EXAM 4 LECTURE 1: VIRUSES単語カード | Quizlet
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
virus
a submicroscopic particle made up of nucleic acid that replicate inside living cells using the cellular synthetic machinery for production of progeny virions
either RNA or DNA, NEVER BOTH!
host range
range of animal spp and tisue cells that a virus can infect (can be broad or limited)
capsomeres
morphological subunits from which the virus capsid is built
determines the shape of virus
capsid
protein shell or coat that encloses nucleic acid genome (virus)
envelope
lipid-containing membrane that surrounds some viruses
nucleocapsid
capsid together with enclosed nucleic acid
virion
complete infective virus particle (synonym)
incomplete virion
virion without nucleic acid (empty capsid)
pseudovirion
during viral replication, capsid sometimes encloses host nucleic acid rather than viral nucleic acid; looks like ordinary virus particles when observed by electron microscope, but do not replicate
provirus
viral DNA that is inserted into host cell chromosome in latent state and must be activated before it is transcribed, leading to production of progeny virions;
transmissible from parent cell to daughter cell
- made up of nucleic acid & has a capsid (protein coat)
- very small in size (smaller than even E. coli) and contains very few genes
- contain either RNA or DNA (not both)
- lack cellular components needed to generate energy & synthesize proteins (need host)
- contain few enzymes
- contain min. amount of genetic info
What are the general characteristics of a virion (bacteriophage)?
only needs info for:
- making its special protein coat
- assure replication of its own chromosome
- move the virons in and out of host cell
Why do viruses contain min. amount of genetic information?
capsid made up of identical capsomeres
can be helical or spherical
What is the shape of the virus determined by?
envelope (double layer of lipids)
has spikes (help attach to host cell) - made up of protein and glycoprotein
Some viruses have an additional lipid membrane called what?
- hepatitis B virus
- has a lipid containing envelope
Hepadna-viridae

- HPV virus
- naked structure (no outer membane)
Papova-viridae

- tumor causing virus
- naked structure (no outer membrane)
Adeno-viridae
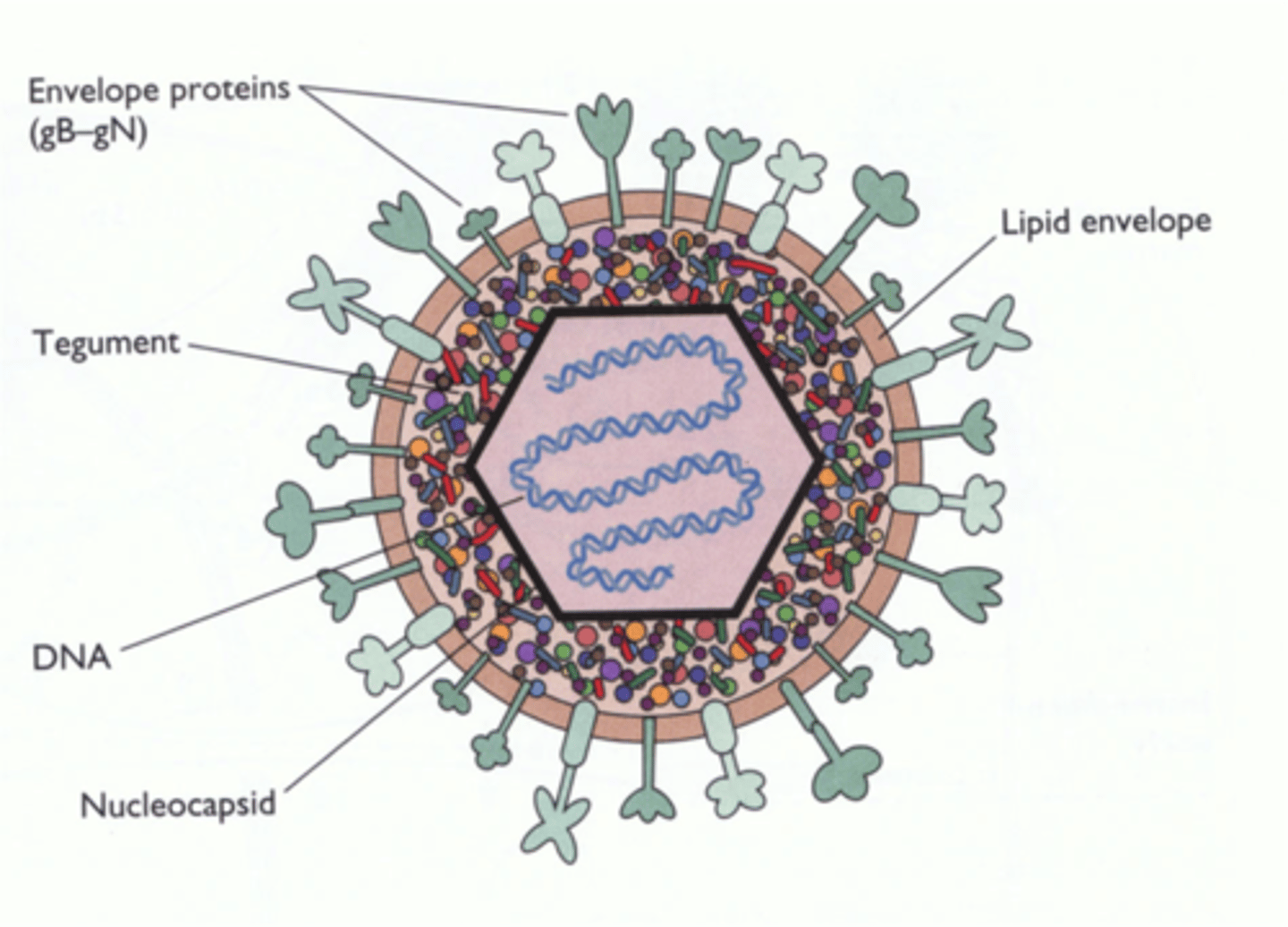
- Herpes simplex virus
- enveloped with surface projections
herpes-viridae
- smallpox virus
- enveloped; large brick-shaped
pox-viridae
Zika virus
- single stranded (ssRNA)
- causes microcephaly in babies (Brazil)
- caused by a mosquito
- headache
- conjuctivitus
- fever
- pain behind eyes
- joint pain
- vomiting
- skin rash
