Constitutional Clauses
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Elastic Clause (Necessary and Proper Clause)
The clause in Article I, Section 8, that grants Congress the power to do whatever is necessary to execute its specifically delegated powers.

Emoluments Clause
Prohibits any "Person holding any Office of Profit or Trust under [the United States]" from accepting any compensation from "from any King, Prince, or foreign State." (Article I Sec. 8)
![<p>Prohibits any "Person holding any Office of Profit or Trust under [the United States]" from accepting any compensation from "from any King, Prince, or foreign State." (Article I Sec. 8) </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8a73a61e-5f9c-4d4e-928b-2e62efa3dd1c.jpg)
Full Faith and Credit Clause
Constitution's requirement that each state accept the public acts, records, and judicial proceedings of every other state (Article IV)

Implied Powers Clause (Elastic)
Powers not mentioned specifically in the Constitution as belonging to Congress but inferred as necessary and proper for carrying out the enumerated powers. (Article I)
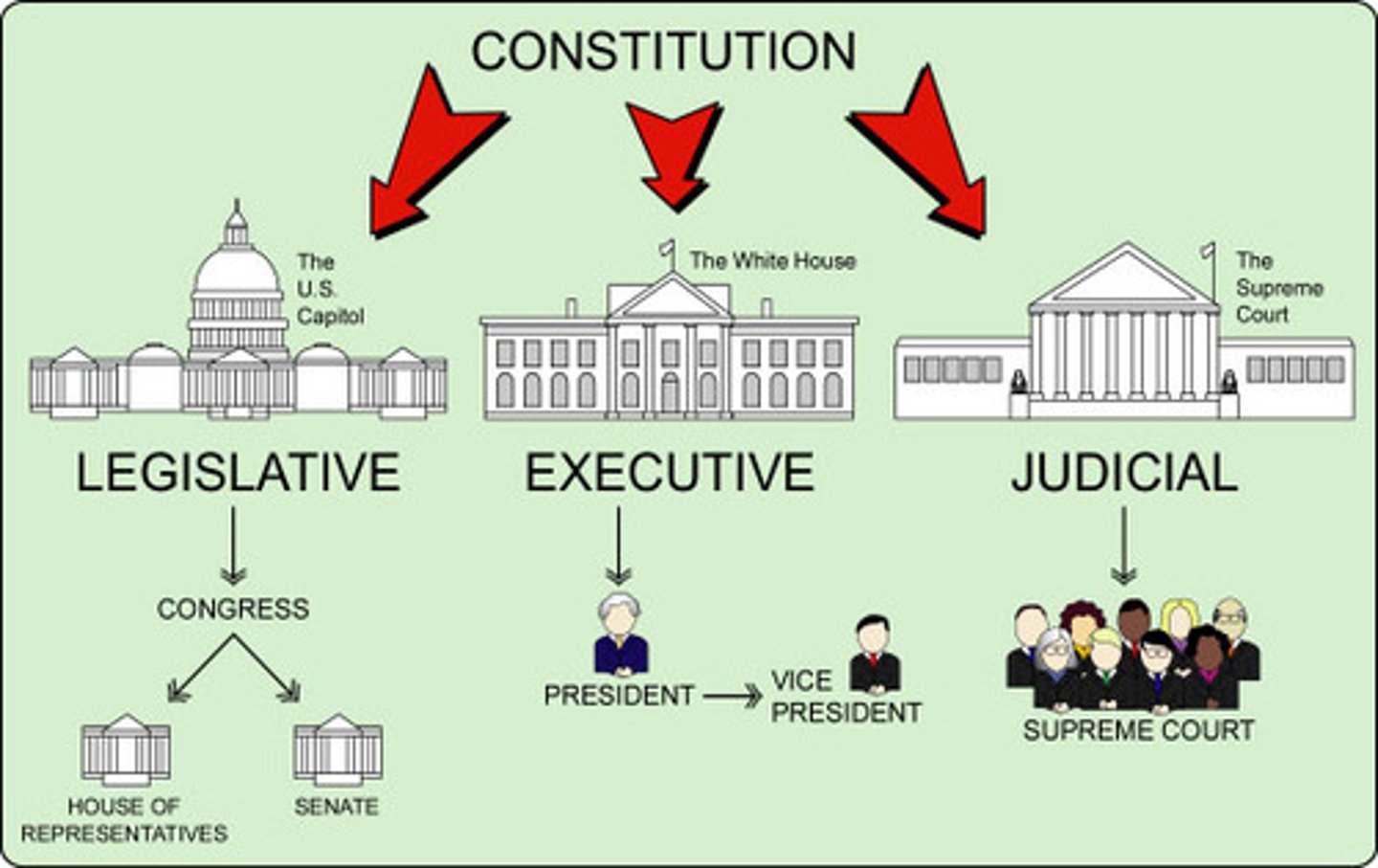
Supremacy Clause
Article VI of the Constitution, which makes the Constitution, national laws, and treaties supreme over state laws when the national government is acting within its constitutional limits.

