Exam 3
1/371
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
372 Terms
Temazepam brand
Restoril
Temazepam class
Benzodiazepine
Temazepam use
Insomnia
Temazepam MOA
Binds to benzodiazepine receptors, enhances GABA effects
Temazepam dose
7.5-30 mg PO qHS PRN
Temazepam contraindications
Avoid abrupt withdrawal
Temazepam BBW
Use with opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, or death
Clonazepam brand
Klonopin
Clonazepam class
Benzodiazepine
Clonazepam use
Seizure disorders, panic disorder
Clonazepam MOA
Binds to benzodiazepine receptors, enhances GABA effects
Clonazepam dose
0.5-5 mg PO TID
Clonazepam contraindications
Hepatic impairment, avoid abrupt withdrawal
Clonazepam BBW
Use with opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, or death
Lorazepam brand
Ativan
Lorazepam class
Benzodiazepine
Lorazepam use
Anxiety, status epilepticus
Lorazepam MOA
Binds to benzodiazepine receptors, enhancing GABA effects
Lorazepam dose
2-6 mg PO/IM/IV divided BID or TID
Lorazepam contraindications
Sensitivity to polyethylene glycol, respiratory impairment, sleep apnea, avoid abrupt withdrawal
Lorazepam BBW
Use with opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, or death
Diazepam brand
Valium, Diastat
Diazepam class
Benzodiazepine
Diazepam use
Seizure disorders, anxiety, sedation
Diazepam MOA
Binds to benzodiazepine receptors, enhances GABA effects
Diazepam dose
2-10 mg PO BID-QID or 5-10 mg IM/IV q3-4h
Diazepam contraindications
Avoid abrupt withdrawal
Diazepam BBW
Use with opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, or death
Alprazolam brand
Xanax
Alprazolam class
Benzodiazepine
Alprazolam use
Anxiety, panic disorder
Alprazolam MOA
Binds to benzodiazepine receptors, enhances GABA effects
Alprazolam dose
IR: 0.5-3 mg PO TID, ER: 3-6 mg PO qD
Alprazolam contraindications
Avoid abrupt withdrawal
Alprazolam BBW
Use with opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, or death
Trazodone brand
Trazodone
Trazodone class
Serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressant
Trazodone use
Major depressive disorder, insomnia
Trazodone MOA
Antagonizes serotonin 5-HT2A/C and alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, inhibits serotonin reuptake
Trazodone dose
50-100 mg PO BID or TID
Trazodone contraindications
Avoid abrupt withdrawal
Trazodone BBW
May cause suicidal thoughts in children and young adults
Hydroxyzine brand
Atarax, Vistaril
Hydroxyzine class
H1 antihistamine
Hydroxyzine use
Anxiety, pruritus, urticaria
Hydroxyzine MOA
Non selectively antagonizes central and peripheral histamine H1 receptors
Hydroxyzine dose
25-100 mg PO/IM q4-6h PRN
Hydroxyzine contraindications
QT prolongation, hypersensitivity to cetirizine or levocetirizine
Hydroxyzine BBW
None
Zolpidem brand
Ambien
Zolpidem class
Anxiolytic, hypnotic
Zolpidem use
Short term insomnia
Zolpidem MOA
Interacts with GABA-benzodiazepine receptor complexes
Zolpidem dose
IR: 5-10 mg PO qHS, ER: 6.25-12.5 mg PO qHS
Zolpidem contraindications
Alcohol use, hepatic impairment, history of complex sleep behavior
Zolpidem BBW
Complex sleep behaviors may occur including sleep walking, sleep driving, and other activities
Ramelteon brand
Rozerem
Ramelteon class
Sedative/hypnotic, melatonin receptor agonist
Ramelteon use
Delirium
Ramelteon MOA
Potent selective agonist of melatonin receptors (MT1, MT2), little affinity for MT3, acts within the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus
Ramelteon dose
8 mg PO within 30 minutes of bedtime
Ramelteon contraindications
Avoid alcohol
Ramelteon BBW
None
Eszopiclone brand
Lunesta
Eszopiclone class
Non-benzodiazepine hypnotic
Eszopiclone use
Insomnia
Eszopiclone MOA
Interacts with GABA-receptor complexes coupled to binding domains close to benzodiazepine receptors
Eszopiclone dose
1-3 mg PO qHS
Eszopiclone contraindications
Use with caution in patients with a history of drug dependence
Ezoclipone BBW
None
In general what is the order of effect as the dose of CNS depressants increase?
