human digestive system 🥗
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/79
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
1
New cards
what are the four steps of digestion?
ingestion, digestion, absorption, elimination
2
New cards
what are the 2 parts of the digestive system?
the digestive tract and the accessory digestive organs
3
New cards
what are the 7 parts of the digestive tract in order?
1. Mouth
2. Pharynx
3. Esophagus
4. Stomach
5. Small intestine
6. Large intestine
7. Anus
4
New cards
what do accessory digestive organs do?
add substances to food that help digest it, but do not make contact with food
5
New cards
name the accessory digestive organs (4)
salivary glands, pancreas, gallbladder and liver
6
New cards
how long is the digestive tract?
9 metres
7
New cards
what happens in the digestive tract?
food enters one end of a tube and waste/feces exits the other end
8
New cards
what subunits does digestion break food into?
CHOs become monosaccharides, lipids become glycerol and fatty acids, nucleic acids become nucleotides, proteins become amino acids
9
New cards
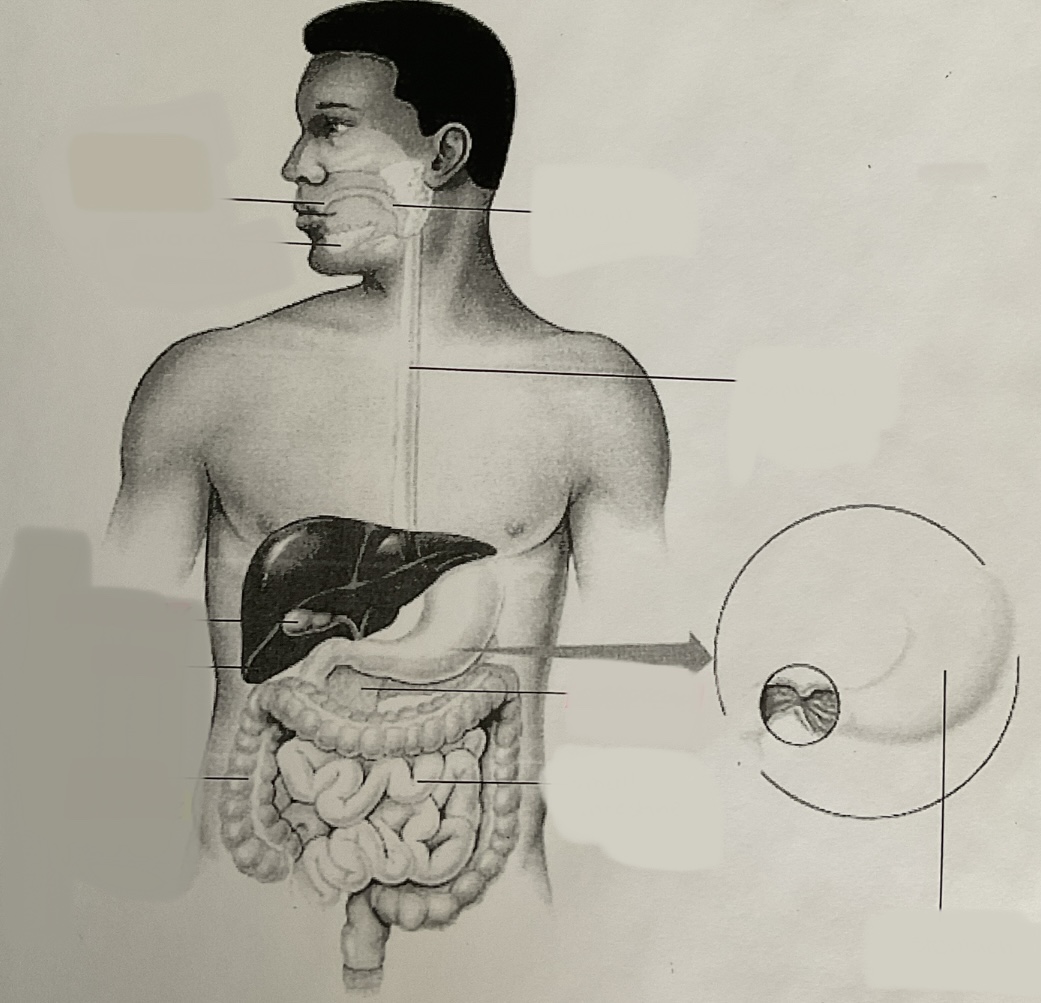
label
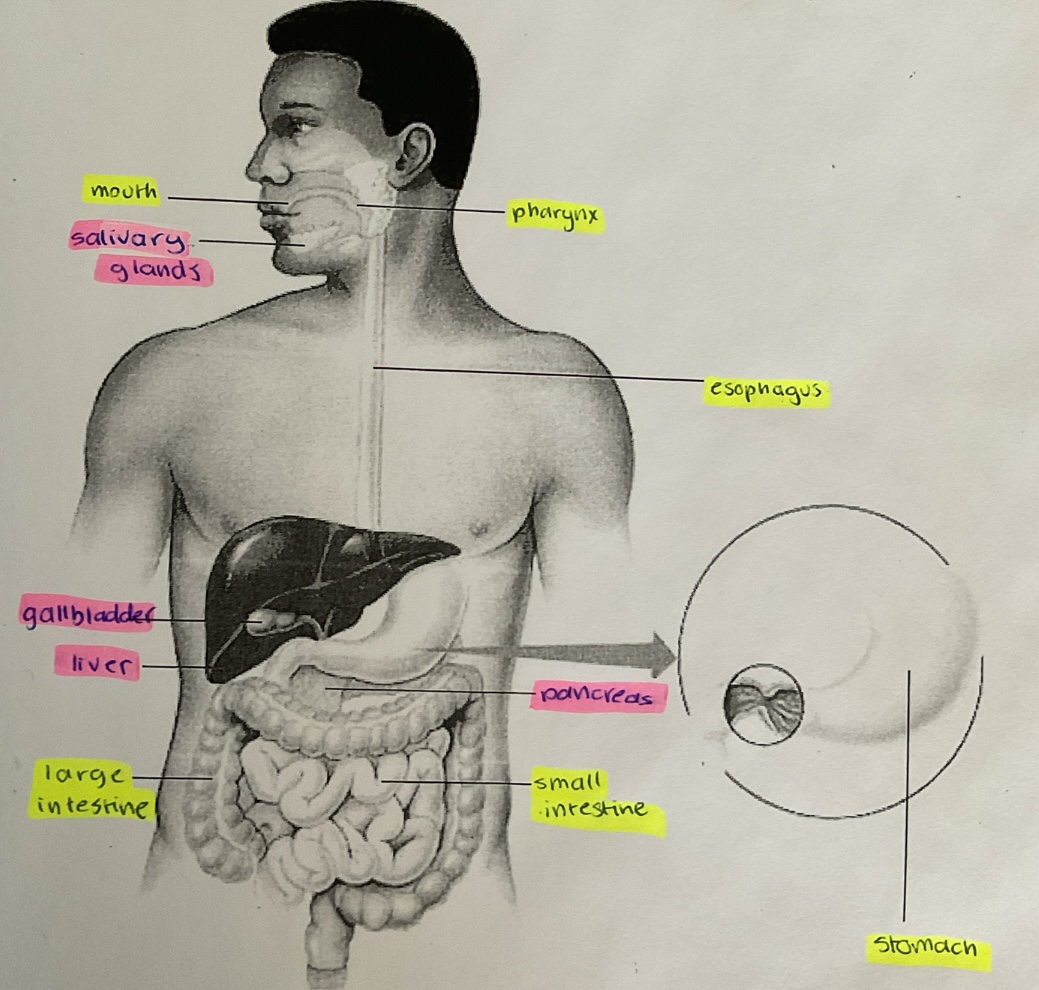
10
New cards
what are the 2 types of digestion?
mechanical digestion and enzymatic digestion
11
New cards
what does mechanical digestion do?
breaks food down into small pieces using the teeth
12
New cards
what does enzymatic digestion do? (2)
\- digests food using different enzymes
