BIO 1200 - Exam 3 Review
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Gene expression is the process whereby genetic information in the cell is used to produce proteins. This is referred to as the central dogma. Match the descriptions of the components of gene expression with the correct terms.
A. The molecule that carries information from the DNA specifying a polypeptide to ribosomes
B. The synthesis of an RNA copy of a gene
C. The synthesis of a specific sequence of amino acids on a ribosome
D. A molecule found in the nucleus of cell that contains the cell's genome
E. A molecule made of amino acids that correspond to the genetic information in a structural gene
A. mRNA
B. Transcription
C. Translation
D. DNA
E. Polypeptide
During the process of transcription in a eukaryote
RNA polymerase synthesizes new nucleotide chains in the 5' to 3' direction
Place the following events of TRANSCRIPTION in the correct order.
1. RNA polymerase binds to promoter
2. DNA is unwound, forming an open complex
3. RNA is synthesized in the 5' ---> 3' direction
4. RNA polymerase reaches the terminator
5. The new mRNA is released
Select the correct terms or phrases to complete the sentences that compare DNA replication with transcription.
1. In transcription, the goal is synthesis of
2. In DNA replication, the goal is synthesis of
3. RNA polymerase and primase both add nucleotides to a
4. During ____________, both strands of the DNA will function as a template
5. During ___________, only one strand of DNA will function as a template
6. The enzyme that is involved in replication but not transcription is
1. RNA
2. DNA
3. 3' OH
4. DNA replication
5. Transcription
6. DNA polymerase
What is a 3' OH?
The 3' carbon of DNA and RNA sugar backbone that has hydroxyl group attached to it
In eukaryotes, transcription to produce an mRNA must occur in
The nucleus, where the chromosomal DNA is found
Select the correct terms or phrases to complete the following sentences on RNA modification in eukaryotes.
1. Shortly after RNA polymerase begins to transcribe a pre-mRNA, a ____________ is added
2. In the nucleus, both 5' and 3' modifications to mRNA are important for
3. In the cytosol, the 5' cap is recognized by proteins that enable the mRNA to be
4. A mature mRNA will have a ________ added
5. In the cytosol, the poly A tail is important for __________ of the mRNA
1. 5' cap
2. Export of the mRNA to the cytosol
3. Translated
4. Poly A tail
5. Stability
The following sentences are about the relationship of codons to amino acids. Fill in the blanks from the items provided.
1. There is only one codon, 5'-UGG-3', for the amino acid tryptophan (trp), therefore the anticodon in the tRNA for tryptophan must have the sequence
2. A tRNA with anticodon 3'-GGG'-5' would be attached to the amino acid
3. A tRNA with anticodon 3'-UAC-5' would be attached to the amino acid
4. The amino terminus of a polypeptide will contain amino acids whose codons are closer to the_______ end of the mRNA
5. The carboxyl terminus of a polypeptide will contain amino acids whose codons are closer to the _______ end of the mRNA
6. Part of a gene sequence on the DNA reads 5'-ATGCGC-3'. The mRNA will therefore read ________ in that region
7. The template strand of a gene includes the sequence 3'-AGT-5'. The mRNA will therefore have the sequence_________ in the same position
1. 3' - ACC - 5'
2. Proline (pro) the anticodon for 3'-GGG-5' is 5'-CCC-3'
3. Methionine (met) the anticodon for 3'-UAC-5' is 5'-AUG-3'
4. 5'
5. 3'
6. 3'-UACGCG-5'
7. 5'-UCA-3'
Structural RNA that links an amino acid to an anticodon
tRNA
Contains information to be translated (as codons)
Gene
mRNA
Forms part of the enzyme that drives translation
Ribosomal protein
Ribosomal RNA
What is tRNA and what does it do?
