Anatomy Tissues
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
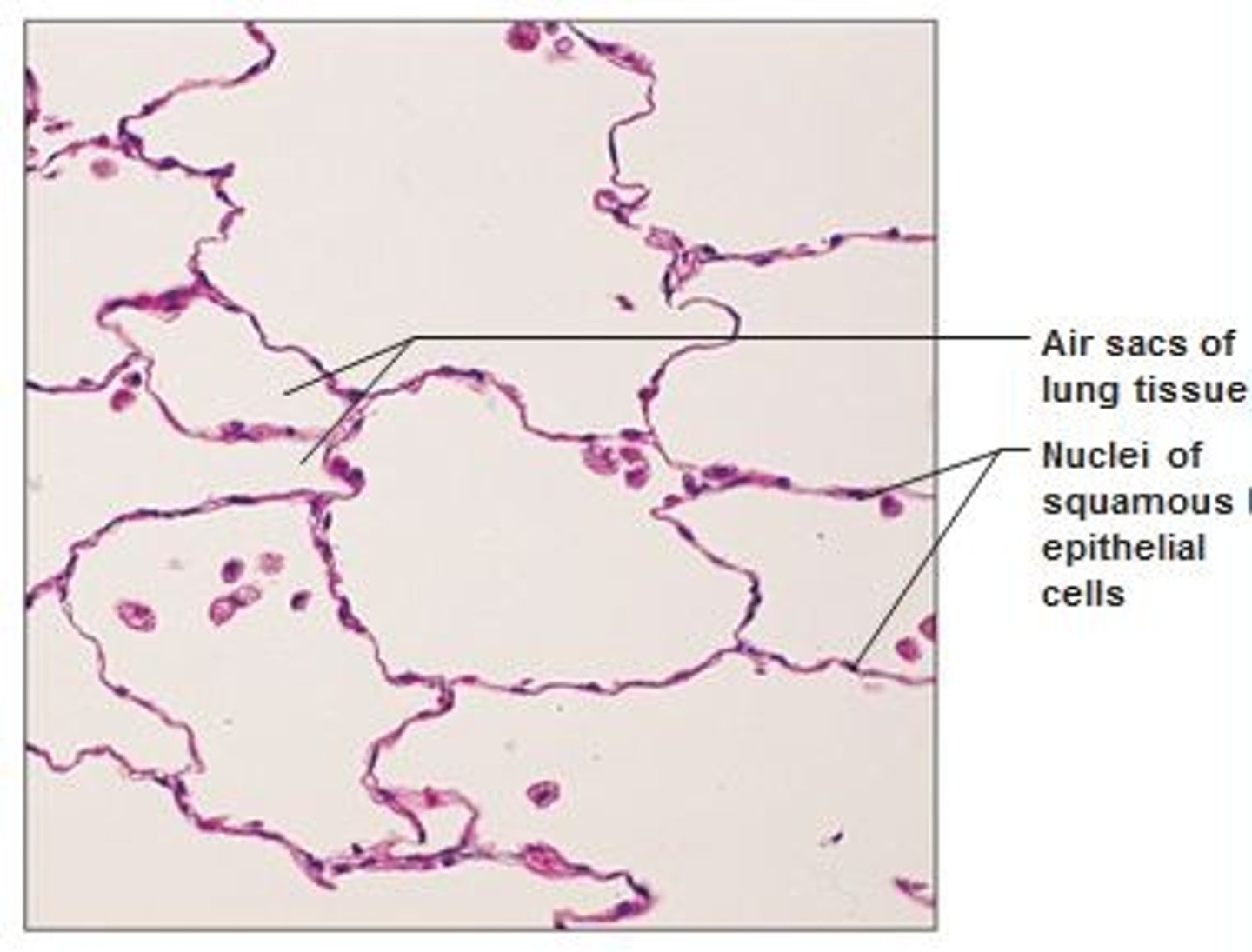
simple squamous
location- excretory, respiratory, cardiovascular
function- filtration, secretion, diffusion
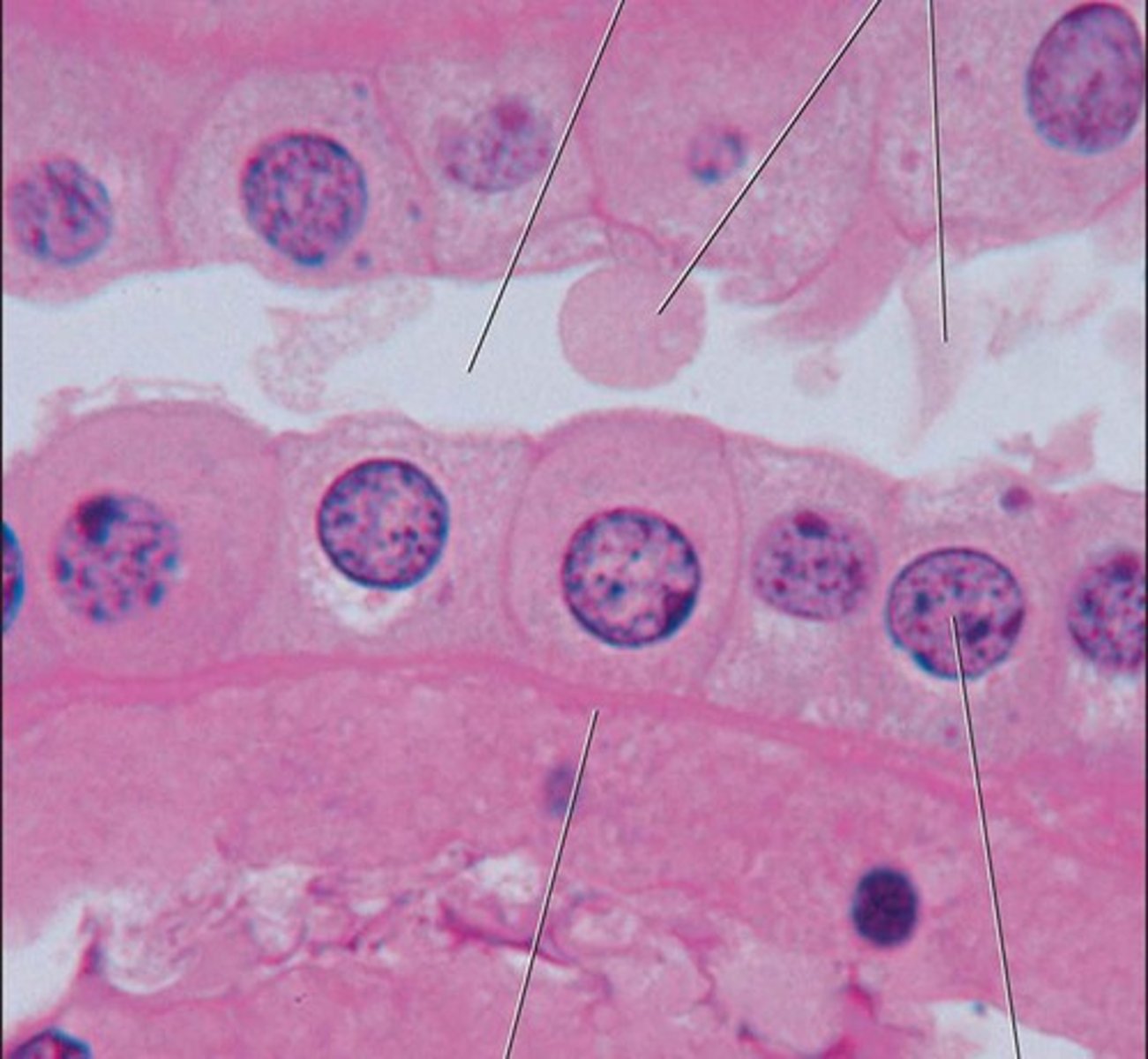
simple cuboidal
location- excretory, reproductive
function- secretion, absorption
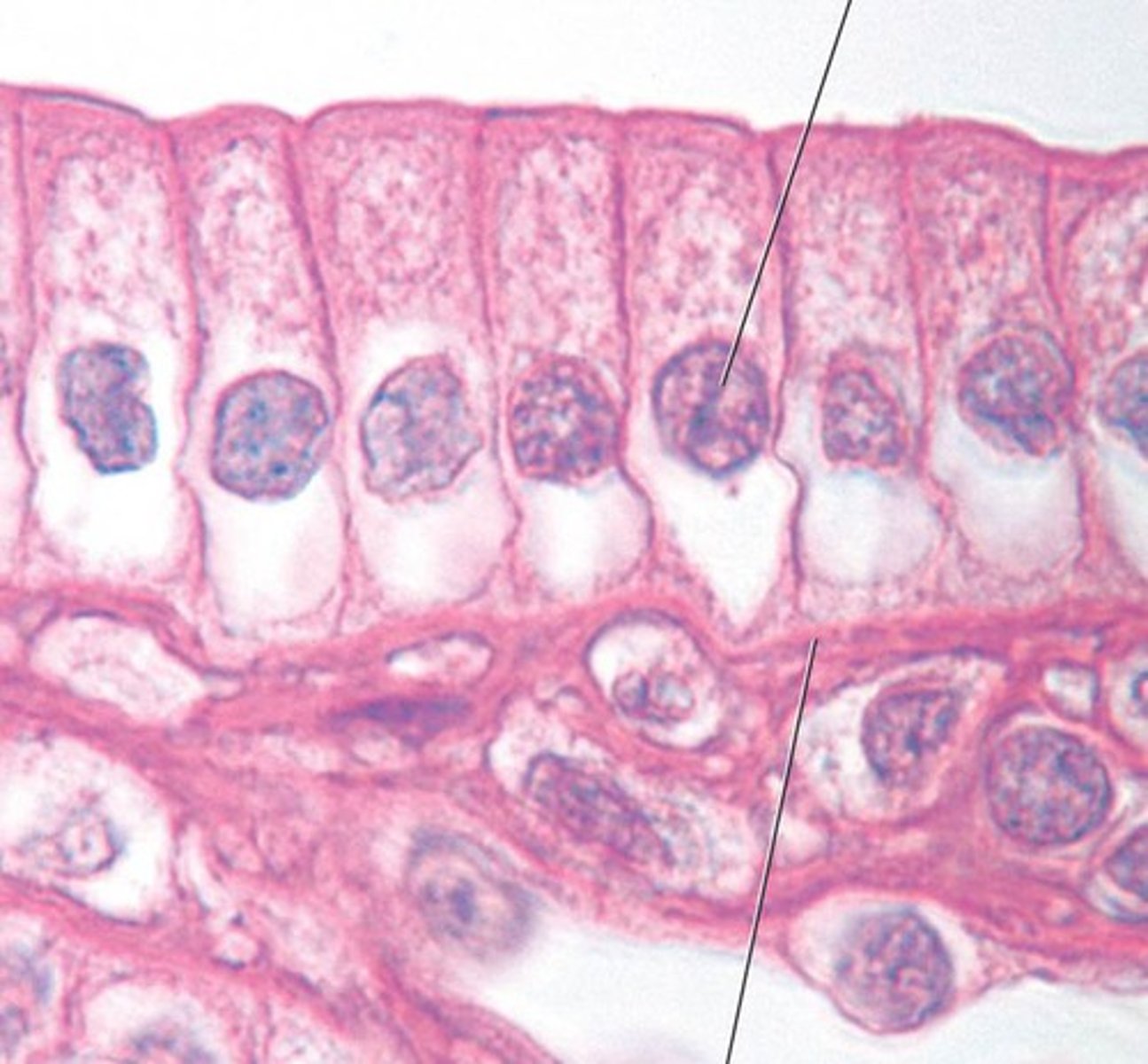
simple columnar
location- digestive
function- absorption, secretion
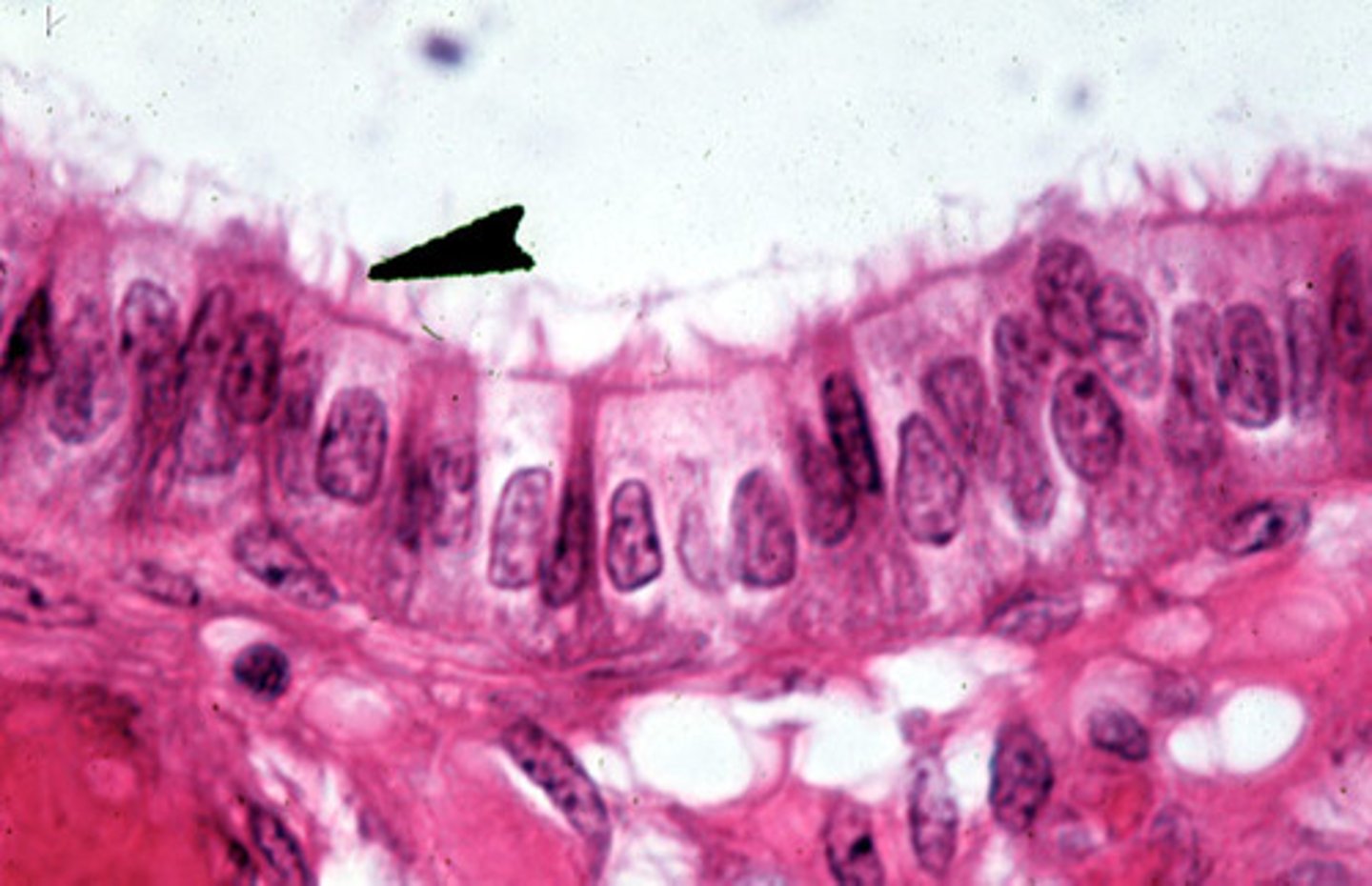