\-there is at least one digestive enzyme produced by the digestive system for each of the four types of organic molecules
\-there is at least one digestive enzyme produced by the digestive system for each of the four types of organic molecules
13
New cards
what are salivary glands/ what do they do (3)
\-release saliva into the mouth
\-lubricates food so that it slides down the esophagus more easily
\-produces salivary amylase
\-lubricates food so that it slides down the esophagus more easily
\-produces salivary amylase
14
New cards
what is peristalsis?
smooth muscle forming part of the digestive system wall causes wave like contractions to push food forward
15
New cards
where is peristalsis found? (in order)
esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine
16
New cards
what does the epiglottis do?
prevents food from entering the larynx and trachea by covering them when eating
17
New cards
what are the folds in the stomach called?
rugae
18
New cards
where are gastric glands found?
in pits on the inner surface of the stomach
19
New cards
what do gastric glands secrete (3)
mucus, pepsinogen/pepsin and hydrochloric acid
20
New cards
what does mucus do in the stomach?
coats the inside to protect it from acid
21
New cards
when is pepsinogen activated and what does it become?
activated by HCl in the stomach and becomes pepsin
22
New cards
what does HCl do in the stomach? (2)
activates pepsin, kills microorganisms in food
23
New cards
what does -ogen indicate?
