Topic 2 - States of Matter and Mixtures
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Which state of matter has the strongest forces of attraction between particles?
Solid.
Which state of matter has the weakest forces of attraction between particles?
Gas.
Which state of matter has the highest density?
Solid.
Which state of matter has the lowest density?
Gas.
Describe the arrangement of solid particles.
Regular and close together.
Describe the arrangement of liquid particles.
Irregular, random and quite close.
Describe the arrangement of gas particles.
Irregular, random and far apart.
Describe the movement of solid particles.
Vibrate in fixed positions.
Describe the movement of liquid particles.
Slide and move around each other.
Describe the movement of gas particles.
Move randomly in all directions.
Can solids be compressed?
No.
Explain why solids cannot be compressed.
The particles are already close together her in a fixed lattice and cannot be pushed closer together.
Can liquids be compressed?
No.
Explain why liquids cannot be compressed.
Particles are already close together so cannot be pushed any closer.
Can gases be compressed?
Yes.
Explain why gases can be compressed.
Particles are far apart so can be pushed closer together.
Can solids take the shape of the container?
No.
Can liquids take the shape of the container?
Yes.
Can gases take the shape of the container?
Yes.
Describe the difference between particles in the substance when it is in a liquid state is when it is a liquid state.
In a liquid state, particles are constantly moving and have a lot of energy compared to solid particles with less energy and particles that vibrate in fixed positions.
Are changes of state physical or chemical changes?
Physical.
Explain why changes of state are called physical changes rather than chemical changes.
Physical changes do not result in the formation of a new substance annd are easily reversible.
What is melting?
Solid to Liquid.
What is evaporation/boiling?
Liquid to Gas.
What is freezing?
Liquid to Solid.
What is condensation?
Gas to Liquid.
What is deposition?
Gas to Solid.
What is sublimation?
Solid to Gas.
What is it called when a solid becomes a gas?
Sublimation.
What is it called when a gas becomes a solid?
Deposition.
What is it called when a liquid becomes a solid?
Freezing.
What is it called when a solid becomes a liquid?
Melting.
What is it called when a liquid becomes a gas?
Evaporation/Boiling.
What is it called when a gas becomes a liquid?
Condensation.
If a substance is below its melting point, what state of matter is it?
Solid.
If a substance is above its melting point and below its boiling point, what state of matter is it?
Liquid.
If a substance is above its boiling point, what state of matter is it?
Gas.
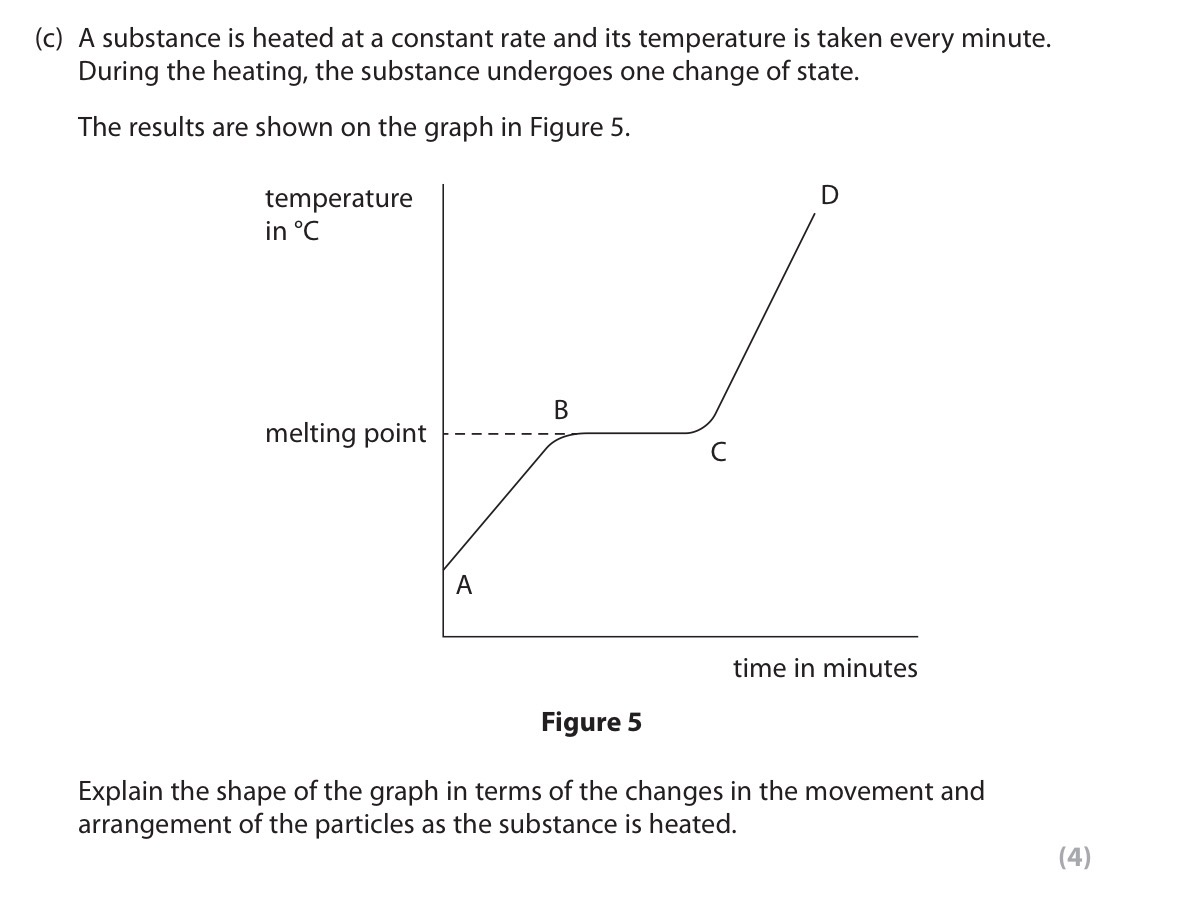
Explain the graph.
