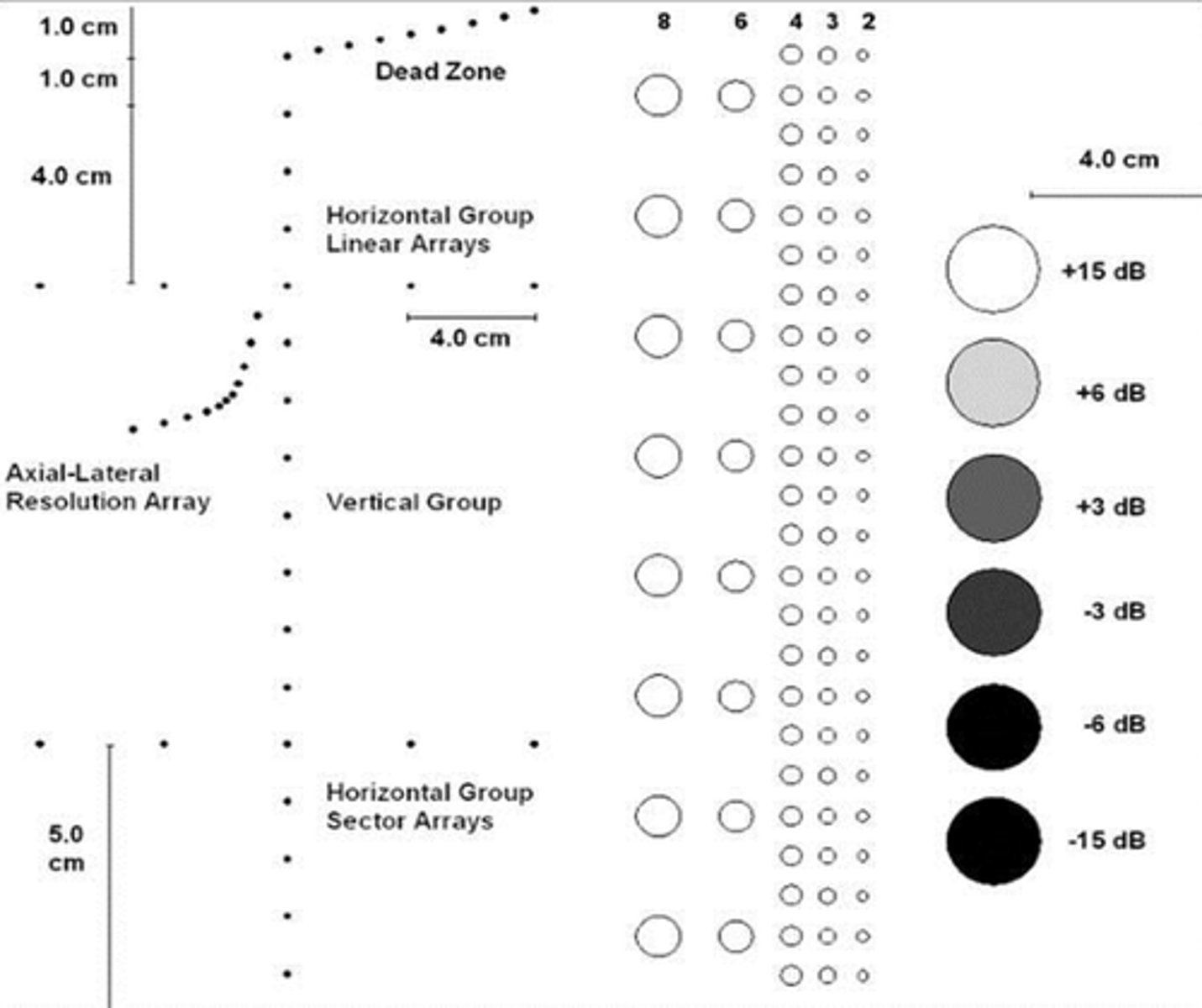
Are vertical or horizontal measurements usually more accurate and why?