ciliated simple columnar
location- respiratory, reproductive
function- propels
pseudostratified columnar
location- reproductive
function- secretion
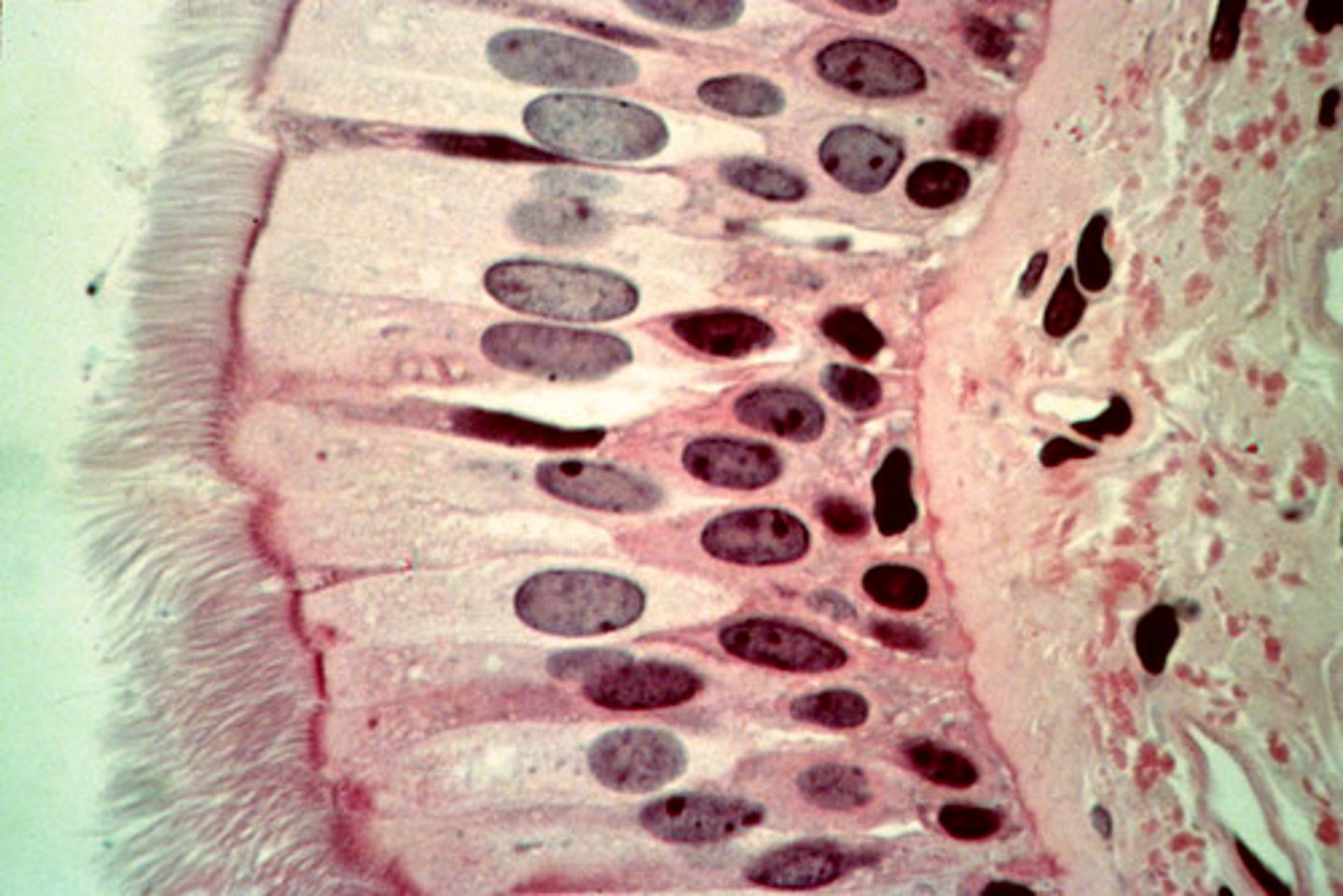
pseudostratified ciliated columnar
location- respiratory
function- propels
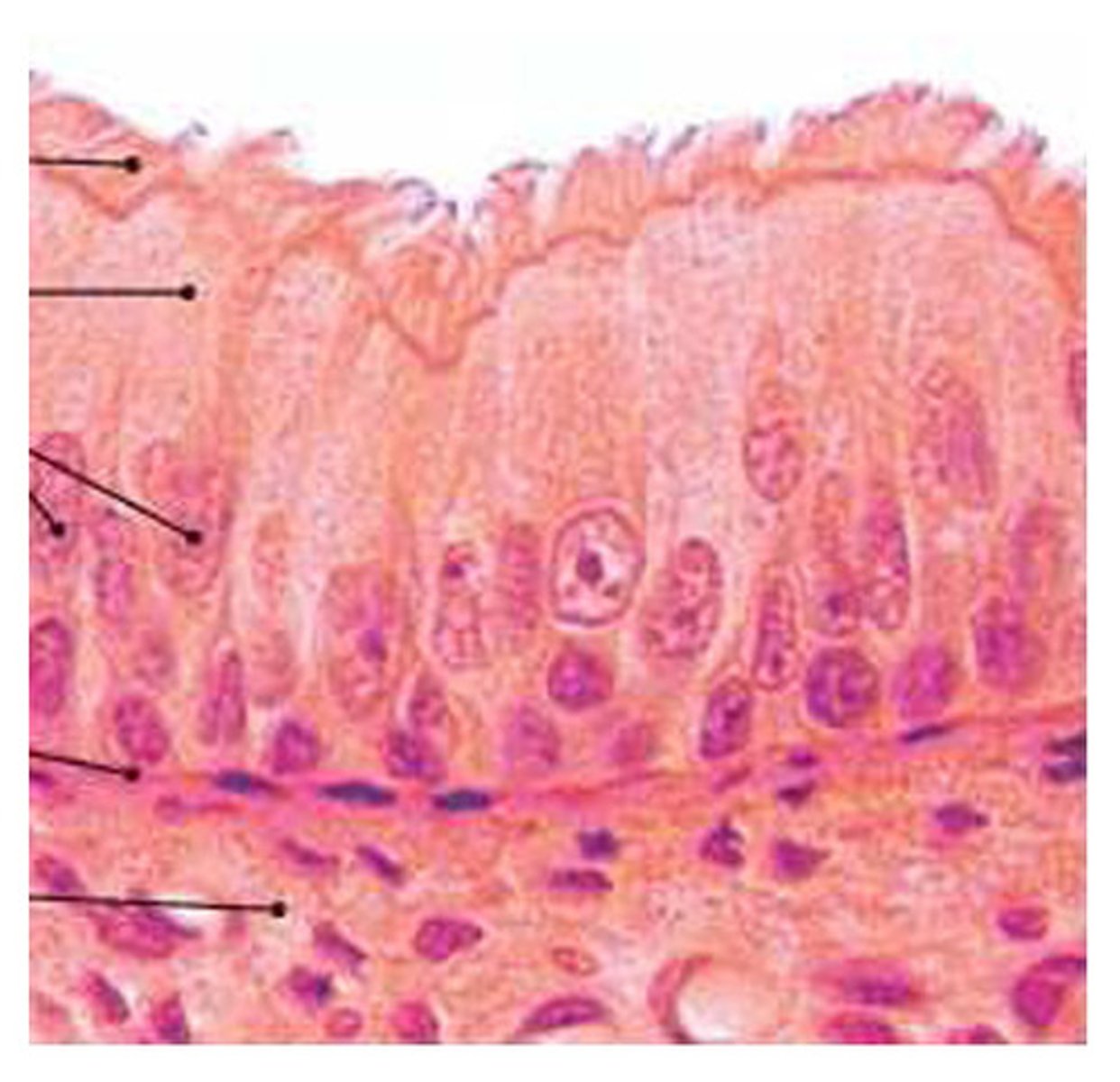
stratified squamous
location- digestive, reproductive, integumentary
function- protect
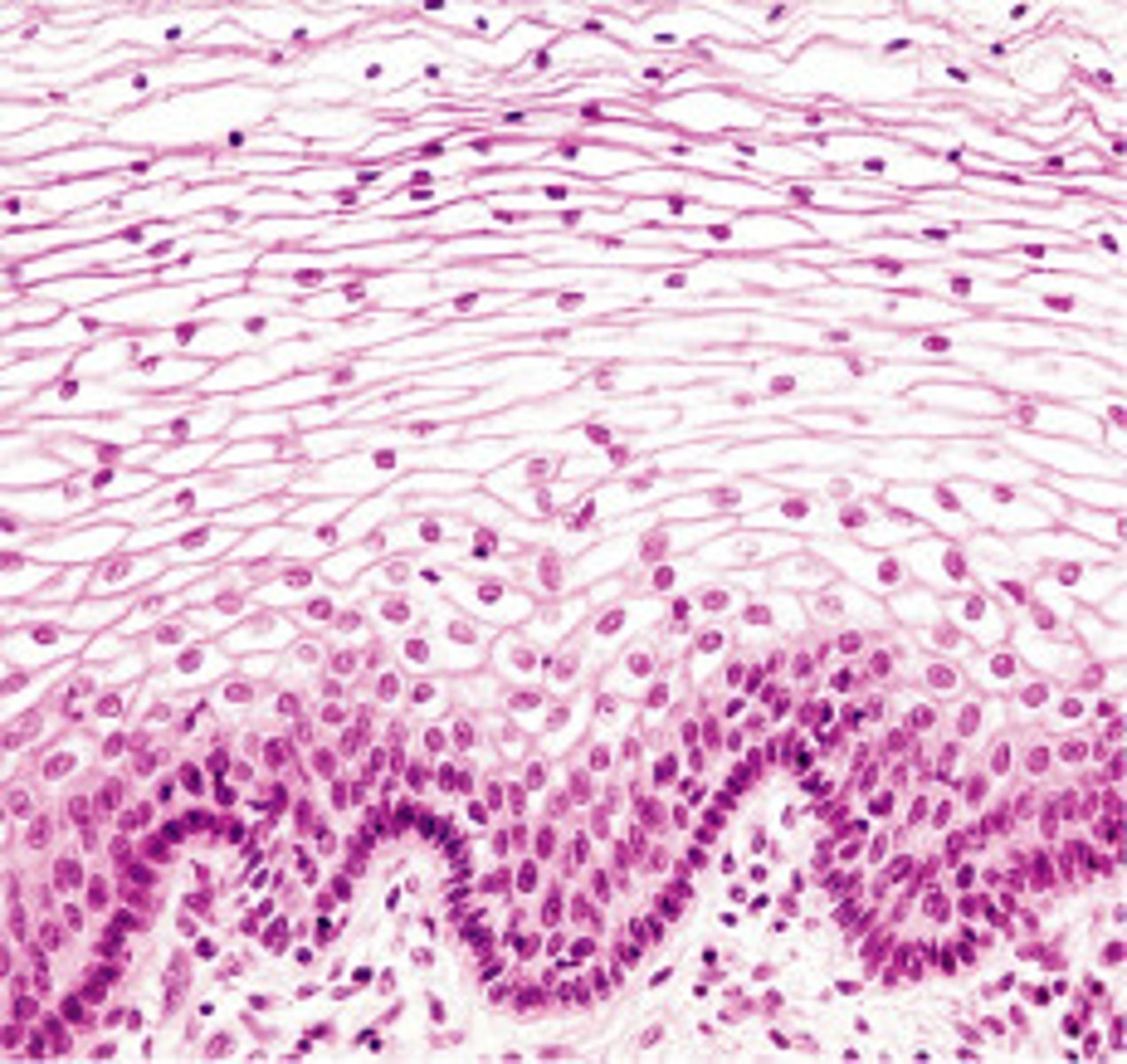
transitional
location- excretory
function- stretches
