Biology: Cockroach
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:46 PM on 10/28/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
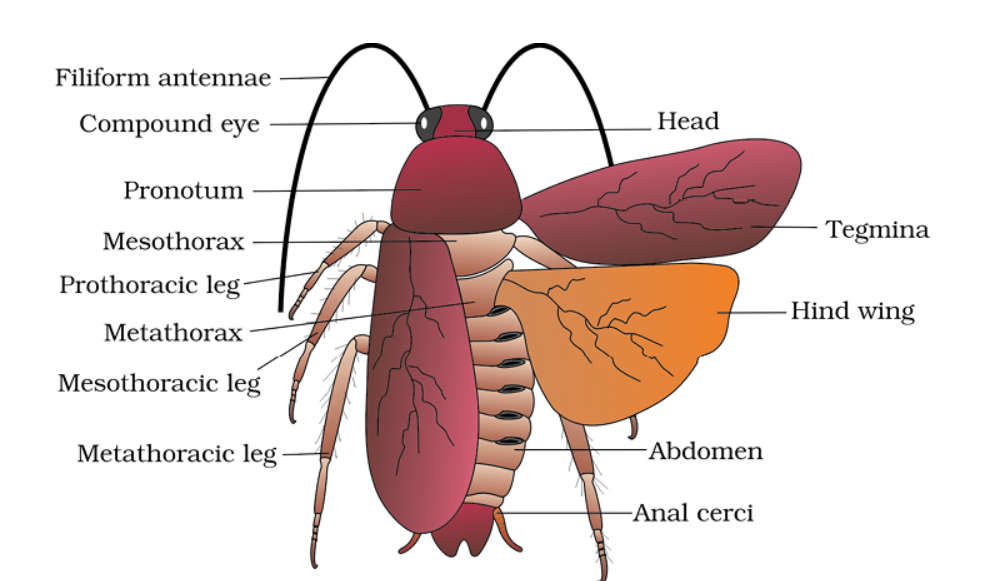
external features of cockroach
• The cockroach is nocturnal, omnivorous, and cursorial.
• Size: 34-53 mm long with wings that extend the abdomen of males.
• Size: 1/4 inches to 3 inches (0.6-7.6 cm).
• Bright yellow, red, and green, cockroaches have been reported in the tropical region.
• 3 pairs of jointed legs
• Size: 34-53 mm long with wings that extend the abdomen of males.
• Size: 1/4 inches to 3 inches (0.6-7.6 cm).
• Bright yellow, red, and green, cockroaches have been reported in the tropical region.
• 3 pairs of jointed legs
2
New cards
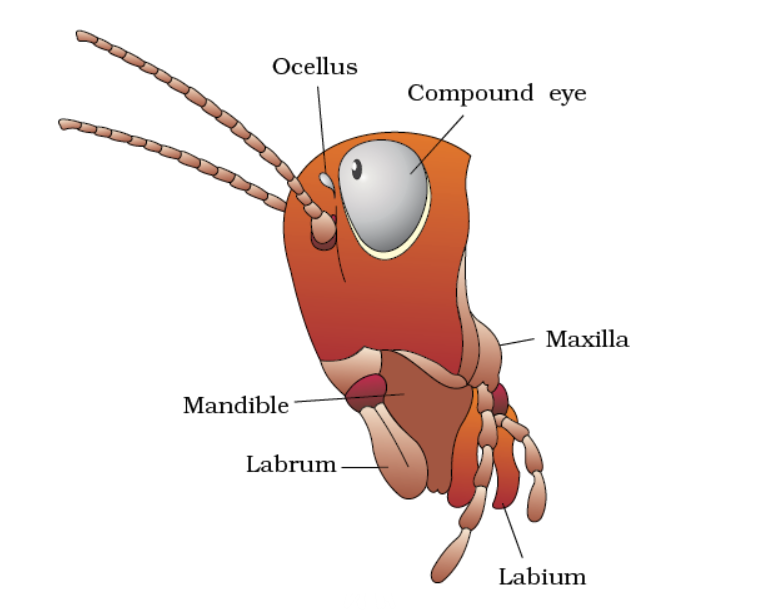
parts of head region
• Head is triangular and hypognathous.
• Top part of the head is called the vertex. Chitin plate below it Frons.
• Lateral side: 1 pair of the compound eye; 1-pair of antennae; flattened plates called gena.
• Dorsal side: Fenestra/ Ocellar spot
• Anterior side: Clypeus
• Top part of the head is called the vertex. Chitin plate below it Frons.
