form and fucntion
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
… species of insects discovered and described but estimated up to … insect species on earth
>1 million, 10 million
all arthropods have…
Segmented bodies, Chitinous exoskeleton, Jointed appendages, Bilateral symmetry
what is part of the insect body plan?
head, thorax, abdomen, antennae, compound eye, mouth parts, fore leg, mid leg, hind leg, 2 pairs of wings, spiracle
what are 3 reasons for insect adaptations?
Find/eat food, Avoid predation/parasitism, Reproduce
what are the parts of the insects head?
compound eye, ocelli(simple eye), antennae, complex mouth part
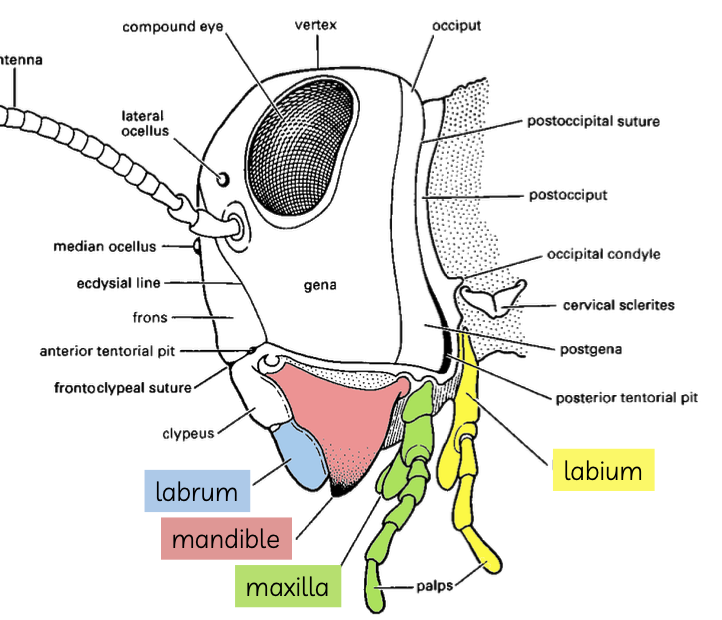
what are the parts of the complex mouth part?
labrum, mandible, maxilla, labium
mandibles help with…
eating solid foods
Haustellate help with…
sucking up liquid
Insect mouthparts are highly modified for…
Chewing/biting
Lapping/sucking
Sponging
Piercing & Sucking
Siphoning
what are mandibles used for?
biting/chewing, defense, burrowing
what insects have mandible?
grasshopper, may fly, army ants
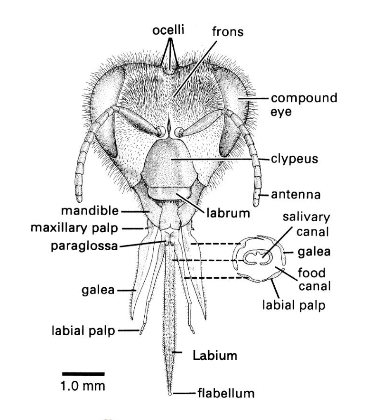
what insects have lapping/sucking mouth parts?
bees
what insects have piercing/sucking mouthparts?
aphids, assassin bugs, mosquitos
why are mosquitos carries of diseases?
coming in to contact with tissues and internal fluid
what insects have sponging mouthparts?
blow and house flies
what are insects with siphoning mouth parts?
Butterflies and moths
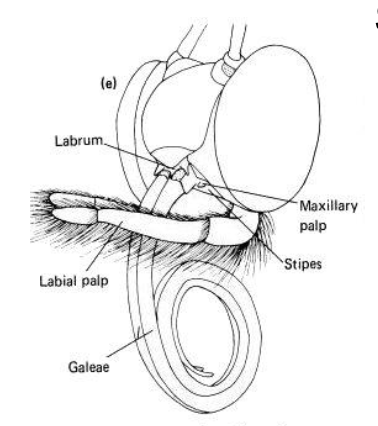
what is the key part of siphoning mouth part?
galeae
Generalist species can…
feed on a wide variety of things and thrive in various environments
Specialist species eat…
a limited diet and occupy a much narrower niche
what are the three feeding guild?
grazers, seed predators, parasites
primary defenses…
Avoid interaction with predator
secondary defenses…
Scare predator off or escape
tertiary defenses…
fight after capture
examples of primary defensive behavior…
Crypsis, Mimesis, Aposematism

Crypsis is…
blending in with background, paired with still behaviour
what are two examples of crypsis?
peppered moth, orchid mantis
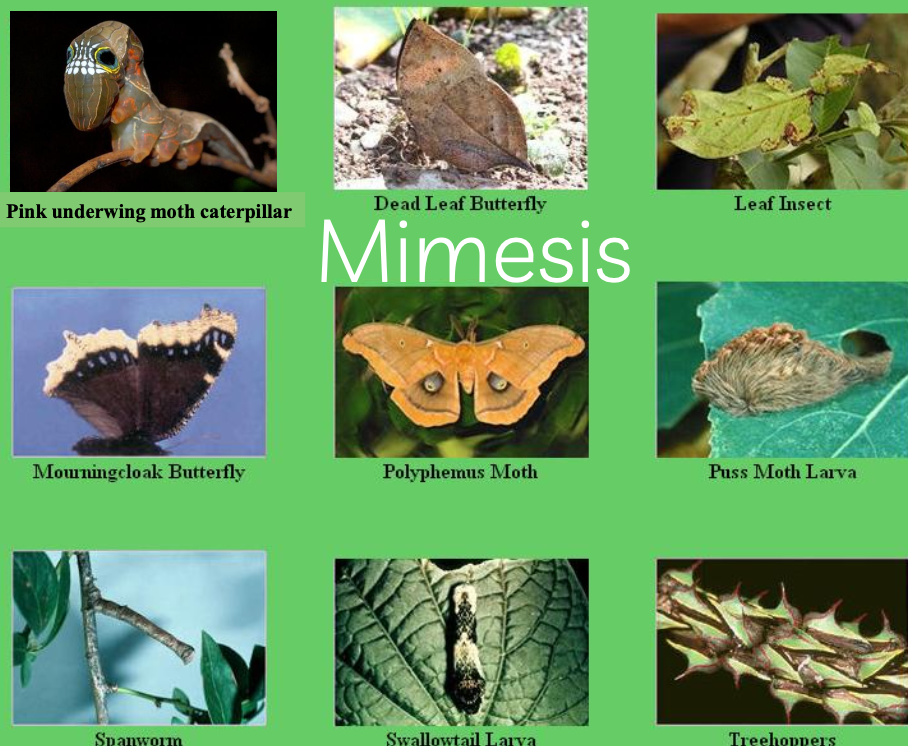