Vertical because axial resolution is generally superior to lateral resolution
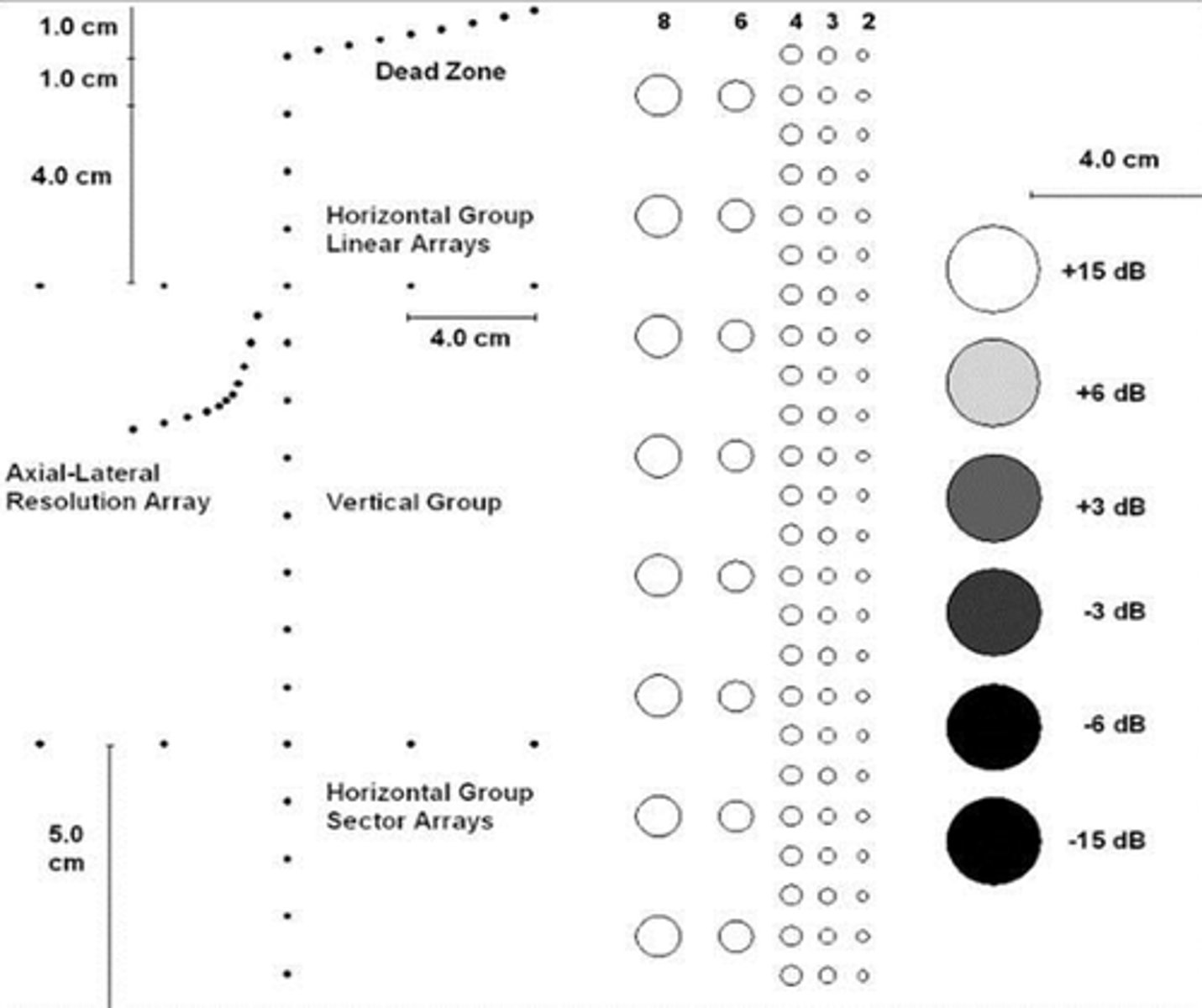
Tissue equivalent phantom: Focal lesion resolution
The focal zone is the region around the focal point where the intensity and lateral resolution are the greatest. Cysts and tumours with in the phantom represent realistic imaging tasks and can demonstrate the system's resolution capability.