Sedation → Hypnosis → Anesthesia
What effect does an anxiolytic have?
Mild calming effect
What effect does a sedative have?
Greater calming effect which typically includes drowsiness
What effect do hypnotics have?
Induce and sustain sleep from which the patient can be aroused
What effect do anesthetics have?
Intense, non-selective CNS depression which requires the removal of drug for patient arousal
What is the MOA of benzodiazepines?
Cause conformational change in receptor which leads to greater frequency of GABA binding
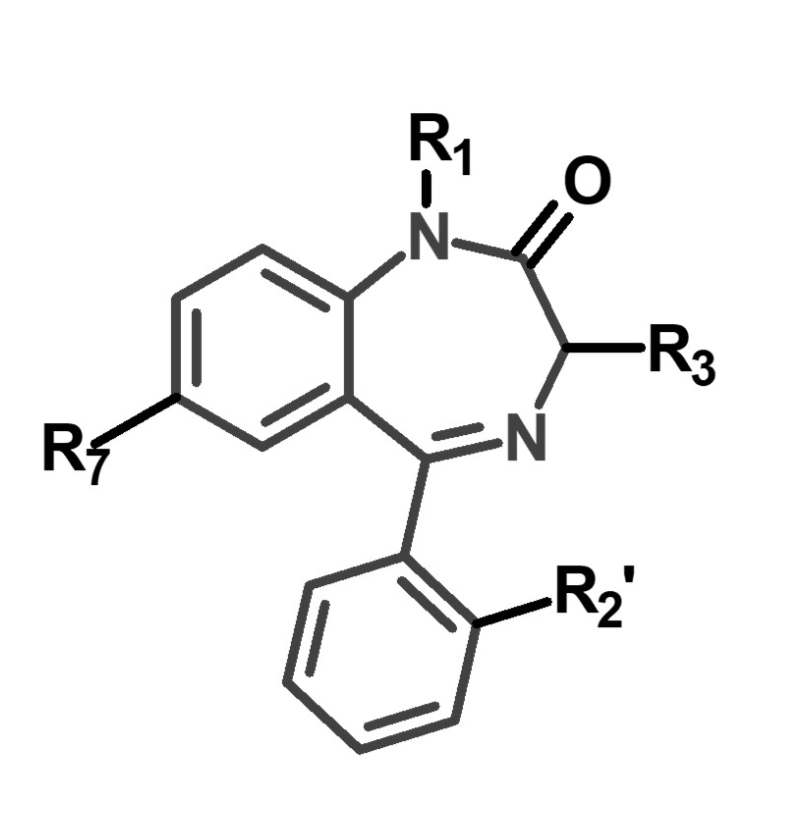
What drug class is this?
Benzodiazepine
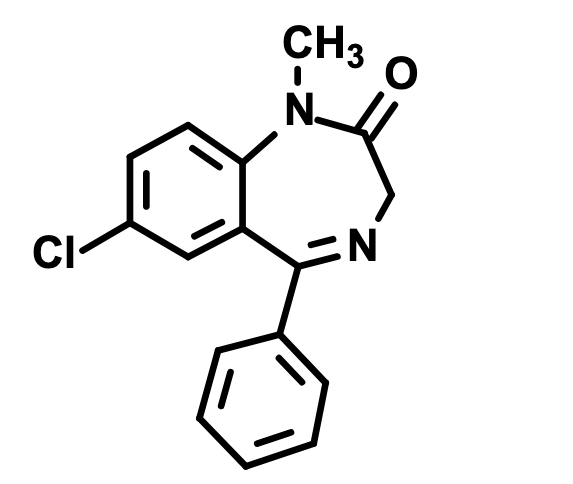
What is this?
