Cariology Exam One [Plaque Development Part 1 & 2: Banas]
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Sterile
We used to teach that the womb is a ____ environment and that we begin to acquire a microflora the moment we are born
Placenta
New evidence supports that some bacteria may cross the ______
in the oral cavity (most similar to tongue and tonsil) of the mother
The microorganisms that cross the placenta appear to have originated
Latest thinking is that antigens of the microbiome, rather than viable organisms, cross over to train the immune system of the fetus
Latest think on microbiome and placenta
birth delivery
Most studies have found that bacterial diversity in the oral cavity is affected by mode of
vaginally compared to those delived by C-section
Greatest diversity of microbiome in infants that were delivered
- Environment
- Baby's put things in their mouth
- Salivary droplets (kisses etc)
- Food (not sterile)
- Caretakers, relatives
- Skin microflora
- Bacteria in milk
How do we get these bacteria (Other than birth)
The bacteria most likely to stay long term would be from the mouth of other people.
- Other mouth bacteria is already equipped for that way of live dawg
What bacteria is most likely to take resident in the babies mouth
vertical transmission of bacteria
Conventional wisdom is that the mother is the primary source of
Recovery of identical clonal types of cariogenic species (strep mutans) from mother and child more often than from the child and other family members
At the time of the study the mother was typically a stay at home mom. Meaning mothers were spending the most time with child.
- Pretty much when they tested mom and child they had similar bad bacteria (mutans)
Vertical transmission of bacteria primarily from the mother is based on
colonize
- Mouth bacteria is more likely to take up resident and push out the bacteria less equipped for the oral cavity.
Some bacteria species will transiently ______ but will eventually be replaced
colonize
- She just not equipped to live in the mouth homie
Some bacteria will never _____ and will be swallowed
The oral cavity will become home to those species that can utilize, and effectively compete for, the nutritional sources available, and withstand host defense mechanism
Why do only some species colonize
fissures of teeth
Adhesion is almost alway a prerequisite for colonization, though retentive site such as ___________ may obviate that need
enamel
Bacteria don't adhere directly to the
adhesins
Many bacteria have multiple specific ______ to promote efficient adhesion and/or adhesion to multiple receptors
Salivary proteins, glycoproteins, and other constituents
The enamel gets coated by _______ forming the pellicle
pellicle
Bacteria actually adhere to the ______ (not the tooth surface directly)
Electrostatic interactions (charged amino acids to a opposite charged surface)
Hydrophobic attractions
Hydrophilic attractions
Van der waals forces
Cationic bridging
Nonspecific weak-force mechanisms
adhesion
Nonspecific weak force interaction can initiate
Adhesins and receptor interaction
Weak force interactions can initiate stronger forces of
salivary pellicle, epithelial cells, matrix proteins (fibronectin or collagen), and platelets (important in endocarditis)
Oral bacteria will bind to
carbohydrates such as sialic acid, galactose, and fucose that are part of oligosaccharide chain on glycoproteins
The chemical composition of the receptors are often
other bacteria that have bound host receptors
In addition to binding host receptors, oral bacteria sometimes adhere to
coaggregation
Bacteria-to-bacteria adherence is called
- Fimbriae (also called pili or fibrils)
Bacterial adhesins
helically assembled proteins called fimbrillin or pilin.
Fimbriae are composed of
contains the particular adhesin
Often the tip of the fimbriae structure
Forces similar to those discussed for receptor ligand interactions
Adhesion by fimbriae is mediated by
proteins or lipoproteins that are anchored to the cell wall
- even some cell wall components have had adhesion properties attributed to them (teichoic acids)
Some adhesins are
Oral Streptococci
A lot of the primary plaque colonizers are
Is the quintessential bridging organism of early dental plaque to late dental plaque.
Fusobacterium nucleatum...
