Microbial Genetics: DNA Structure and Function
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Genetics
Study of inheritance and inheritable traits as expressed in an organism's genetic material.
Genome
The entire genetic complement of an organism, including its genes and nucleotide sequences.
Gene
a particular section of dna that codes for proteins
Gene product
Protein.
Flow of genetic information
DNA → RNA → Protein (the central dogma of molecular biology)
Levels of Genetic Study
Organism level, Cell level, Chromosome level, Molecular level.
Prokaryote
A type of cell that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. (haploid)
Eukaryote
A type of cell that has a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
haploid
one set of chromosomes
diploid
two sets of chromosomes
Chromosomes
Structures within cells that contain DNA and carry genetic information.
structure of chromosomes in prokaryotic cells
typically a circular molecule of DNA in the nucleoid
structure of chromosomes in eukaryotic cells
linear chromosomes within the nucleus
Nucleus
The membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell's genetic material.
Plasmids
Small molecules of DNA that replicate independently and carry information for cellular traits.
fertility factors
proteins that enable them to engage in conjugation with other bacteria more effectively
resistance factors
encode antibiotic resistance
bacteriocin factors
carry genes for proteinaceous toxins (which are proteins that kill or stop the growth of other bacteria)
virulence plasmids
carry genes that cause disease or to make the bacteria more harmful
cryptic plasmids
plasmids that do not encode any known accessory function.
Mitochondrion
An organelle that produces energy for the cell through respiration.
Viruses
Infectious agents that can only replicate inside the living cells of an organism.
gene therapy
a technique that places a gene into a cell to correct a hereditary disease or to improve the genome
Recombinate cell
a cell that contains DNA from two different sources, combined together using genetic engineering.
polymer
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
Extra chromosomal DNA
DNA that is not part of the chromosomal DNA and can exist independently.
ether linkage
a type of chemical bond where an oxygen atom connects two carbon atoms.
antiparallel
two strands going in opposite directions, like the two sides of a zipper.
RNA
A nucleic acid involved in protein synthesis and gene expression.
-single stranded
DNA
The molecule that carries the genetic instructions for life.
purines
Bases with a double-ring structure. (A&G) -larger
pyrimidines
single-ring structure made of carbon and nitrogen atoms (C&T) -smaller
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant cells that conducts photosynthesis.
nucleotide
a building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
Double helix
The structure of DNA, consisting of two strands twisted around each other.
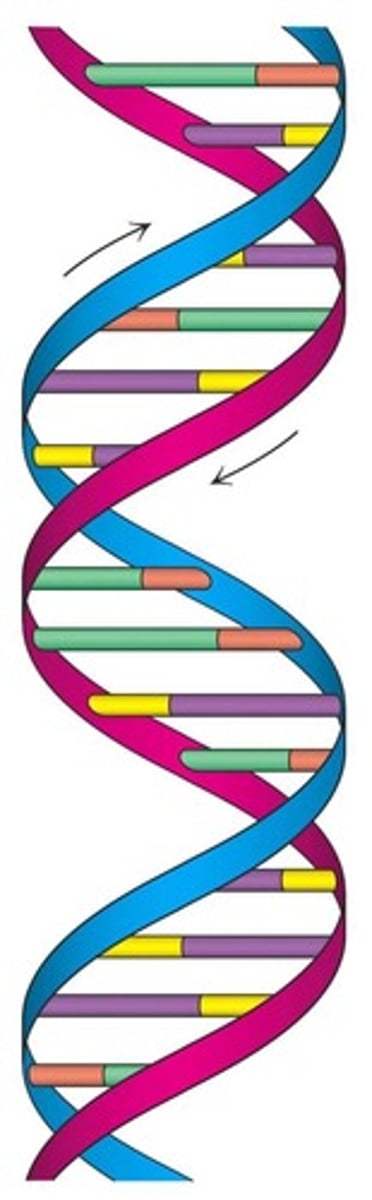
Base pair
A pair of complementary nitrogenous bases in DNA, held together by hydrogen bonds.
