4.1.5.5 - oligopoly
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
oligopoly new ppt
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Strengths of the kinked demand curve model? (EISI)
Explains price stickiness, interdependence of firms, simplicity and intuition, empirical relevance
Weaknesses of the kinked demand curve model? (FANS)
focus on price competition only, assumption of competitor behaviour, no explanation for price level, static nature
What does collusion refer to?
Businesses working together to agree on prices or restrict output.
What are network effects in oligopoly?
A phenomenon where the value of a service increases as more people use it, enhancing interdependence among firms.
Why is price competition often avoided in oligopolistic markets?
Because firms anticipate the reactions of competitors, leading to price stability.
What is the impact of high barriers to entry in an oligopoly?
They make it difficult for new firms to enter the market and disrupt collusive agreements.
What role does brand loyalty play in oligopolies?
It serves as a barrier to entry and helps established firms retain customers.
What is the relationship between interdependent decision-making and competitors in an oligopoly?
Firms' decisions depend on the anticipated reactions of their competitors, highly noticeable decision
How can firms benefit from collusion in an oligopoly?
By setting higher prices or restricting output, firms can maximize their total profits.
What is an example of a concentrated market structure besides oligopoly?
Monopoly, where a single firm dominates the market.
How do firms in an oligopoly react to price changes by competitors?
They often match price decreases but may not follow price increases, leading to price rigidity.
Define price wars in the context of oligopoly.
Intense competition where firms repeatedly lower prices to gain market share, often harming profitability.
What is the significance of product differentiation in oligopolistic markets?
It allows firms to compete on factors besides price, helping maintain market power.
How does advertising affect competition in an oligopoly?
It can strengthen brand loyalty and differentiate products, impacting consumer choices.
What is the role of regulatory agencies in oligopolistic markets?
They monitor and regulate business practices to prevent anti-competitive behavior.
What does a high price elasticity of demand indicate in an oligopoly?
It suggests that consumers are sensitive to price changes, influencing firms' pricing strategies.
What is vertical integration, and how can it be utilized in an oligopoly?
It’s when a firm controls its supply chain to reduce costs or limit competition.
What is predatory pricing, and why is it risky for firms in an oligopoly?
Setting prices low to drive out competitors, which can lead to legal issues and loss of profits.
Describe how innovation plays a role in oligopolistic competition.
c
Oligopoly
Market structure with few dominant firms, high level of market concentration
Examples of oligopoly
Telecommunications - Vodafone and Sky
Banking and Finance - Barclays and NatWest
Supermarkets and Retail - Tesco and Asda
barriers to entry in an oligopolistic market (CHELNS)
collusion, high capital requirements, E of S, brand loyalty, legal and regulatory barriers, network effects, strategic behaviour by existing firms
C5 Concentration Ratio
Top 5 firms account for over 60% sales.
In an oligopoly each firm supplies…
branded products, which may or may not be properly differentiated
What is meant by price rigidity in an oligopoly?
Prices tend to be stable and firms avoid undercutting each other's prices.