Establishment Clause
Clause in the First Amendment that says the government may not establish an official religion.

Free Exercise Clause
A First Amendment provision that prohibits government from interfering with the practice of religion.

Equal Protection Clause
14th amendment clause that prohibits states from denying equal protection under the law, and has been used to combat discrimination

Expressed/ Delegated/Enumerated Powers
Powers specifically given to the federal government by the US Constitution, for example, the authority to print money. (Article I)

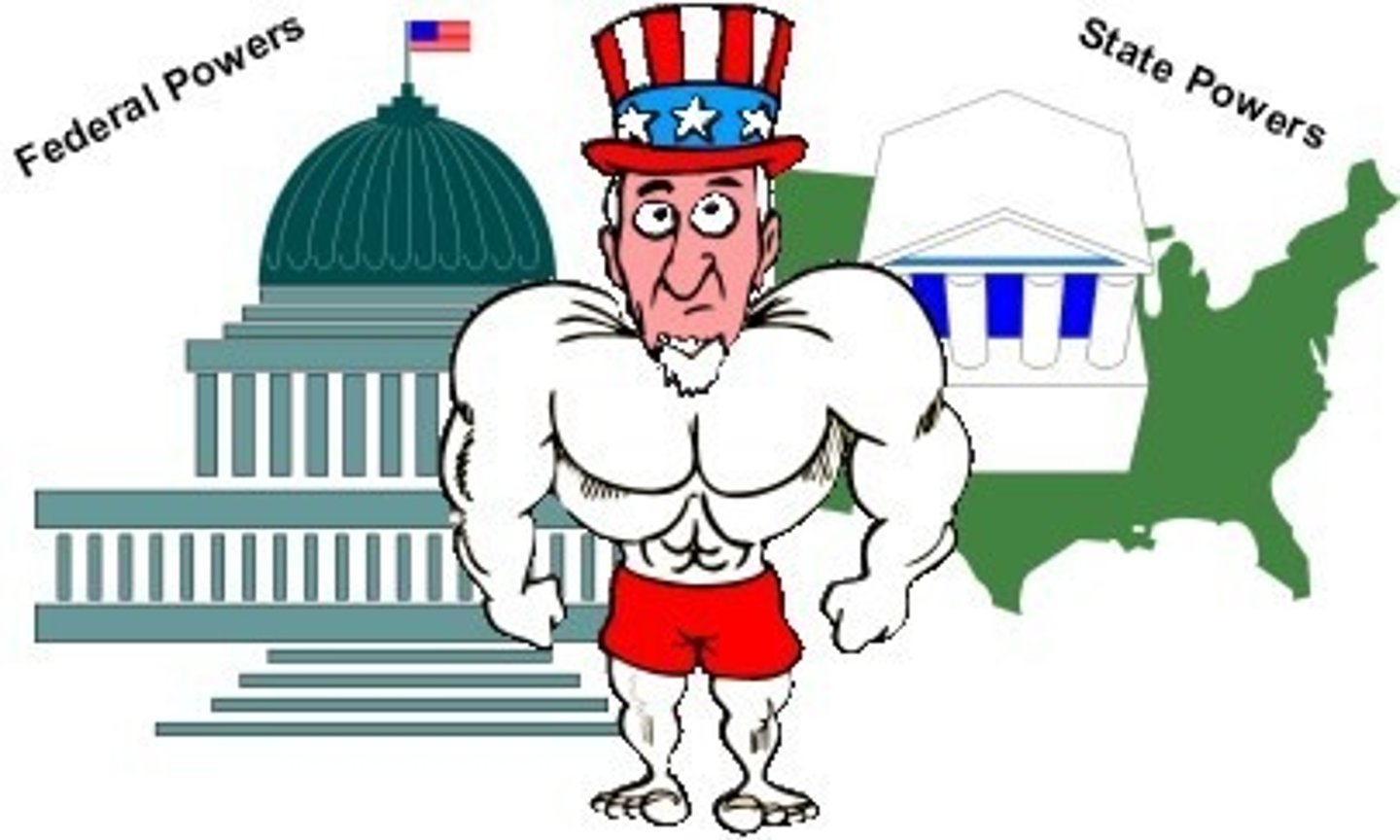
concurrent powers
Powers held jointly by the national and state governments.
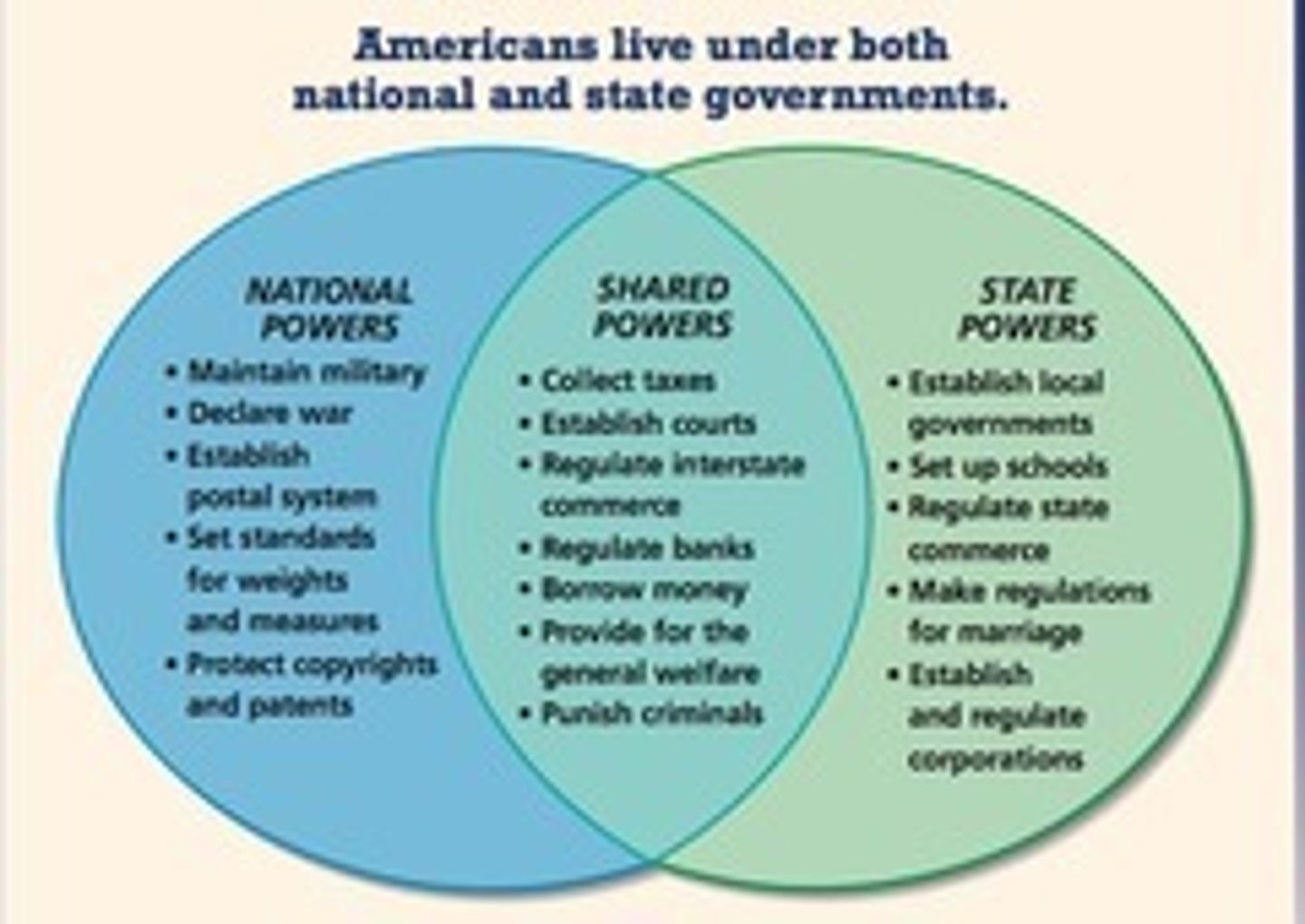
Federalism
A system in which power is divided between the national and state governments
Confederation
an alliance of independent states