Diazepam
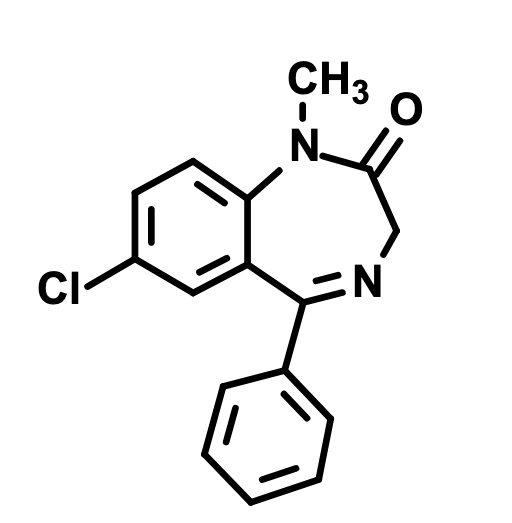
How is this structure transformed into nordiazepam?
N-demethylation by CYP2C19
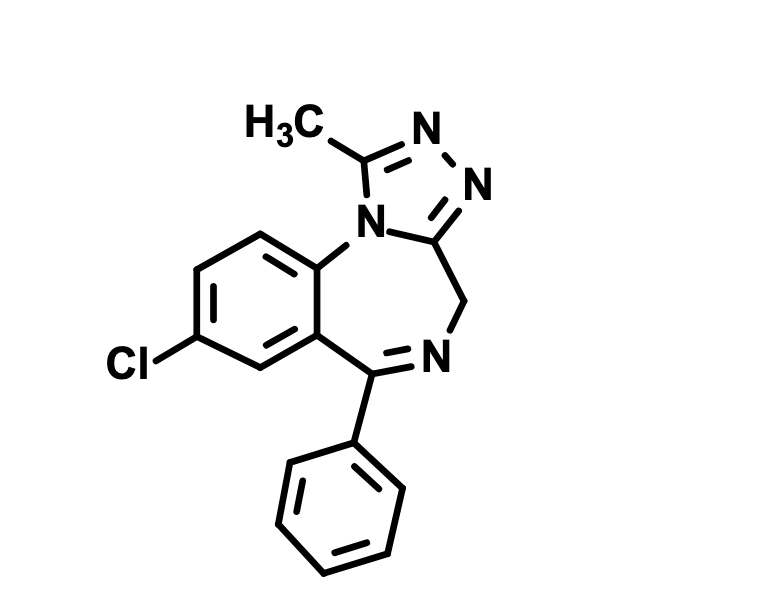
What is this?
Alprazolam
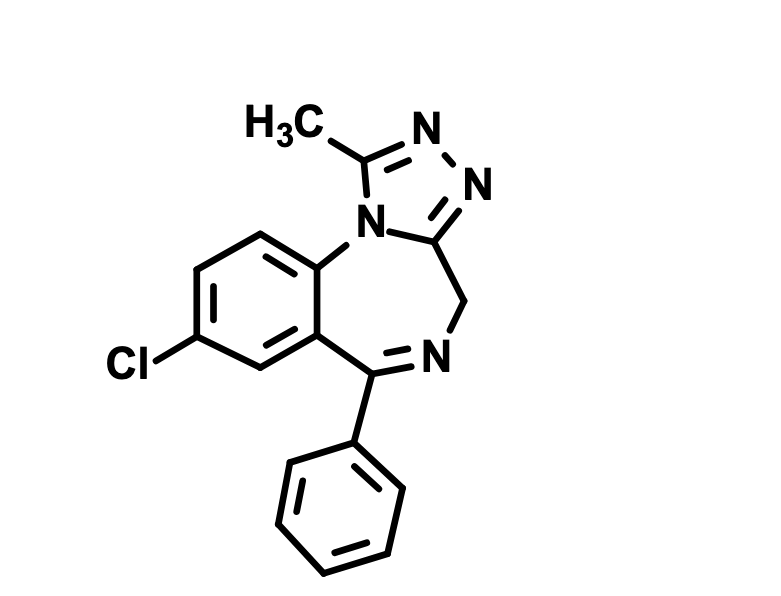
What does the fixed triazole group do to this structure’s activity?