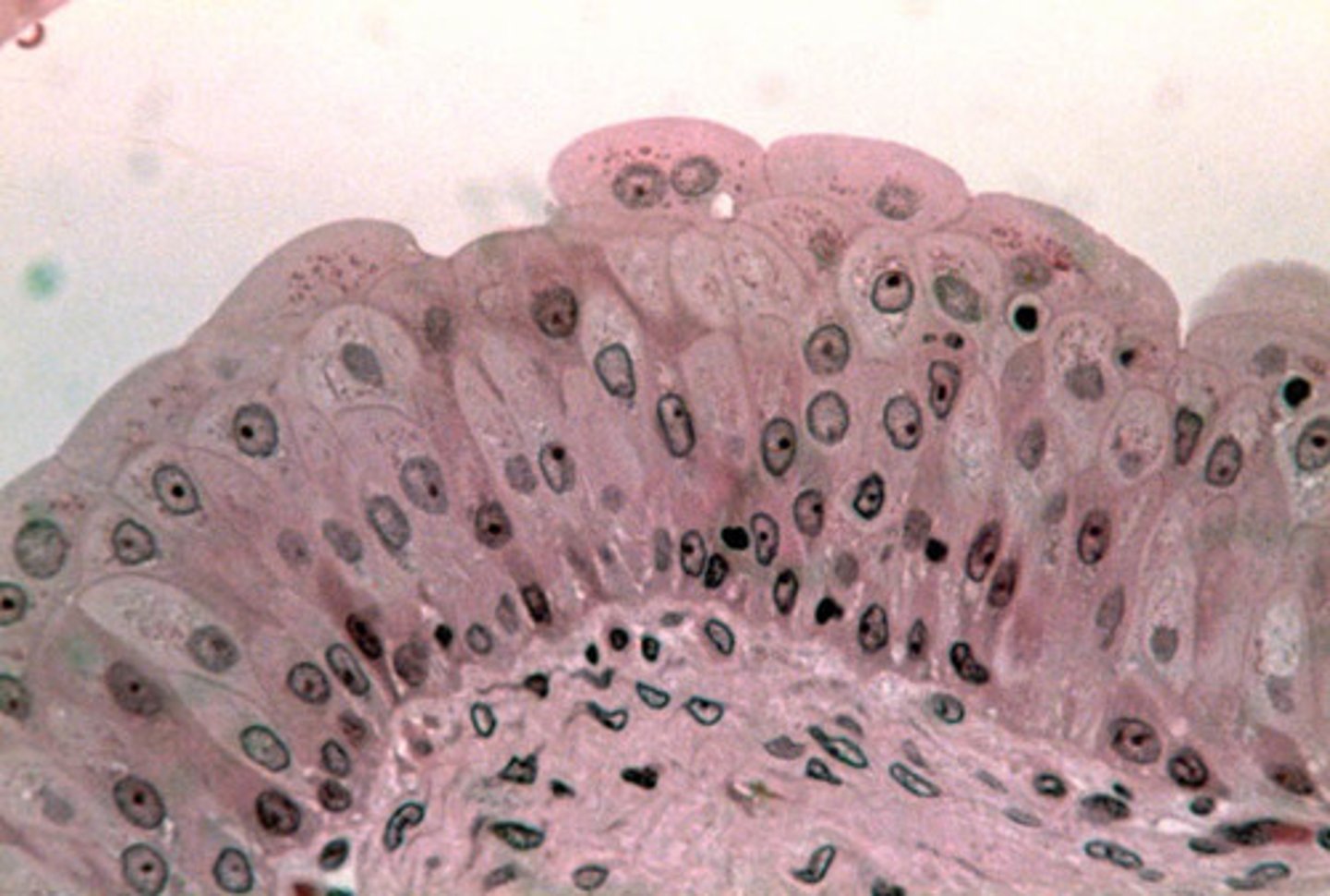
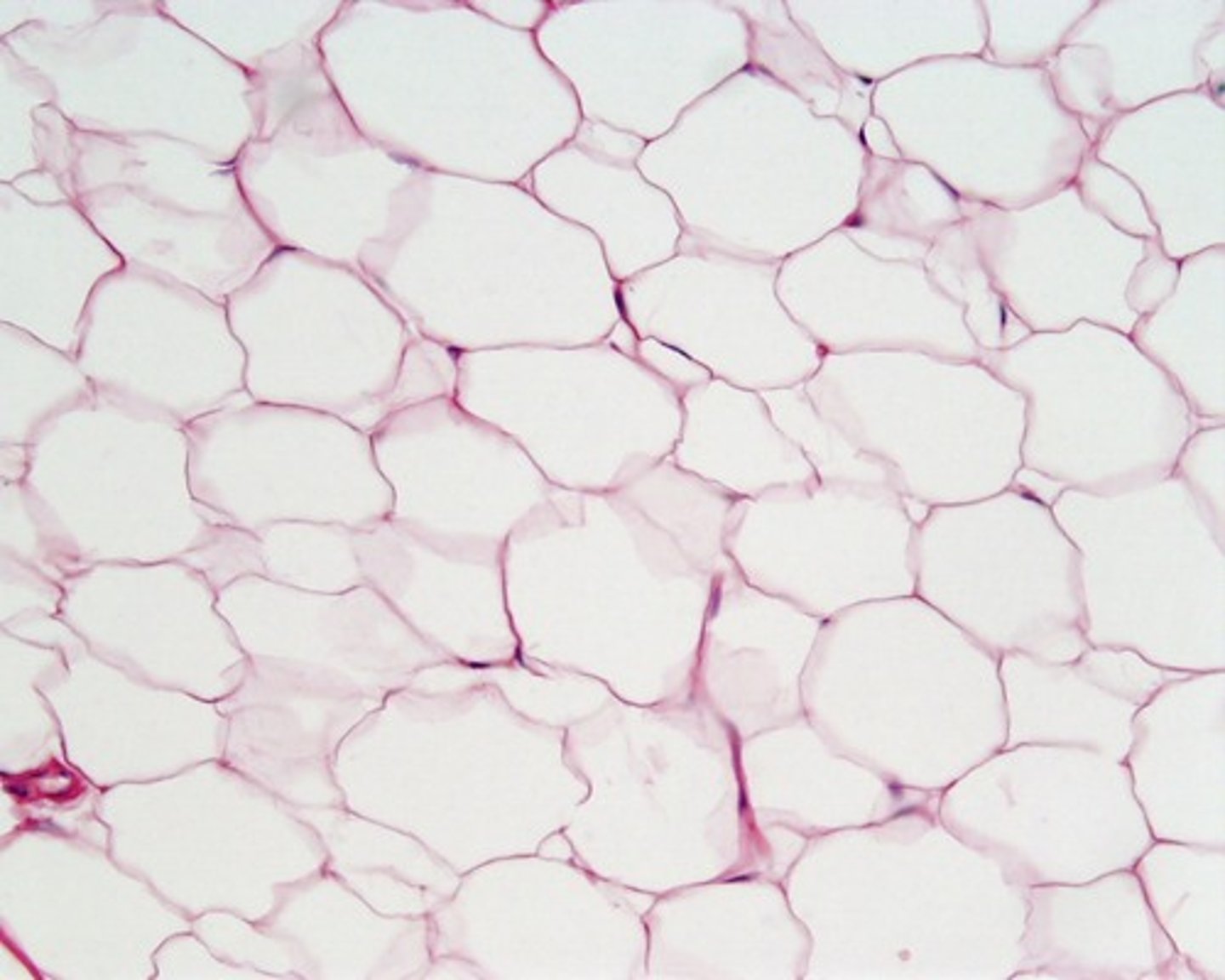
adipose
location- integumentary
function- insulates, supports, protects, reserve fuel
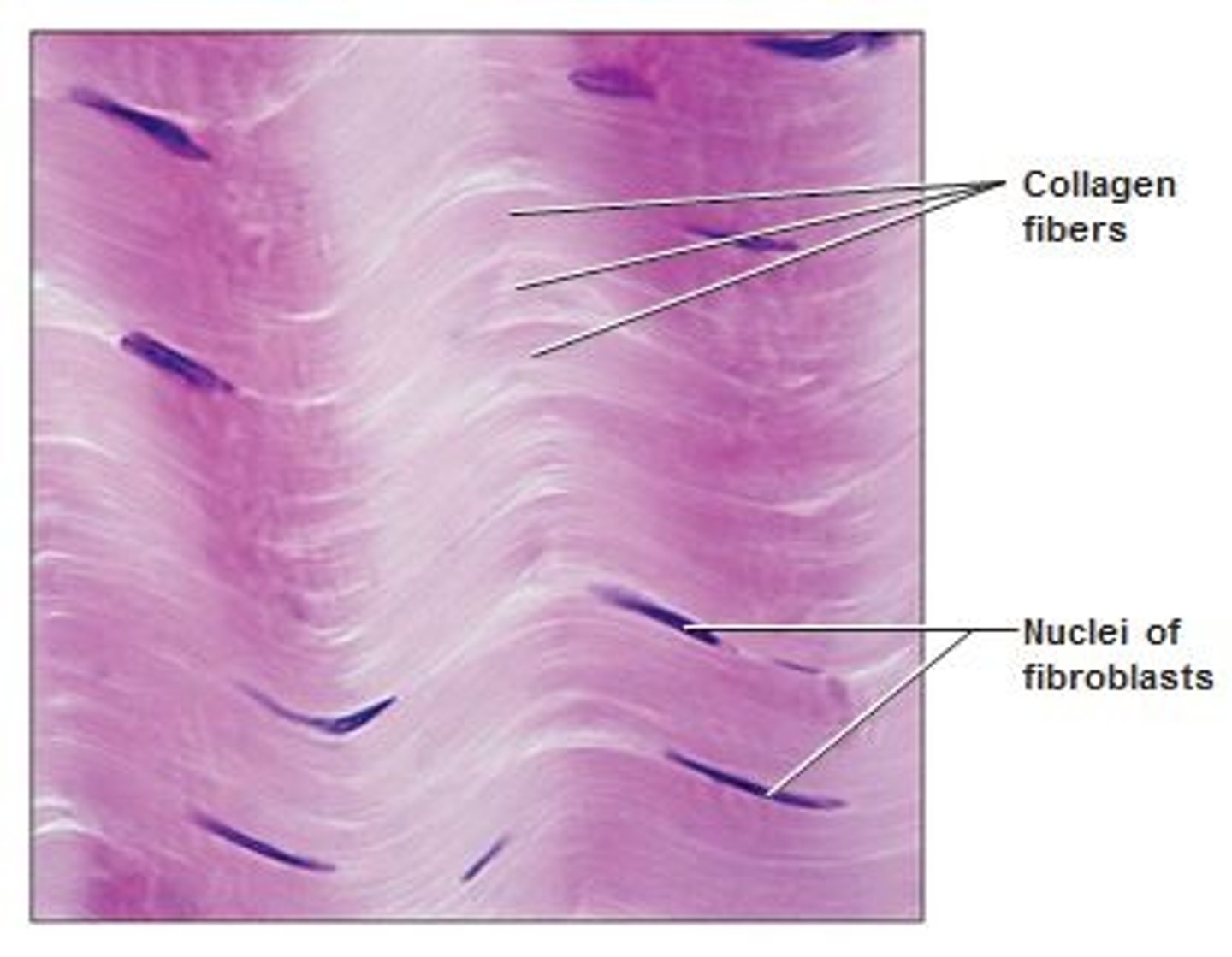
dense regular
location- skeletal, muscular
function- attaches, provides strength
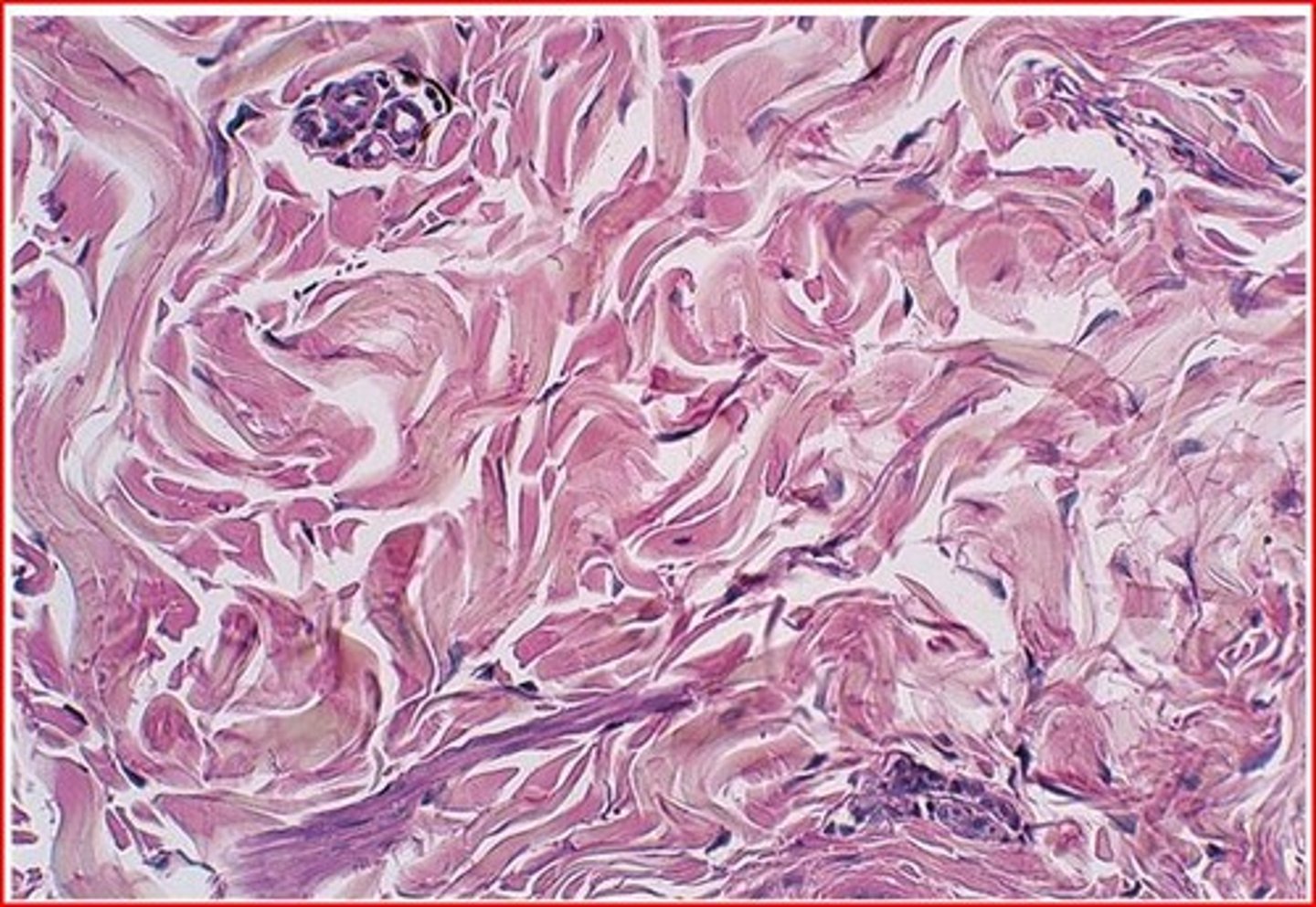
dense irregular
location- integumentary, digestive, skeletal
function- tension, provides strength
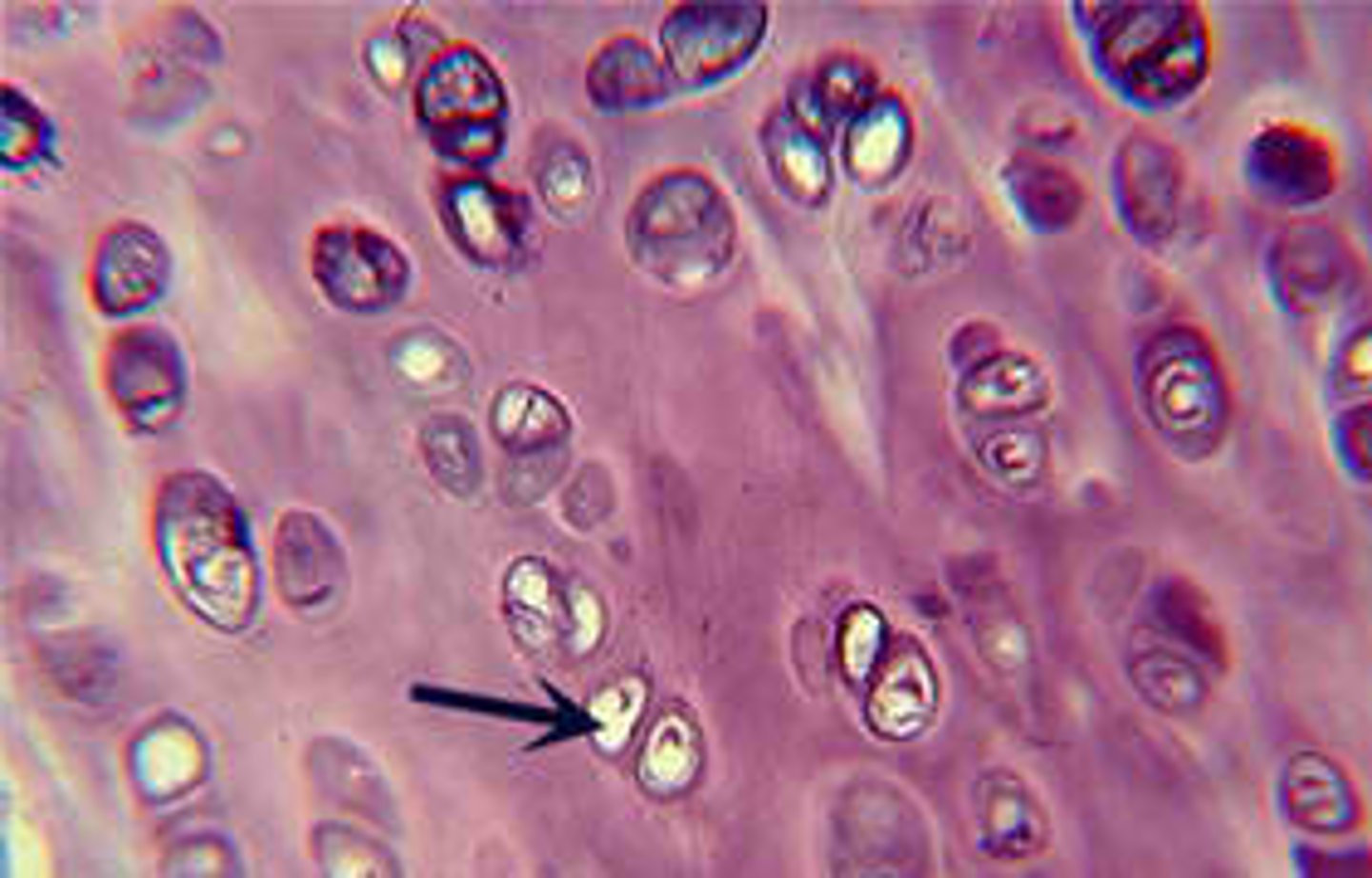
hyaline