Tissue equivalent phantom: contrast resolution
Ability to distinguish echoes of slightly different intensities (dB)
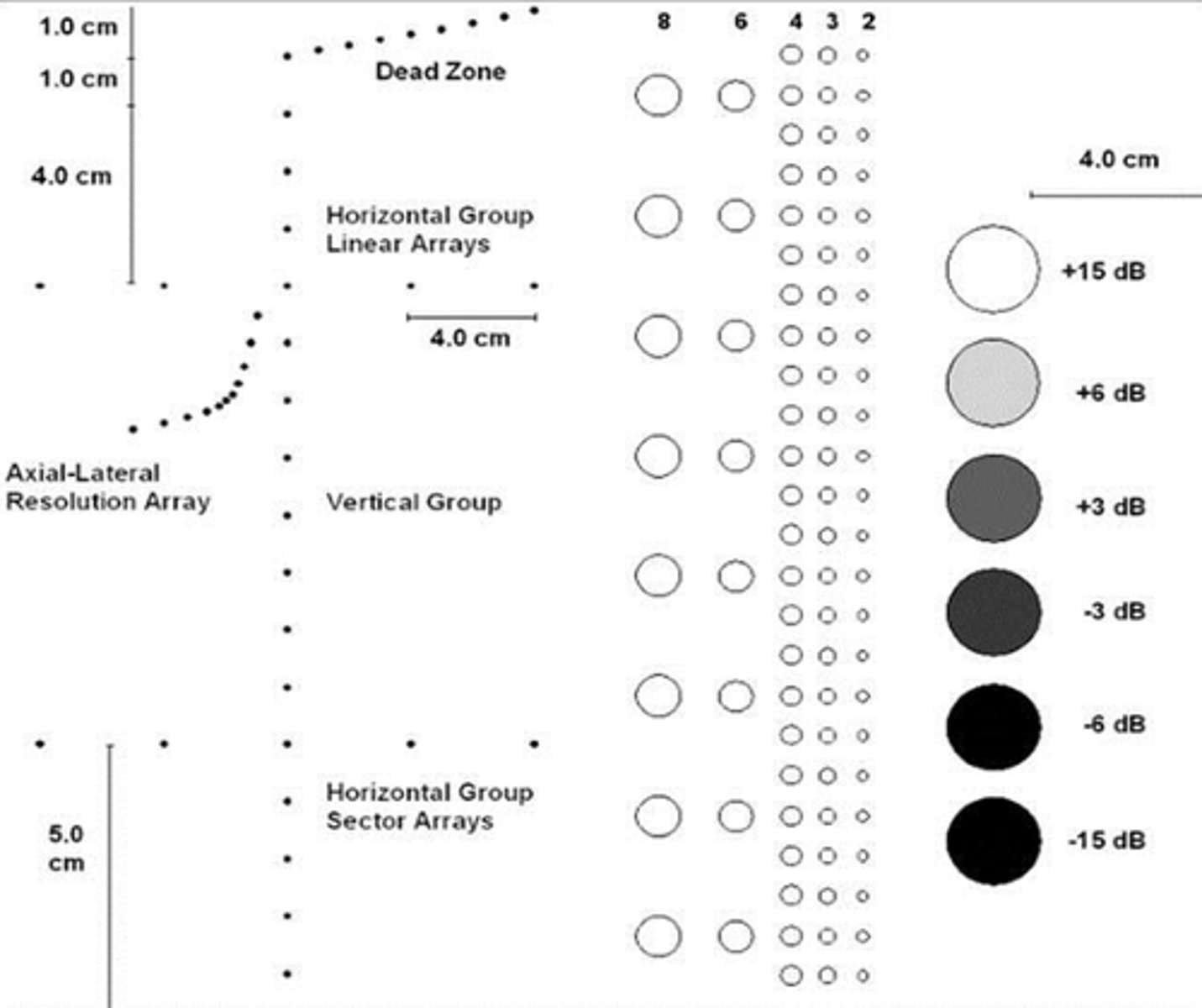
Test objects
Do not simulate tissue but do provide specific measurements of instrument performance
How is doppler testing performed?
A Doppler test object use a moving solid object (usually on a string). A Doppler flow phantom uses a flowing blood-like liquid to evaluate the Doppler instrumentation
What is a true test result?
When the test matches the gold standard
True positive vs. true negative
TP test is when the test matches the gold standard and is positive for disease. TN test is when the test matched the gold standard and is negative for disease
False positive vs. false negative
FP test is when the test does not match the gold standard and shows positive for disease. FN is when the test does not match the gold standard and shows negative for disease
What is sensitivity?
The ability to detect disease when it is actually present (shows how sensitive a test is to the presence of disease)
What is specificity?
The ability to determine that a test is normal (negative) when there is no disease (shows how specific a test is in separating normals from patients with disease)
What is a positive predictive value?
The likelihood that a positive test is actually a true positive
What is a negative predictive value?
The likelihood that a normal test is actually a true normal
What is diagnostic accuracy?
An overall measure of how frequently the test and gold standard are in agreement (percentage of how often the test results are correct)
What is prevalence?
The percentage of patient evaluated who have disease present according to the gold standard
What system adjustments affect the TI?
Output power, focus (number), M-mode, Doppler
What is TI?
Thermal index- the potential for tissue heating (relative probability that a system could induce thermal injury)
When are temperature increases considered significant?
More than 2 degrees celsius
What tissue has the highest absorption coefficient?
Bone
What does tissue temperature increase depend on?
