L2 - avidity, cooperativity and allostery
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is avidity?
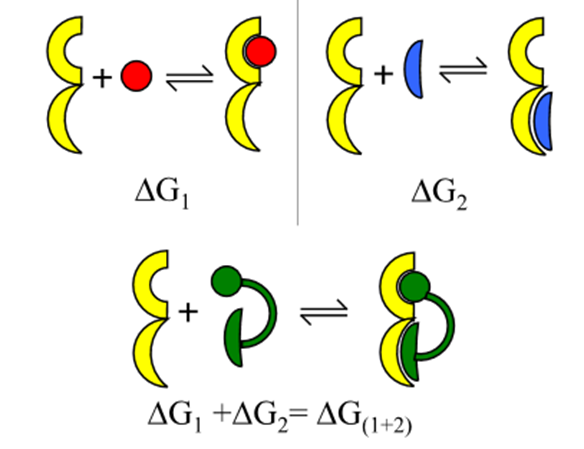
when a macromolecule has more than 1 independent binding site and the binding partner has multiple ligating groups the binding is enhanced (binding to multivalent ligands) eg binding of antibodies to antigens
How can we start to quantify the increase in affinity?
Starting from the free energy of association
If a reaction if spontaneous, what is gibbs?
Negative
What does Gibbs = under equilibrium conditions?
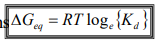
How do we find this?
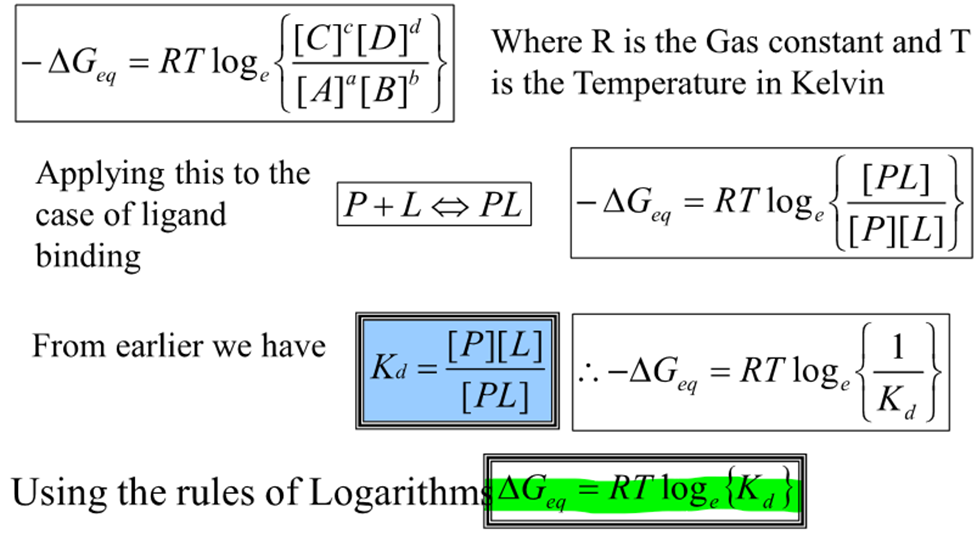
What does this show?
There is a direct relationship between the equilibrium dissociation constant and the free energy
If Kd is less than 1, what will happen?
Log Kd will be negative and therefore so will delta G so will be spontaneous

What is the composite Kd?
The product of individual Kds
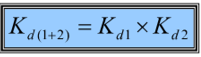
What is composite Kd important in?
o Important in fragment-based drug design
o Number of elements with weak affinity for a target molecule can be combined
What is cooperative binding?
In some cases, the binding of a ligand alters the affinity of the macromolecule for binding successive ligands
How is cooperative binding communicated?
by allostery – structure changes a bit when ligand binds, increasing affinity of other sites
Binding of ligand can also decrease the affinity
What do you get in cooperative binding?