• Lateral side: 1 pair of the compound eye; 1-pair of antennae; flattened plates called gena.
• Dorsal side: Fenestra/ Ocellar spot
• Anterior side: Clypeus
3
New cards
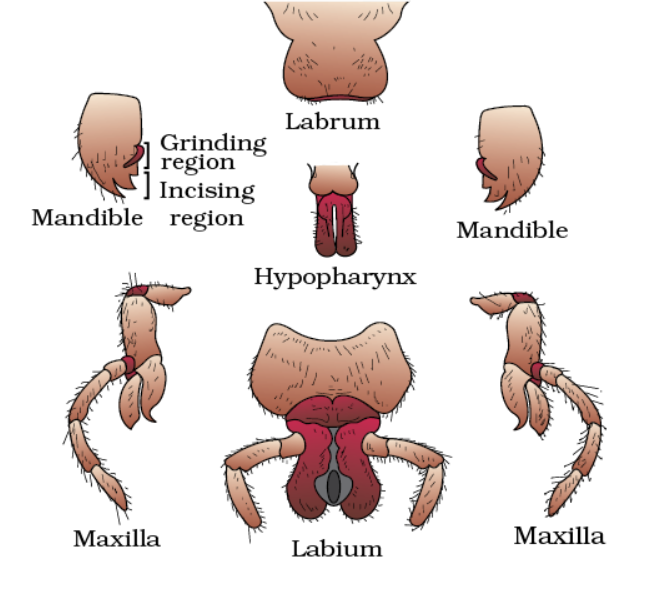
mouth parts
• Bitting and Chewing type
• Labrum: upper lip, which is broad, flattened, and movable sclerite of the dorsal side of the head capsule.
• Mandible: 1-pair of triangular structures with chitinous teeth. (Grinding of food) (lateral side)
• 1st Maxillae: 1 pair and form lateral wall of the pre-oral cavity. Pickup of food and clean antennae and wing.
• 2nd Maxillae (Labium): a platform for food and lower lip. (ventral side)
• Hypopharynx: tongue, salivary duct at the base of the hypopharynx, a median lobe, flexible, lies within cavity enclosed by mouth parts.
• Labrum: upper lip, which is broad, flattened, and movable sclerite of the dorsal side of the head capsule.
• Mandible: 1-pair of triangular structures with chitinous teeth. (Grinding of food) (lateral side)
• 1st Maxillae: 1 pair and form lateral wall of the pre-oral cavity. Pickup of food and clean antennae and wing.
• 2nd Maxillae (Labium): a platform for food and lower lip. (ventral side)
• Hypopharynx: tongue, salivary duct at the base of the hypopharynx, a median lobe, flexible, lies within cavity enclosed by mouth parts.
4
New cards
body
• Entire body is covered by a chitinous exoskeleton.
• Sclerites (each segment)
• Sclerites are joined by a flexible membrane called an arthrodial membrane.
• Dorsal: Tergites
• Ventral: Sternites
• Lateral: Pleurites
• Head (6) + Thorax (3) + Abdomen (11): (20) segments in embryo.
• Head (1) + Thorax (3) + Abdomen (10): (14) segments in adult.
• Sclerites (each segment)
• Sclerites are joined by a flexible membrane called an arthrodial membrane.
• Dorsal: Tergites
• Ventral: Sternites
• Lateral: Pleurites
• Head (6) + Thorax (3) + Abdomen (11): (20) segments in embryo.
• Head (1) + Thorax (3) + Abdomen (10): (14) segments in adult.
5
New cards
wings
• Fore wings/ Elytra/ Tegmina: mesothorax; opaque; long; narrow; dark; leathery.
• Hind wings: metathorax; small; broad; transparent; membranous; help in flight.
• Hind wings: metathorax; small; broad; transparent; membranous; help in flight.
6
New cards
thorax
• prothorax
• mesothorax
• metathorax
• mesothorax
• metathorax
7
New cards
legs
• Coxa (broadest segment)
• Trochanter (smallest segment)
• Femur
• Tibia
• Tarsus
• Trochanter (smallest segment)
• Femur
• Tibia
• Tarsus
8
New cards
arolium & claws
arolium helps the cockroach to walk on smooth surfaces. claws help the cockroach to walk on rough surfaces.
9
New cards
abdomen
• 10 segments (9 in male; 7 in female)
• Sexual dimorphism characters are present in it.