Heavily Gram +
Early dental plaque
Shifted to Gram -
Late dental plaque
the pellicle, or other host receptors on oral soft tissue
Some oral species are more proficient than others in adhering to the ____ or other _____
primary plaque colonizers or early colonizers
When referring to teeth, the species which are more proficient than others at adhering to the pellicle and other host receptors on oral soft tissue are called
more efficient at adhering to the early colonizers
Secondary or late colonizers
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
Various groups have found they can do "FISH". Whats this stand for
Fluorescent labels that admit ad different wavelengths. Can construct a map of plaque organism development
FISH allows for
more anaerobic the plaque gets
The older the plaque gets the
- Early on you can see that strep and Gemella are found in all children
- As you go on the number of genera in every child increases dramatically
- Gemella and Step are the ones that you have a good exposure to and establish well
- Later you find a vast diversity
- Prevotella is significant
- Mainly facultative or aerobic species
- After eruption get more anaerobic species
Interpret the graph
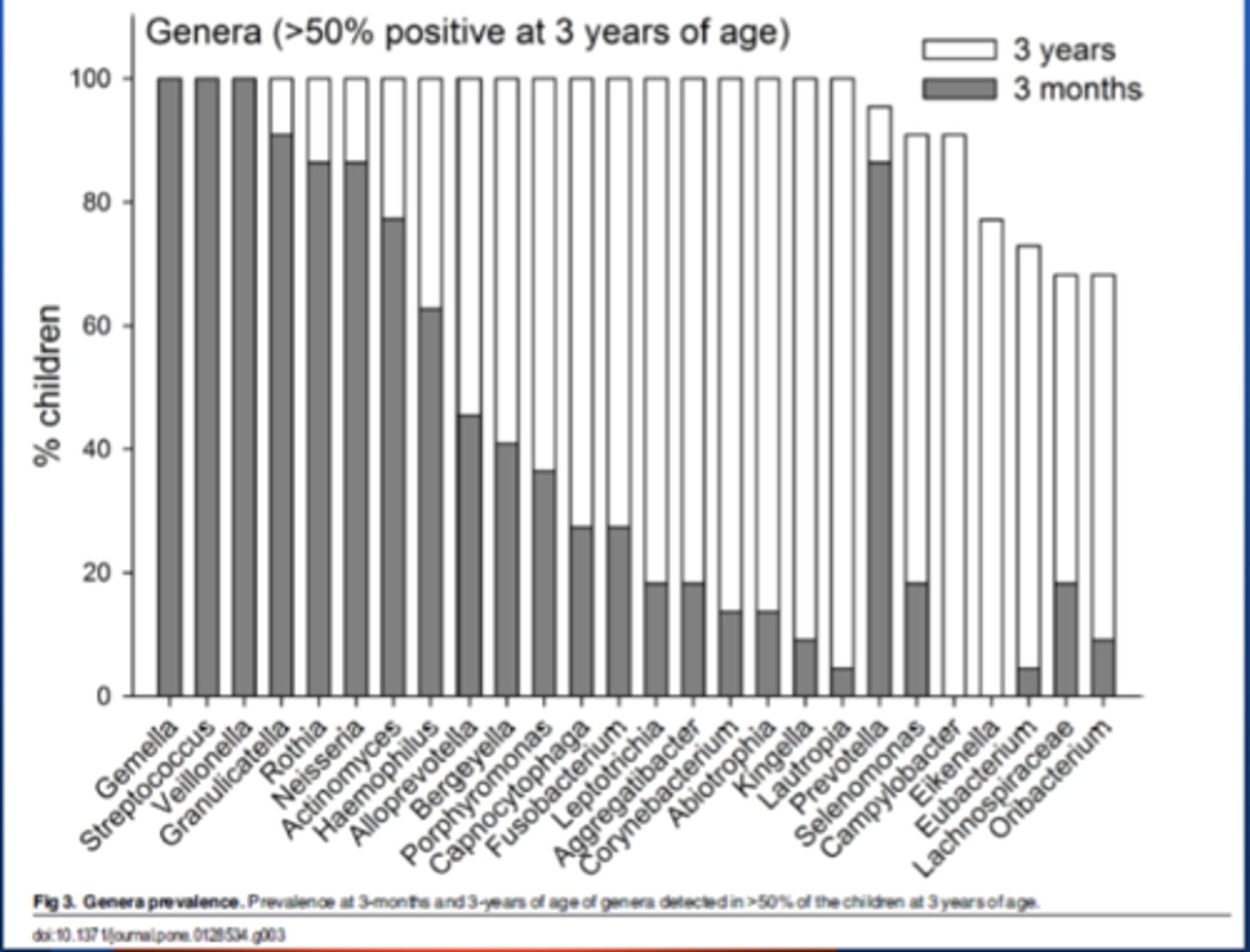
Don't have a lot of anaerobic species until the teeth erupt (except in this case)
- She an outlier
Why is Prevotella significant in the previous graph
Streptococcus, Veillonella, Gimella
Species of the genera ____,____,___ were found in 100% of infants at three months
Prevotella
_____ was a highly represented anaerobic genus at 3 months but in general the diversity of anaerobes increases with age, likely as teeth erupt creating subgingival niche
diversity
Species ____ increases with age
lactobacilli
- He did not mention lactobacilli but its on the slide
- We know this from micro though because we are geniuses
The microbiome composition at 3 months did not with future caries, with the exception of
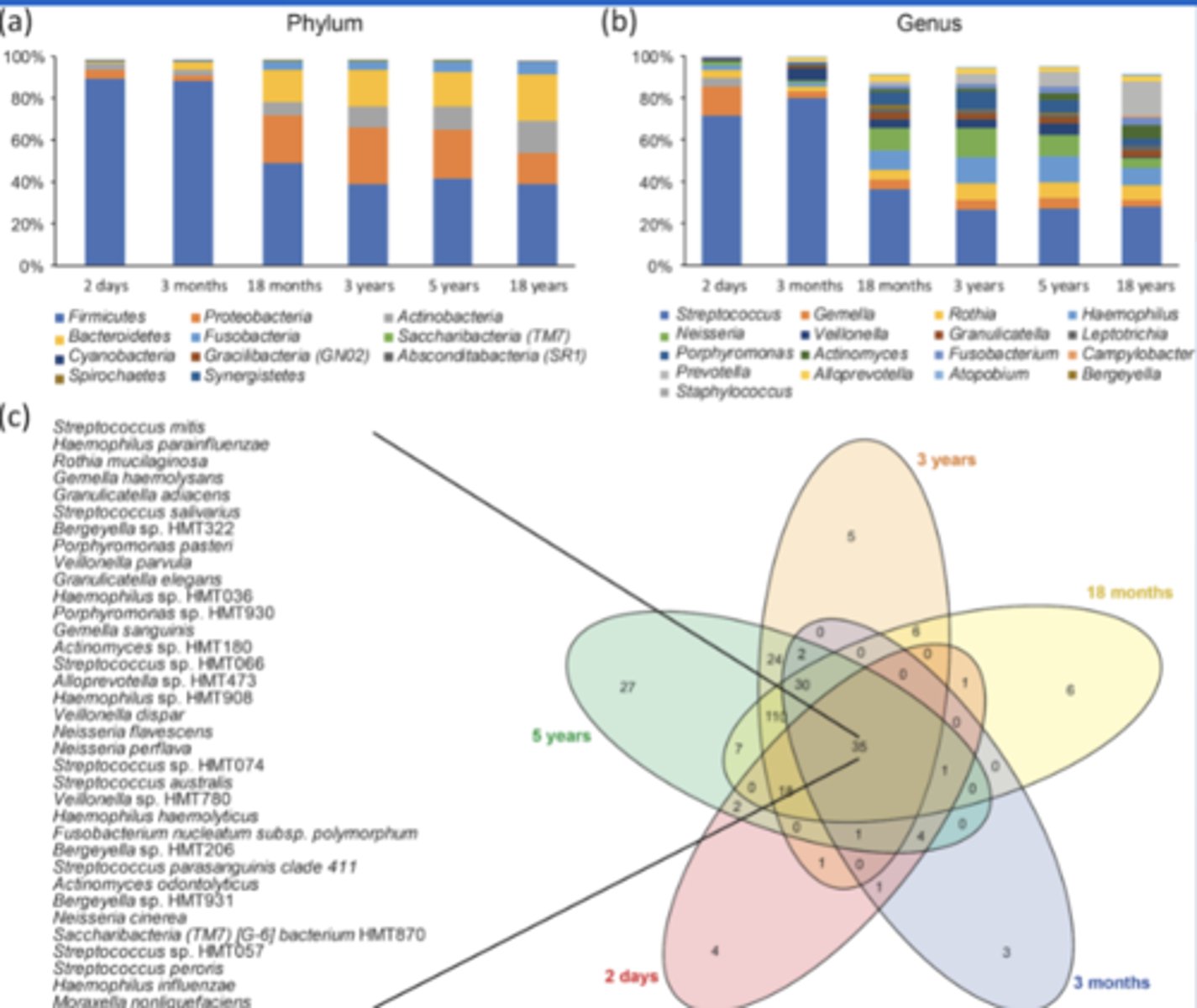
Interpret this graph
- This figure is for Illustrative purpose only - Dr. Banas
- We see at 18 month more stability of the distribution of the different types of organisms
END OF PART ONE
END OF PART ONE
START OF PART TWO
START OF PART TWO
18
Generally around ____ months you start to see a more stable biofilm
biofilm
A ____ is a collection of bacterial microcolonies on a surface
Polysaccharide matrix, and are metabolically heterogeneous
The bacteria within the microcolonies of a biofilm are structured within a _____ and are ________
antimicrobials, quorum sensing
