PSYCH 207 All Modules
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
225 Terms
Empiricism
Knowledge comes from individual’s OWN experience
Thru observing and analyzing
Nativism
Native to biological factors
Hard-wired into brain at birth
Wilhelm Wundt
Used lab-setting for research
Wanted to discover building blocks of mind and combine them to discover complex mental concepts
Structuralism
The study of how our minds make meaning through small step-by-step cognitive processes.
Wilhelm Wundt & James Baldwin’s Technique of Investigation
Introspection
Give observers stimuli and have them describe their conscious experiences
Limitation: Many cognition abilities happen without conscious awareness
William James
Interested in conscious experiences like Wundt
Not interested in elementary units of consciousness though
Functionalism
Functionalism
Explains the functions of mind
Outside of lab, observing in natural habitat
Behaviourism
OBSERVABLE behaviour
Says that psychology’s goal is to predict and control behavior
Skinner objected mental representations as scientific
Developed rigorous experimental methods
Gestalt Psychology
Holistic Approach
Psychology must be studied in entirety and not reduced to elements
Sir Francis Galton
Individual Differences, Natural Selection (Darwin)
Looked at family trees to see cognitive ability
Found that individuals differed in ability to make mental images
Cognitive Revolution
Rejected that mental events were BEYOND science and that mental representations didn’t exist
Human Factors Engineering
Person-Machine System
Should be designed to interact within physical, cognitive limitations
Framed humans as limited capacity processors of information
Noam Chomsky’s Factors Contributing to Psychology Revolution
Linguistics
Showed behaviorism doesn’t explain language
Localization of Function
Naturalistic Observation
Observer watching people in everyday contexts
Ecological Validity
Lack experimental control
Introspection
Person thinks about their experience while performing a task
Between Subjects Design vs Within Subjects Design
Differences in performances between two groups
Compares different conditions of same group of participants
Quasi Experiments
Characteristics already assigned (gender, race)
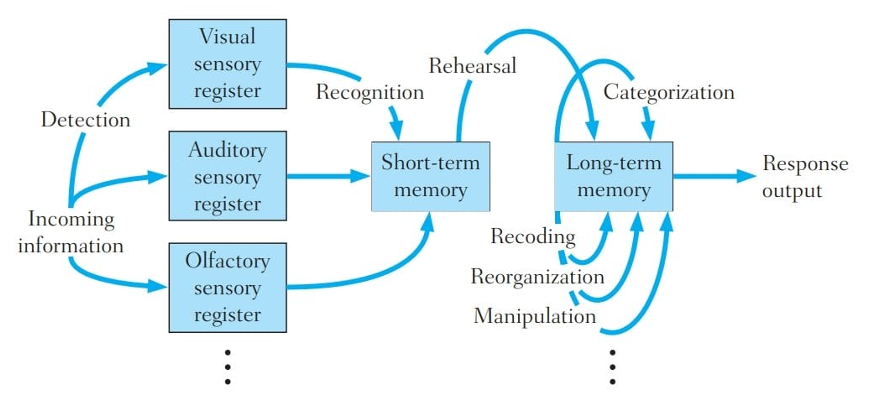
Information Processing Approach
Info is processed from our senses
Stored in stages (long, short term)
Connectionism
Cognition is made of interacting network of connections
Not sequentially, occurs simultaneously
Not localized but distributed among neurons
(+) Connection = Activation
(-) Connection = Inhibition
Evolutionary Approach
Understanding ancestor pressures
Human mind changed in response to evolutionary pressures
Cosmides and Tooby believed…
Most significant issue our ancestors faced involved social issues
Ecological Approach
Context of cognition shapes processes
Must examine in natural environment
Paradigm
An intellectual framework used to guide research and to identify what is and is not important in a field of research.