an inactive protein/enzyme
24
New cards
what happens during:
a) ingestion
b) digestion
c) absorption
d) elimination
a) ingestion
b) digestion
c) absorption
d) elimination
a) taking in food
b) food is broken into subunits we can use
c) subunits are absorbed into the blood which transports them throughout the body
d) get rid of indigestible materials
b) food is broken into subunits we can use
c) subunits are absorbed into the blood which transports them throughout the body
d) get rid of indigestible materials
25
New cards
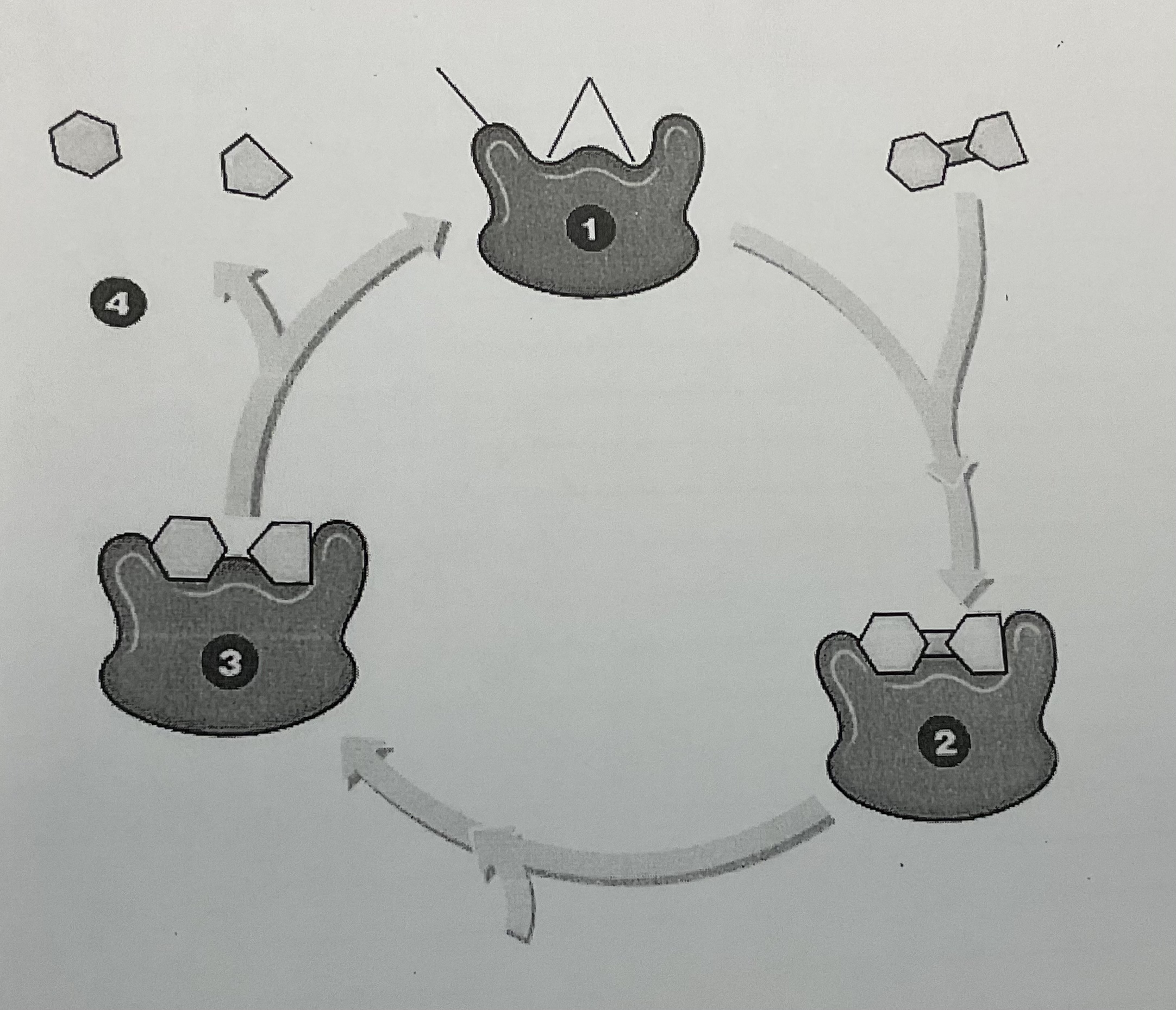
label
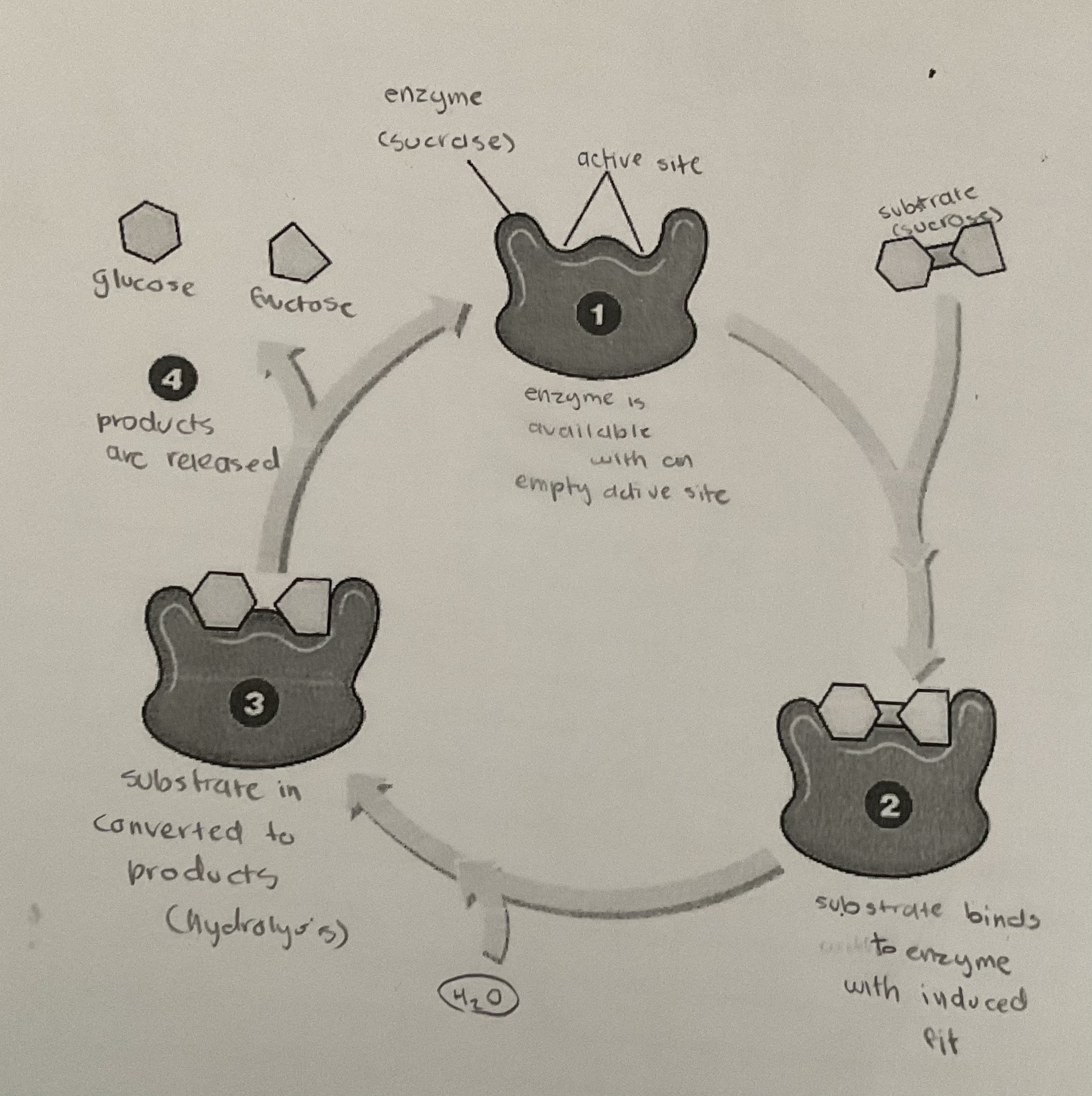
26
New cards
what is an ulcer?
a sore in the stomach that occurs when there isn’t enough mucus coating the inner wall
27
New cards
a) what did we previously think caused ulcers?
b) what actually causes ulcers?
b) what actually causes ulcers?
a) stress and spicy food
b) a bacteria called __Helicobacter__ __pylori__
b) a bacteria called __Helicobacter__ __pylori__
28
New cards
how are ulcers treated?
antibiotics
29
New cards
what is bolus?
a mass of chewed food mixed with saliva
30
New cards
what is chyme?
bolus that has mixed with gastric juice in the stomach
31
New cards
what happens to the pyloric sphincter after a meal?
it opens every few seconds to allow a small amount of chyme to enter the SI
32
New cards
what is a non digestive function of the liver?
to make blood clotting proteins
33
New cards
what are the digestive functions of the liver? (3)
1. filters extra sugar from the blood and stores it as glycogen
2. detoxifies harmful chemicals like alcohol and drugs
3. produces bile
34
New cards
what does bile do?
\-helps digest lipids by breaking large fat droplets into smaller ones
\-is NOT enzymatic
\-is NOT enzymatic
35
New cards
what is emulsification?
the process by which bile breaks down lipids
36
New cards
what does the gallbladder do?
stores bile until it is released into the duodenum via the bile duct
37
New cards
what is the function of the pancreas?
to produce digestive enzymes that mix with chyme in the SI
38
New cards
what digestive enzymes does the pancreas produce? (4)
pancreatic amylase, trypsin, chymotrypsin, lipase
39
New cards
where does most nutrient absorption occur?
the small intestine
40
New cards
in what ways does the small intestine increase its surface area?