Output characteristics and tissue properties
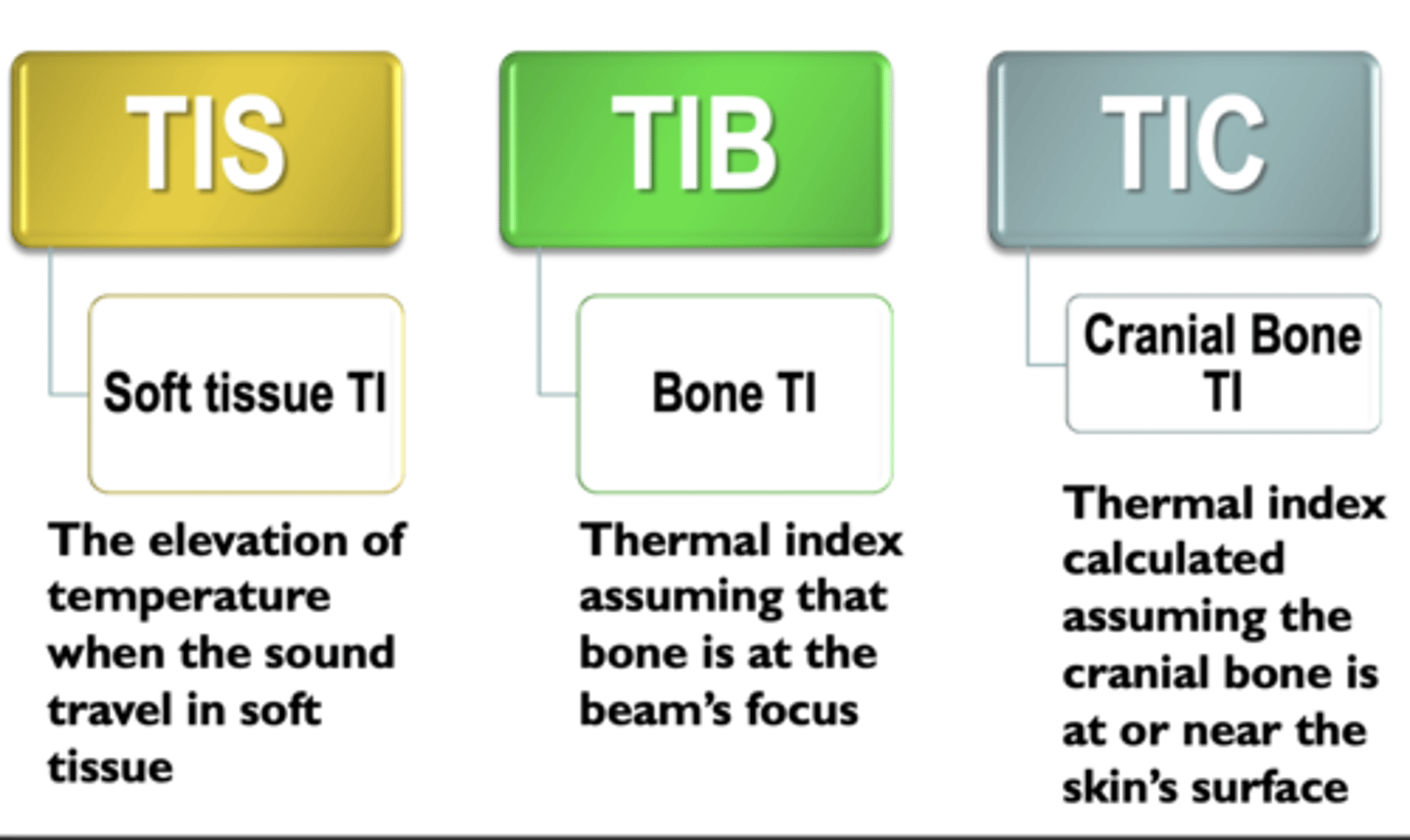
TIS vs TIB vs TIC
Thermal index for soft tissue- when the beam travels through soft tissue and not bone, bone- focus is at or near bone, cranial- scanning with transducer near bone
What do mechanical (non-thermal) mechanisms depends on?