• 4 chitinous plates (1 tergum + 1 sternum + 2 pleuron)
• 10th tergum: Anal cerci (segmented: 15 in number)
• Stink gland present between 5 and 6th tergum. Repel enemies.
• 7th tergum largest covers the 8th and 9th tergite.
• 9th sternum: Anal styles (male)
• 7th sternum: boat shaped; gyno valvular plates (female)
• Sexual dimorphism characters are present in it.
• 4 chitinous plates (1 tergum + 1 sternum + 2 pleuron)
• 10th tergum: Anal cerci (segmented: 15 in number)
• Stink gland present between 5 and 6th tergum. Repel enemies.
• 7th tergum largest covers the 8th and 9th tergite.
• 9th sternum: Anal styles (male)
• 7th sternum: boat shaped; gyno valvular plates (female)
10
New cards
anatomy
• Basement layer: Simple squamous epithelium.
• Hypodermis: columnar epithelium.
• cuticle is made up of an alternate layer of protein and chitin.
• large fat bodies in hemocoel are analogous to the liver.
• Hypodermis: columnar epithelium.
• cuticle is made up of an alternate layer of protein and chitin.
• large fat bodies in hemocoel are analogous to the liver.
11
New cards
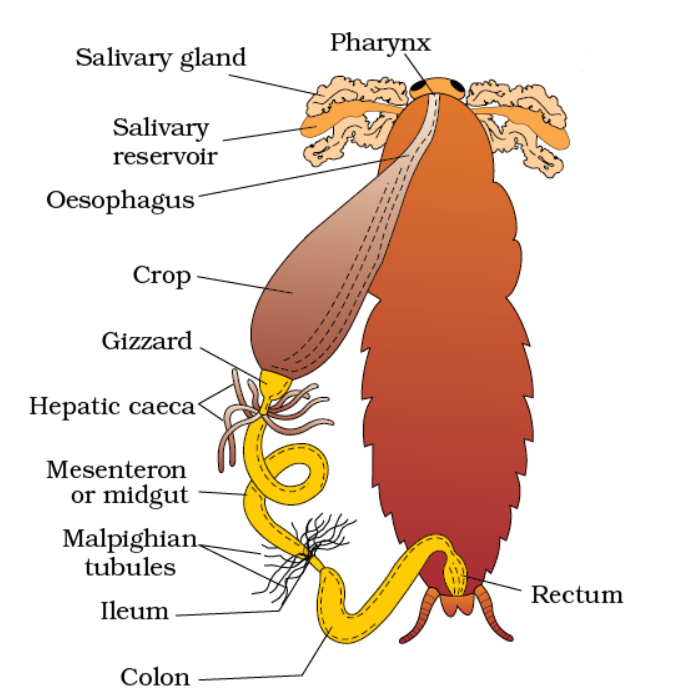
digestive System
• Foregut: Ectodermal
Mouth to gizzard
cuticle present in the inner side of the foregut
six cuticular teeth for grinding the food
gizzard: circular muscle; thick-walled; upper part (grinding); lower part (filtration).
cuticle hairs in the posterior part of the gizzard called sieve
• Mid gut: Endodermal
stomodial valve: gizzard to mesenteron
muscular; 6-8 tubular and small blind tubules called hepatic caeca.
digestive juices secretion.
• Hind gut: Ectodermal (broader than mid gut)
Malpighian tubules (100-150)
ileum: cuticle bears spines to break the peritrophic membrane
colon: longest and broadest part
rectum: 6 folds rectal papillae
anus: end of 10th abdominal segment
Mouth to gizzard
cuticle present in the inner side of the foregut
six cuticular teeth for grinding the food
gizzard: circular muscle; thick-walled; upper part (grinding); lower part (filtration).
cuticle hairs in the posterior part of the gizzard called sieve
• Mid gut: Endodermal
stomodial valve: gizzard to mesenteron
muscular; 6-8 tubular and small blind tubules called hepatic caeca.
digestive juices secretion.
• Hind gut: Ectodermal (broader than mid gut)
Malpighian tubules (100-150)
ileum: cuticle bears spines to break the peritrophic membrane
colon: longest and broadest part
rectum: 6 folds rectal papillae
anus: end of 10th abdominal segment
12
New cards
digestion and absorption
• digestion: anterior part of the midgut
• absorption: posterior part of the midgut
• Most of the digestion occurs in crop
• Water absorption in rectal papillae.
• absorption: posterior part of the midgut
• Most of the digestion occurs in crop
• Water absorption in rectal papillae.