Get a continuum of observed Kds because some sites modified and unoccupied ect
What is usually used in cooperative binding and why?
Fractional saturation so can look at a whole molecule rather than specific sites
What does fractional saturated = ?

What does a fractional saturation vs [L] curve look like?
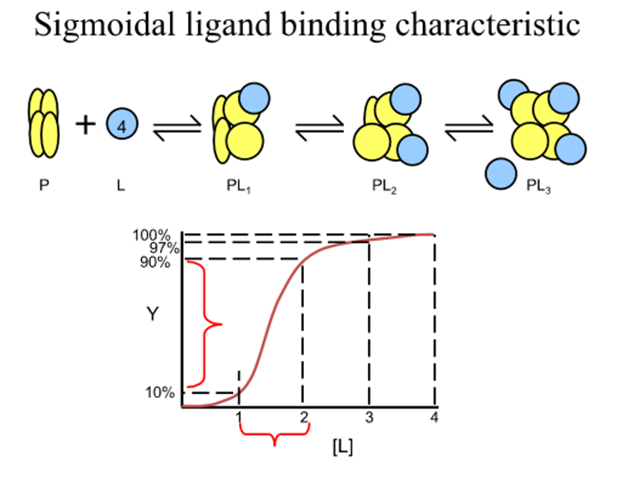
What happens at the extremes of the fractional saturation versus [L] curve
the macromolecule effectively has a fixed Kd, that of the first or last sites to be filled
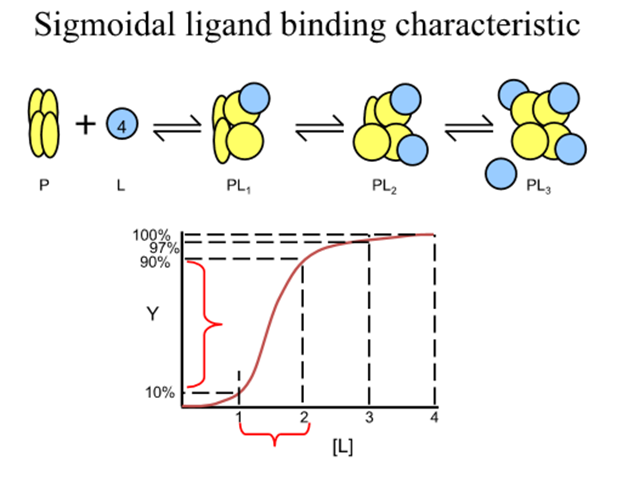
In between extremes what does observed Kd depend on?
The amount of ligand bound to each macromolecule
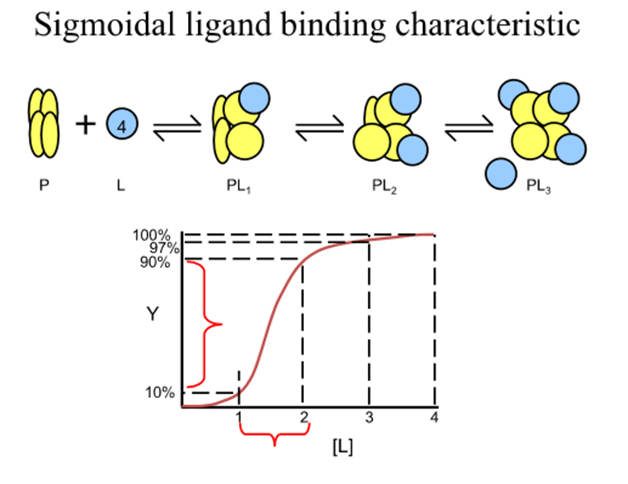
How do you quantify Kd in a cooperative system?