Radiation force (force exerted by the sound beam), streaming (shear stress on cells) and cavitation (production and behaviour of bubbles in a liquid medium)
Stable cavitation
bubbles oscillate in size in response to pressure changes, but do not burst
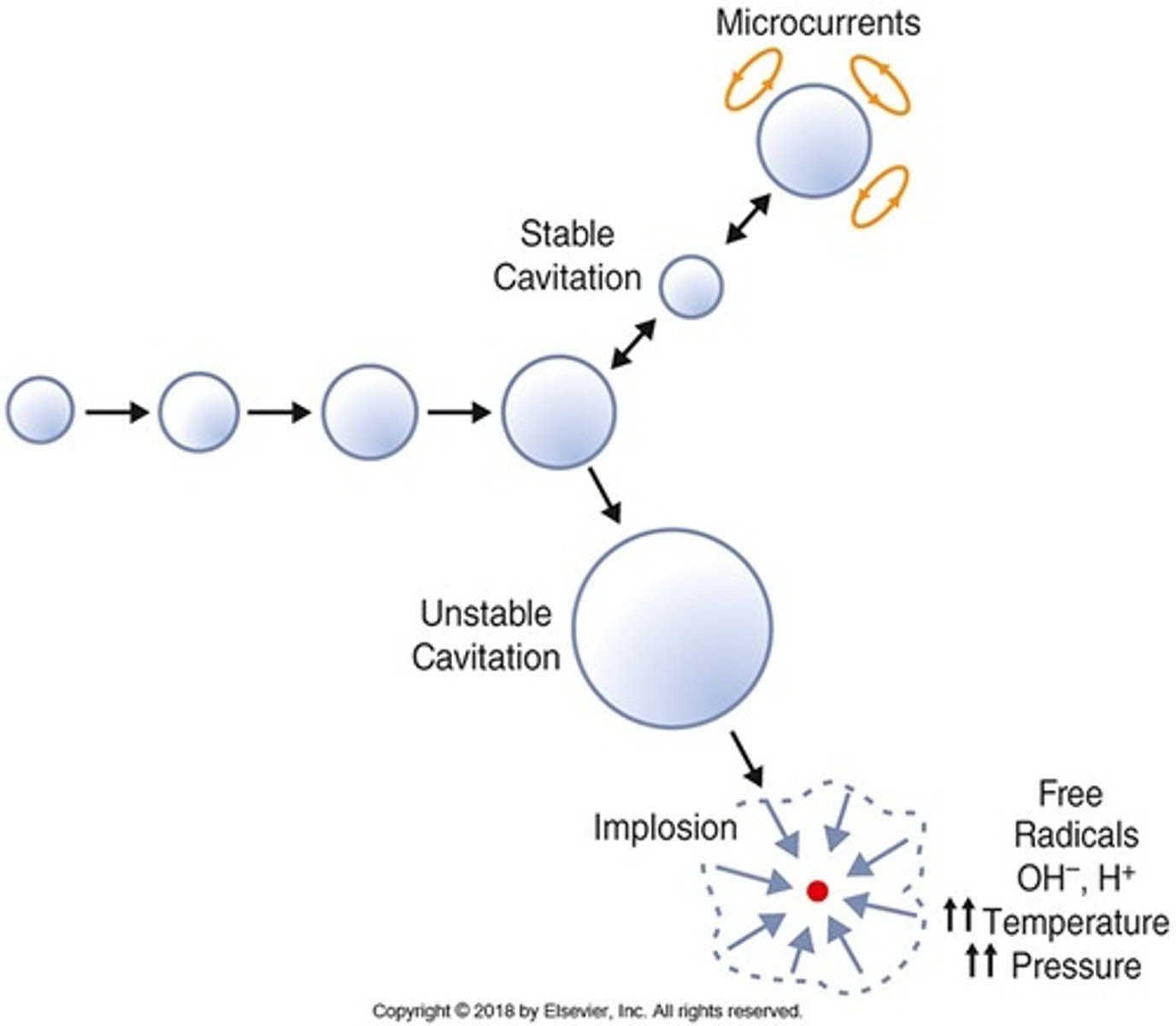
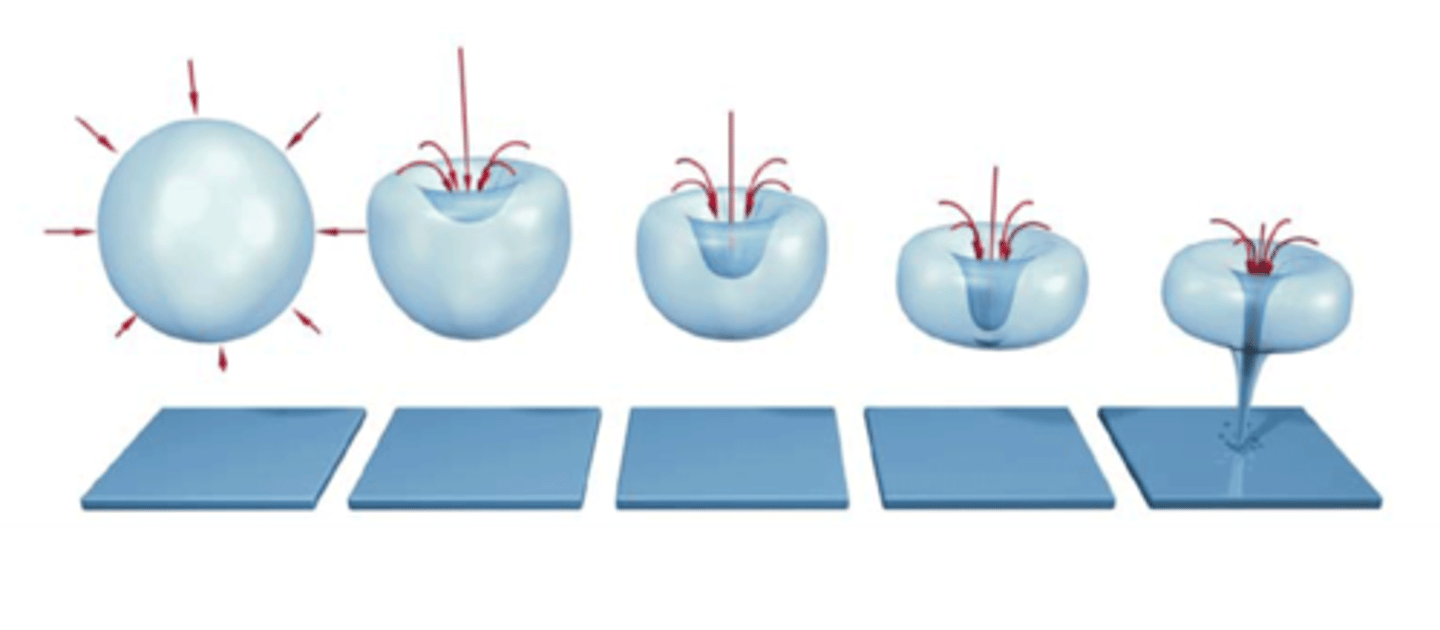
Transient cavitation
Bubble oscillations become large -> bubbles collapse -> shock waves -> high temperatures -> tissue damage
What is MI?
The likelihood of cavitation-related adverse biological effects
What is the maximum MI for tissues with gas bodies?
<1.9
What contemporary feature carries potential for non-thermal bioeffects?