13
New cards
Compound Eyes
• Apposition/Mosaic Vision: Apposition vision forms in bright light. (less sensitivity, more resolution)
• Superposition Image: In dim light in nocturnal insects. (more sensitivity, less resolution)
• Superposition Image: In dim light in nocturnal insects. (more sensitivity, less resolution)
14
New cards
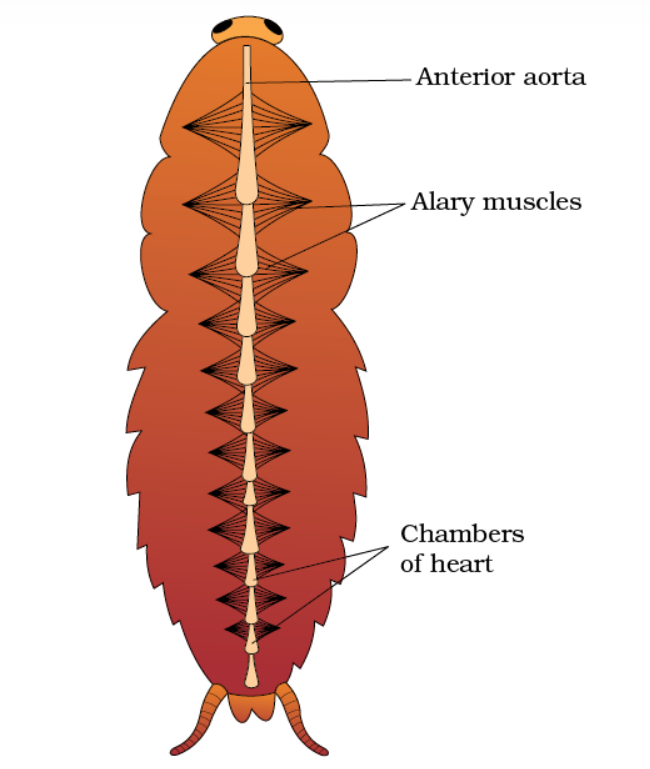
circulatory system
• open type circulatory system
• blood vessel is poorly developed and falls into tissue space called hemocoel.
• hemolymph: colorless plasma + haematocytes
• blood is not related to respiration.
• dorsal sinus: heart
• middle sinus: alimentary canal and fat body
• ventral sinus: nerve cord
• elongated muscular tube lying in the mid-dorsal line of thorax and abdomen.
• dorsal, tubular, 13 chambered
• ostia act as valves
• nephrocytes: regulated heartbeat 49beats/min
• tergosternal muscle
• alary muscle: 12 pairs (24)
• blood vessel is poorly developed and falls into tissue space called hemocoel.
• hemolymph: colorless plasma + haematocytes
• blood is not related to respiration.
• dorsal sinus: heart
• middle sinus: alimentary canal and fat body
• ventral sinus: nerve cord
• elongated muscular tube lying in the mid-dorsal line of thorax and abdomen.
• dorsal, tubular, 13 chambered
• ostia act as valves
• nephrocytes: regulated heartbeat 49beats/min
• tergosternal muscle
• alary muscle: 12 pairs (24)
15
New cards
excretory system
• malphigian tubules (100-150)
• potassium urate ---> (uric acid)
• yellow colored, thin, filamentous, blind tubule located at the junction of midgut and hind gut.
• glandular and ciliated epithelium.
• fat bodies + nephrocytes + uricose glands + body wall
• excretory substances get stored in the cuticle which is rid of during molting.
• potassium urate ---> (uric acid)
• yellow colored, thin, filamentous, blind tubule located at the junction of midgut and hind gut.
• glandular and ciliated epithelium.
• fat bodies + nephrocytes + uricose glands + body wall
• excretory substances get stored in the cuticle which is rid of during molting.
16
New cards
respiratory system
• respiratory tubules/ tracheal system
• spiracles (network open outside the body)
• 10 pair spiracles (20): 2 in the thorax and 8 in the abdomen
• spiracles located on pleurone (lateral side)
• valve absent in 1st pair of spiracles
• last branches of the trachea are called tracheal capillaries or tracheoles.
• spiracles (network open outside the body)
• 10 pair spiracles (20): 2 in the thorax and 8 in the abdomen
• spiracles located on pleurone (lateral side)
• valve absent in 1st pair of spiracles
• last branches of the trachea are called tracheal capillaries or tracheoles.