1) 7m long
2) folded inner surface
3) lined with tiny, finger like projections called villi
4) each villus is covered in smaller finger like projections called microvilli
2) folded inner surface
3) lined with tiny, finger like projections called villi
4) each villus is covered in smaller finger like projections called microvilli
41
New cards
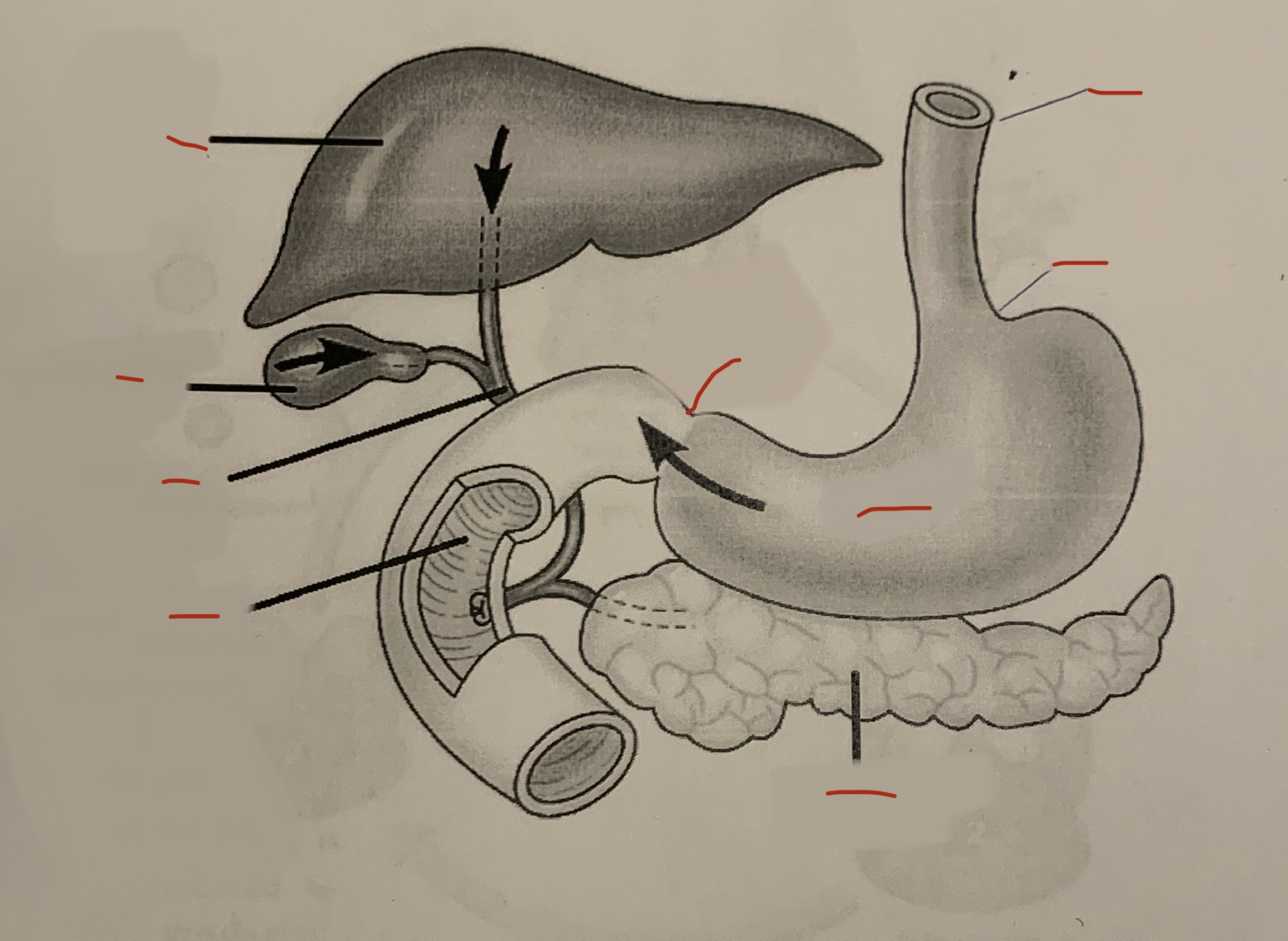
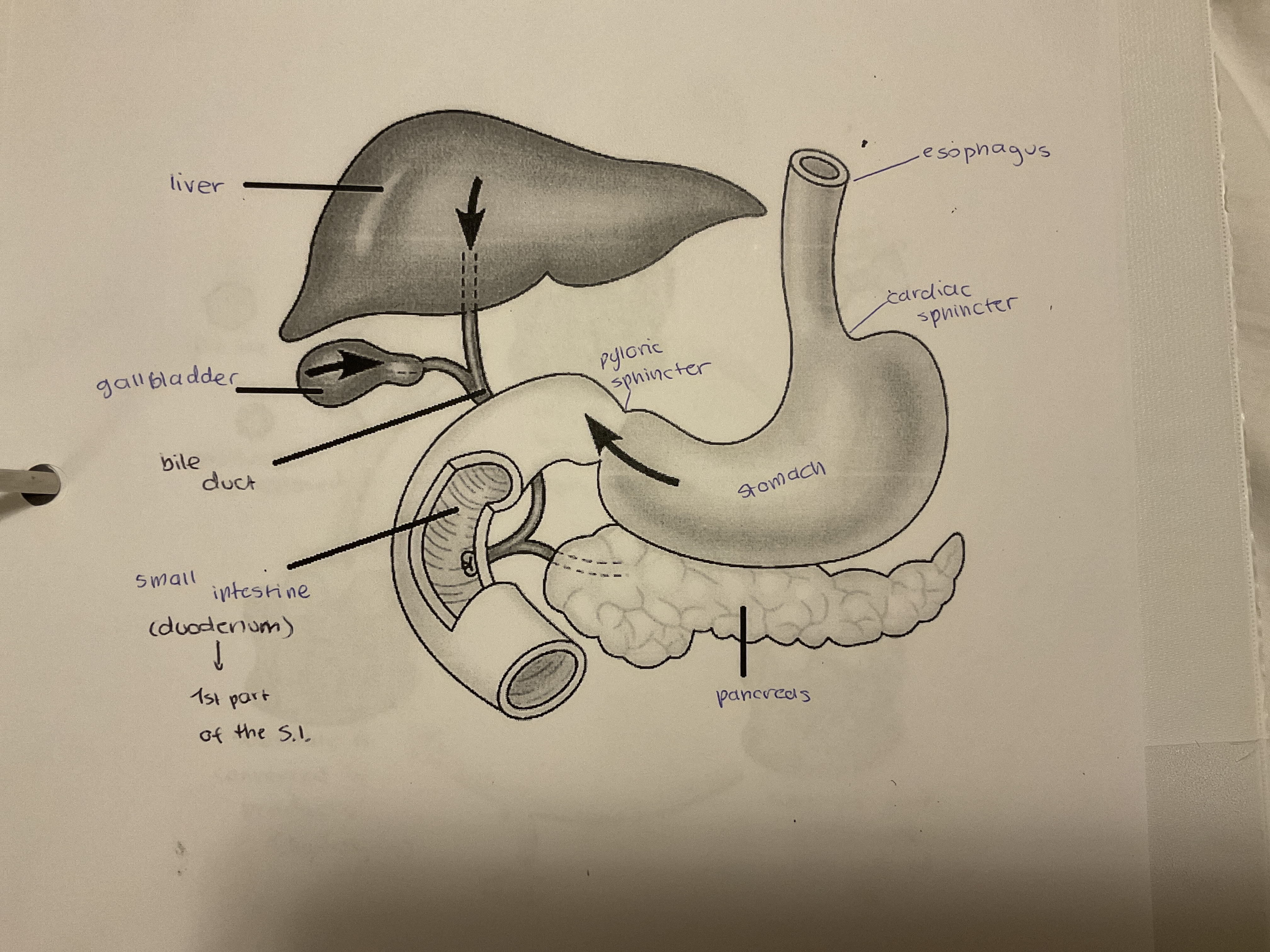
label
42
New cards
what is a hormone?
a substance secreted directly into the blood that has a specific effect on certain tissue
43
New cards
what stimulates the flow of gastric juices? (3)
1) thought/sight/smell/taste of food causes the brain to tell the gastric juices to secrete
2) food touching the stomach lining
3) the production of gastrin
2) food touching the stomach lining
3) the production of gastrin
44
New cards
what causes gastrin production? (4)
stretching of the stomach wall, proteins, caffeine, alcohol
45
New cards
how long does it take liquids to pass through the stomach?
20 minutes or less
46
New cards
how long after a meal is the stomach empty?
2-6 hours
47
New cards
what is the stomach’s capacity?
over 2L
48
New cards
what causes mechanical digestion in the stomach?
the stomach wall contracting
49
New cards
what causes heartburn?
the cardiac sphincter relaxes and HCl reaches the esophagus
50
New cards
how many pairs of salivary glands are there?
3
51
New cards
what are the 2 types of saliva?
1) thin and watery, wets the food
2) thick and mucus, acts as a lubricant and helps bolus form
2) thick and mucus, acts as a lubricant and helps bolus form
52
New cards
what is another name for the disgestive tract?
alimentary canal
53
New cards
what are the two types of glands in the stomach and what do they secrete?
gastric-gastric juice
pyloric-mucus
pyloric-mucus
54
New cards
what does gastric juice contain?
HCl and pepsin
55
New cards
where is gastrin secreted from?
the stomach lining
56
New cards
what are the three sections of the small intestine in order?
duodenum, jejunum and ileum
57
New cards
what is the shortest section of the SI?
the duodenum (25cm)
58
New cards
what is extracellular digestion and name an example
digestion that occurs outside of cells (ep salivary amylase in the mouth)
59
New cards
how long is a villus?