location- skeletal, integumentary, respiratory
function- support, reinforce, cushion
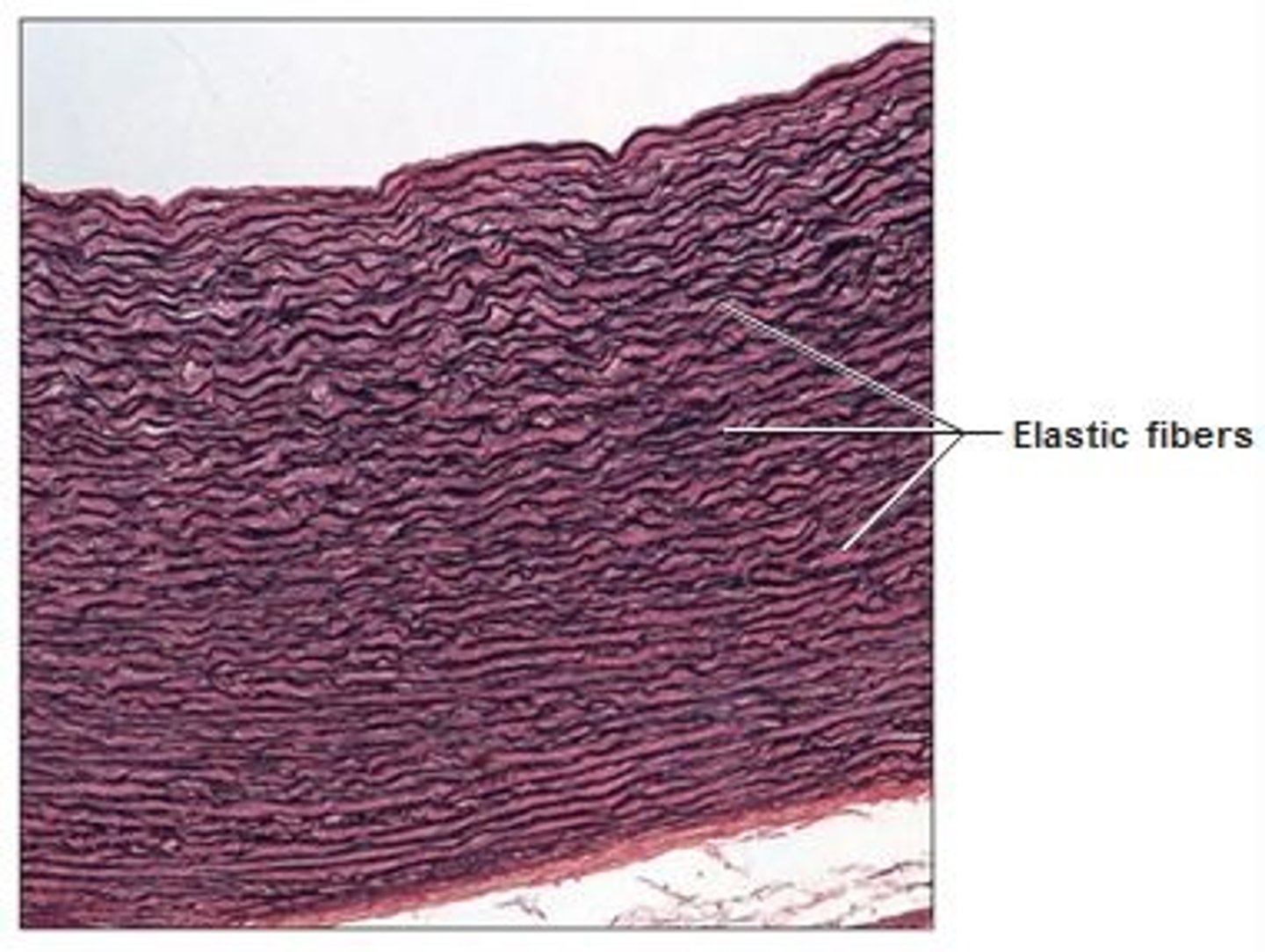
elastic
location- integumentary, digestive
function- flexibility, provides shape
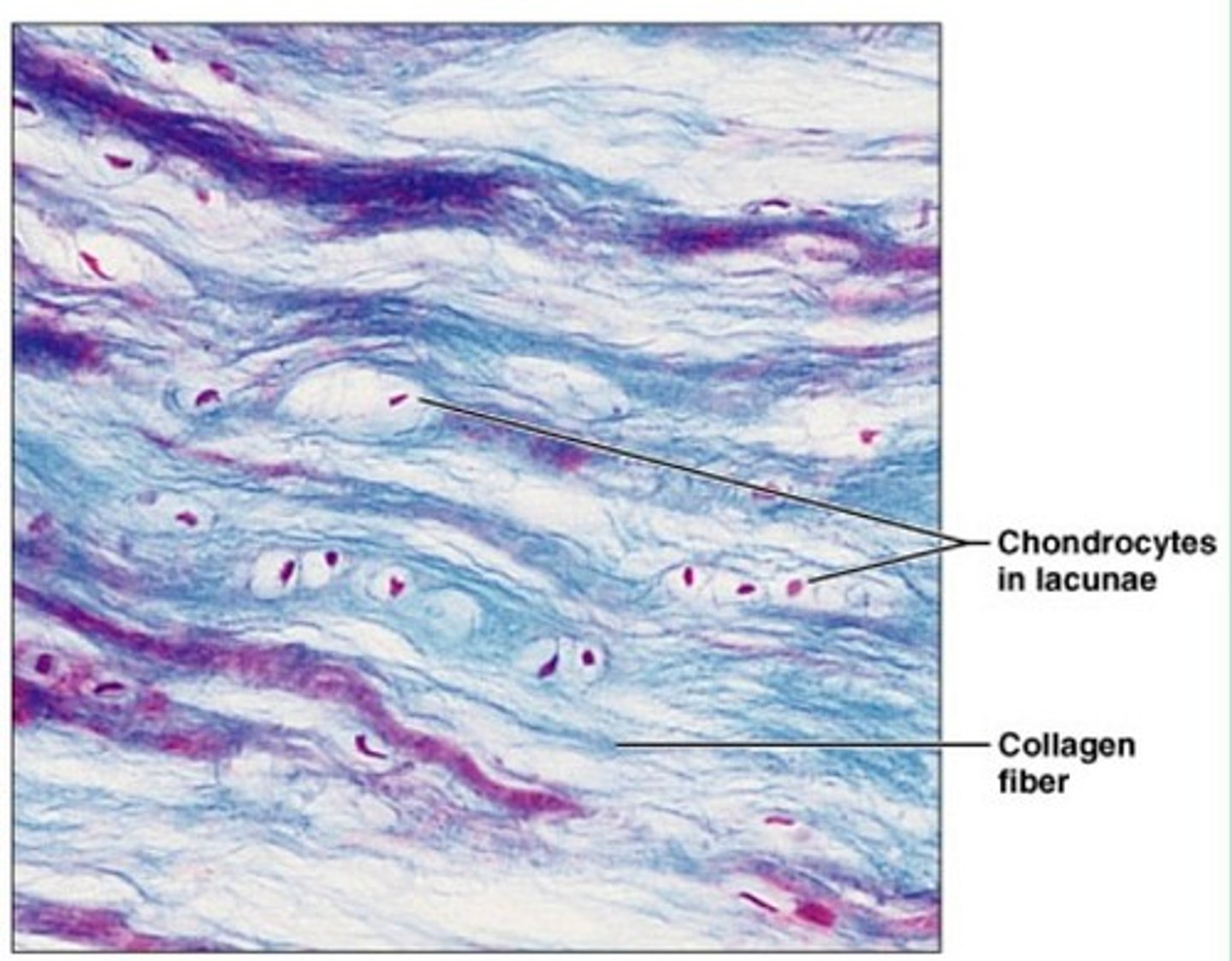
fibrocartilage
location- skeletal
function- strength, allows compression
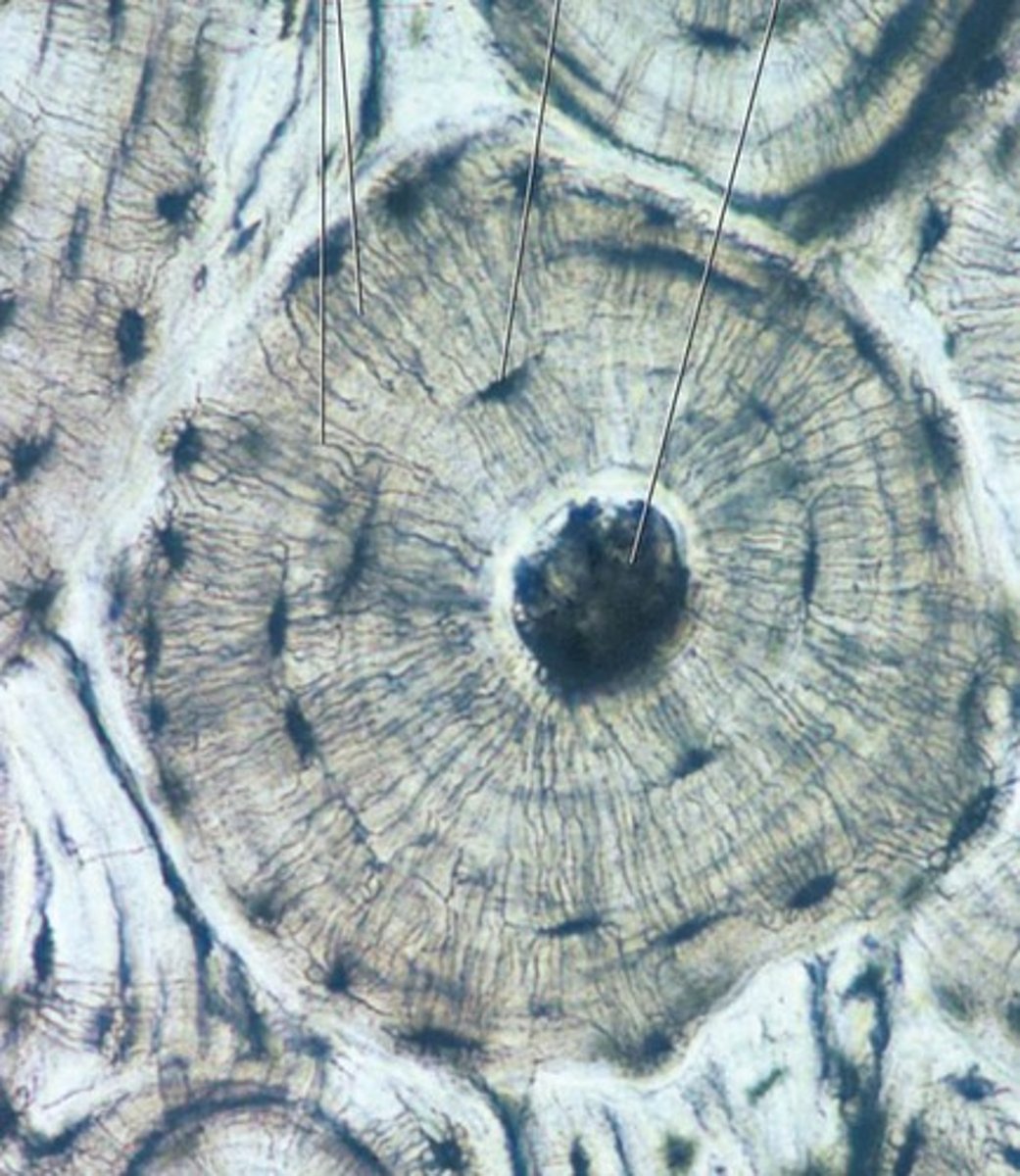
osseous
location- skeletal
function- supports, protects, stores
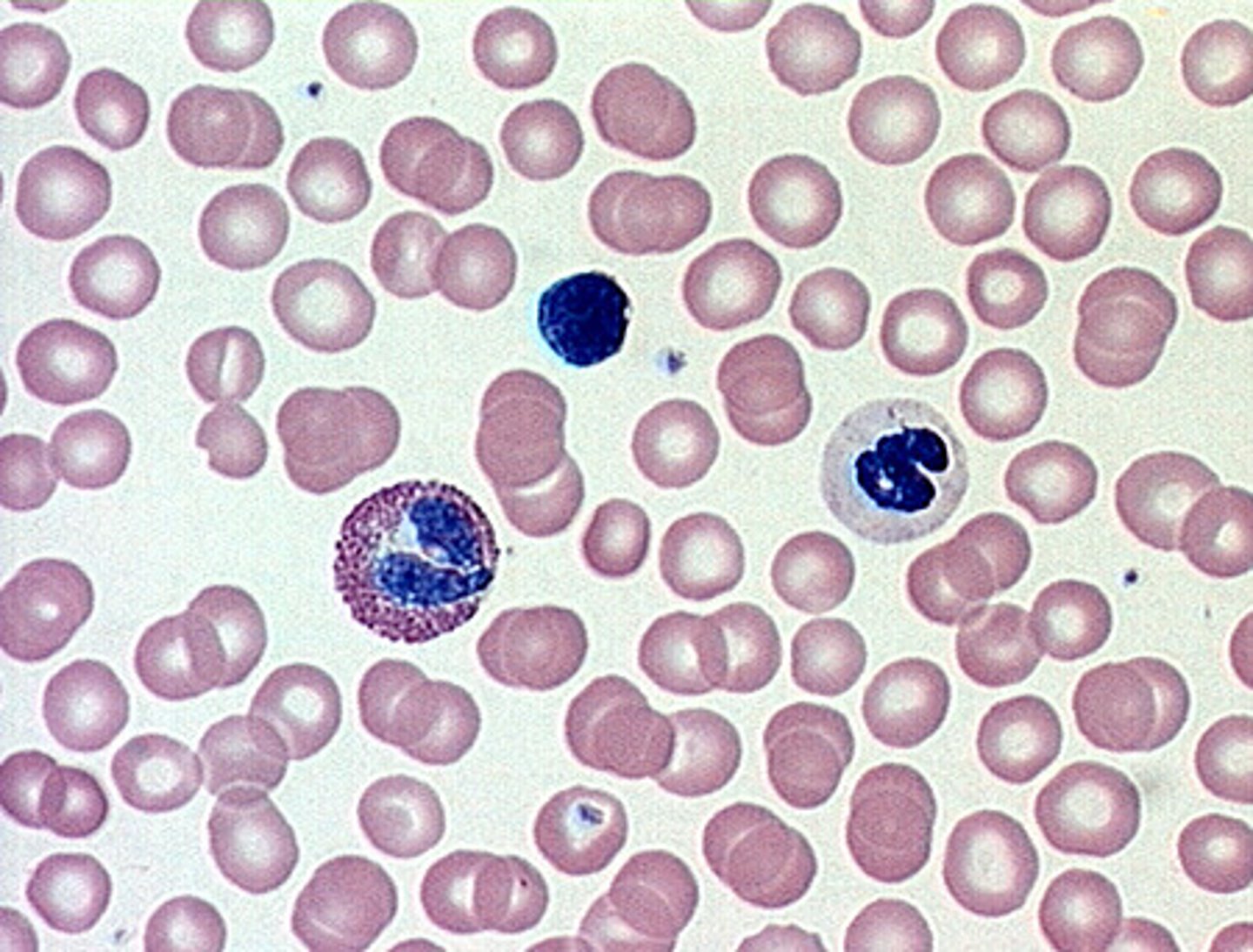
blood
