Module 2 : Atomic Theory and Periodic Table
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:18 AM on 9/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
Atomic Theory
The historical concept that matter is made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms.
2
New cards
Democritus
He gave the first idea of the composition of matter which is ATOM.
3
New cards
Atom
It is the smallest indivisible and indestructible particle of matter.
4
New cards
A-tomos
It is a Greek word which means not to cut or cannot be cut.
5
New cards
John Dalton
He is a English chemist that developed the first modern theory of atom.
6
New cards
John Dalton’s Atomic Theory summarized as follows:
1. Matter consists of tiny indestructible particles called *atoms*.
2. Atoms of the *same elements* are all alike.
3. In *chemical reactions*, the combination of atoms may break down but the atoms themselves are unchanged.
4. When *atoms form molecules*, they unite in small whole numbered ratio such as 1:1, 2:1, 2:3, and so on.
7
New cards
Joseph John Thomson and Julius Plucker
They discovered Electron (e-).
8
New cards
9\.107 x10^-28 g
What is the mass of Electron (e-)?
9
New cards
Electron
It is located in the main energy level/shell or outside the nucleus.
10
New cards
Eugene Goldstein and Ernest Rutherford
They are the one who discovered Proton (p+).
11
New cards
1\.677 x10^-24 g
What is the mass of Proton (p+)?
12
New cards
Protons (p+) and Neutrons (n^0)
They are located in the nucleus.
13
New cards
James Chadwick
Who discovered Nucleus (n^0)?
14
New cards
1\.675 x10^-24 g
What is the mass of Neutron (n^0)?
15
New cards
Nucleus
It is small massive structure located at the center of an atom.
16
New cards
Electron Cloud
Main energy levels or shells can also called as __________?
17
New cards
Atomic Number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which is also equal to the number of electrons in the atom.
18
New cards
Atomic Weight
It represents the relative *weight of an atom* of an element with weight of one atom of carbon conventionally taken as equal to 12.
19
New cards
Number of Neutrons
Atomic weight minus atomic number (no. of protons and electrons) is equal to ______?
20
New cards
Isotopes
They have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons are called ________?
21
New cards
Main Energy Levels or Shells
The orbits where the electrons revolve around nucleus are called _____?
22
New cards
Sublevels
The different types of subshells within an energy level, designated as s, p, d, and f.
23
New cards
s (sharp) = 2
p (principal) = 6
d (diffuse) = 10
f (fundamental) = 14
p (principal) = 6
d (diffuse) = 10
f (fundamental) = 14
What are the are the number of electrons does s p d f sublevels or subshells have?
24
New cards
s = 1, p = 3, d = 5, f = 7
How many orbitals does s p d f have?
25
New cards
Electron Configuration
It is a systematic arrangement of electrons in the main energy levels and sublevels of an atom.
26
New cards
The Pauli Exclusion Principle
It is a principle that the limits of number of electrons in *any orbital to not-more than two*, and this pair of electrons must *spinning in opposite direction.*
27
New cards
The Hund’s Rule or Principle of Maximum
It is a rule that each orbital must be occupied with a single electron before pairing of electrons in any orbital of that sublevel can occur.
28
New cards
Two Methods in Illustrating Electron Configuration
1. s p d f Method
2. Rectangular Arrow Method or Arrow
29
New cards
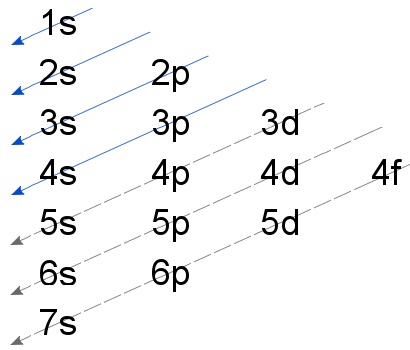
s p d f method
It is a method of distributing the electrons indicating the filling of the energy levels and sublevels.
30
New cards
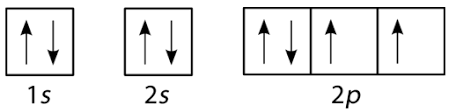
Rectangular Arrow Method or Arrow
It is a box method that uses arrow to represent electrons and boxes for orbital. The Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s Rule are strictly followed in this method
31
New cards
Three Different Methods in Diagramming Atomic Structure
1. Complete Atomic Structure
2. Ionic Method or Half-shell Notation
3. Electron-dot Notation or Lewis Structure
32
New cards
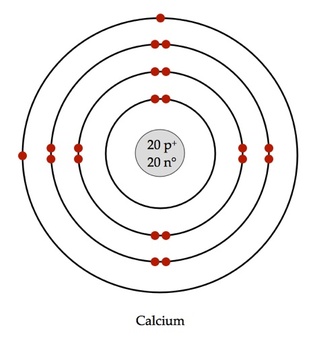
Complete Atomic Structure
It shows the proton and neutron in the nucleus and the electrons found outside the nucleus rotating in a definite path called shells or main energy levels around the nucleus.