17
New cards
nervous system
• brain (supra-oesophageal ganglia in the head region and their nerve supplies to antenna and compound eyes)
• ventral nerve cord: paired and solid
• 9 segmented ganglia (3 in the thorax and 6 in the abdomen)
• last ganglion in 7th abdominal segment.
• ANS: 5 ganglia
• PNS: mixed (motor + sensory)
• ventral nerve cord: paired and solid
• 9 segmented ganglia (3 in the thorax and 6 in the abdomen)
• last ganglion in 7th abdominal segment.
• ANS: 5 ganglia
• PNS: mixed (motor + sensory)
18
New cards
sense organs
• antenna
• anal cerci
• maxillary palps
• labial palps
• eyes
• anal cerci
• maxillary palps
• labial palps
• eyes
19
New cards
segments
• citellum: 14-16
• male genital pore: 18
• female genital pore: 14
• spermathecal apertures: 5-9
• male genital pore: 18
• female genital pore: 14
• spermathecal apertures: 5-9
20
New cards
molting
• 13 times
• external changes: both fore wings and hind wings develop
• the next to last nymphal stage has wing pads but only adult cockroach have wings.
• external changes: both fore wings and hind wings develop
• the next to last nymphal stage has wing pads but only adult cockroach have wings.
21
New cards
genital pouch
• male: 9th and 10th terga dorsally and 9th sterna ventrally
• anal styles: 9th segment only in males
• anal cerci: 10th tergum
• females: 7th-9th sterna
• anal styles: 9th segment only in males
• anal cerci: 10th tergum
• females: 7th-9th sterna
22
New cards
development
• paurometabolous (development through the nymphal stage)
23
New cards
salivary gland
• reservoir part: cylindrical and storage of saliva.
• glandular part: synthesis of saliva occurs in this part.
• carbohydrate digesting enzymes: amylase, cellulase, chitinase, etc.
• glandular part: synthesis of saliva occurs in this part.
• carbohydrate digesting enzymes: amylase, cellulase, chitinase, etc.
24
New cards
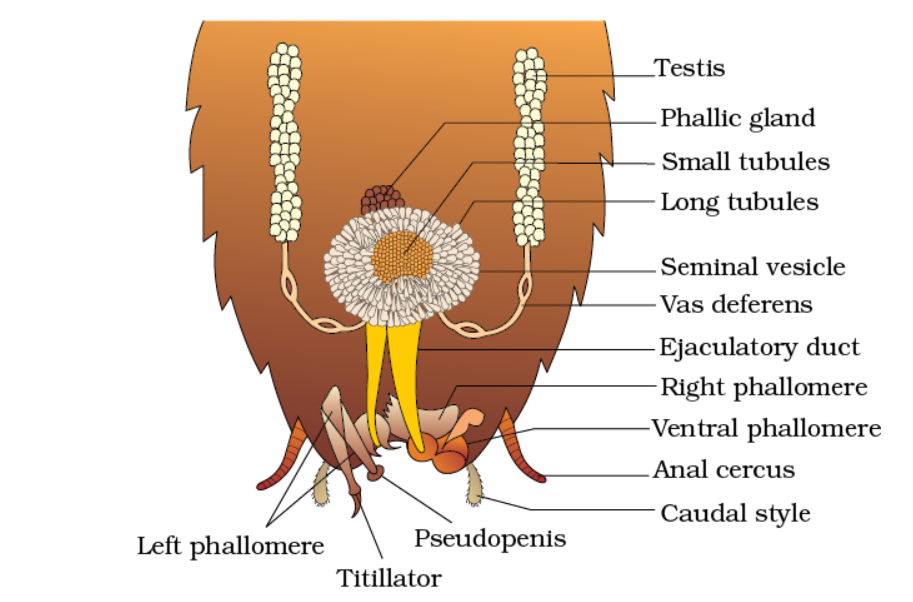
male reproductive system
• 1 pair of testis at 4-6 abdominal segments. (lateral side)
• it consists of 3-4 lobes
• vas deferens
• mushroom/utricular gland: it has two types of tubules long (brevivores) and small (majores)
• tips of long tubules are called uricose gland.
• a gland located on mushroom gland is called phallic/congloblate gland.
• three chitinous structures called male gonopophysis/phallomeres
• left phallomere (largest), tiltator, phallic aperture, pseudopenis
• right phallomere (two large hooks)
• ventral phallomere (it has no hook); male genital pore
• hooks help in opening the female oothecal pore.
• sperms are stored in a seminal vesicle and glued together in a sperm ball.
• before copulation in oothecal pore it is three-layered because of the secretion of phallic gland.