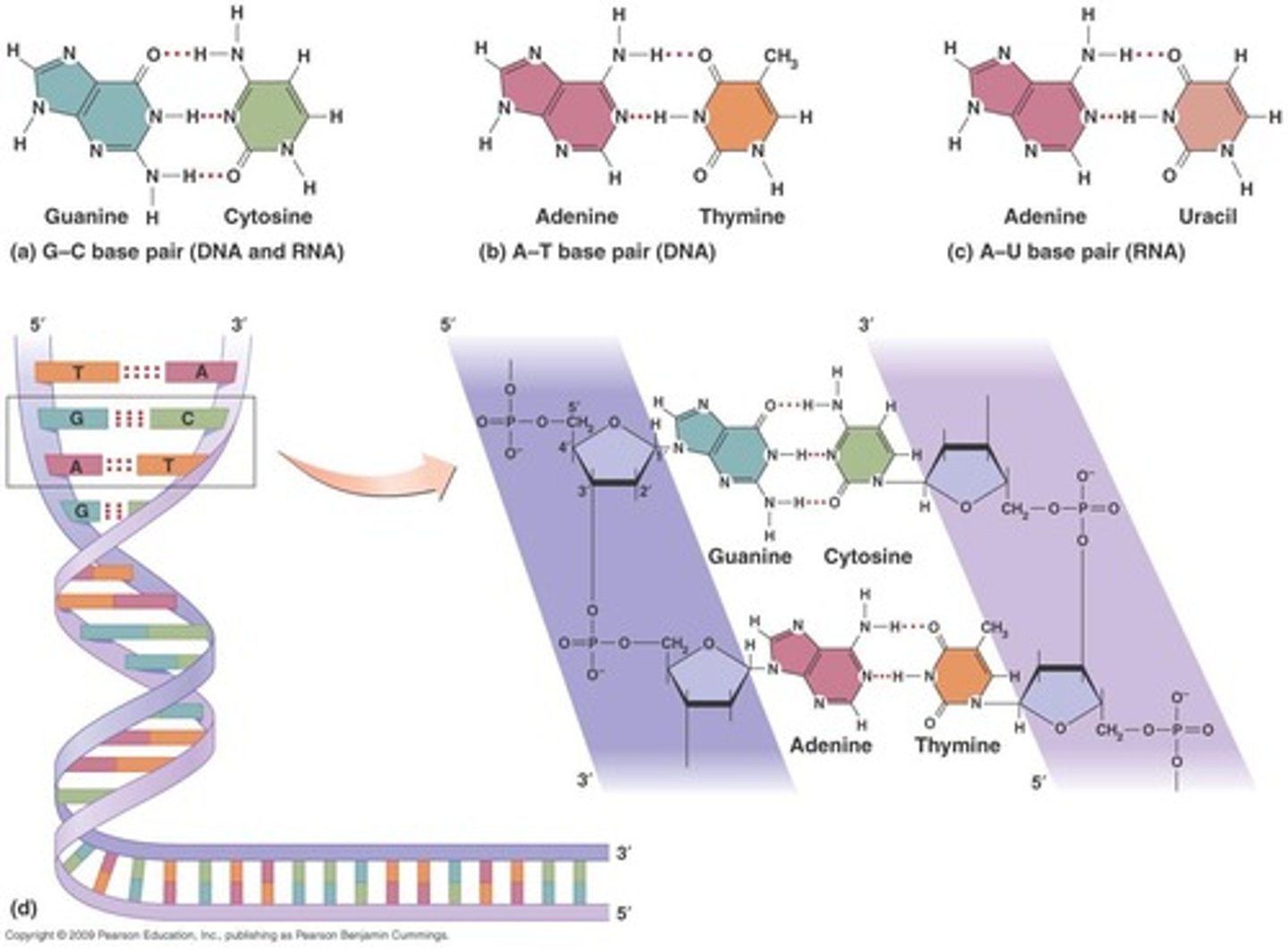
Chargaff's Rules
The principle that %G = %C and %A = %T in DNA.
rRNA
makes structure and catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond
tRNA
carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis.
mRNA
conveys genetic information from DNA to the ribosome.
