(9) Blood vessels
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
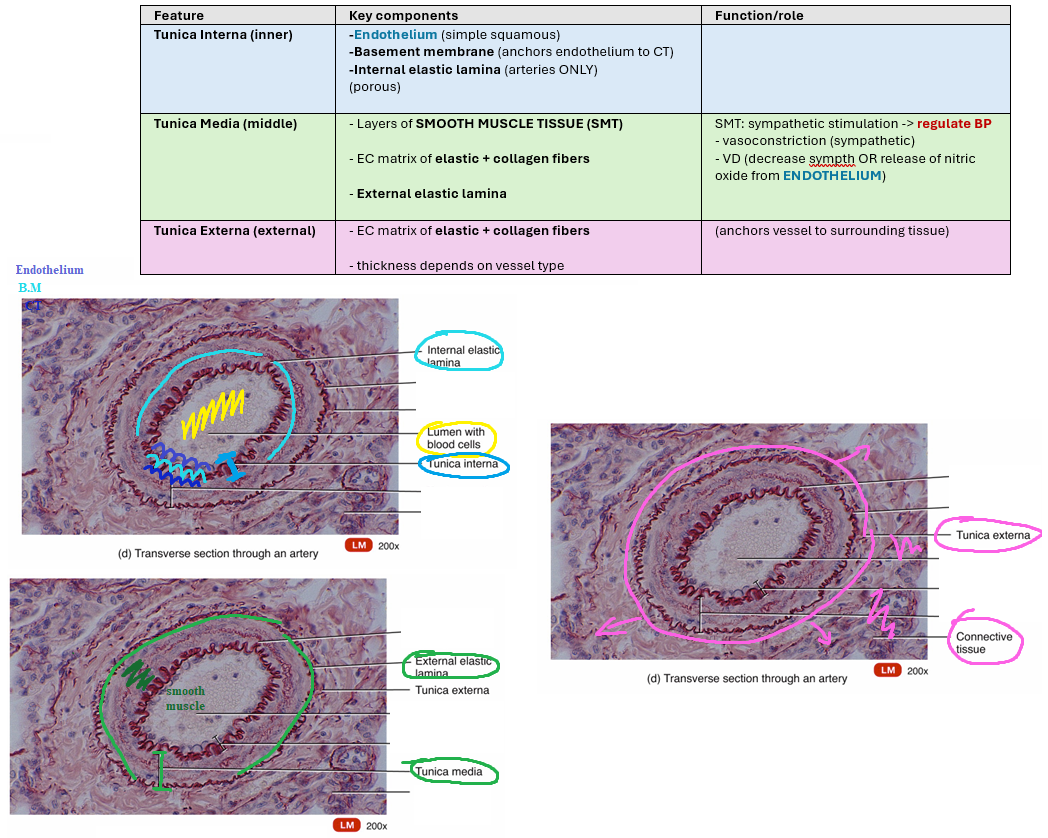
Describe the histological components of the TUNIC LAYERS of blood vessels
What are the blood vessels from heart back to heart.
1) Elastic arteries
2) Muscular arteries
3) Arterioles
4) Capillaries
5) Venules
- post capillary venules
- muscular venules
6) Veins
Discuss 1) Elastic arteries
- structure
- function
Ex. Aorta/pulmonary trunk
-LARGEST arteries in body
-THIN walls
-well defined internal/external elastic lamina
F: elasticity allows to withstand pressure/stretch from blood being ejected
Discuss 2) Muscular arteries
- structure
- function
Ex. brachial, radial artery
-THICKER tunica media (more smooth muscle)
- well defined internal lamina (which helps w/ VC & VD)
F:
- no elastic recoil (little external elastic lamina)
- autonomic innervation of smooth muscle regulates vascular tone
Discuss 3) arterioles
- structure
- function
-sparse internal elastic lamina, no external lamina
-1to2 layers of smooth muscle
F: regulate BF from larger arteries to capillaries
- autonomic innervation controls arteriole diameter
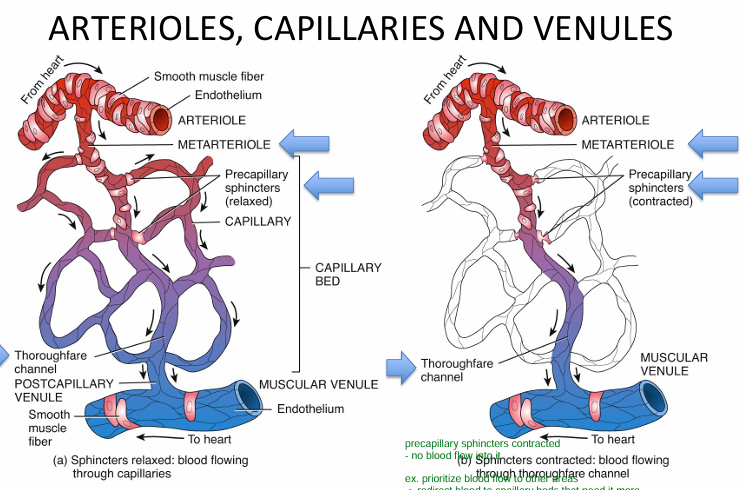
Discuss the relationship between arterioles, capillaries and venules
0) BF from artery
→ arteriole
→ metarteriole
1) if precapillary sphincters RELAXED
(areas where we want blood to flow)
→ blood flows through capillary beds
→ thoroughfare channel