Increases potency
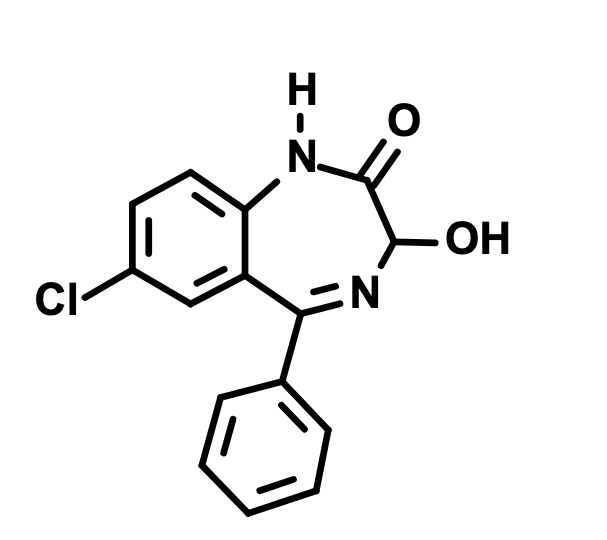
What is this?
Lorazepam
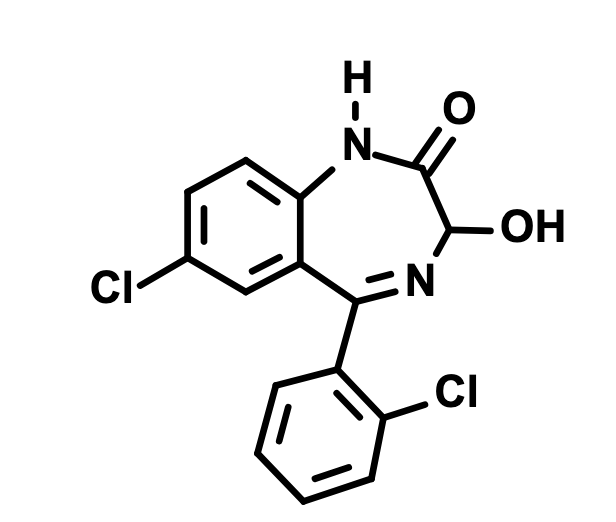
What is this?
Oxazepam
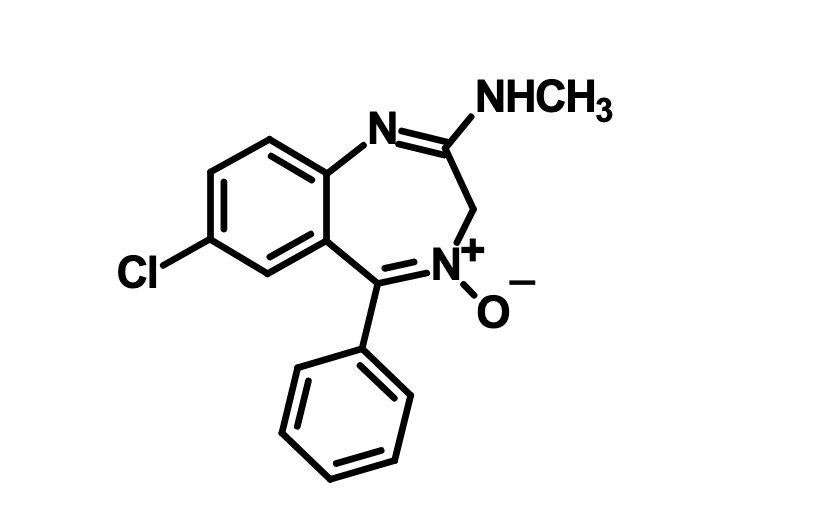
What is this?
