Thẻ ghi nhớ: Seed Plants: Angiosperms | Quizlet
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What are the Unique Chacteristics of angiosperms
Flowers, Fruits. These developed approximately 130 Mya and relied heavy on the convolution with insects.
Flowers
Used for pollination and protection embryo
Fruits
Used for seeds protections and dispersal
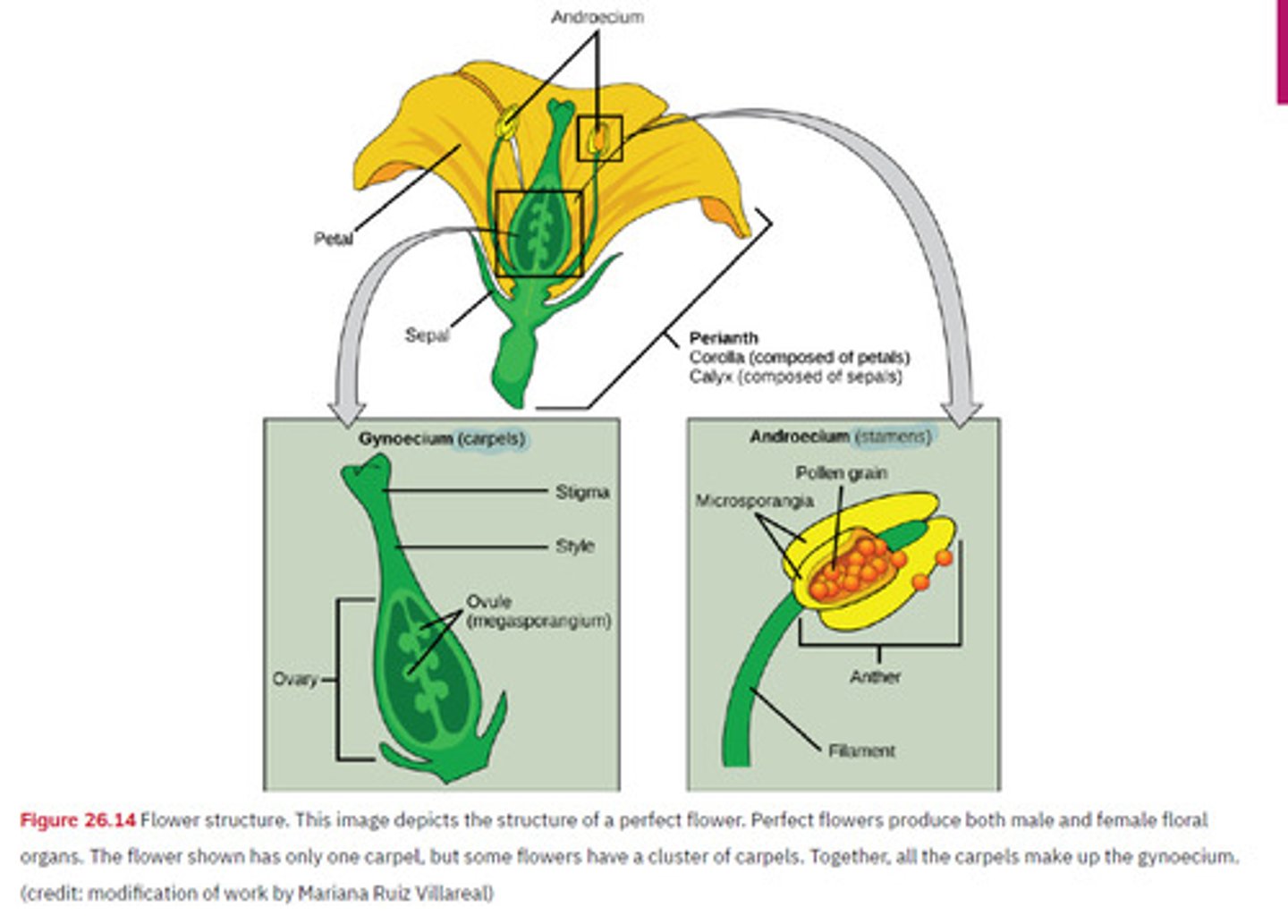
What are parts of a flower
Sepals, petals, carpels, stamens. Flowers can be perfect flowers, monoecious, dioecious.
Sepals
Protects the unopened bud (collectively the calyx)
Petals
Colorful parts that attract pollinators (collectively the Corolla)
Carpels
Females reproductive unit, contains stigma, style, and ovary.
Stamens
Male reproductive unit. Contains the filament and the anther.
Perfect flowers
Contains stamens and carpels
Monoecious
Stamens and carpels are on separate flowers, but the same plant
Dioecious
Flowers with stamens and flowers with carpels are found on completely separate plants.