The bacteria within the microcolonies of a biofilm have increased resistance to ______ and often elaborate a chemical or peptide signals in a process called ___
diffuse
Antibiotics don't _____ very well through the matrix of a biofilm
- Streptococcus (coccus)
- Granulicatella (coccobacillus)
- Gemella (coccobacillus)
- Rothia (coccobacillus)
- Actinomyces (Filamentous rod)
- Corynebacterium (rod)
- Abiotrophia (coccus)
Recognize these common names of genera found commonly in dental plaque [Gram +]
- Veillonella (coccus)
- Neissseria (coccus)
- Haemophilus (coccobacillus)
- Bergeyella (rod)
- Aggregatibacter (rod)
- Capnocytophaga (rod)
- Fusobacterium (anaerobic rod)
- Porphyromonas (anaerobic rod)
- Prevotella (anaerobic rod)
- Alloprevotella (anaerobic rod)
- Leptotrichia (anaerobic rod)
Recognize these common names of genera found commonly in dental plaque [Gram -]
Hemolysis
_____ on blood agar was used to identify Beta-hemolytic strep
alpha-hemolytic strep, nonpathogenic commensal
The _______ or viridans streptococci, were collectively though of as ______ species
Lyse
Beta hemolytic is the ability of organisms to ____ red blood cells
turned the agar (gel shit) a greenish color
Alpha hemolytic means
Fancy for nothing is happening (does nothing)
Gamma hemelytic
This is true
- This is just an adjective describing alpha hemolytic species
There is no specific species named Streptococcus Viridans
4
- We are not born with a genetically determined microbiome however genetics do influence the composition
QUESTION: Each of the following statements is true except?
1. Adhesins and receptors may sometimes be of the same molecular composition, for example both may be proteins
2. Some bacterial species, such as Gram-negative obligate anaerobes, become more abundant as an infant ages
3. The colonization of the tooth surface is aided by bacteria adhering to one another in a process known as coaggregation
4. we are born with a genetically determined oral microbiome; as the infant grows the only change is in an increase in total number of bacteria
5. Saliva coats teeth, forming a pellicle to which bacteria adhere
Ya this is true
Host receptors differ from one site to another in the oral cavity
Erupt
Certain bacterial species in the oral cavity are only acquire once the teeth
niches, or microenvironments, that are shaped by host anatomy and physiology
Overall, the oral cavity is comprised of several distinct
- Gingival crevice (subgingival plaque)
- Coronal plaque (supragingival plaque)
- Tongue
- Buccal mucosa
- The saliva will mostly contain representatives from each of these niches
In the oral cavity we generally consider distinct niches to be
NO, there are distinct differences but there are also distinct commonalities