Ecological Validity Experiment Example
Smilek and Kingston focused on how attention operated
Eyes were focused on eyes and faces of people rather than objects interacting with
Module 2 Begins
Congratulations! Keep going :)
Phylogenetic Division
Divides brain structures in terms of evolution order
Forebrain (cerebral cortex, main cognitive functions)
Hindbrain, midbrain (lower level functions like relay info)
Hindbrain
Medulla oblongata transmits info from spinal cord to brain
Pons (bridge) for information from left to right
Cerebellum has neurons that manage muscles
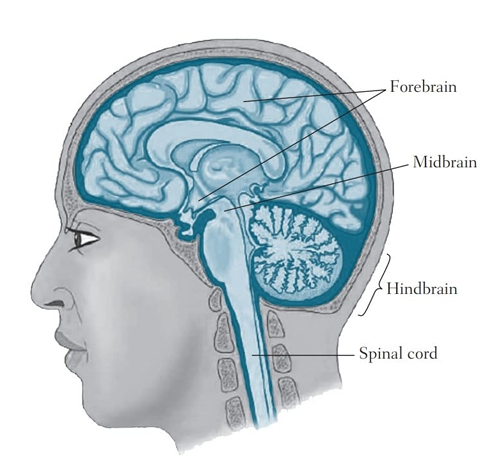
Midbrain
Relays info to other parts of brain
Low level, non-cognitive function
Forebrain
Cortical (Cerebral Cortex)
Sub-Cortical (Under the cerebral cortex)
4 Sub Cortical Regions
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Medulla
Spinal Cord
Cerebellum
Thalamus
Relay station sending info to cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus
Controls pituitary gland by releasing hormones
Controls eating, drinking, temperature, sleeping
Hippocampus
Formation of long-term memories
Amygdala
Emotional memories
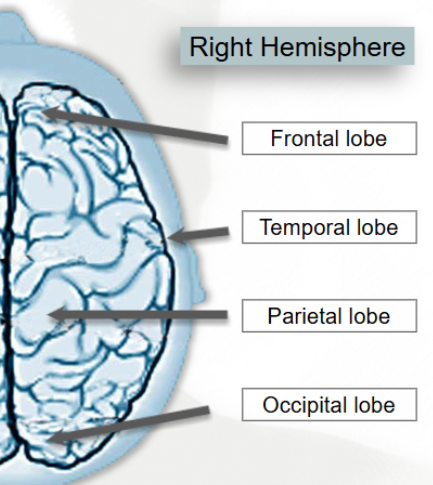
Cerebral Cortex Four Lobes
Frontal (under forehead)
Parietal (under top rear, spatial processing and attention)
Occipital (back, visual)
Temporal (side, auditory)
Three Parts of Frontal Lobes
Motor Cortex (fine motor movement)
Premotor Cortex (planning movements)
Prefrontal Cortex (executive functioning, decision making)
Cerebral Cortex
Densely packed neurons with white matter
Localization
Franz Gall
Believed faculty psych (mental abilities are independent)
Phrenology was found
Discredited because SIZE does not correlate to POWER
Not INDEPENDENT, but interact
Aphasia
Language disorder that affects how you communicate
Wernicke’s Area
Temporal Lobe, Left Hemisphere, Auditory
Involved in comprehension
Broca’s Area
Left Hemisphere
Involved in language production
How Did Wilder Penfield Help With Localization
Localized source of seizures
Searched for scar tissue causing epilepsy
Helped map specific functions of regions
Brain Imaging Techniques
Structural/Static (CAT, MRI)
Functional (fMRI, ERP, PET)
CAT (computerized axial tomography)
Focused beams of X RAYS are passed thru head from diff angles
Tissue has different density so deflect rays differently
MRI
Uses magnetic properties of tissues to produce signal
No radiation, preferred over CAT, more detailed
Event-Related Potentials (ERP) and EEG
Measures electrical activity in the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Measures metabolism and blood flow in the brain using radioactive tracers.
fMRI
Measures blood oxygenation levels (BOLD function) to infer neural activity
BOLD Function (Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent)
Measures the inflow and outflow of oxygenated blood in the brain as a response to neural activity.
BOLD signal peaks around 10–15 seconds after a cognitive task begins due to the slow nature of blood flow changes
Subtractive Logic
A method to isolate specific cognitive processes by subtracting a simpler task from a more complex one to measure the difference.
Idea originated with studies of reaction time differences
Describe example of subtractive method
Activity is generated when participant is in a control state (pressing a button when seeing a color)
Control state subtracted from task state (deciding about two colors)
Can subtract BACKGROUND brain activity unrelated to task
Module 3
33% Done :O
Lateralization of Function
