oil and gas, part 3
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what are some alternative energy sources
not coal, natural gas, and oil
which to country’s rely on fossil fuels for 83% of the total energy and together they account for 42% of the world’s energy consumption?
USA and China
nonconventional fossil fuels are fossil fuels not including:
coal, natural gas, and light crude oil
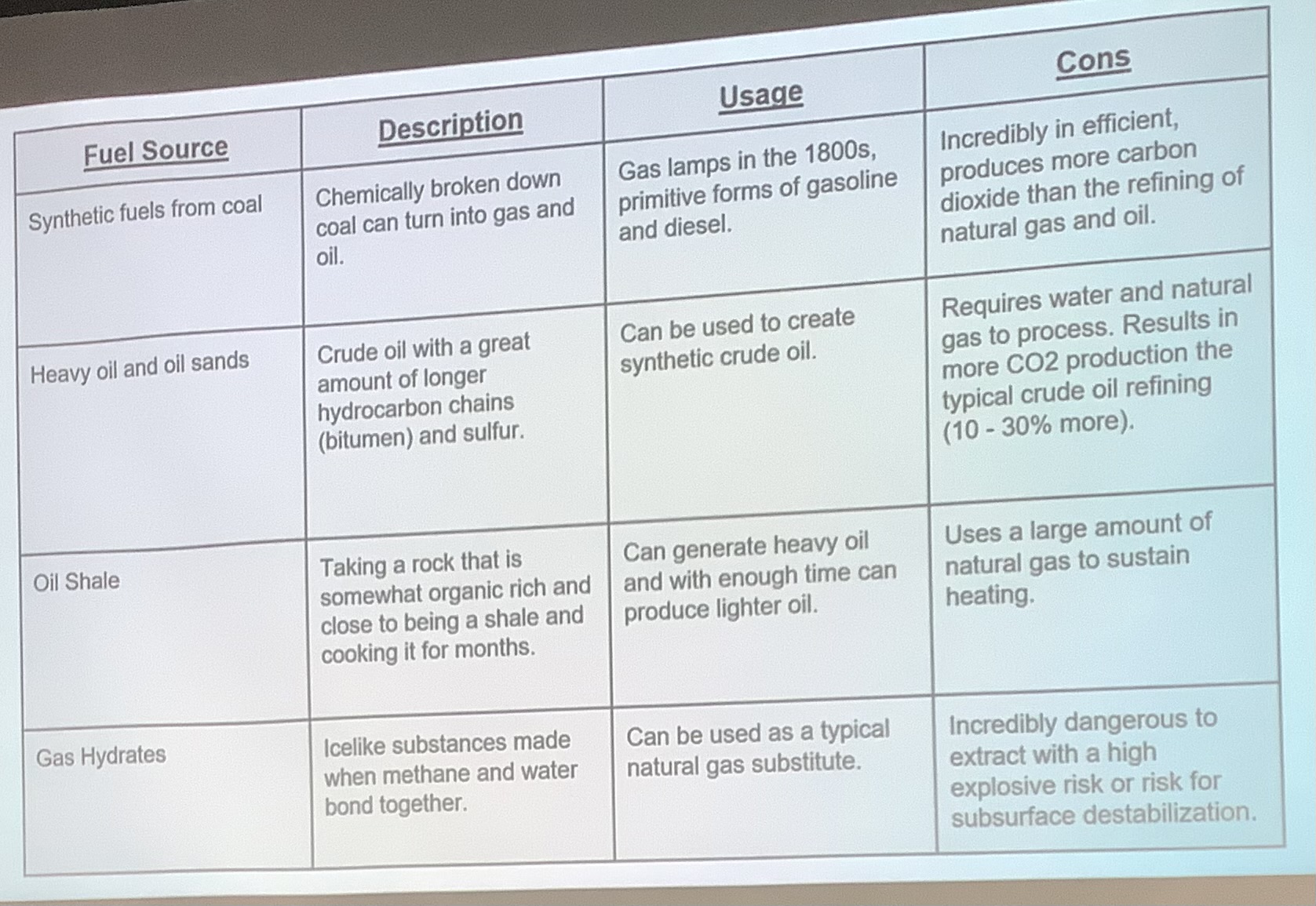
what is a shale?
a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock composed primarily of clay and silt particles that forms in low-energy environments like ancient lakes, river floodplains, and marine basins
what are some carbon free and renewable energy sources:
sunlight, wind, water, geothermal, biomass
what are some carbon free and renewable fuels:
biofuels
hydroelectric power
nuclear power
solar power
wind power
geothermal power
ocean thermal energy conversion
tidal power
what are biofuels?
combustible materials derived from modern (non-fossilized) organic matter.
ex. ethanol and biodiesel fuels
whaat are the two predominant types of biofuels?
ethanol - made from the fermentation of plant material
biodiesel -fatty acids from vegetable oil and animal fats
define hydroelectric power:
the mechanical energy obtained from falling water used for generating electricity
this is both renewable and does not produce carbon dioxide
define nuclear power:
the bonds that hold protons, neutrons, and electrons together in the nucleus of an atom are energetic
what are the two primary ways of producing nuclear energy:
nuclear fission - the process of splitting the nucleus of an atom, resulting in the release of neutrons and conversion of mass into energy
nuclear fusion - a natural process that takes place in the sun, in which the nuclei of hydrogen atoms combine or fuse, releasing large amounts of energy
what is solar power:
the process that takes place when solar radiation strikes a solid object and is transformed into thermal or heat energy
what are photovoltaic cells (solar panels)?
thin slabs of material composed of silicon alloys, which produces electricity when sunlight is allowed to strike the slab
what is wind power?
taking the mechanical energy of the wind to turn a turbine that generates electricity
does not produce any greenhouse gases and is renewable
what is geothermal energy?
the heat energy contained within the earth that can be used to drive a steam turbine for producing electricity or serve as a hear source and sink for a geothermal heat pump
what is tidal power?
energy that is obtained from the cyclical lowering and raising of sea level due to the tides and is used to turn a generator to produce electricity
what is energy conservation?
the process of reducing energy consumption through decreased human activity and is more efficient use of the energy itself