Unit 8 Pancreatic Pathology- Congenital Anomalies (Elie)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
How many types of Cystic lesions of the pancreases are there?
2 types
What are the two types of cystic lesions of the pancreas?
True cysts
Pseudocysts- most common
Unilocular or multilocular
True cysts can either be ________ or ________
Congenital or acquired
What are true cysts description?
Microscopic sacs
Multiple- no septations
Where do true cysts arise from?
Arise from within the gland
What do true cyst contain?
Pancreatic enzymes
Acquired cysts are:
Pseudocysts – most common
Retention cysts
Parasitic cysts
Neoplastic cysts
What is a congenital cyst?
Abnormal development of pancreatic ducts
Multiple
What is the measurement of congenital cysts?
3-5 cm
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Disease is an extrarenal cyst most commonly found where?
In the liver
Where can an Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Disease, extrarenal cyst also be found?
In the pancreas
Other organs
What is Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome?
Autosomal dominant condition with formation of tumors and cysts in many different parts of the body
US findings for Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome?
Well-defined mass with thick fluid
Calcifications
Single or Multiple
Vary in size from microscopic to several cm
Cystic Fibrosis is also what disease of the pancreas?
Fibrocystic Disease
What is Fibrocystic Disease of the pancreas?
Hereditary Disorder of Endocrine Glands
Dilated Acini & Ducts
Acini replaced by fibrous tissue
What does fibrocystic disease of the pancreas look like overall?
Nodular and firm pancreas
Hyperechoic (^ echogenicity)
Well-defined mass with serous fluid
What are the 4 classifications of Cystic Pancreatic Neoplasms?
Serous Cystic Neoplasms
Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms
Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasms
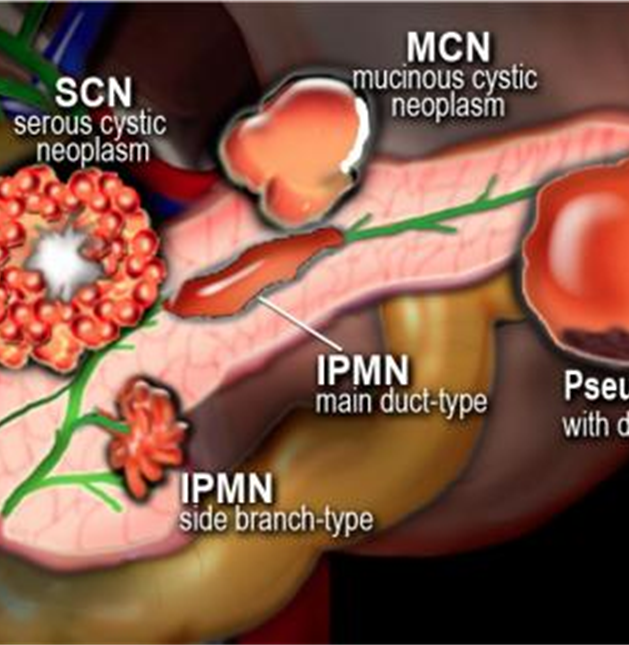
What is this image showing?
Cystic Pancreatic Neoplasms
What is a Serous Cystadenoma also called?
Microcystic Adenoma Cystadenoma
Is serous cystadenoma a benign or malignant disease?
Benign disease
A serous cystadenoma is considered:
Rare
Serous Cystadenoma is more common in:
Females > Males
Serous Cystadenomas are tiny cysts with 60% in the _____ and ____; and 30 % in the ______.
Body and tail; head
US appearance for a Serous Cystadenoma:
Similar to pseudocysts – cystic, solid or echogenic
May have internal septa
Thick walls
Single or multiple
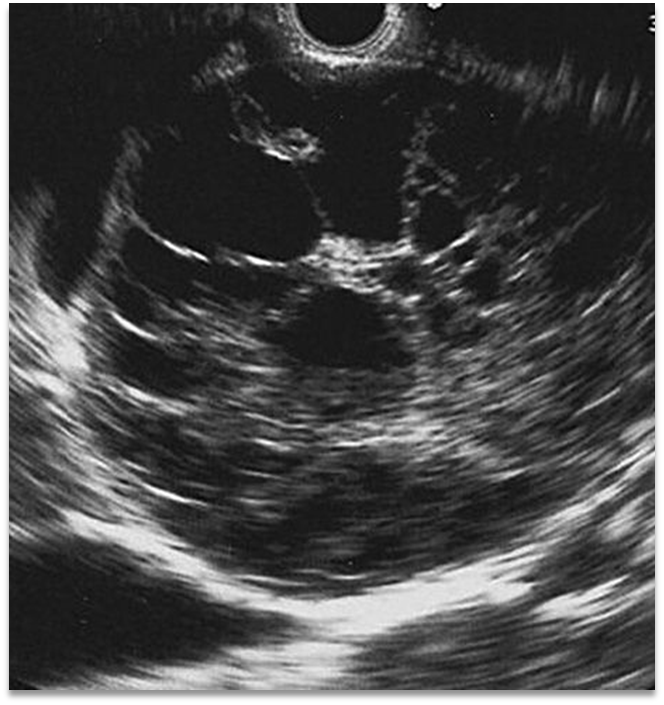
What is this image showing?