need to consider a model system where the cooperativity is infinitely high
For a protein with n ligand binding sites each with a finite Kd, infinite cooperativity means that as soon as one site binds a ligand all the other sites immediately bind ligand
The only species in solution are then free protein, free ligand and saturated protein ligand complex
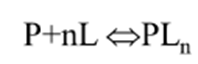
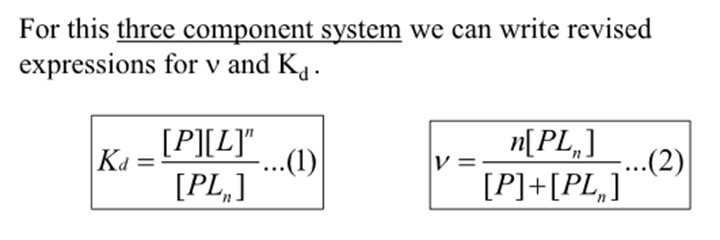
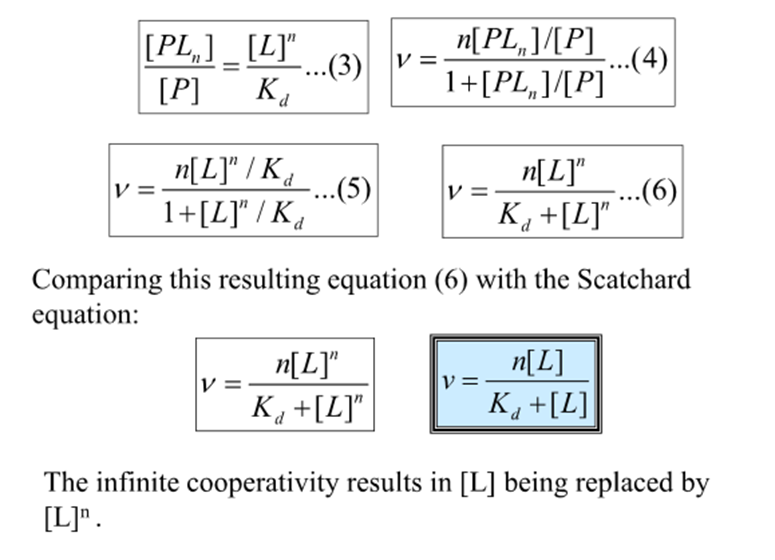
For this 3 component system what is the revised expression for binding function and Kd
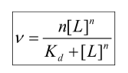
What expression is used if cooperativity is present but not infinite?
h = hill constant
Takes a non-integer between 1 (no cooperativity) and n (infinite cooperativity)
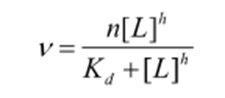
How do you find the saturation binding function and when is it used?
It is used in cases where cooperativity is analysed
Kd is observed Kd

What is the straight line equation for the hill constant? in terms of saturation binding function and normal binding function?
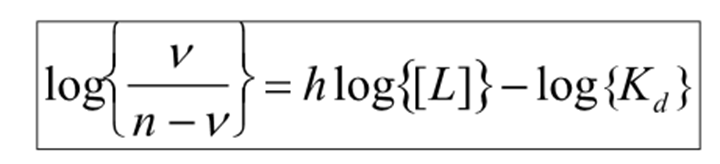
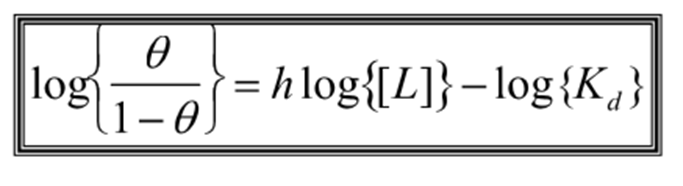
What does the gradient = ?
h
What is the reality of the Hill plot?