• small tubules secrete a nutritive fluid.
• ejaculatory duct secrete another coat.
• it consists of 3-4 lobes
• vas deferens
• mushroom/utricular gland: it has two types of tubules long (brevivores) and small (majores)
• tips of long tubules are called uricose gland.
• a gland located on mushroom gland is called phallic/congloblate gland.
• three chitinous structures called male gonopophysis/phallomeres
• left phallomere (largest), tiltator, phallic aperture, pseudopenis
• right phallomere (two large hooks)
• ventral phallomere (it has no hook); male genital pore
• hooks help in opening the female oothecal pore.
• sperms are stored in a seminal vesicle and glued together in a sperm ball.
• before copulation in oothecal pore it is three-layered because of the secretion of phallic gland.
• small tubules secrete a nutritive fluid.
• ejaculatory duct secrete another coat.
25
New cards
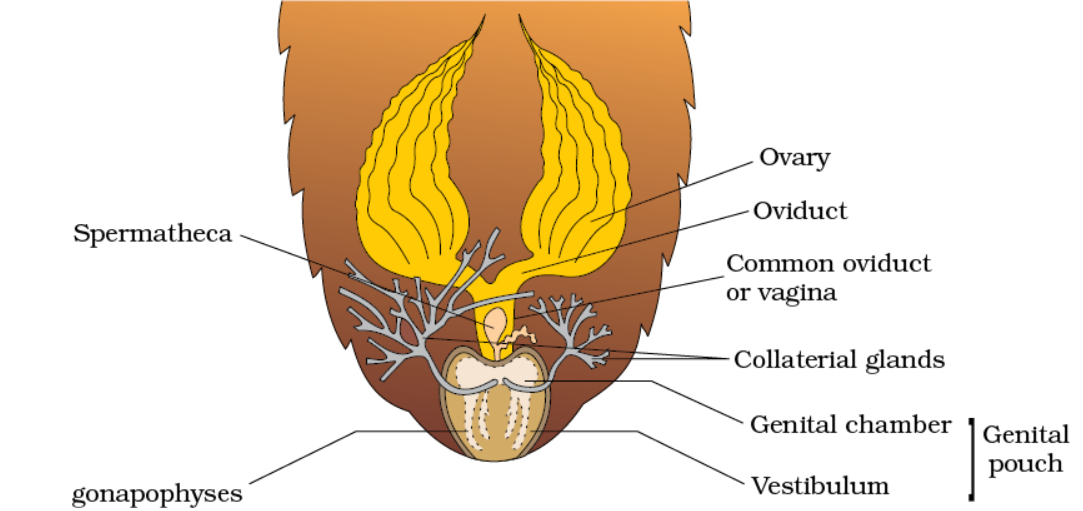
female reproductive system
• 1 pair of ovaries situated at 2-6 segments (lateral side)
• each ovary contains 8 long tubules called ovarioles
• 1 egg in each ovariole (16)
• genital chamber formed by the fusion of three abdominal sterna.
• 7th sternum is boat-shaped and along with the 8th and 9th sternum forms the brood or genital ouch in which the anterior is the genital chamber and the posterior is the oothecal chamber.
• genital chamber (female genopore + spermathecal pore + collaterial glands)
• ovipositor/female gonapophyses
• each ovary contains 8 long tubules called ovarioles
• 1 egg in each ovariole (16)
• genital chamber formed by the fusion of three abdominal sterna.
• 7th sternum is boat-shaped and along with the 8th and 9th sternum forms the brood or genital ouch in which the anterior is the genital chamber and the posterior is the oothecal chamber.
• genital chamber (female genopore + spermathecal pore + collaterial glands)
• ovipositor/female gonapophyses
26
New cards
copulation
• female secrete pheromones
• antenna in males helps to perceive this scent.
• copulation time: 1 hour
• 16 ova in each ovariole.
• fertilisation is internal and encased in capsules called oothecae
• sclero protein (ootheca)
• female produces 9-10 ootheca containing 14-16 eggs
• development (4-8 weeks)
• time interval between two moulting called stadium
• in between moulting nymph (instar)
• antenna in males helps to perceive this scent.
• copulation time: 1 hour
• 16 ova in each ovariole.
• fertilisation is internal and encased in capsules called oothecae
• sclero protein (ootheca)
• female produces 9-10 ootheca containing 14-16 eggs
• development (4-8 weeks)
• time interval between two moulting called stadium
• in between moulting nymph (instar)