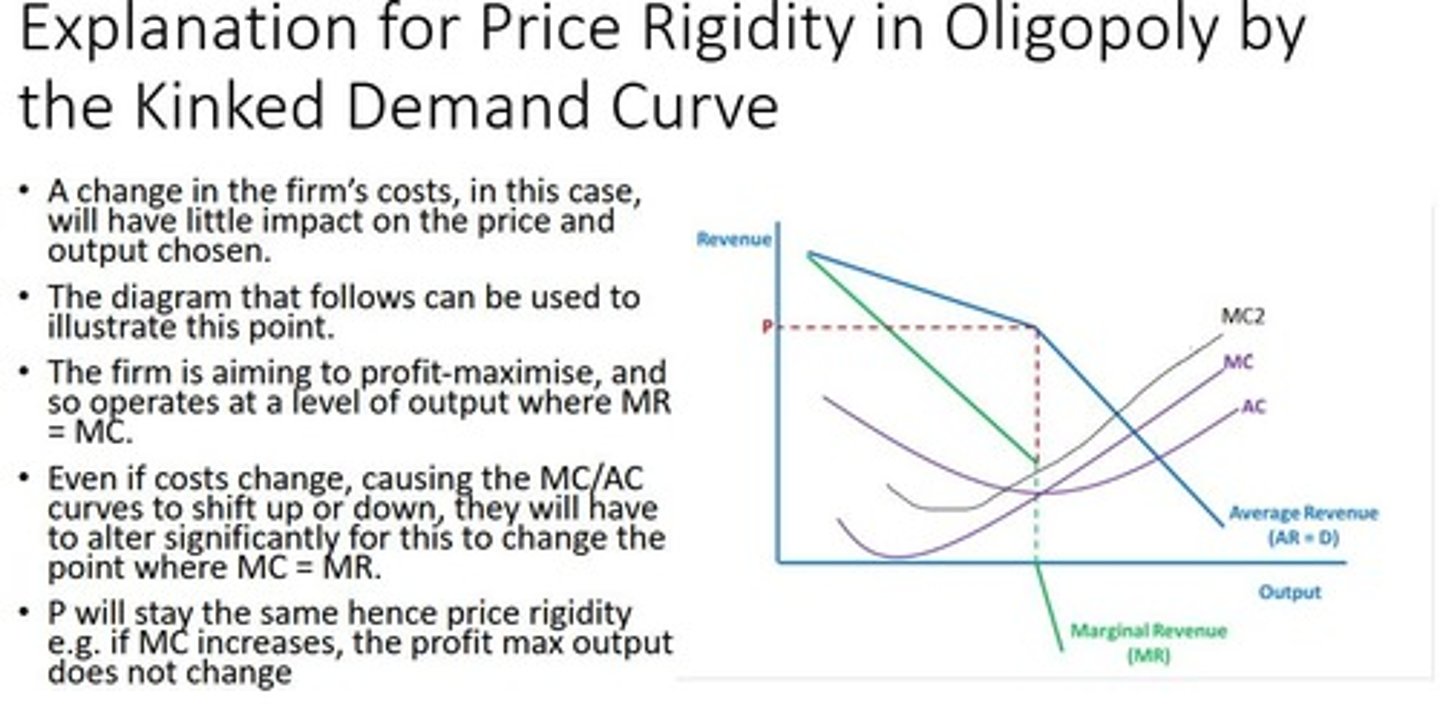
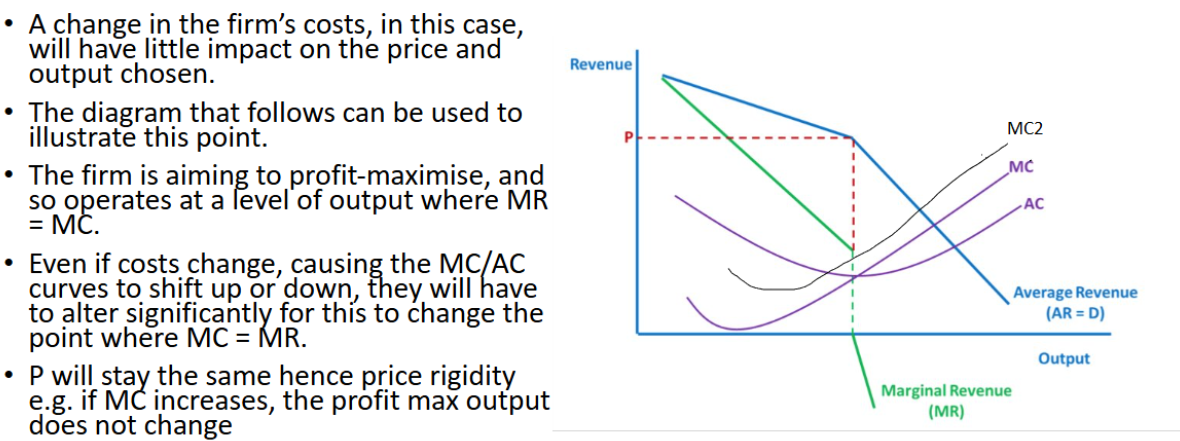
Non-price Competition
Strategies other than price to attract customers.