Individuals show specialization for language in left due to larger in size
Two hemispheres play different roles in different functions like language
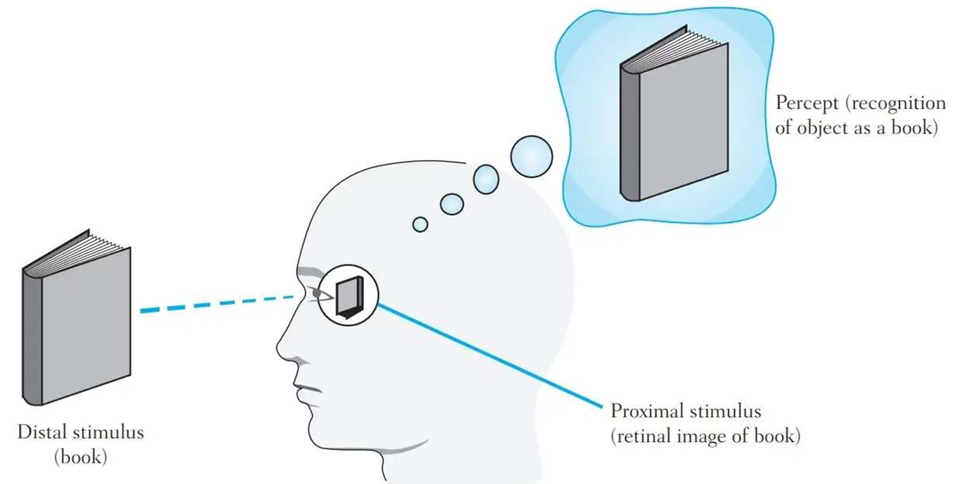
Perception
Interpret sensory input meaningfully
Percept
Recognition of proximal stimulus (retinal image)
Bottom Up Processing
Small amounts of information combined to form a percept
Three classes:
Template matching, feature analysis, prototype matching
Template Matching
Object registered as stimulus on eye
Compared to templates in memory until match is made
Doesn’t capture flexibility in human perception (exact match isn’t always found)
Doesn’t explain how to recognize NEW objects right
Feature Analysis
Objects are recognized by components/features
To recognize grey O, must recognize circular shape then color
More flexible from template matching
Prototype Matching
Best fit template instead of EXACT match like template matching
Why we can identify different fonts of M as M
Percept is compared to IDEALIZED representation in memory and matched to an approximate one
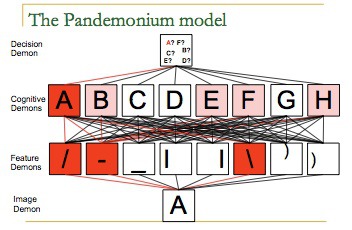
Selfridges’ Pandemonium Model
Bottom-Up Processing
Feature Analysis
Data Demons see image
Feature Demons yell when they see a their feature in the image
Cognitive Demons see if there's enough yelling to match a identified stimulus
Decision Demons listen to Cognitive Demons to see what stimulus is most likely perceived
Top Down Processes
Conceptually driven
Come from us, past experiences, environment, context
Visual Agnosia
Can’t identify object by sight
Visual skills not impaired just can’t identify by sight
Apperceptive Agnosia
Can see contours/outlines but can’t RECOGNIZE them to distinguish objects
Only process LIMITED amount of perceptual info
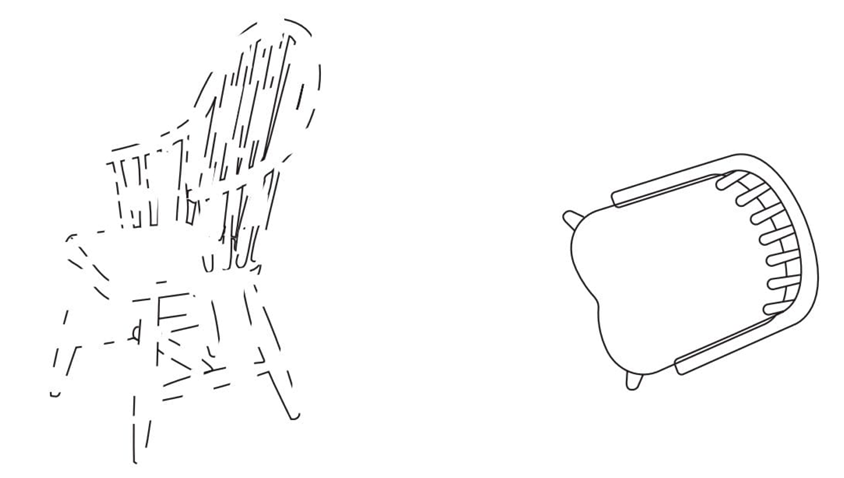
Associative Agnosia
Can match objects but do it SLOWLY
Cannot name objects JUST seen
Can’t access MEANING!!! (semantics) from just visual description
Prosopagnosia
Can’t identify faces of family members/own photographs
See individual features but can’t put them together
GSR produced
Capgras Syndrome
Impaired implicit/covert face recognition
Can’t produce galvanic skin response for their loved ones
Module 4
Woo! Halfway :)
Broadbent’s Filter Theory
Info enters our unlimited capacity sensory buffer
One input is selected based on physical characteristics (pitch or loudness)
People can only PROCESS a limited amount of sensory info at a time, filtered out to be further processed based on physical attributes
Dichotic Listening Task
Different sound playing in each ear
Attention only to focused one, couldn’t remember anything from other
Reveals limit on how much info a person can attend to at any given time
Treisman’s Attenuation Theory
Unattended messages aren’t completely blocked, but at a lower volume unless a meaningful word (our name) is spoken
Moray’s study where name is spoken in loud party
Corteen and Wood
Paired Canadian city names with electric shocks to produce Galvanic Skin Response (GSR)
Even though cities were played in unattended ear, people still got GSR
Shows that meaning was processed even when full attention not given
Deutsch Late-Selection Theory
All information is processed until we can access it's meaning in long term memory
Then, selective attention guides our awareness to that info
Stroop Effect
Shows how we automatically think with practice
Participants given colour bars vs words with different color (labeled green but blue)
Asked to name ink of each item without error, but found it difficult to not read label
Example of automaticity
Rules of Automatic Processing