1mm
60
New cards
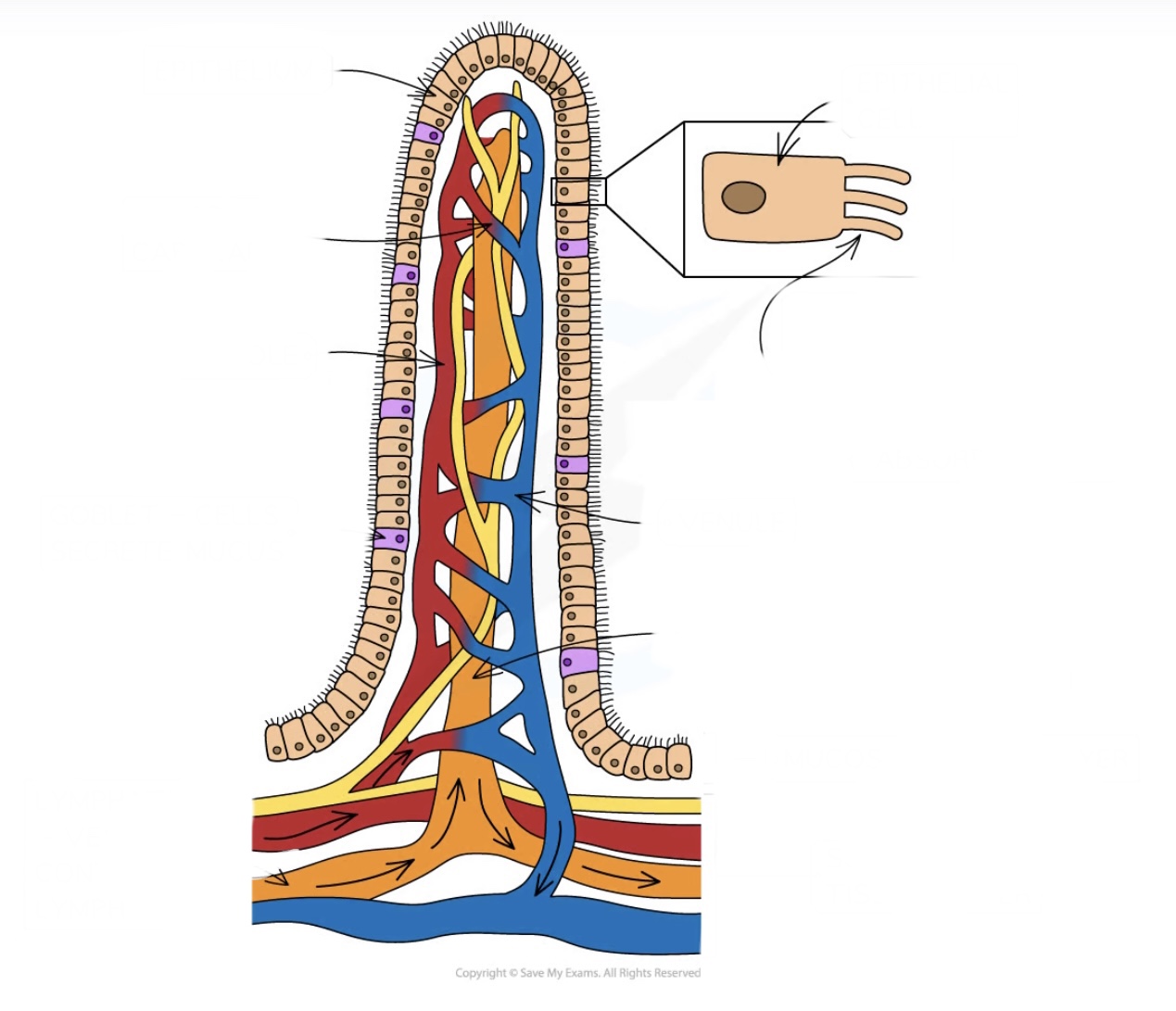
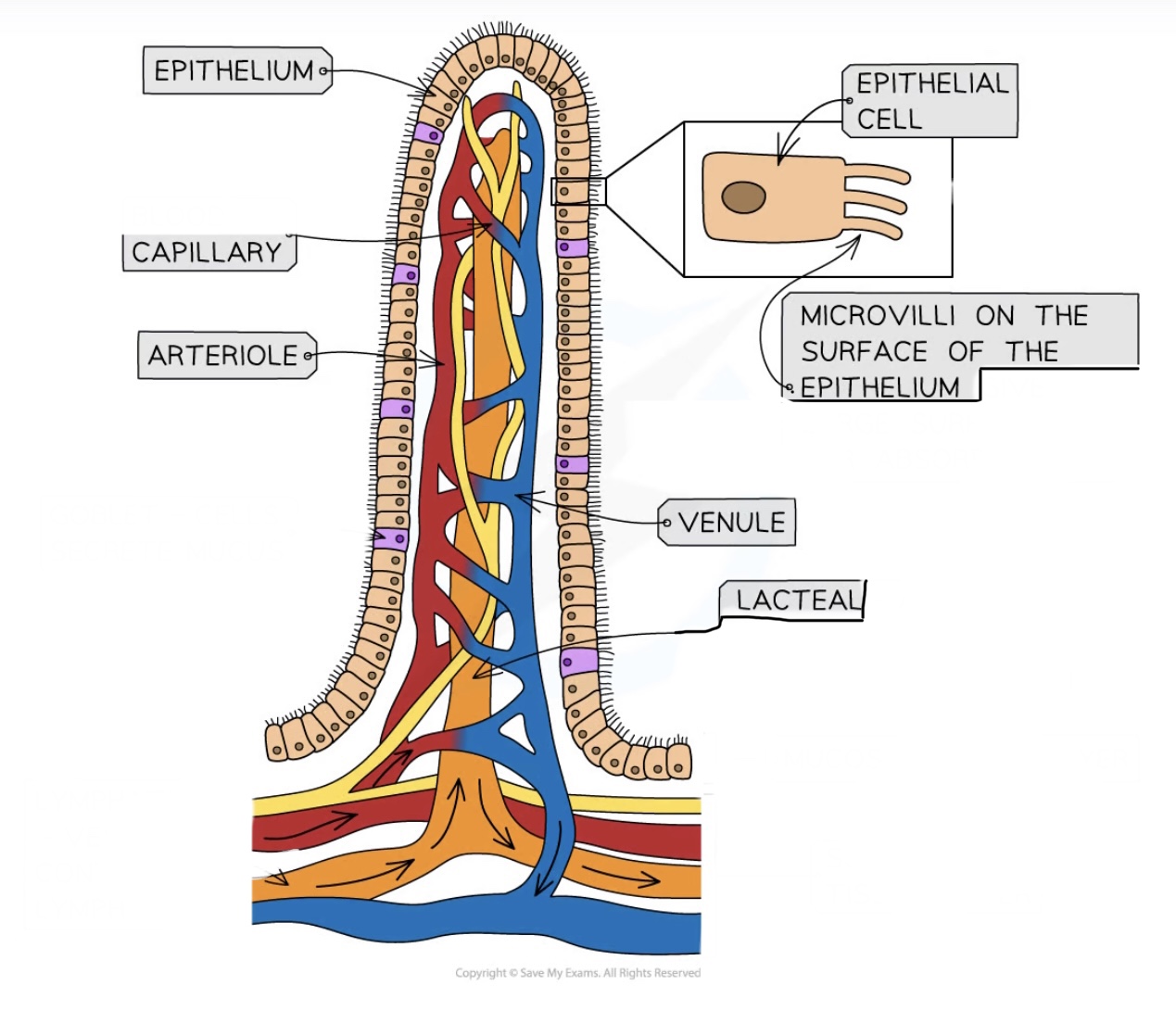
label (7)
61
New cards
how are monosaccharides, amino acids and nucleotides absorbed?
by diffusing through the epithelium of a villus into capillaries. they are then sent around the body through blood
62
New cards
how do fatty acids and glycerol enter the blood?
the lacteal
63
New cards
what is the LI also known as?
the colon
64
New cards
what are the three functions of the LI? (3)
1) absorbing excess water into the blood
2) some bacteria in the LI make vitamins we need
3) indigestible materials like cellulose collect in the rectum
2) some bacteria in the LI make vitamins we need
3) indigestible materials like cellulose collect in the rectum
65
New cards
name 3 sphincters
anus, pyloric sphincter and cardiac sphincter
66
New cards
what happens when the anus relaxes?
feces elimination
67
New cards
what are the 8 digestive enzymes?
salivary amylase, pepsin, trypsin, chymostrypsin, pancreatic amylase, peptidase, maltase and lipase
68
New cards
what does each digestive enzyme break down?
\-salivary amylase, maltase and pancreatic amylase-CHOs
\-lipase-lipids
\-pepsin, trypsin, chymotrypsin, peptidase-proteins
\-lipase-lipids
\-pepsin, trypsin, chymotrypsin, peptidase-proteins
69
New cards
what are the effects of the SI’s constant movement? (4)
1) chyme is squeezed through the intestine