Reserved Powers
The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people. (10th Amendment)

ex post facto law
a law that makes an act criminal although the act was legal when it was committed (Article I)

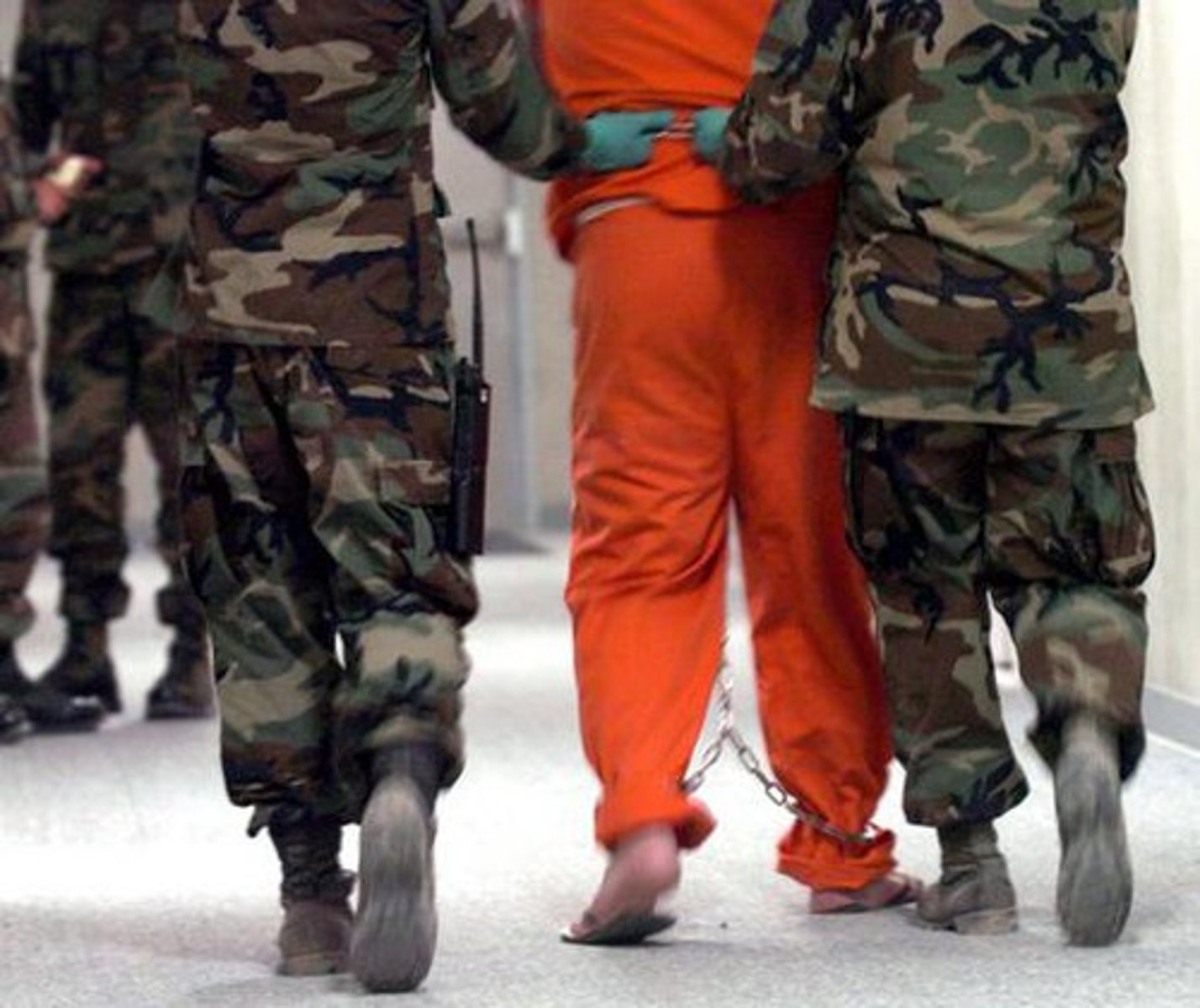
Habeas Corpus
An order to produce an arrested person before a judge. (Article I)

bill of attainder
a law that punishes a person accused of a crime without a trial or a fair hearing in court (Article I)
Due Process Clause
14th amendment clause stating that no state may deprive a person of life, liberty, or property without due process of law