mimesis is…
you mimic something inedible

aposematism is…
show predators how unpalatable they are
what is one downside of aposematism?
there is a sacrifice for the prey so the predator can learn the signal
Cover your tracks E.g. concealing feeding damage, sneak by guard is a…
defensive behavior
Secondary defensive behavior is….
Escape mechanisms, startle behavior and evasive behavior
what are examples of tertiary defensive behavior?
Spines, bristles, hairs, armor, Chemical defences
Stink bugs have…
specialized exocrine glands that produce foul-smelling hydrocarbons
Blister beetles…
discharge cantharidin in their haemolymph from their leg
Bombardier beetles… produce
forceful discharges of boiling hot quinone and steam
Nasute termite soldiers have…
nossle-like projections through which they secrete immobilising cocktails
Saddleback caterpillars have…
hollow body hairs that contain a painful irritant
what are the chemical defenses?
Repellency, Induce cleaning, Adhesion, Cause pain/discomfort
what sensory systems do insects have?
vision, chemoreception, sound, hygoreceptors, mechanoreceptors
what do simple eyes detect?
light intensity, Photoperiod
what do compound eyes detect?
shape, movement, distance, color
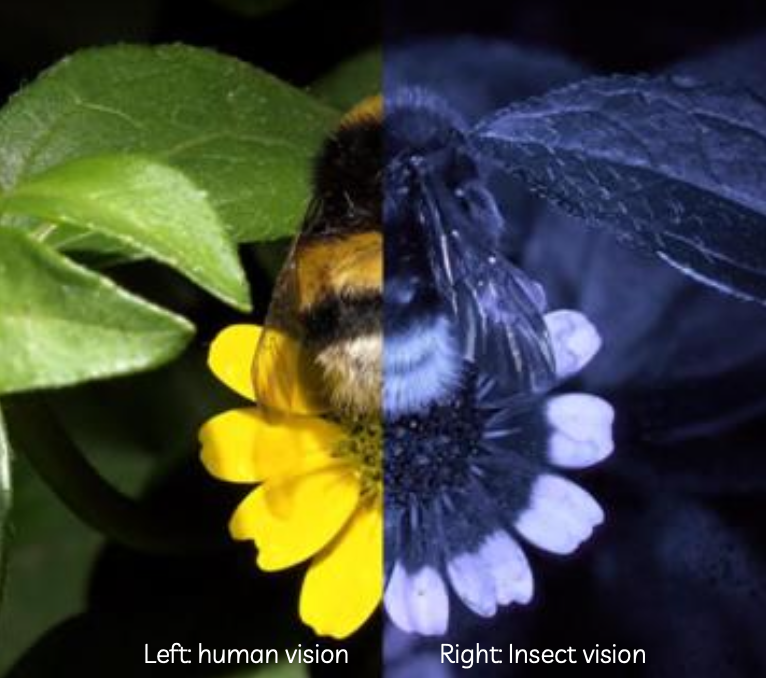

what are examples of bee vision?
UV, Polarisation, Distance, Speed
bees can’t see…, but can see…
red, uv light
flowers have evolved to…
have marking in uv light to attract bees
Bees calculate…
distance from the speed of image movement across their eyes = “optic flow”
the waggle dance: how long=…, angle=…
how far food is, where the food is
insect olfaction
form of antennae tells…
how much the insect relies on it
Antennae are used to detect…
plant chemistry, animal chemistry, decaying material, pheromones
pheromones =
chemicals made to alter behavior
Pheromones used for…
Sex, Aggregation, Warning (alarm), Trail-marking (ants)
Electroantennogram measures…
the response of insect antennal receptor cells to smells
what are the types of insect movements?
walking, digging, flying, jumping, wriggling, swimming
what adaptations are there for walking?
Adaptations for adhesion / gripping surfaces
why is it important for insects to be highly maneuverable?
find resources, escape predators, colonize new habitats, territorial behavior
why do wings allow?
Flying insects are highly maneuverable, Visual signals (toxicity, attraction), Provide protection
flight patters…
To find food, mates, oviposition sites
what are dispersal flight patterns?
Colonising new resources, Responding to change
Why are insects so successful?
Exoskeleton and tracheal system
Evolution of flight
specialised appendages
Small size
High reproductive capacity
Metamorphosis
Ecosystem processes of insects…
Primary production consumers, Food sources for secondary consumers, Decomposers, Disease vectors, Population regulators, Pollinators