Chlordiazepoxide
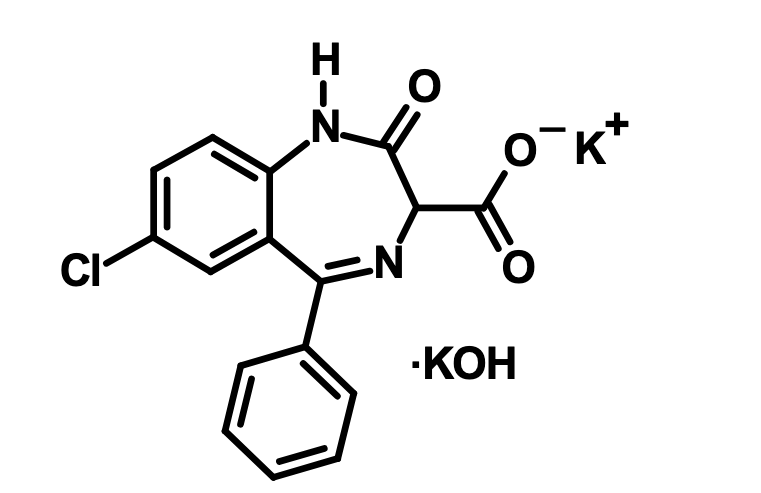
What is this?
Clorazepate dipotassium
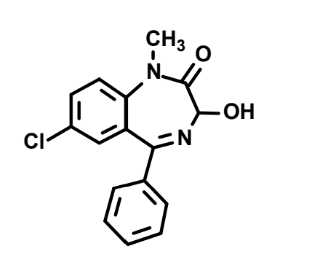
What is this?
Temazepam
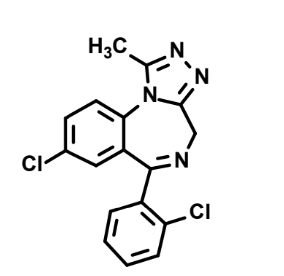
What is this?
Triazolam
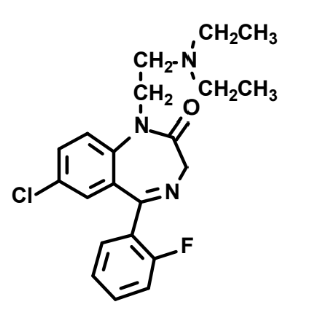
What is this?
Flurazepam
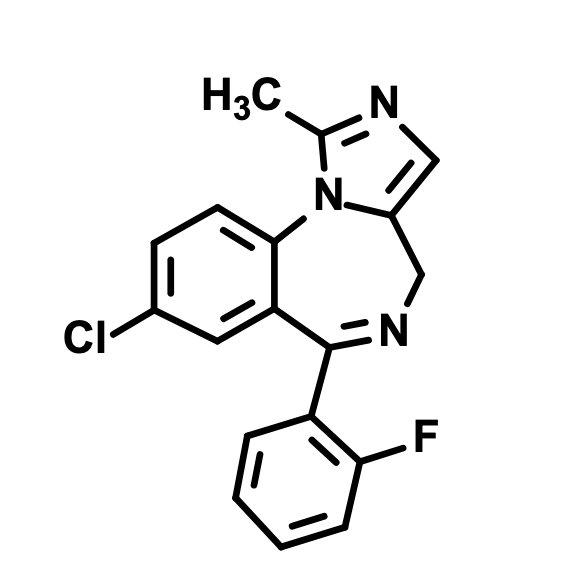
What is this?
Midazolam
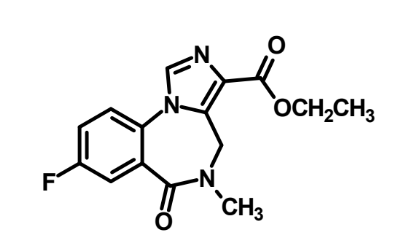
What is this?