Contrast agents
What form of intensity needs to be considered most for bioeffects?
SPTA- spatial peak temporal average
For an unfocused beam, what is the maximum SPTA intensity? For a focused beam?
Below 100 mW/cm^2. Less than 1W/cm^2
According to AIUM statements, what MI value for tissue with gas-bodies does not have bioeffect? Tissue without gas-bodies?
With= less than 0.4. Without= less than 4.0
What is the maximum TI value for unlimited time scanning of OB, neonatal transcranial and neonatal spine?
0.7
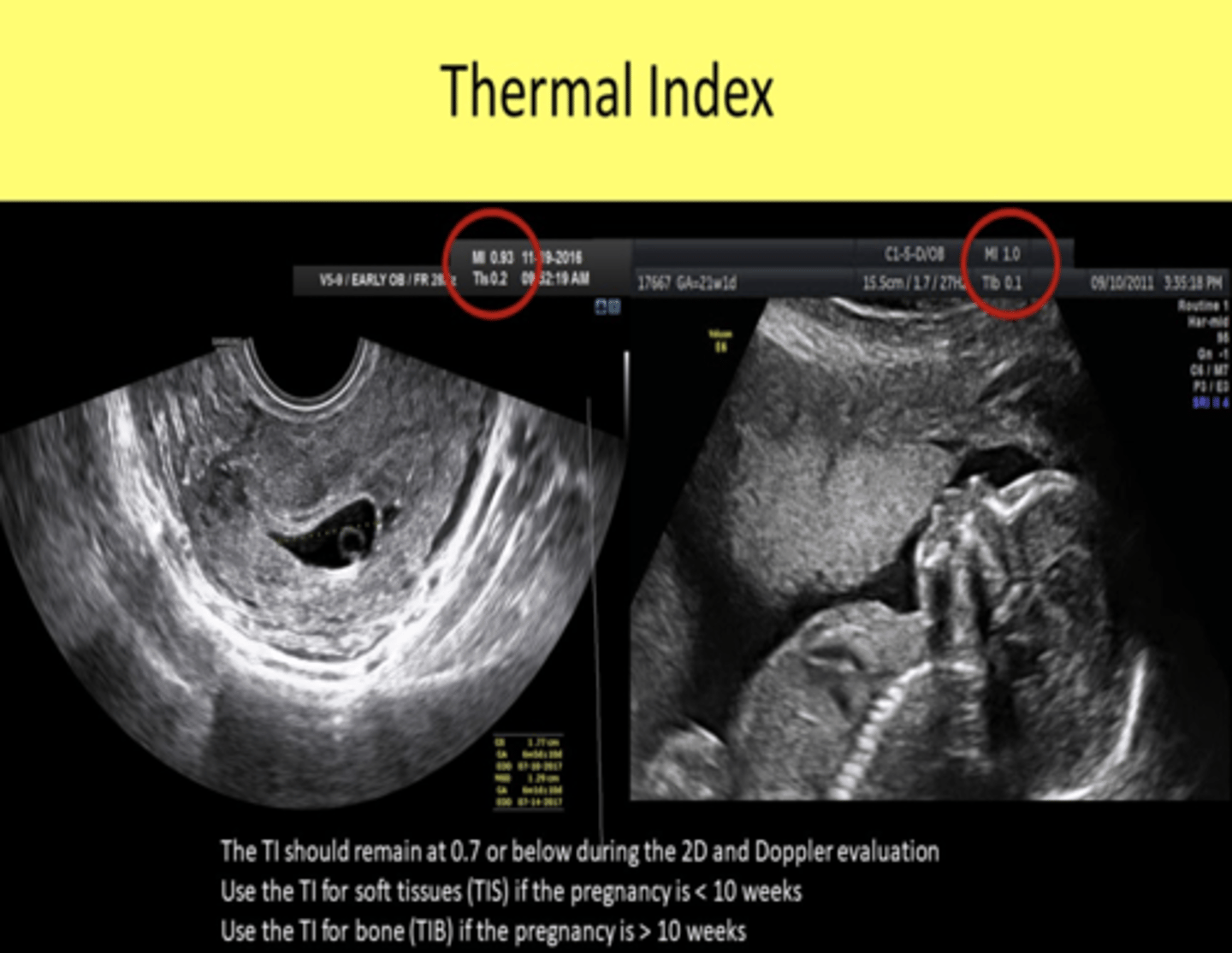
For obstetric exams, when is TIS vs TIB monitored?