No intention
No conscious awareness
Does not interfere with other mental activity
Unilateral Neglect
If damage to RIGHT parietal lobe occurs, person will neglect stimuli on the LEFT visual hemi-space
Can SEE stimuli but can’t pay attention to it
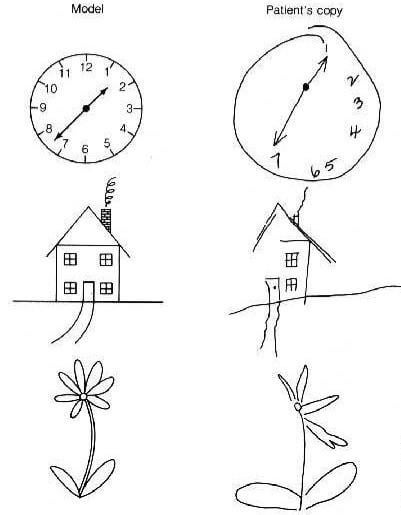
Line Bisection Task
Shows effect of unilateral neglect
Attentional disorder, not visual
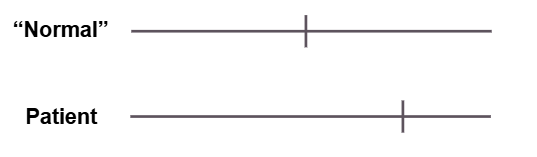
Bisiach and Luzzati
Shown scene of Italian plaza
Patients ignored all buildings on left side, regardless of direction
Straynor and Johnston’s Single and Dual Tasks
Participants asked to keep cursor on moving target
Press a button if target turns red/green
While listening to radio/telephone
More errors in dual task condition when talking on phone
Not radio though
Module 5
So close!
Clive Wearing
No short term memory
Plays piano really well but forgets wife
Atkinson and Shiffrin
Modal Model of Memory
Sensory Memory (brief storage, visual/iconic, auditory/echoic)
STM
LTM
Iconic Memory
Feels lightening bolt lasts longer but it’s very quick
Sensory memory stores brief imprint of image before you
Lasts 1 second
Sperling’s Experiment
Determine capacity of sensory memory
Briefly shown matrix of letters
Asked to report all letters
Participants started forgetting as they reported them
Added partial report condition
Only report a row based on the tone
9/12 available in sensory memory
Primacy Recency Effect
More rehearsal to words at start
Can easily offload last words right away before they decay
Short Term Memory Capacity
7 +/ 2 bits of information (chunks)
Trace Decay (Forgetting)
Automatic fading of the memory trace
Interference (Forgetting)
Disruption of the memory trace by OTHER traces
Proactive: Old info makes it hard to acquire new
Retroactive: New info makes it hard to recall old info
Brown-Peterson Paradigm
Forgetting with Trace Decay
Given three letter trigrams and recall
Prevents rehearsal by counting backwards
Wickens, Born, and Allan
Forgetting with Interference
Extended Brown’s paradigm but switched categories within trials
Switching categories was a release from proactive interference
Changing categories improved recall performance
How is long-term memory coded?
Semantics (meaningful features)
Bahrick
Retention of Spanish language
Permastore: 40 years, lots of spanish knowledge remembered
Forgetting happens rapidly but tapers off
Retrieval Cue
Point to recover target memory (sticky note)
Multiple memories to a cue makes it less memorable due to interference
Encoding and Specificity Principle
Recollecting event happens only if the properties of the trace are similar enough to the retrieval info
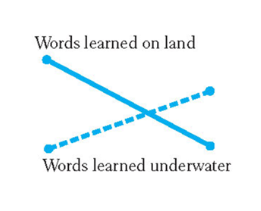
Gaudin and Baddeley
Look at effect of encoding specificity with context
Asked scuba divers to learn words on land or underwater
Given memory test on land or underwater
Perfect double dissociation relationship
Land words recalled best on land
Baddeley and Hitch
Two tasks at same time
1. Hold number in mind
2. Verify statement (A follows B)
3. Recall numbers
Shows 7 +/ 2 isn’t correct
Participants can carry on both tasks simultaneously
Working Memory
Central Executive - Directs info to…
Phonological Loop - Rehearsal and hold verbal info
Visuospatial Sketch Pad - Hold visual info
Endel Tulving
Long term memory consists of 2 distinct but interactive systems
Episodic Memory
Info about one’s personal experience with time and date attached
Semantic Memory
General knowledge and facts about world
Anterograde Amnesia
Can’t build new memories
Affects episodic memory