DNA Replication
An anabolic polymerization process that requires monomers and energy to produce two identical copies of DNA. (semiconservative)
semiconservative
method of replication that implies that each new strand of DNA is half original and half new
monomer unit of DNA
triphosphate deoxyribonucleotides
5 prime
the end of the phosphate group
3 prime
a nucleotide with a free OH group on its sugar
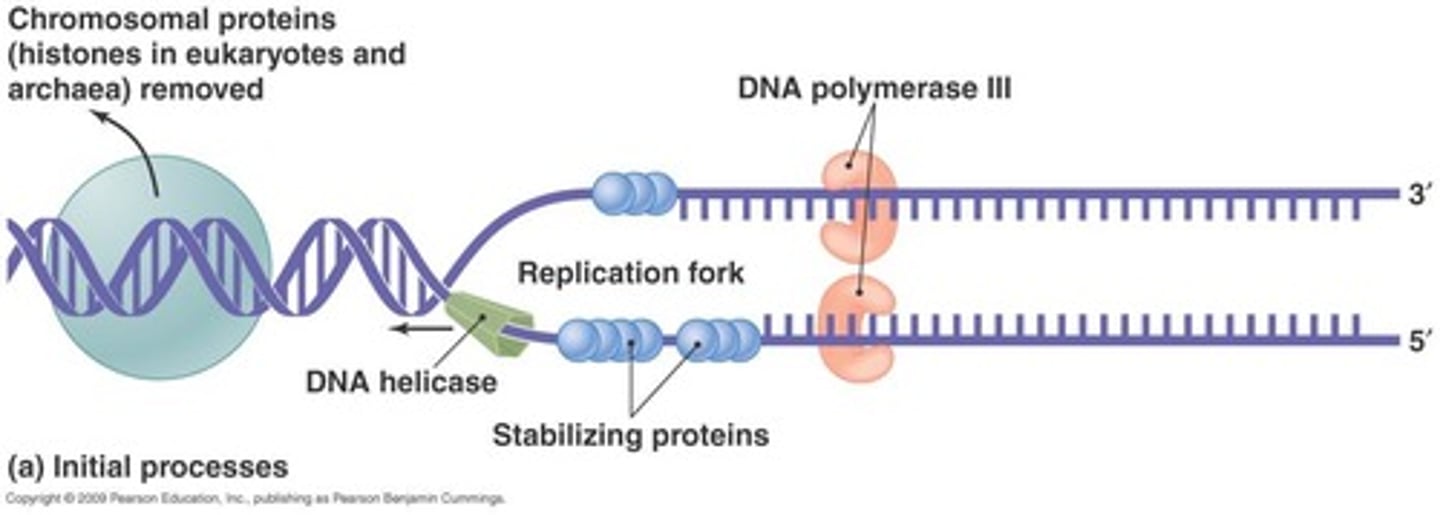
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides. (Replicates DNA only 5ʹ to 3ʹ)
Leading strand
The DNA strand that is synthesized continuously during replication. (follows parent strand)
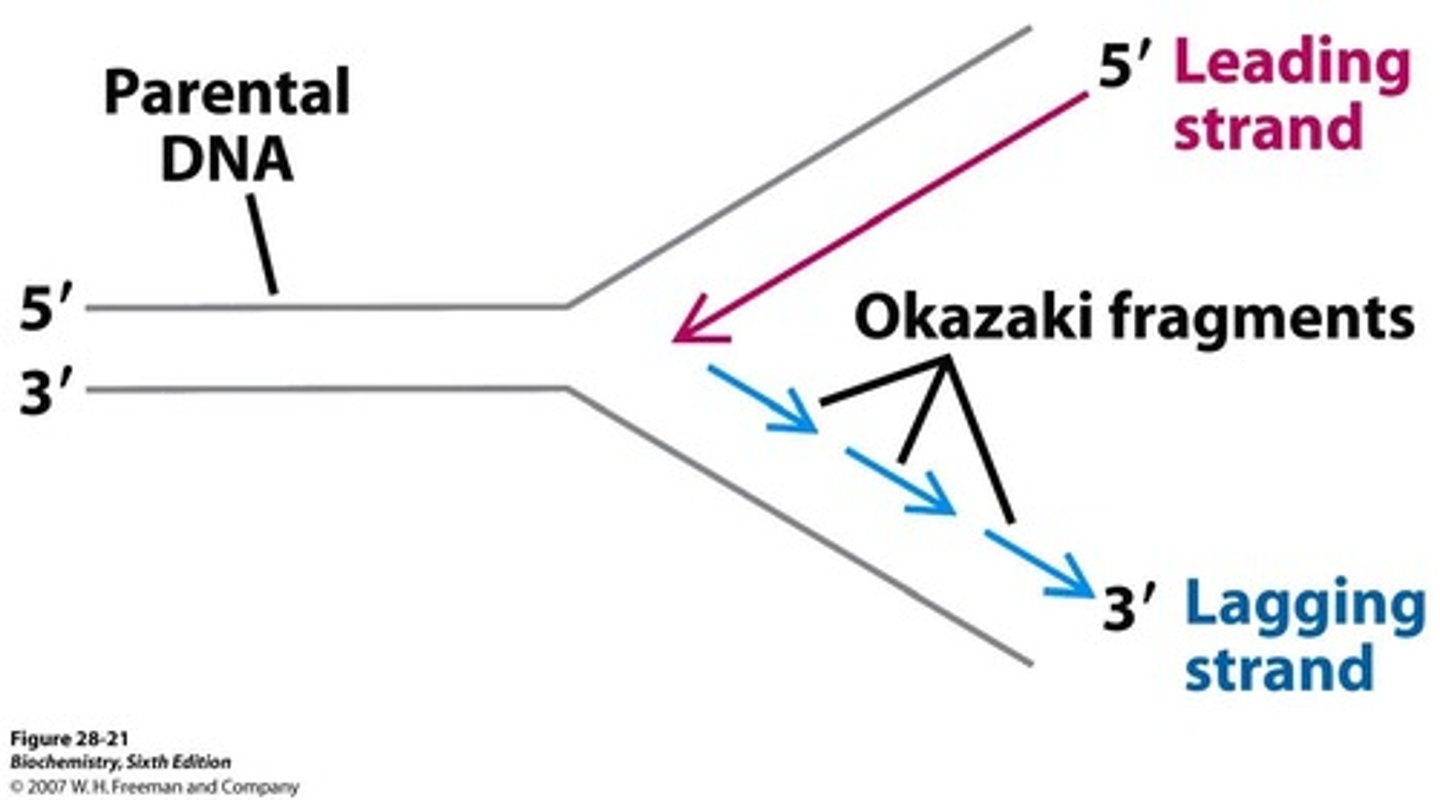
Lagging strand
The DNA strand that is synthesized discontinuously in short segments during replication. "Okazaki fragments"
Bidirectional
A characteristic of bacterial DNA replication where replication occurs in both directions from the origin.
Topoisomerases
Enzymes that remove supercoils in the DNA molecule. (specifically dna gyrase)
Methylation
A process where DNA is modified with methyl groups, playing a role in genetic expression, initiation of DNA replication, protection against viral infection, and DNA repair.
histones
Globular proteins in eukaryotic cells that assist in DNA packaging/organizing into chromatin
dna replication steps
1) Helicase- unwinds the parental double helix
2) DNA topoisomerase - upstream of helices alleviating torsional strain
3) Single-strand binding proteins (SSBP) stabilize unwound DNA, aided by DNA gyrase.