Is your oral microbiome the same as your neighbor
Lesser Diversity
- Similar sites; same tooth
- Same tooth; Buccal vs Lingual, Mandibular vs Maxillary
- Similar sites; Different teeth
- Same tooth; Supragingival vs subgingival
- Similar teeth, similar sites; different individuals
Big take away is that different niche's have greater diversity as well as from person to person
Location: Rank microorganisms in terms of Lesser diversity ---> Greater diversity
State of knowledge and culturing techniques sometimes made it difficult to compare studies. Many distinct species were at one time classified as a single species
Pre-1960s: In vitro culture of oral samples:
Greater precision in taxonomy. Begin to realize the extent to which a substantial portion of the oral microbiota cannot be cultivated
1980s: Dawn of the age of molecular Biology/Genetics:
Examine the oral microbiota in health and disease. these are largely based on DNA hybridization or sequencing
2000's: New non-culture based taxonomic studies:
800
Some believe that the number of species is considerably higher
Non-cultured based studies have determined that there are in excess of ___ species in the oral cavity
30-70, 20-30
Any given individual will have about __-____ predominant species in the oral cavity, or about __-___ per site
the microbiome will almost certainly be more similar from site to site (within a niche) in a given individual than between identical sites in two different individuals
Some species and relative proportions will be similar from individual to individual BUT
sites of most common dental pathologies- caries and periodontal disease
Of all the niches in the oral cavity the greatest focus is on supra and sub- gingival plaque. That is because these are the sites of the most ___________
- Microbiota of the tongue may be associated with halitosis (bad breath)
- Saliva and plaque organisms are probably the source of endodontic infections
- Any site in the oral cavity, but most likely dental plaque, can be a source of systemic infection such as endocarditis
Other oral microbiome disease association
- Heavily Gram +
- Predominance of cocci
- Mostly facultative anaerobes
Early plaque
- Increasing representation of Gram -
- Many morphological types
- Facultative anaerobes and obligate anaerobes
Mature plaque
- Mix of Gram + and -
- Mix of cocci and rods
- Mix of facultative and anaerobes
- More carbohydrate fermenters
- Firmly adherent
Supragingival plaque
- Higher proportion of Gram -
- More Gram - rods and spirochetes
- More obligate anaerobes
- More proteolytic species
- less adherent, more motile (less host defenses)