Transfer RNA; tRNA carries a specific anticodon that matches with the codon of the mRNA; this provides tRNA with the instructions of what amino acid to bring to protein synthesis in the ribosomes
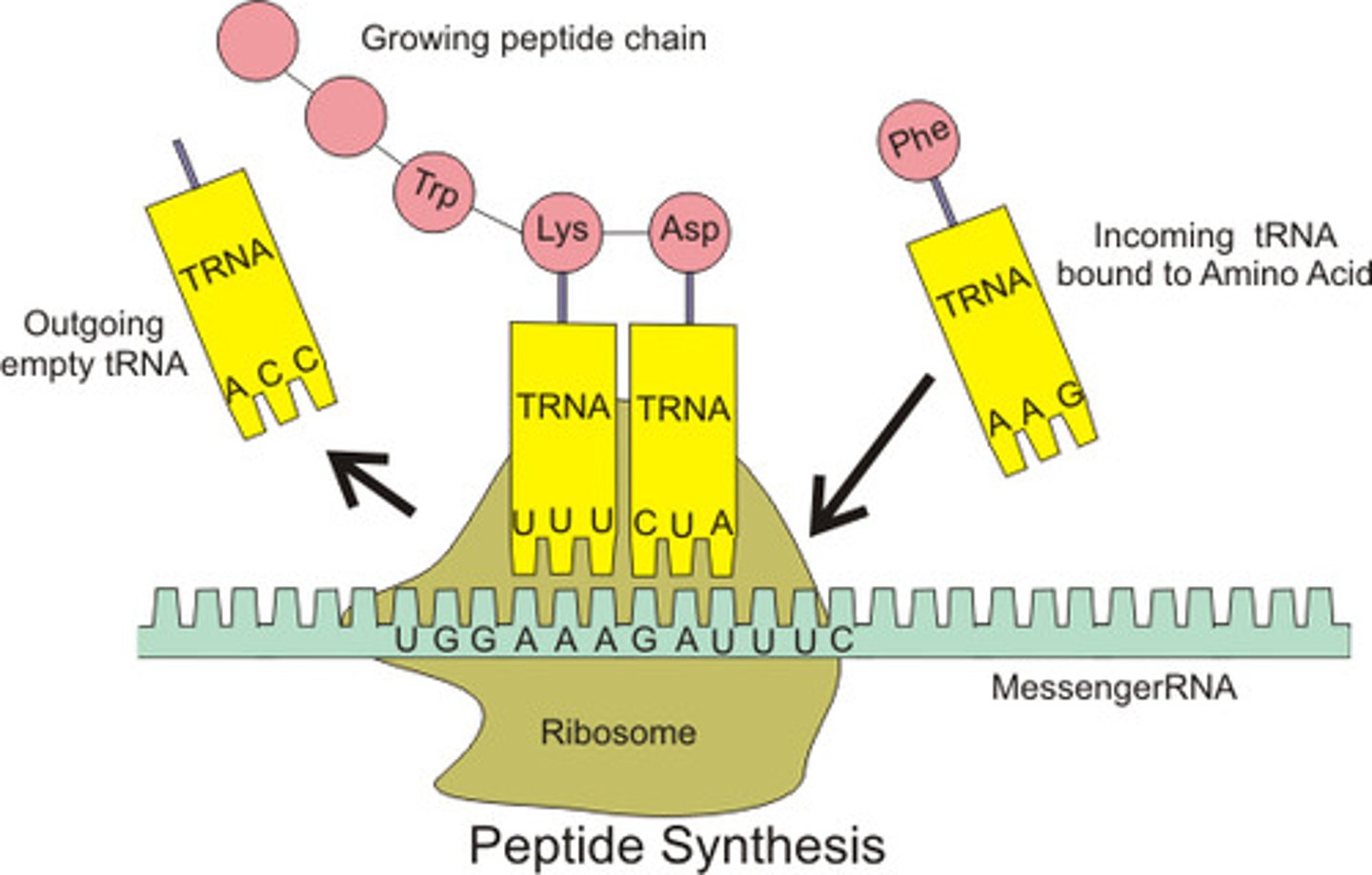
A charged __________ enters in the A site
tRNA
The polypeptide grows by ______ amino acid
One
The __________ translocates to the right and an uncharged tRNA is released
Ribosome
The cell is capable of regulating gene expression in a variety of situations and environments. Valid reasons for a cell to regulate gene expression include its ability to:
A. make additional cells of the same type in response to a demand
B. synthesize enzymes to metabolize a particular nutrient
C. keep a gene product available under all conditions
D. execute a specific program of development (e.g. to become a blood cell or immune cell)
E. stop synthesis of a cellular component when there is enough available in the cell
F. synthesize mRNA for every gene in the genome at all times
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
F.