2) chyme is mixed with the digestive enzymes
3) food particles are broken down mechanically
4) absorption is sped up because the movement forces the chyme to make contact with the SI wall
2) chyme is mixed with the digestive enzymes
3) food particles are broken down mechanically
4) absorption is sped up because the movement forces the chyme to make contact with the SI wall
70
New cards
what 2 hormones does the pancreas secrete and what do they do?
cholecystokinin and secretin stimulate the pancreas and gallbladder to release digestive enzymes/pancreatic juice/bile
71
New cards
what stimulates the release of bile from the gallbladder?
the hormone cholecystokinin
72
New cards
what is the point of emulsification?
it increases the surface area of lipids, making then easier to digest
73
New cards
what enzymes does the SI secrete?
maltase and peptidase
74
New cards
how long is the LI
1\.5m
75
New cards
what is appendicitis?
the appendix becomes inflamed and must be removed
76
New cards
which vitamins do LI bacteria produce?
vitamin K and some B vitamins
77
New cards
what is vitamin K essential for?
blood clotting
78
New cards
what does feces consist of? (5)
cellulose, bacteria, bile, mucus and worn out cells
79
New cards
what are the hormones? (3)
gastrin, cholecystokinin, secretin
80
New cards
what are proteases?
enzymes that break down proteins