Product dfferentiation, branding, customer loyalty programmes
Interdependent Decision-making
Each firm’s decisions depend on the anticipated reactions of their competitors (Not in perfectly competitive markets where firms act independently)
Example of interdependent decision-making
When Asda is considering whether to reduce the price of produce it will consider the possible reaction of Sainsbury and Tesco first. If they follow, will Asda benefit from the price cutting? If not, Asda may think it’s better not to cut at the first place
Interdependent decision making creates an ___ to ___. The ___ originates from cooperation between firms under the eye of ___ operations the firms can ___
incentive, collude, incentive, regulatory, gain
incentive to collude in an oligopoly
Firms inside oligopoly are very interdependent on each other and if they compete against each other everyone will lose. If they cooperate and make secret deals, they will gain and only consumers will suffer
example of non-collusive behavior in an oligopoly
Firms competing through price discounts and promotions without colluding.
How interdependent decision making creates incentive to collude (MPH)
Mutual Awareness of Impact – knowledge of potential price wars
Profit Maximisation – joint profit max
High Barriers to Entry – new competitors cannot easily enter market to disrupt collusive agreements, makes collusion more sustainable
What is game theory in the context of oligopoly?
Models strategic interactions between firms.
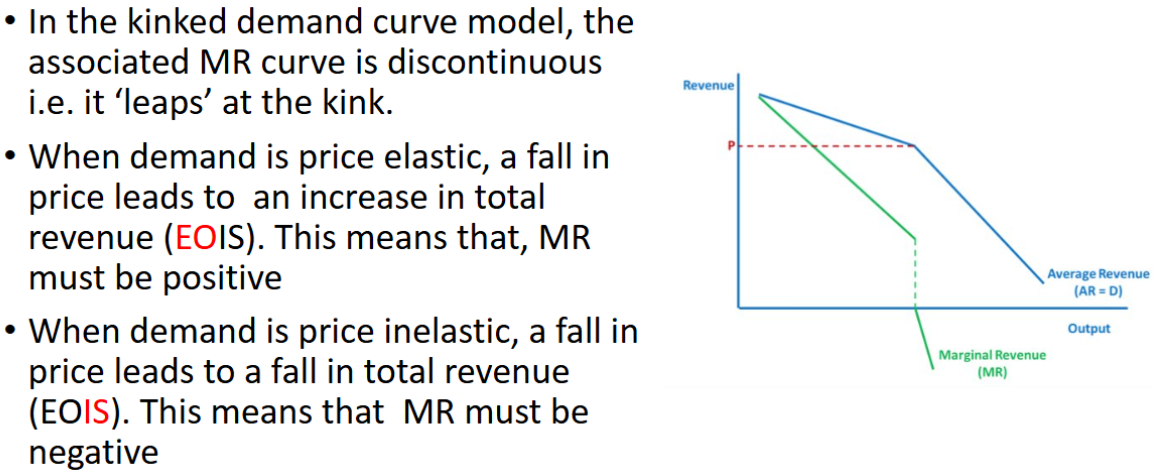
Kinked Demand Curve graph
Shows that price in an oligopoly is very stable at price P.
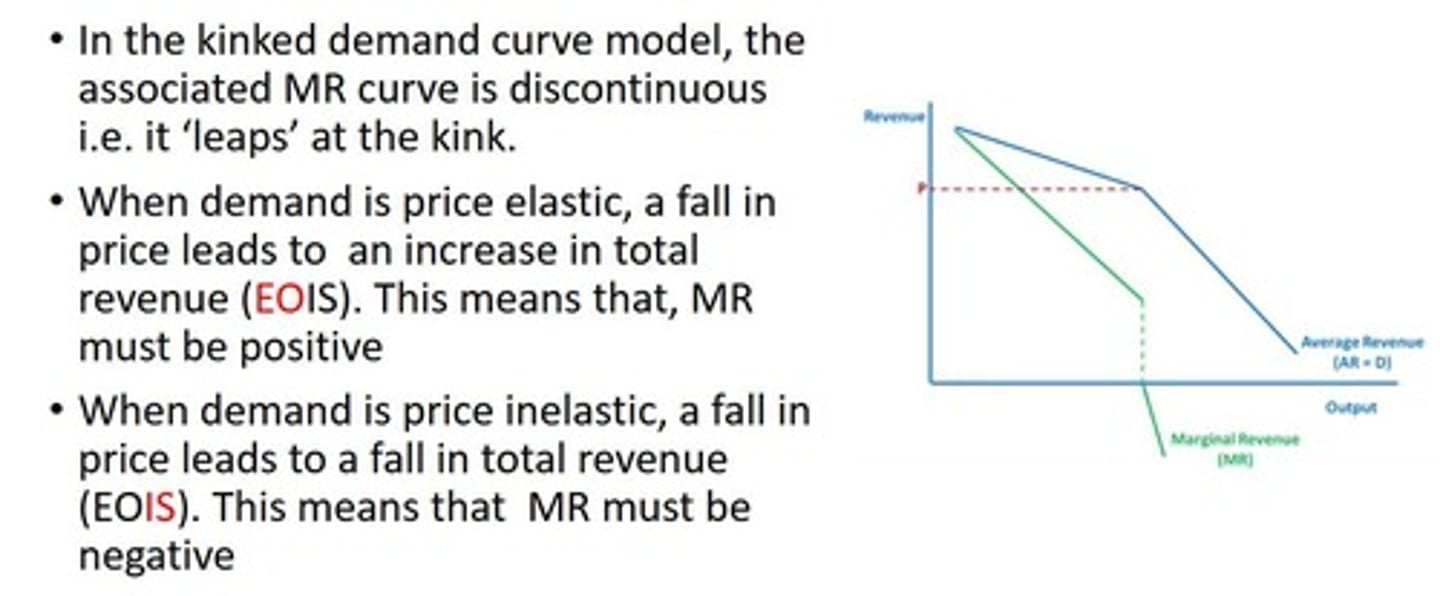
Explanation of kinked demand curve, assuming prof max
If firm raises price above P, demand will be very price elastic, TR drop (EOIS) because competitors may not follow the price rise to capture more market share
If firm reduces price below P, demand is inelastic, TR drop (EOIS) because competitors likely to follow and engage in price war
Therefore, firm should stay at P – price rigidity
Explicit Collusion
Formal agreements between firms to fix prices.
Discontinuous demand curve in kinked demand curve bc..
Tacit Collusion
Unspoken coordination among firms to limit competition.
Horizontal Collusion
Collusion between firms at the same production stage.
Vertical Collusion