Before 10 weeks from LMP -> TIS
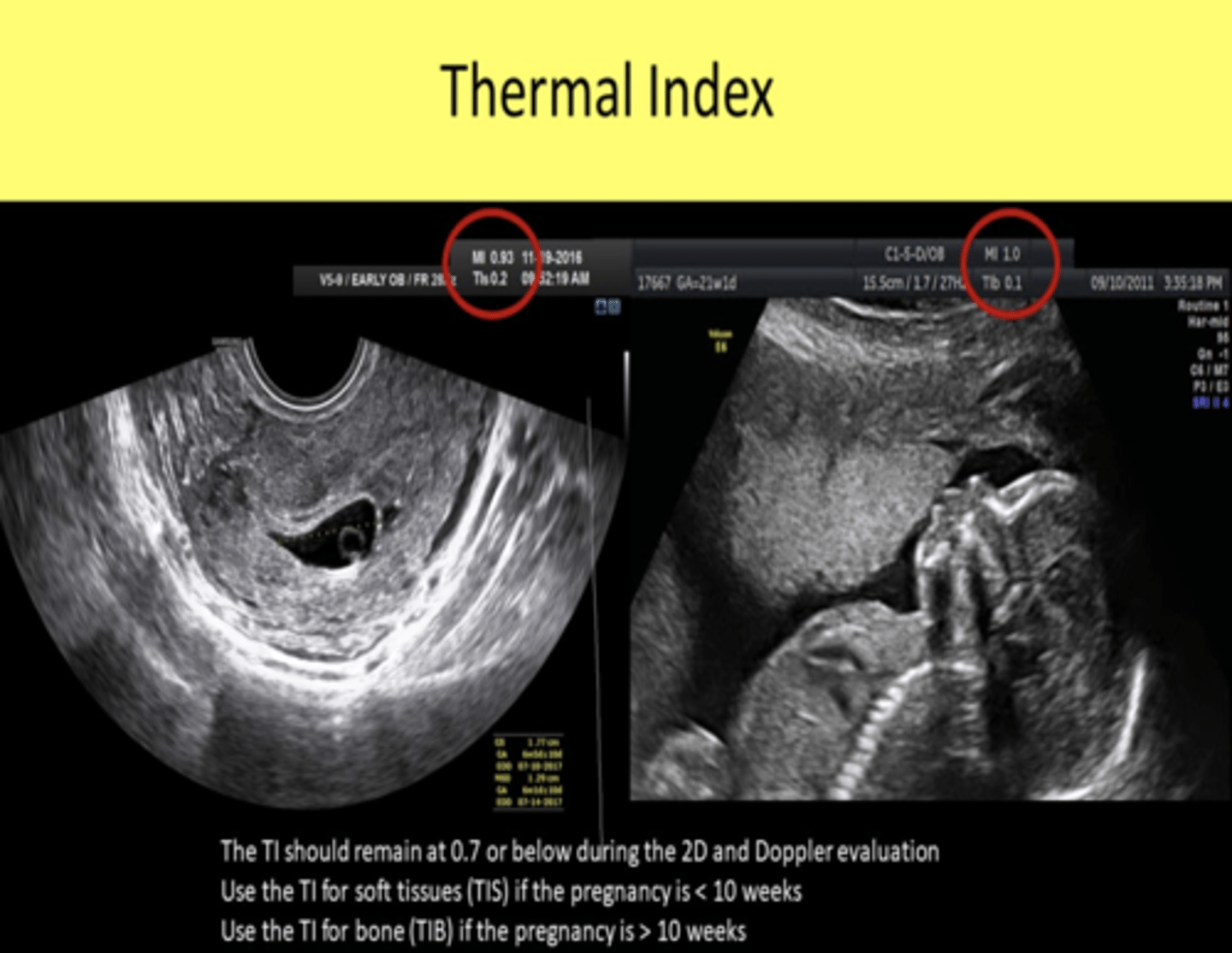
What is the maximum TI value for unlimited time scanning of all adult and neonatal (except the eye)?
