Week 5- carbohydrates and lipids
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Lipids function
signalling, energy storage, structure
does the presence of double bonds increase or decrease the melting point of fatty acids?
decrease- it prevents the tight packing of molecules in the way cis/trans structure bends them
Fatty Acid properties
Are carboxylic acids with long C chains 12-20 C atoms
Contain C-C bonds or C-H bonds
fewer functional groups
hydrolysable lipids are derived from these
How to determine omega 3, 6 or 9 fatty acid?
whichever carbon (from CH3 end start counting) has the double bond
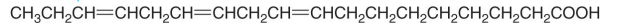
Is this an Omega 3, 6, or 9 fatty acid?
Omega 3
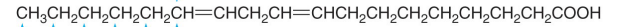
Is this an Omega 3, 6, or 9 fatty acid?
Omega 6
Properties of Waxes
simplest hydrolysable lipids
can undergo hydrolysis in presence of acid or base
esters formed from fatty acid and alcohol
hydrophobic due to non-polar chains
which has this property?
can undergo hydrolysis in the presence of acid or base
waxes
Properties of Triacylgycerols’s
triesters from glycerol and three fatty acids
are simple or mixed
What makes a triacylglycerol simple or mixed?
Simple = saturated (do double bonds)
mixed = means one of the fatty acid chains may be saturated
Properties of Soaps
Metal salts of fatty acids
Produced by hydrolysis of triacylglycerols in the presence of a base
They have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
This allows them to form micelles in water which can carry particles of oils and dirt
2 common types of phospholipids
Phosphoacylglycerols
Sphingomyelins
Properties of phosphoacylglycerols
Most common phospholipid
Phosphodiester bond to alcohol, this end is charged - Polar head
non polar tails
2 types:
– Cephalin: Contains ethanolamine or serine.
– Lecithin: Contains choline.
Properties of Sphingomyelins
• Second major class of phospholipids
– They DO NOT contain a glycerol backbone
• They contain a sphingosine instead
– They DO NOT contain an ester
– They only contain one fatty acid
Function of sphingomylins
axon sheaths in the nervous system
function of phosphoacylglycerols
major constituents of cell membranes
Steroid
An organic compound a carbon skeleton with four fused rings arranged in a specific configuration.
Phospholipid
• Lipids containing a phosphorus atom.
• Polar head and nonpolar tail making them amphipathic.
Lipids
A broad group of naturally occurring organic compounds that are generally insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Biological functions of cholesterol
Cholesterol is a steroid
Adds rigidity to the cell membrane
Elevated cholesterol in the bloodstream is in indicator for increased risk of coronary artery disease (heart disease)
transported in the blood by LDLs and HDLs
Biological functions of Adreno-cortical
regulate electrolytes in kidney (adrenal-means renal)
What are the four fat soluble vitamins?
vitamin A, D, E, K
Vitamin A
fat soluble vitamin
vision, immune, bone health, hair growth
non-polar
Vitamin D
fat-soluble vitamin
Can be synthesized from UV light
very little polarity
Vitamin E
fat-soluble vitamin
antioxidant
non-polar
Vitamin K
fat-soluble vitamin
essential for blood clotting
given to newborns to prevent bleeding disorders
non polar
Which vitamins are non-polar
A, E, K
Biological function of steroids
• Components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity
• Signaling molecules.
How are fat-soluble vitamins obtained?
With the exception of Vitamin D which can be synthesized from cholesterol, cells cannot synthesize these compounds and must be obtained in the diet.
Carbohydrates
Biomolecules made from monosaccharides (sugars).
Largest groups of organic molecules in nature.
Tree trunks, leaves, vegetables, fruits, honey, milk, alcohol
Functions of carbohydrates
fingerprint of cells
backbone of other molecules
How are carbohydrates represented?
By size:
Monosaccharides-one
Disaccharides-two
Polysaccharides-many
Structural features of monosaccharides
Location of carbonyl group (Aldose vs Ketose)
C1: aldehyde (monosaccharide is called aldose)
C2: ketone (monosaccharide is called ketose)
Why are monosaccharides easily dissolved in water?
highly polar
many hydroxyl groups form hydrogen bonds with water
Anabolism
Synthesis of larger molecule from smaller subunits
Catabolism
: Break down of a larger molecule into smaller subunits
How are carbohydrates built up and broken down?
Dehydration- build up
Hydrolysis- break down
How are disaccharides linked together?
glycosidic linkage / glycosidic bond / glycoside.
What monosaccharides make maltose?
glucose + glucose
What monosaccharides make sucrose?
glucose + fructose
What monosaccharides make lactose?
glucose + galactose
A and B glycosidic linkages
In an alpha (α) glycosidic linkage the bond goes down from the C1; in a beta (β) glycosidic linkage the bond goes up from the C1.