Collusion between firms at different production stages.
What does Nash equilibrium represent in the context of oligopoly?
Optimal strategy where no firm benefits from changing, price competition, best option, no collusion
Profit Maximization
Achieving highest possible profit under given conditions.
Describe how innovation plays a role in oligopolistic competition.
increased competitiveness, higher profits, and improved product quality
Explanation for price rigidity in oligopoly by kinked demand curve
High Capital Requirements
Significant financial investment needed to enter market.
Collusion Incentive
Firms benefit from cooperating rather than competing.
Empirical Relevance
Real-world evidence supports theoretical models.
Non-collusive behaviour in an oligopoly
firms do not work together, and instead they compete with each other, either in terms of price competition and/or non-price competition
Regulatory Failure
Ineffective enforcement of competition laws.
Enforcement Problems
Challenges in maintaining cartel agreements.
Cartel aims to restrict production to maximise total profits
But each individual seller finds it profitable to expand their production.
Other firms who are not members of the cartel may take a free ride by selling under the cartel price
Consumer Impact
Collusion typically harms consumers through higher prices.
Price competition examples
Discounts and promotions, price matching, dynamic pricing
What causes the kink in the kinked demand curve?
Firms' varying reactions to price increases versus decreases, leading to price rigidity.
Conditions when price-fixing cartels are likely to happen in an oligopoly
Industry regulators are ineffective, Penalties for collusion are low relative to gain in profits, Few firms in the market and price inelastic demand (PED<1), Participating firms have a high percentage of total sales, Firms can communicate well and trust each other, Brands are strong so consumers won’t switch demand when collusion raises price,If all firms collude consumers will have no alternative choice
oligopoly case study
Firms fined for fixing prices fans pay for Rangers FC merchandise, Fines totalling over £2 mil on Elite Sports, JD Sports and Rangers FC, regulator CMA, horizontal collusive behaviour
Nash equilibrium represents no ___, but it does represent ___ ___, whatever happens is the ___ option
collusion, price, competition, best