Not linear because binding of the ligand to the macromolecule is not cooperative over the full range
The end of the curve have slopes of unity
Segments correspond to the binding of the first and last ligand
Slope greater than unity in middle
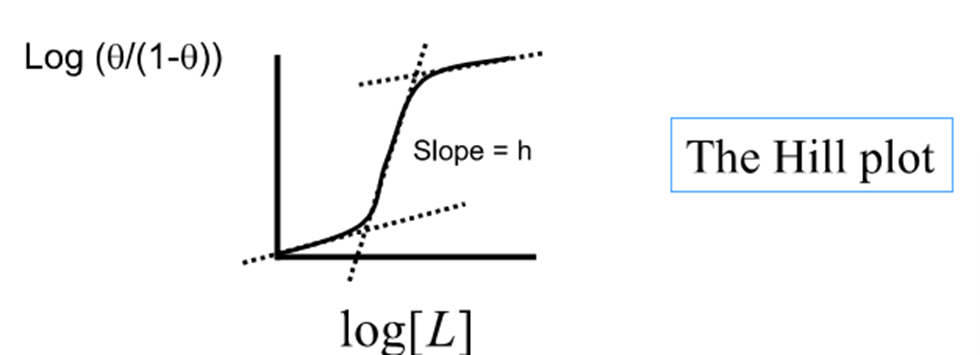
What is h?
The maximum slope of the curve
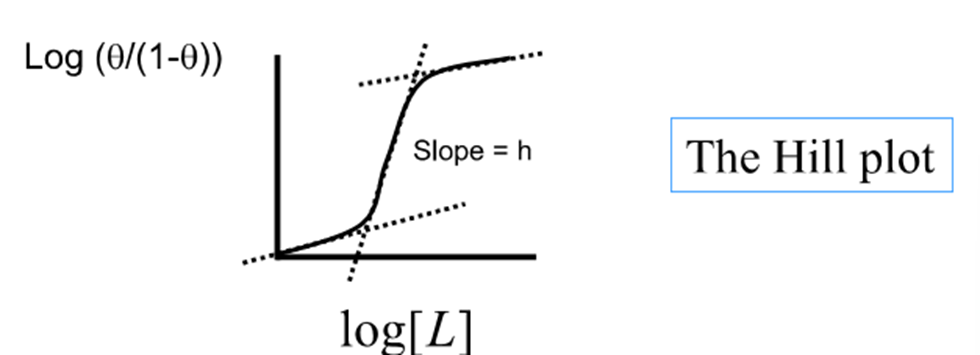
What is the largest value h can take?
n ( the number of binding sites)
Simple, scratchard and Hill plots
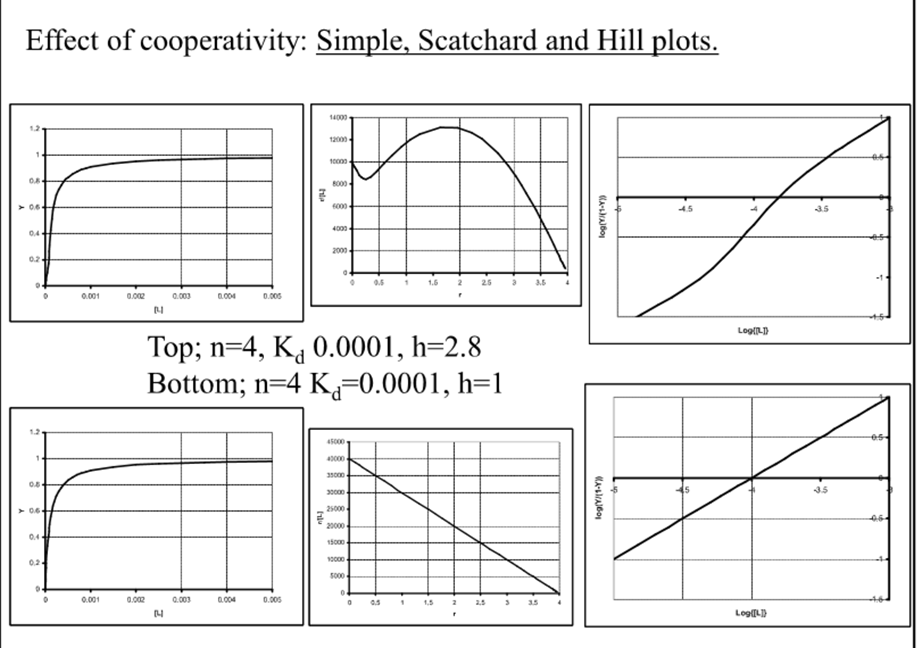
When h=1, what is Kd directly related to?