Cellulose
type of polysaccharide
source: plant
Subunit: B-glucose
Bonds: 1,4
Branches: none
Shape: straight sheets, parallel chains
Starch
type of polysaccharide
amylose, amylopectin
source: plant
Subunit: A-glucose both
Bonds: 1,4 amylose 1,6 amylopectin
Branches: none for amylose, branched for amylopectin
Shape: straight or branched
Glycogen
type of polysaccharide
in animals liver and muscles
highly branched
α-1,4 glycosidic linkages & α-1,6 glycosidic linkages
source: animal
Subunit: a-glucose
Bonds: 1,4 1,6
Branches: yes
Shape: super branched, largest
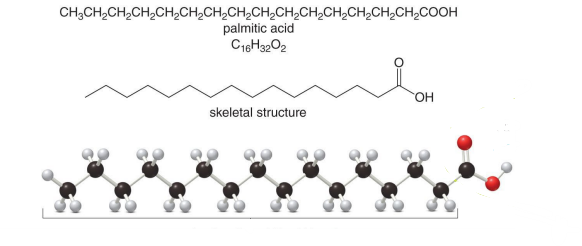
A lipid
Which compound is the following?
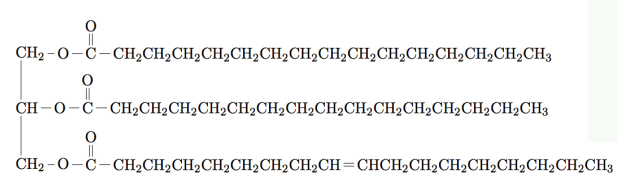
A fatty acid
Which compound is the following?
a Wax
Which compound is the following?
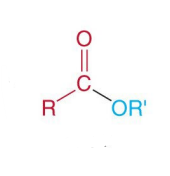
a Triacylglycerol
Which compound is the following?
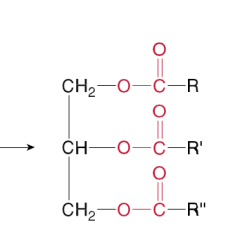
a Soap
Which compound is the following?
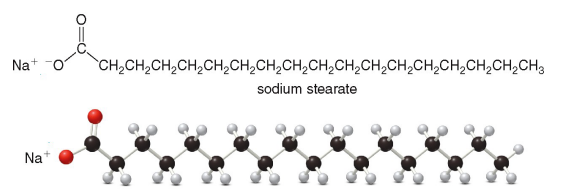
Which compound is the following?
a Steroid
Which compound is the following?
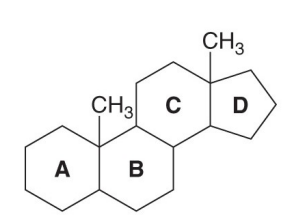
a Vitamin
Which compound is the following?
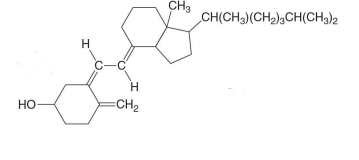
Which compound is the following?
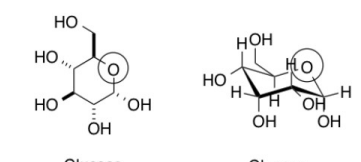
a monosaccharide/carbohydrate
Which compound is the following?
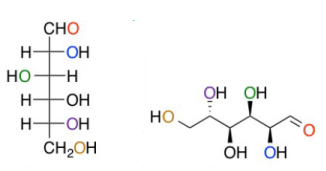
a Dissacharide/carbohydrate
Which compound is the following?
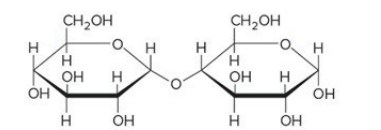
a Polysaccharide/carbohydrate
Which compound is the following?
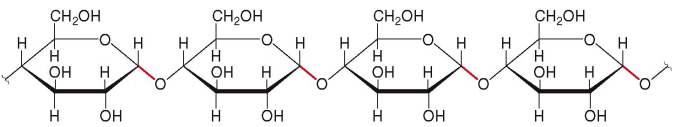
a monosaccharide
Which compound is the following?

What are the Hydrolysable lipids and Non hydrolysable lipids
Hydrolysable:
waxes
triglycerols
phospholipids
Non-hydrolysable:
Vitamin
Steroid
Eicosanoids
Fats and oils are triglycerols
What is the fingerprint of cells?
Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids?
Carbohydrates
How are disaccharides formed and broken down?
Two monosaccharides come together with glycosidic linkages
Are broken apart by enzyme-mediated hydrolysis
Which polysaccharide is obtained from animals?
Glycogen
Which polysaccharide is b-glucose?
cellulose
The enzyme lactase breaks the bonds between which two monosaccharides?
glucose and galactose