→ postcapillary venule
→ muscular vneule
2) if precapillary sphincter CONTRACT
(areas where we DON’T want BF, want to divert it to other tissues that need it)
→ blood doesn’t cease BUT
→ goes directly through thoroughfare channel (allows for SOME gas exchange)
→ post capillary venule
→ muscular venule
1) Capillaries consist of __
2) Capillaries are a site of __
3) Capillaries empty deoxygenated blood into the __
1) Tunica interna ONLY
2) GE
3) post-capillary venule
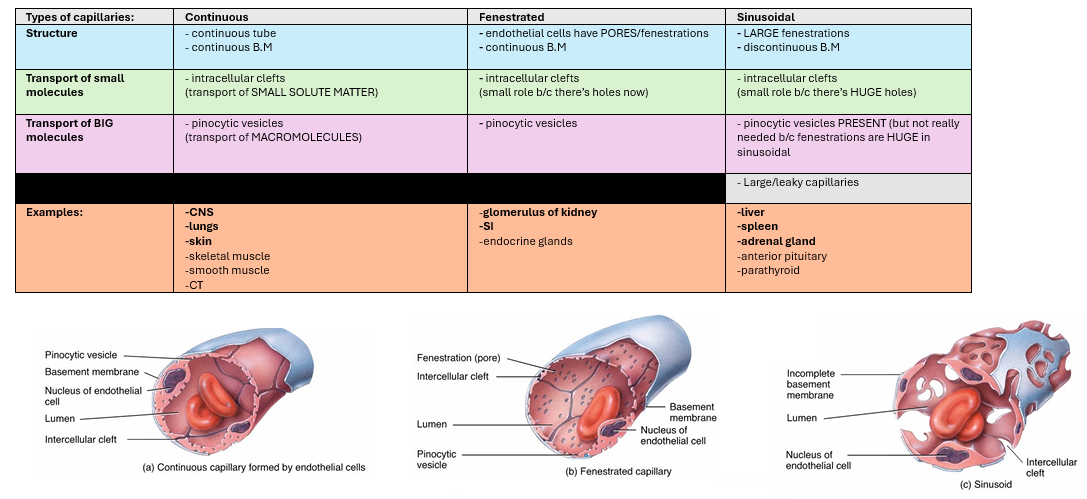
What are the different TYPES of capillaries? (#4)
1) Continuous
2) Fenestrated
3) Sinusoids
Discuss 5) venules
- structure
- function
drain deoxygenated blood from capillaries
1) Post-capillary venules
- highly porous
2) muscular venules
- thicker walls than post-capillary vneules
- distensible, acts as blood reservoirs
Discuss 6) veins
has same 3 layers as arteries BUT VEINS:
-lack internal/external elastic laminae
-lumen is larger than their equivalent artery
-*has prescence of VALVES (1 way flow)
***fight of flight -> smooth muscle contraction in these venules -> lumen size decrease -> RBC pushed UPWARDS/OUT to the heart
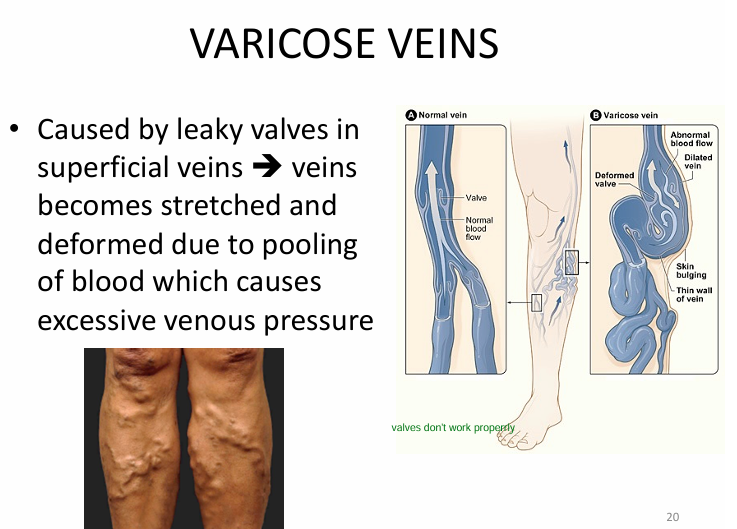
What is varicose veins?
leaky valves in superficial veins
→ veins become stretched/deformed
→ cause excessive venous pressure
64% of total blood is located in the systemic veins and venules which is known as the __
blood reservoir