Cystadenoma
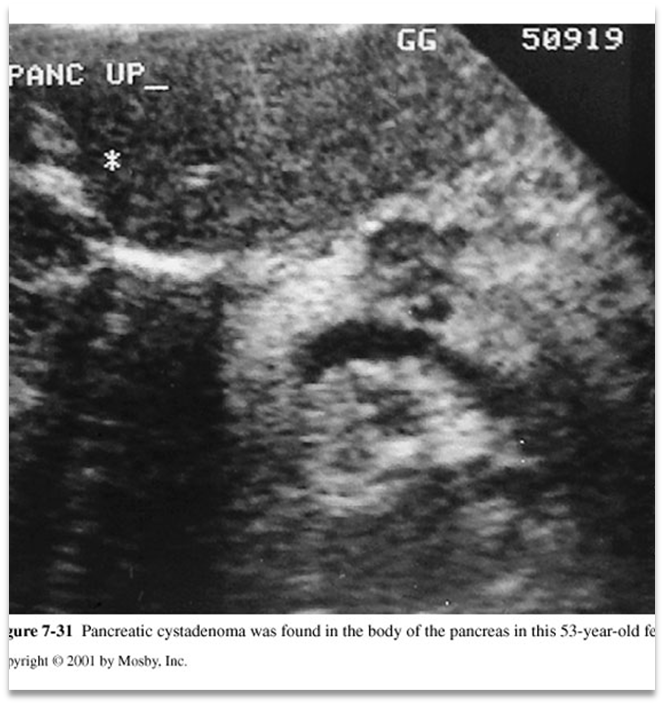
What is this in the image above?
Cystadenoma
A mucinous Cystadenoma/ Cystadenocarcinoma is also called?
Macrocystic Adenocarcinoma
What is a Mucinous Cystadenoma?
Rare, slow-growing neoplasm
Significant malignant potential
Arises from the ducts
Large cyst w/wo septations
With a Mucinous Cystadenoma, it arises more in the body or tail with the tail equaling what percentage?
60%
A mucinous cystadenoma will have:
pain/palpable mass
What are the concurrent diseases for a mucinous cystadenoma?
Diabetes
Biliary calculous
Arterial hypertension
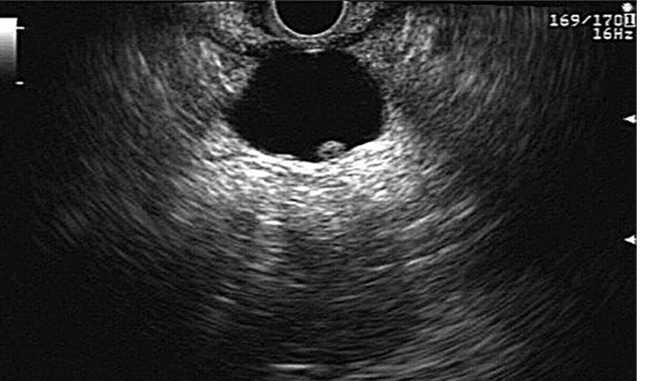
What is this image showing?
Mucinous Cystadenoma
US appearance for Mucinous Cystadenoma:
Well-circumscribed
Smooth-surfaced
Thin or thick walled
Unilocular or multilocular
Cystic lesions
Variable sizes
Thick mucinous fluid
Internal septations or mural nodules
Pancreatic calcifications frequent
When scanning a mucinous cystadenoma what should you also evaluate for?
Mets
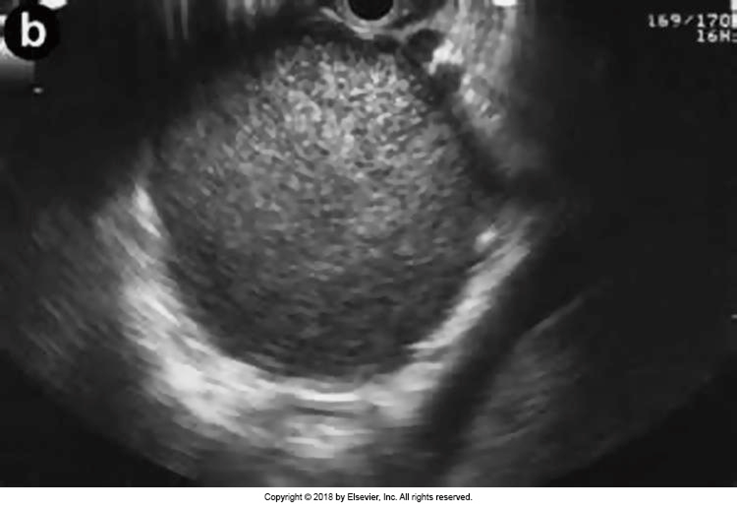
What is this image showing?
Mucinous Cystadenoma/Cystadenocarcinoma/Macrocystic Adenocarcinoma
What is an Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm?