Know the parts of a flower
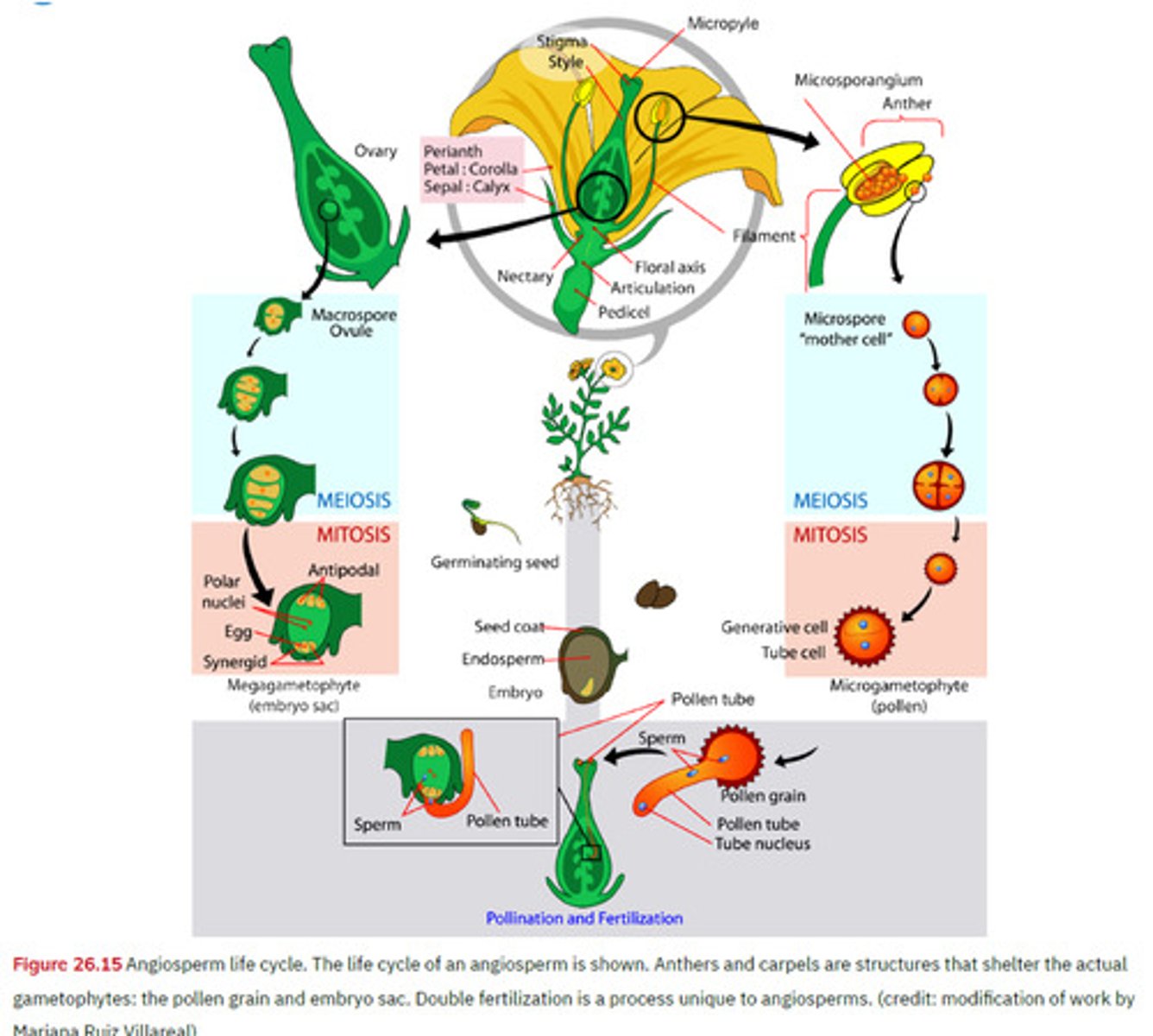
Angiosperms fertilization and life cycle
2n phase is the dominant phase in the life cycle. Are heterosporous. Involved in double fertilization
Microspores
Pollen in male gametophyte
Megaspores
Ovule is female gametophyte
Double fertilization
Each pollen grain contains 2 sperm. 1 sperm fertilizes the egg and produces a diploid embryo. Another fertilizes the polar nuclei and produces the endosperm.
Angiosperm life cycle
Fruits
Anything that contains a seed and is grown from an ovary is a fruit. Fleshy fruit and dry fruits are involve. Main goal is seed dispersal.
Fleshy fruit
Berries, peaches, grapes, tomato, etc.
Dry fruit
Rice, acorns, wheat, etc.
Examples of seed dispersal
dandelion seeds: wind dispersal. Burrs: catching in fur. Fleshy fruits: being eaten and dropped or pooped out.
Characteristics of Angiosperm DIversity
All belong to the phylum Anthophyta. Made up of three groups: basal angiosperms, monocots, and dicots.
Basal Angiosperms
Water littles, magnolia trees, and spice peppers.
Monocots
True littles, orchids, rice, sugar cane, asparagus. One cotyledon, Parallel veins in leaves, scattered stem vascular tissue, networks of fibrous roots, Mono sulcate pollen, and flower parts are in three or multiples of three.
Dicots
Mangos, tomatoes, roses. Two cotyledon, Network (branched) veins in leaves, stem vascular tissues are arranged in a ring pattern, tap roots with many lateral roots, Tri sulcate pollen, and flower parts are four, five, or multiple of four or five and whorls.
Plants evolution and the role of herbivores
Plants became a major food source for many animals, including large herbivores, millions years ago. This possibly drove the evolution of plant defenses. Many plants also used this to their advantage.
Evolution of plant defenses
Bark, Thorns, Poisons/bad taste
Plant advantages used from animals eating plants
Seed dispersal and pollination.
Economic Botany
Human use of plants. Cultural, commercial, and medicinal uses, Include seeds and agricultural plants.