B-C: Particles in solid use energy to break intermolecular bonds between
particles, making them more randomly arranged as they turn from a solid to liquid.
A-B: Particles in solid in a lattice vibrate in fixed positions. They vibrate more as temperature
increases.
C-D: Particles in a liquid move past one another randomly. Particles move more as temperature increases.
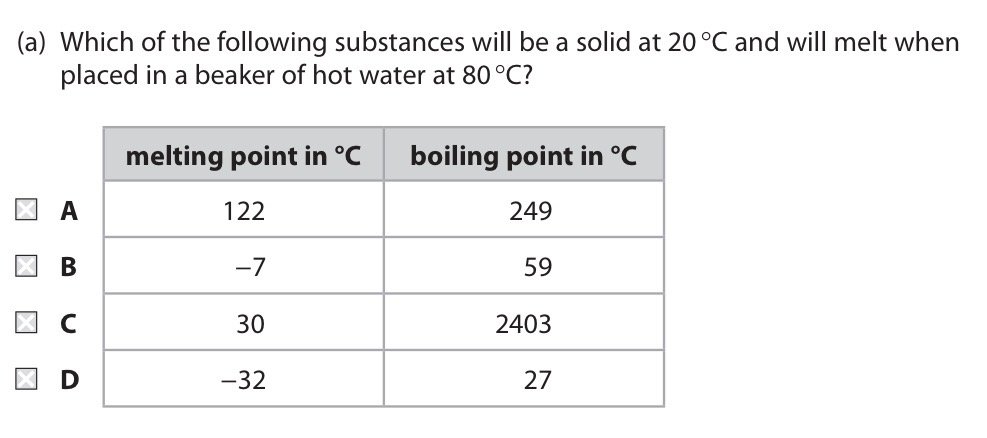
Pick A, B, C or D.
C.
What is a pure substance?
Contains a single element or compound and has a fixed position.
Describe the melting and boiling points of a pure substance.
Melt and boil at specific temperatures.
What is the purpose of filtration?
A separation technique used to separate mixtures of insoluble/undissolved solids from a mixture of solid and liquid. For example, sand from a mixture of sand and water.
Explain the process of filtration.
Filter paper placed in a filter funnel above a beaker.
Mixture of insoluble solids and liquid poured into a funnel.
Filter paper only allows small liquids to pas a through. These liquids become known as the filtrate.
Solid particles are too large to pass through the filter paper so stay there. These solids become known as the residue.
What is the purpose of crystallisation?
A separation technique used to separate a dissolved solids from a solution.
Explain the process of crystallisation.
Solution is heated for a solvent to evaporate.
Saturated solution left behind.
Allowed to cool before removing from heat.
Crystals for along the edges.
Wash crystals with cold distilled water to remove impurities.
Leave to dry in a warm place like an oven and pat dry with filter paper.
What is the purpose of simple distillation?
A separation technique used to separate a solvent from a solution.
What is the purpose of fractional distillation?
A separation technique used to separate two or more liquids that are miscible with one another (similar boiling points).
Which piece of equipment does fractional have that simple distillation does not?
Fractioning column.
Explain the process of filtration.
Solution is heated.
Liquid evaporates producing a vapour which rises.
Vapour passes through condenser to cool and condense, becoming a pure liquid that is collected in a beaker.
Describe how a sample of pure dry nickel sulfate crystals can obtained from the mixture of nickel solution and excess solid nickel carbonate in the beaker.
Filtration.
Crystallisation.
Heat solution.
Allow to cool.
Dry crystals between
Filter papers or in a warm oven.
What is the purpose of chromatography?
Used to separate substances of different solubilities in a given solvent.
In chromatography, what is the mobile phase?
Solvent as molecules can move here.
In chromatography, what is the stationary phase?
Chromatography paper as molecules cannot move here.
In chromatography, what is the solvent front?
The highest point that the mobile phase can reach.
In chromatography, what is the baseline?
The start line where the sample is applied to the stationary phase.
In chromatography, why is the baseline drawn in pencil?
Pencil is insoluble in water and therefore doesn’t dissolve in the solvent.
In chromatography, is the baseline drawn above or below the solvent?
Above so that the samples don’t wash into the container.
In chromatography, if a substance has a higher solubility, will it travel a shorter or further distance?
Further,
In chromatography, if a substance has a lower solubility, will it travel a shorter or further distance?
Shorter.
How do we calculate RF value?
Distance travelled by substance / distance travelled by solvent.
In chromatography, if a substance’s RF value is closer to 1, is it more or less soluble?
More soluble.
In chromatography, if two substances have identical chromatograms, what does this suggest?
Same substance.
In chromatography, if a substance has multiple spots, what does this suggest?
Impure.
In chromatography, if a substance has one spot, what does this suggest?
Pure.
What is potable water?
Water that is safe to drink,
Explain how waste/ground water is purified.
Water is sourced from rivers, lakes and underground aquifers.
Screening and sedimentation - water passes through a sieve to remove large debris. The larger insoluble particles sink to the bottom.
Filtration - water is filtered through beds of sand/gravel to remove remaining small, solid and soluble substances.
Chlorination - chlorine is added to kill harmful bacteria and other microorganisms that can’t be removed by filtration.
Why is the chlorination stage important in purifying waste wate?
This prevents diseases like cholera which is caused by untreated water.
How can seawater be purified?
Simple distillation.