location- cardiovascular
function- transport
nerve
location- nervous
function- transmits
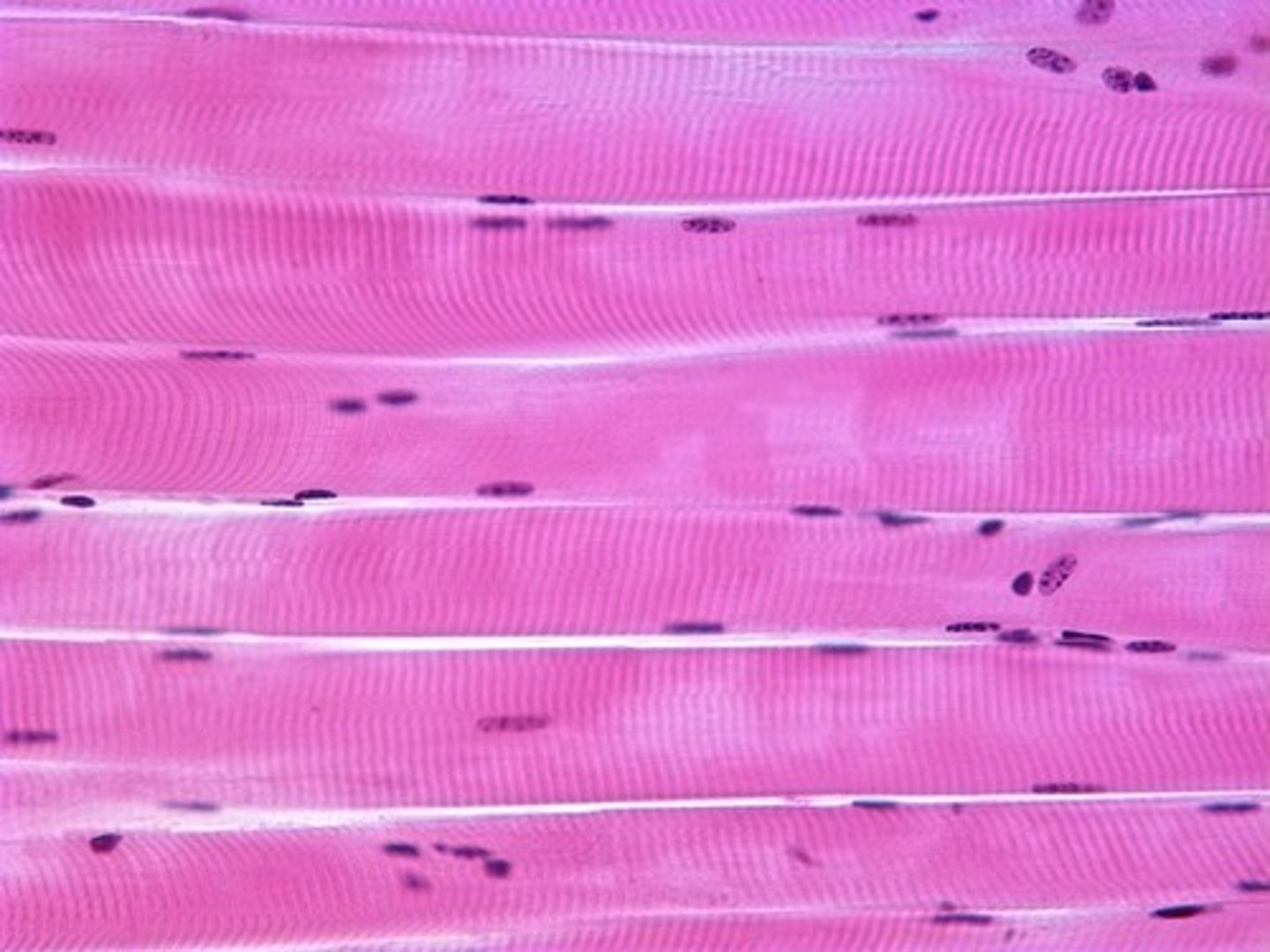
skeletal muscle
location- muscular
function- movement
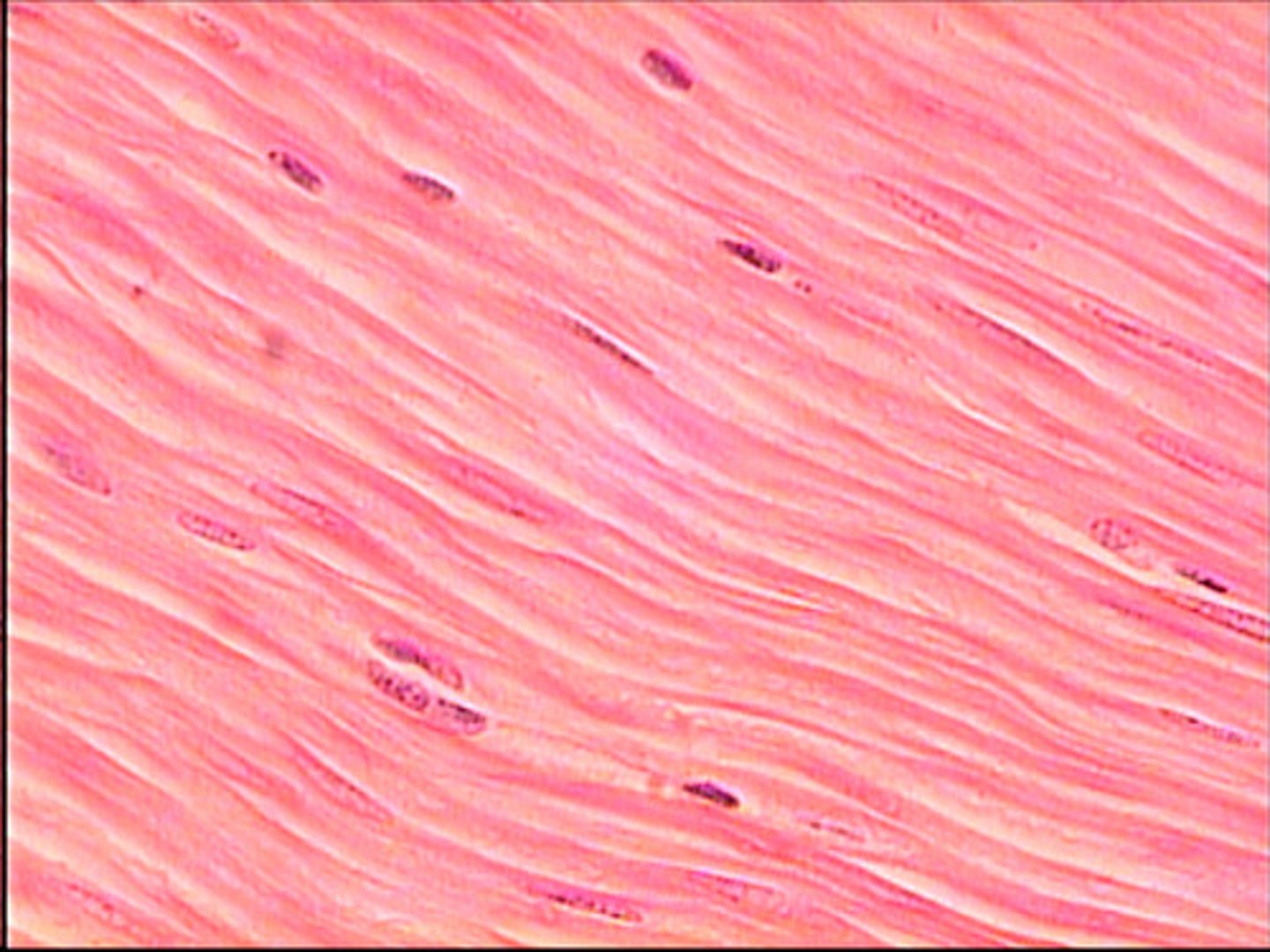
smooth muscle
location- digestive
function- propels
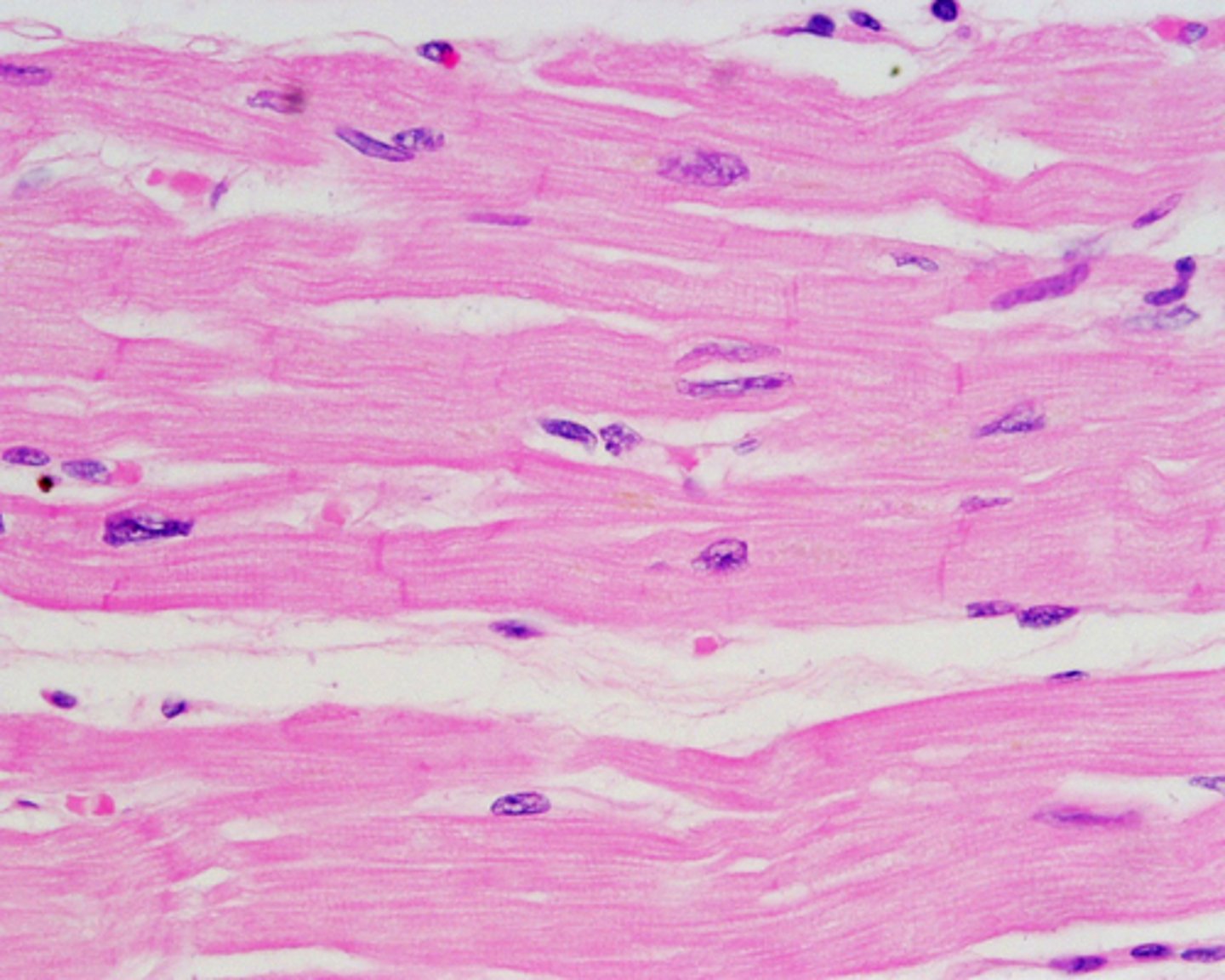
cardiac muscle
location- cardiovascular
function- contracts, propels
Epithelial tissues (3)
Anything that lines something
Composed entirely of cells
Forms sheets held together by junctions and desmosomes