1. A protein that binds to DNA and blocks activation of a small number of genes is a/an
2. A protein that binds to DNA and activates transcription of some genes is a/an
3. Modification of bases in DNA, usually resulting in inhibition of transcription, results from
4. The idea that gene regulation involves multiple factors is called
5. Function of __________ can be modulated by binding of small effector molecules, protein-protein interactions, or covalent modifications
1. Repressor
2. Activator
3. Methylation
4. Combinatorial control
5. Activators and repressors
What is NOT a mechanism used by activators and repressors to affect gene expression?
All of these are mechanisms used by activators or repressors to affect gene expression
Transcription
An activator binds to an enhancer
A repressor binds near a promoter
RNA modification
The correct removal of introns of a pre-mRNA is prevented
The stability of an mRNA is regulated
Export of an mRNA to the cytoplasm is blocked
Translation
The ability of an mRNA to bind to ribosomes is changed
The 5' end of an mRNA forms a shape that blocks translation
Post-translation
The rate of degradation of a protein is increased
A phosphate group is added to make a protein, making it inactive
Strong effect
CGA ---> TGA near the beginning of the gene
GAG --> GTG change in an important part of the coding region
Insertion of one base (+1) shortly after the start codon
No effect
Change of a C to a G before the ATG
TGA --> TAA at the end of the coding region
AAG ---> AAA in the middle of gene
Weak effect
Change of a codon for one acidic amino acid into another acidic amino acid
Which of the following would occur from a mutation in the gene's promoter region?
The rate of transcription may increase or decrease
The following sequence of DNA is part of the normal, wild-type gene.
5' ATG CGG GTA GTT AGC CGA TAG 3'
A deletion occurs during DNA replication, causing the underlined guanine (also shown in red) to be removed from the nucleotide strand. What effect is this most likely to have on the final protein?
The deletion of the G will cause a frame shift, resulting in a premature stop codon and a truncated protein
Oncogenes and tumor-suppressor genes have the shared property that
When either type of gene is mutated, cancer can result
Insert the most correct term(s) as they apply to eukaryotic chromosomes.
1. The parts of chromosomes where the spindle apparatus will attach are called
2. When a single chromosome has undergone DNA replication, it consists of two
3. The human ___________ consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes
4. Each pair of human chromosomes (for example, two copies of chromosome 17) is called a pair of
1. Centromeres
2. Sister chromatids
3. Genome
4. Homologous chromosomes
The two long structures indicated by "d" are
Sister chromatids
Complete the sentences that describe the four phases in the life cycle of a cell.
1. The _______ phase is when most cell growth will occur; DNA is unreplicated.
2. During _______ phase, the genetic material undergoes replication.
3. The ________ phase occurs between chromosome replication and mitosis.
4. During _________phase, the shortest phase, the cell undergoes both nuclear division (mitosis) followed by cell division (cytokinesis).
1. First gap (G1)
2. Synthesis (S)
3. Second gap (G2)
4. M
The cell cycle consists of several checkpoints at which the cycle can be stopped before continuing to the next phase. Which of the following is not a function of these checkpoints?
Supplying energy for the replication of chromosomes into pairs of sister chromatids
Which of the following events occur during prophase I?
Breakdown of nuclear envelope, condensation of chromosomes, and movement of centrosomes
How many bivalents are formed in a cell with 20 chromosomes at the beginning of meiosis I?
10
Which of the following events occur during anaphase I?
Separation of homologous chromosomes
How can you compare the collection of DNA in an interphase ( G1G1 ) diploid cell and a cell that has just completed meiosis I?
They have the same amount of DNA, but the meiotic cell has half as many chromosomes
In meiosis I
Homologous chromosome pairs are separated, producing haploid daughter cells
A 2n = 6 germline cell completes meiosis I. Each daughter cell
Contains three chromosomes, each composed of two sister chromatids
Random orientation of homologous chromosomes occurs in _________ of meiosis.
Metaphase |
Consider a cell that has four pairs of chromosomes. How many orientations of all chromosomes are possible during meiosis I in that cell?
16