1.5
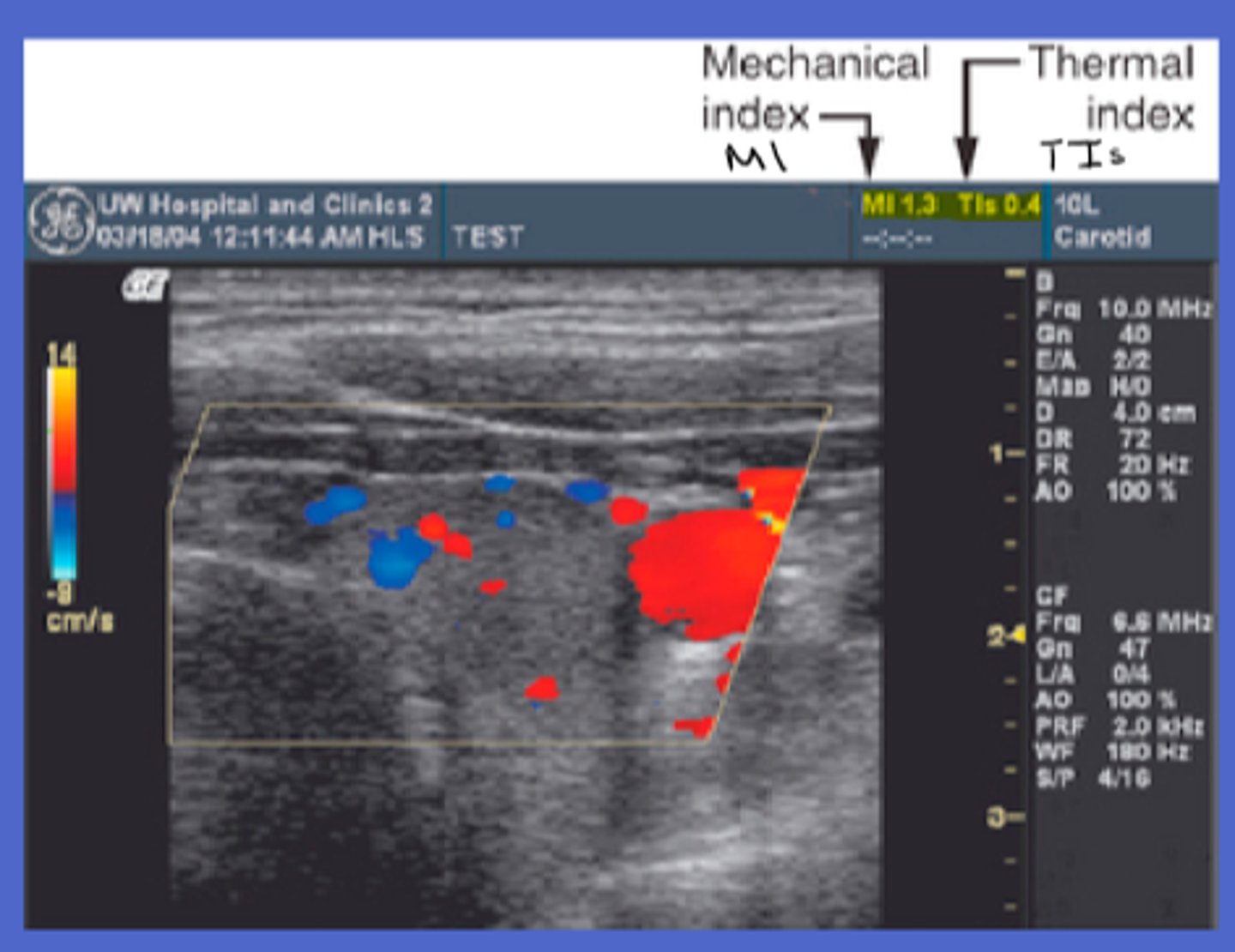
What is ALARA?
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
ALARA principles
Keep exposure to minimum, keep acoustic output to minimum, use only when medically indicated, potential risks/benefits should be considered
Electrical hazards may be due to?
The transducer holds the most likely component for electrical harm as it has direct contact with the patient