AP Stats Ch.11/12 Vocab
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
voluntary response sample
usually biased since most that volunteer have strong opinions or are more motivated than others
Convenience sampling
only accounts for those that are convenient for an outcome
Undercoverage
when certain groups of a population are not counted
Nonresponse bias
when people don’t respond to a survey
Response bias
when the wording of questions might influence a particular answer
simple random sample (SRS)
ex. assigning sample frame like #’s to a roster of people then using a random # sequence to choose a number of people.
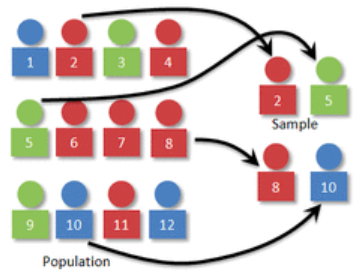
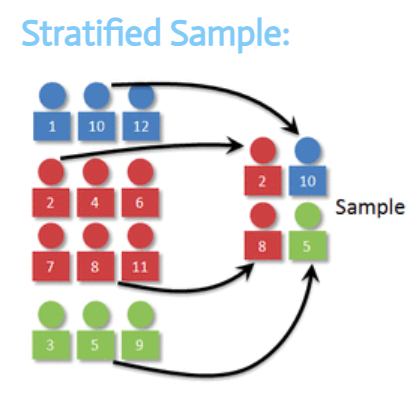
stratified random sample
the population is split into groups (strata) and then random #’s would be assigned and randomly chosen using a random # sequence
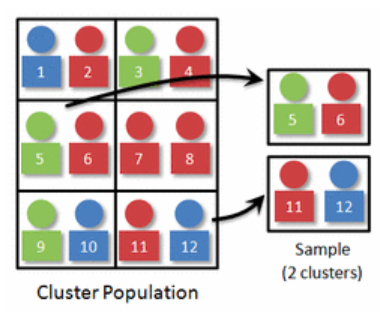
cluster sample
population is naturally separated into clusters that resemble the population, then some of those groups are picked
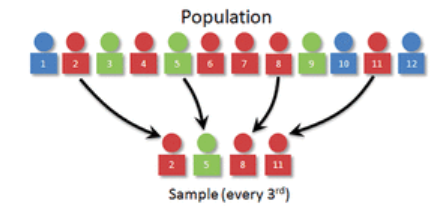
Systematic sample
uses a list of individuals that are given numbers in numerical order. A random number generator generates a number that will select the start of the list. From that number, the list will continue with every nth number.
Multistage sampling
Uses a combination of different types of sampling methods. This method is used when the population is very large.
retrospective
collecting past data
prospective
collecting future data
Experimental units (subjects in people)
The individuals upon which an experiment is conducted
Controlled experiment
all treatment groups have the same environment
Randomized participants
equalize the effects of unknown or uncontrollable sources of variation
Why replicate treatments/experiments?
Itgives more consistent feedback over time
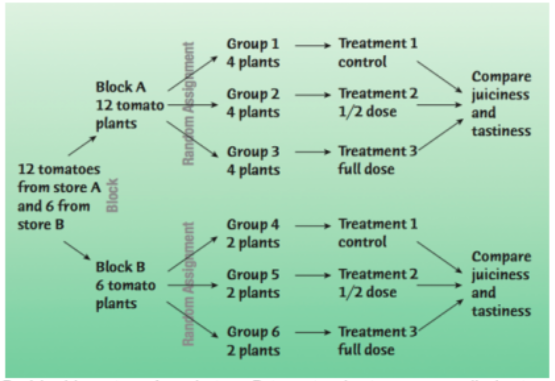
Blocking (not required)
may help separate confounding variables and lead to better results
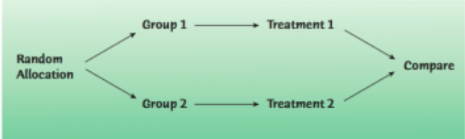
control group
baseline untreated group/basis of comparison
single blinding
patients do not know which study group they are in
double blinding
neither the patients nor the researchers/doctors know which study group the patients are in
placebo effect
when the fake treatment yields a change in the response variable (usually mental)
randomized block design (matching)
confounding
When the levels of one factor can entangled with another factor