Flumazenil
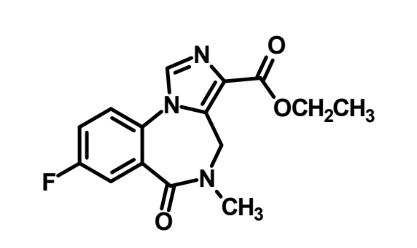
What does this do?
Reverse sedative effect of benzodiazepines
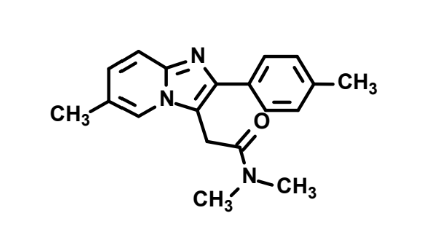
What is this?
Zolpidem
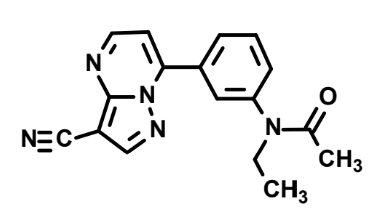
What is this and how is it metabolized?
Zaleplon, aldehyde oxidase
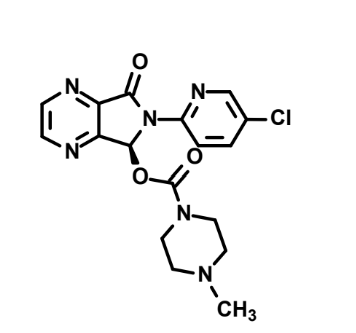
What is this?
Eszopiclone
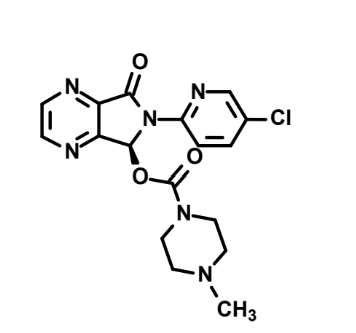
How is this metabolized?
N-oxidation and N-demethylation via CYP3A4 and CYP2E1
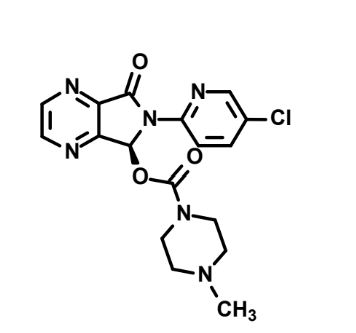
In what situation do we need to reduce the dose of this drug?
Severe hepatic impairment
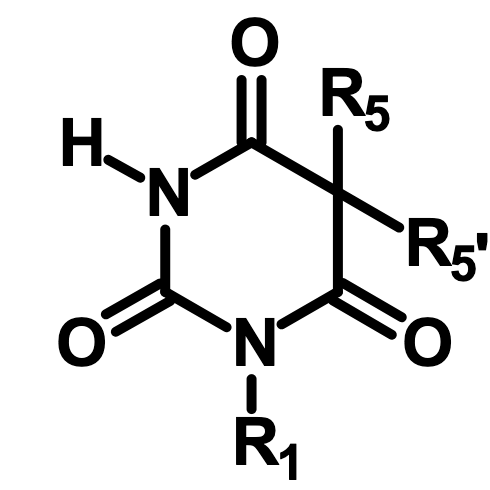
What is this drug class?
Barbiturate
If someone uses alcohol acutely, how does this affect CYP450 metabolism?
Inhibits CYP450
If someone uses alcohol chronically, how does this affect CYP450 metabolism?
Induces CYP450
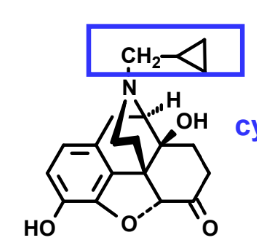
What does the highlighted group do?
Antagonizes opioids (structure is naltrexone)