Subgingival plaque
beneficial and antagonistic
While the physical properties of the environment will shape microbial ecology, so will __________ and _______ interactions between bacterial species
- Enzyme complementation
- Coaggregation
- Inactivation of inhibitors
- Subversion of host defenses
Beneficial (Cooperation) interactions within Plaque
- Bacteriocins
- Organic acids
- Low pH
- Nutrient competition
Antagonistic (competitive) interaction within Plaque
Food webs
Beneficial and antagonist interactions means the plaque can be described in terms of
good microbiome than it is to correct a bad dysbiosis
It is a lot easier to maintain a _____
It can't be changed
Once your microbiome is stabilized after 18 months doesn't mean
dietary
______ choices and smoking can bring about substantial changes
This is a fact
There are also changes that accompany maturation
environment has a influence on the microbiome
Twin studies show increasing divergence with age, indicating that
3
QUESTION: Each of the following statement is TRUE except
1. Dental plaque is considered a biofilm with a composition that is strongly influenced by ordered colonization, host differences, and behavioral choices such as diet
2. Hundreds of bacterial species may be found in the oral cavity but the number of predominant species in any given individual is in the range of 30-70
3. The composition of supragingival plaque is predominantly Gram - whereas subgingival plaque is predominantly Gram +
4. Generalities regarding the composition of the microflora within different oral niches can be made even though individual differences can be significant
reproduce
The goal of bacteria, like any biological entity, is to
Give and take
Bacterial interaction with the host is an evolution-driven ______
normal microbiota stays under control
The bacteria evolve to take advantage of an environment, which in this case is in the host. The host evolves, to ensure that its
- Flow of saliva; swallowing
- Slough off cells
- Chewing
- Movement of the tongue
Physical host plaque control
adhesion
Bacteria use ____ mechanisms to counter mechanical removal
This is true
All microbes need iron
Clumps up bacteria and makes it difficult for them to adhere
Agglutinin
- Saliva harbors anti-microbial factors
- Lysozyme
- Histatins (histidine-rich proteins)
- Peroxidase and thyiocyanate
- Lactoferrin
- Salivary mucins and parotid agglutinnin
- Several other salivary factors
Biochemical or enzymatic host plaque control
- Break bond in peptidoglycan
- Kill via amphipathic sequences
- Induce bacteria to kill themselves
- Agglutinate bacteria
Lysozyme