The binding affinity
What plots are good to diagnose cooperativity?
Difficult in simple but clear in scratchard
What is an example of allosteric ligand binding?
myoglobin and haemoglobin for transport of molecular oxygen
o Myoglobin has 1 haem co-factor
o Haemoglobin has 4 haems
Shows allosteric modulation of oxgen binding
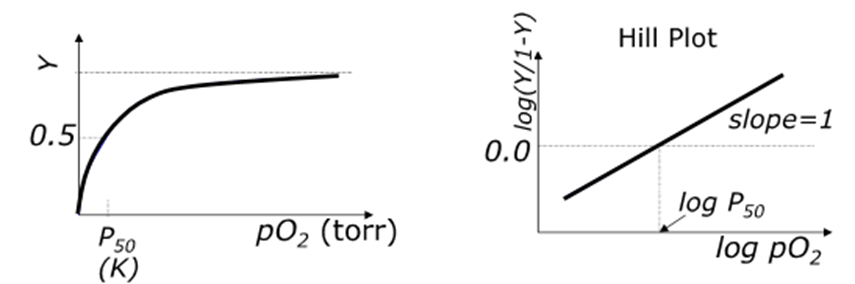
What is the oxygen binding curve for myoglobin?
o Reversible binding
o No cooperativity (only 1 binding site)
o So simple hyperbolic form for a plot of fractional saturation
o Hill plot = straight line gradient 1
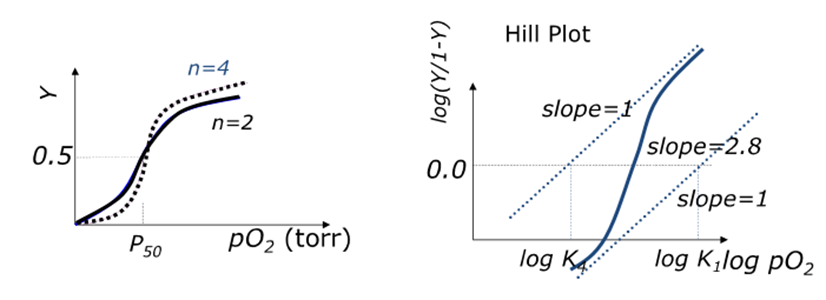
What is the oxygen binding curve for haemoglobin?
Significant cooperative binding
Hill coefficient = 2.8 (has to be between 1 and 4)
Sigmoidal
How does loading and unloading from haemoglobin and myoglobin work?
o Artery = high [O2] loading of protein
o Vein = lower [O2] unloading from protein
o Loading of Hb is better matched to requirements of O2 transport and release
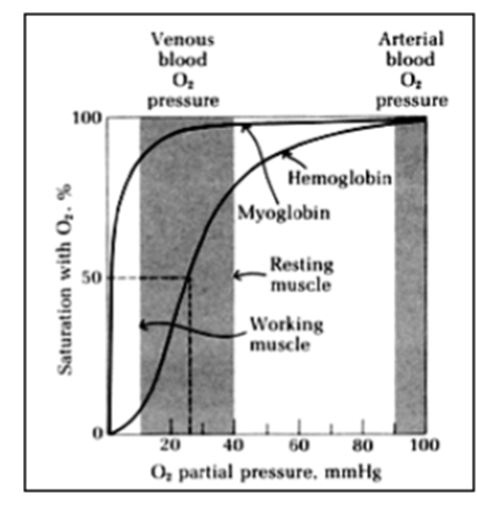
What do haemoglobin properties match?
Change in [O2] over the physiological range