33
New cards
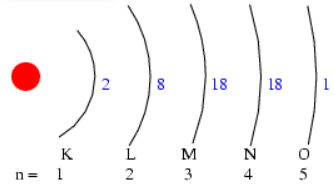
Ionic Method or Half-shell Notation
It shows the symbol of the element and how the electrons are placed
in the different main energy levels represented by the half-shell.
in the different main energy levels represented by the half-shell.
34
New cards
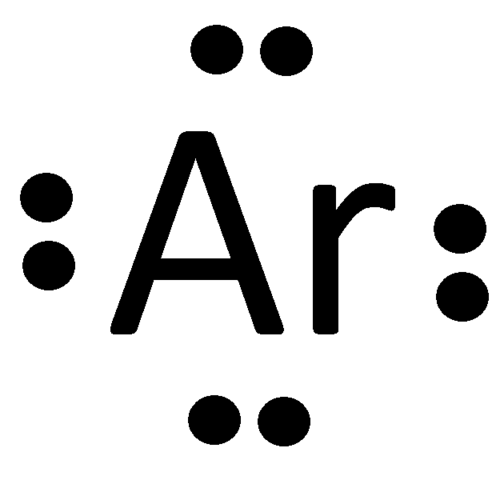
Electron-dot Notation or Lewis Structure
It shows the nucleus represented by the symbol of the element and the valence electron distributed around the symbol by means of dots or dashes.
35
New cards
Periodic Table
A systematic listing or arrangement of elements in order of increasing atomic number.
36
New cards
Periods (other terms: Energy and Series)
The elements are arranged in horizontal rows and designated by numbers 1-7.
37
New cards
Group or Families
The vertical column, which divided into to A & B subgroups.
38
New cards
1800
The year that chemist began to determine the atomic weights of some elements.
39
New cards
Dimitri Mendeleev (1834-1907)
He worked out the periodic table of elements. He arranged the elements in order of their increasing atomic weights, the lowest is Hydrogen and the highest is Uranium.
40
New cards
Dimitri Mendeleev (1834-1907)
In 1890’s, he added an additional element to each period. He left spaces for elements that might some day discovered. He studied the properties of the elements and predicted the properties of would be discovered elements.
41
New cards
Henry Moseley (1887-1915)
He is a young English scientist that used the x-ray to determine the atomic numbers (proton) of the elements.
42
New cards
Henry Moseley (1887-1915)
He concluded that the elements should be arranged in the order of increasing atomic numbers
43
New cards
X-ray
It is the light radiation with high frequency and short wave length.
44
New cards
Moseley found…
* The higher the atomic number the shorter the wave lengths of x-rays, when that element is used as a target.
* In some cases, unusual variations between two successive elements.
* In some cases, unusual variations between two successive elements.
45
New cards
Periodic Law
It states that some of the physical and many of the chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.
46
New cards
Periodic Table
* The elements are arranged according to increasing atomic numbers in the table.
* This lists the elements with their symbols, atomic numbers, atomic weights, and so forth.
* It is composed of 18 vertical columns and 7 horizontal rows.
* This lists the elements with their symbols, atomic numbers, atomic weights, and so forth.
* It is composed of 18 vertical columns and 7 horizontal rows.
47
New cards
Metals
* These elements are mostly solids, have a luster, and can conduct electricity and heat.
* They have high density, high melting and boiling points, and can also combine with non-metals to produce salts.
* They can be found on the left side of the periodic table.
* They have high density, high melting and boiling points, and can also combine with non-metals to produce salts.
* They can be found on the left side of the periodic table.
48
New cards
Mercury (Hg)
Metals are mostly solid except ______, which is liquid at room temperature.
49
New cards
Non-metals
* These elements have poor electrical and thermal conductivity, low density, and low melting and boiling points.
* Several of their elements can exist as gases at room temperature. T
* hey can also be found on the right side of the table.
* Several of their elements can exist as gases at room temperature. T
* hey can also be found on the right side of the table.
50
New cards
Metalloids
* The amphoteric elements border the darkline. These are dull-appearing and brittle solids at room temperature.
* They can also be called semiconductors because they conduct electricity better than non-metals but not as well as metals.
* They can also be called semiconductors because they conduct electricity better than non-metals but not as well as metals.
51
New cards
Representative Elements
The elements in groups 1A through 7A of the periodic table, which have incomplete outer energy levels and occupy the s or p orbitals.
52
New cards
Trends in Periodic Table
1. Atomic Size
2. Ionization Energy
3. Electron Affinity
4. Electronegativity
53
New cards
Atomic Size
The size of an atom becomes bigger as its number of shell increases.
54
New cards
Ionization Energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron form an atom.
55
New cards
Electron Affinity
The energy released when an electron is added to an atom, which generally increases as you move across a period in the periodic table.
56
New cards
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond, which generally increases as you move across a period in the periodic table.