Apical
Top, or free part of epithalial
Basal
Bottom of epithelail
Epithelial regeneration
very fast
Connective tissue
Most diverse and abundant
cartilage
bone
blood
connective tissue proper
Where does connective tissue come from?
mesenchyme
Functions of connective tissue (4)
binding and support
protection
insulation
transportation
Collagen
A connective tissue fiber
tough
tensile strength
skin taughtness
Elastic
Connective tissue fiber
long, thin that allow for stretch
stretch marks
Recticular
branched collagenous fibers
form delicate networks
fibroblasts
cells in connective tissue proper
Chondroblasts
cells in cartilage
Osteoblasts
Cells in bones
hemapoieitc stem cells
cells in blood
Adipose
fat, insulates, stores food, supports and protects
Dense regular
tendons, ligaments, parallel collagen fibers
Hyaline cartilage
supports, reinforces, cushions resists compression
firm and ridgid
nose, trachea
Elastic cartilidge
elastic, structure, flexible
ear
fibrocartalidge
strength and absorbs shock
vertebral disks, knee
Bone
hard, supports, protects, vascular
Blood
transports gas, nutrients, waste
Nervous tissues
transmit electrical signals from receptors
Skeletal muscles
voluntary movements
attached to bones (occasionally skin)
long, cylindrical cells, obvious striped
Cardiac muscles
in heart
involuntary
propels blood
branched, stripes
Smooth muscles
walls of hollow organs
propels materials
spindle cells, NO stripes