- muscle pain
1 in 4
symptoms last up to a week
What are some symptoms of the Zika virus?
How many people develop symptoms? How long do symptoms last?
it causes microcephaly in babies
Why is the Zika virus dangerous to pregnant women?
1. Attachment
2. Penetration
3. Transcription/Translation
4. Replication
5. Assembly
6. Release
What are the 6 steps of Viral Replication?
phages attach to host cell receptors
What happens during the attachment stage of viral replication?
viral nucleic acid is injected into host cell, leaving the empty phage outside still attached to cell
What happens during the penetration stage of viral replication?
phage DNA is transcribed leading to production of specific proteins
(part of the phage DNA is transcribed into mRNA which is then translated into specific proteins used to infect cell)
NUCLEASE - is used to degrade host's DNA and phage make's its own new infected DNA
What happens during the transcription/translation stage of viral replication?
Phage DNA copies itself and structural proteins are synthesized
What happens during the replication stage of viral replication?
Phage DNA and protein assemble together to form mature virions
What happens during the assembly stage of viral replication?
infected host cell lyses and releases many infective phage
What happens during the release stage of viral replication
- cell culture
- serological techniques
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- molecular methods
What are the different laboratory diagnosis used in viral infections?
upper resp:
- swabs, nasal, throat
lower resp:
- bronch washes, lung and bronhial biopsies
- eye swabs
- stools/rectal swabs
- body fluids (CSF, bone marrow, serum, blood)
List some viral specimens types
Ebola
- RNA virus & helical structure
- spread by close contact
- no cure
- extreme symptoms of advance stage includes: bleeding from eyes, nose and mouth (internal & external) and impaired kiney/liver
Bats
What are the normal reservoirs for EBOLA?
HIV
- RNA virus
- causes AIDS and affects immune system
- infects Helper T cells
- without Helper T cells, you cannot fight off other pathogens
secondary infections like pneumonia because their immune system could not fight the infection
What can people with AIDS die of?
RNA
single stranded
DNA
double stranded
severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
- RNA virus
- caused by SARS - coronvirus
- outbreak in China in 2002-2003 resulted in 37 different countries
- typically due from air travel
flu-like: fever, lethargy, myalgia, cough,
only common symptom: fever above 100.4 F
What are some symptoms of SARS?
viroids
only genetic material