A form of mucinous cystic neoplasm
Where does an Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm originate from?
From main pancreatic duct or branches
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms are classified as:
Slow-growing
Benign to malignant
What are the symptoms, lab values, and prevalence for an Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm?
Abdominal pain
Elevated Amylase
Most prominent in elderly men + women
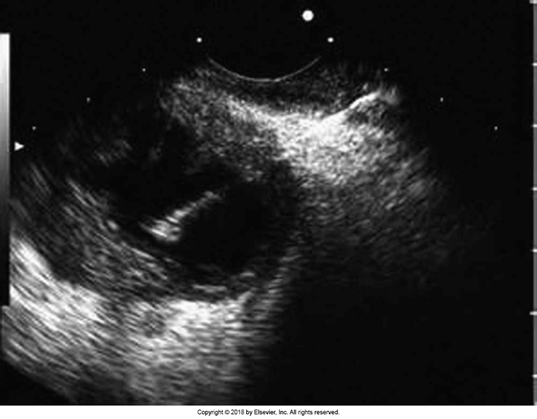
What is this image showing?
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm
A Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm is most common in?
Young women
A Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm has a low incidence of what?
Malignancy
What are the symptoms for a Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm?
Usually asymptomatic
Abdominal pain
N/V
Weight loss
US findings for a Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm:
Frequently seen in tail
Heterogeneous
Solid & cystic components
Smaller in size
MRI is more specific
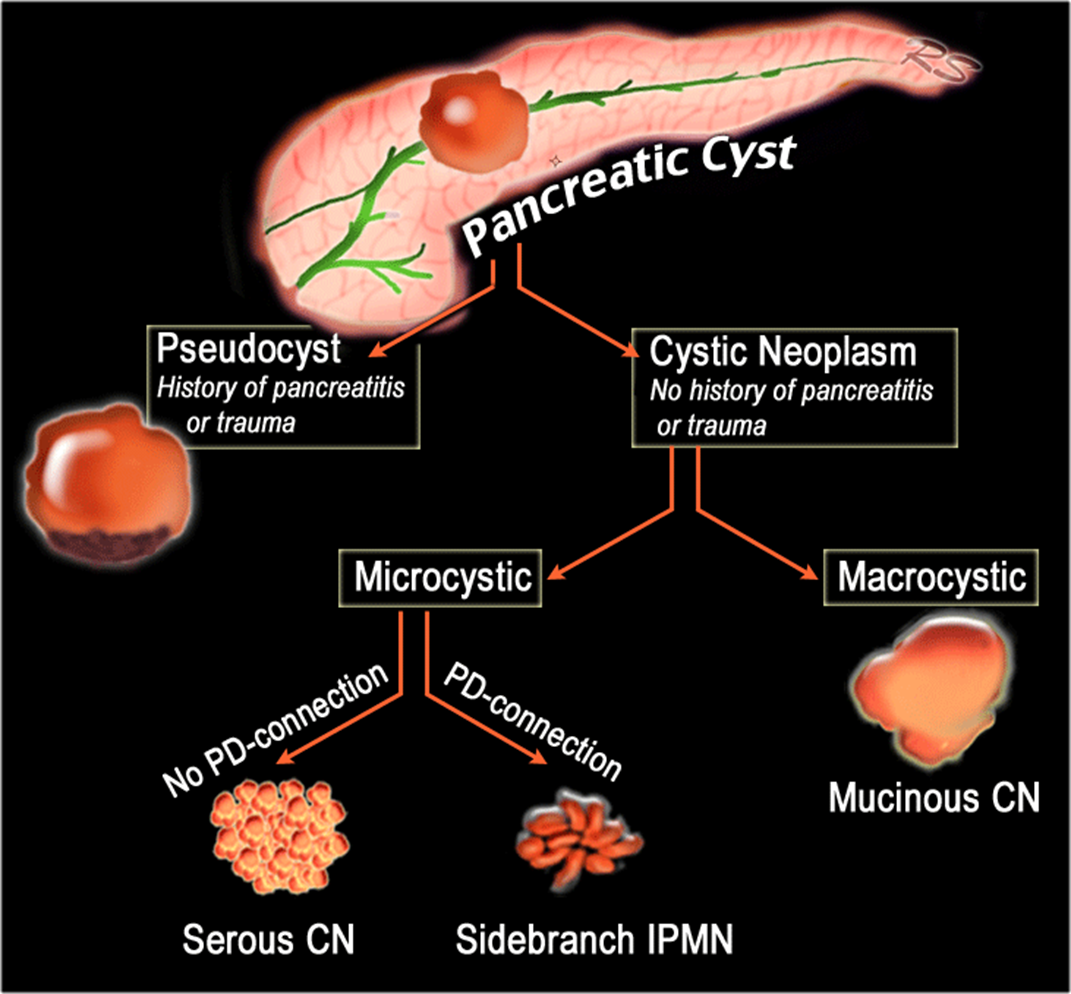
This diagram show?
Different classifications of a pancreatic cyst