4) Primase synthesizes a short RNA primer for DNA polymerase to bind to in the 5' to 3' direction to start replication on each strand.
5) DNA polymerase synthesizes the leading strand in 5' to 3' direction while the lagging strand is made discontinuously by primase making short pieces and then DNA polymerase extending these to make Okazaki fragments.
6) DNA ligase joins the Okazaki fragments together
supercoils
extra turns in the DNA beyond those generated by the shape of the base pairs (make hard to read dna)
replication
two strands being created based on complementary
Genotype
The set of genes in the genome.
Phenotype
The physical features and functional traits of the organism.
gene expression
process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out its function (ex. protein)
Transcription
The process where information in DNA is copied as RNA nucleotide sequences.
Translation
The process where polypeptides are synthesized from RNA nucleotide sequences.
Central dogma of genetics
The framework describing the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein.
Reverse transcription
The process where RNA is converted back to DNA. "reverse of central dogma"
Exonuclease
an enzyme that removes nucleotides from the ends of a DNA or RNA strand.
Four types of RNA transcribed from DNA
RNA primers, mRNA, rRNA, tRNA (Occurs in nucleoid of prokaryotes)
Prokaryotic transcription
occurs in the nucleoid &, involves RNA primers, mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA.
3 steps of prokaryotic transcription
initiation, elongation, termination
Eukaryotic transcription
The process of transcription that occurs in the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts, involving three types of RNA polymerases and numerous transcription factors.
Capping in eukaryotic transcription
A processing step in mRNA transcription where a modified guanine nucleotide is added to the 5' end of the mRNA.
Polyadenylation in eukaryotic transcription
A processing step in mRNA transcription where a poly-A tail is added to the 3' end of the mRNA. (adds a lot of adenine nucleotides)
Splicing in eukaryotic transcription
The process of removing introns from pre-mRNA and joining exons together. (cutting/pasting)
Translation participants
include messenger RNA, transfer RNA, and ribosomes.
Degenerate genetic code
The property of the genetic code where multiple codons can code for the same amino acid.
Ribosome
A cellular structure composed of rRNA and protein that synthesizes polypeptides during translation.
Initiation of translation
The first stage of translation where the ribosome assembles around the start codon of the mRNA.
Elongation of translation
The stage of translation where amino acids are added one by one to the growing polypeptide chain.
Termination of translation
The stage of translation where release factors recognize stop codons, leading to the release of the polypeptide.
coding region
A section of DNA that contains the code for protein synthesis
noncoding regions
DNA segments that do not code for proteins.
exons
a section of mRNA that will translated into protein
intron
sequence of DNA that is not involved in coding for a protein (garbage)
capping & polyadenylated
make the mRNA more stable, help regulate gene expression, allow for nuclear export, and ensure translation by ribosomes happens correctly.
Splieceosmoes
allows for modularity and flexibility by enabling alternative splicing, which lets one gene code for multiple proteins (legos)
codon
three ribonucleotides of mRNA that code for a particular amino acid
start codon
AUG (proteins always start with Methionine)
stop codon
UAA, UAG, UGA (termination of a protein) -Multiple so that it can help with mutations and stuff
anticodon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
additional protein factors
stages of translation require what
Polyribosome
A complex of multiple ribosomes translating a single mRNA strand simultaneously.
Promoter
A DNA sequence that signals the start of a gene and where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription.
Terminator
A DNA sequence that signals the end of a gene and where transcription stops.
RNA strand
The strand of ribonucleic acid that is synthesized during transcription.
Regulation of Genetic Expression
The process by which cells control the timing and amount of gene expression.
bacterial gene expression
bacteria express genes as response to environment, only express genes when products are needed
Operons
Groups of coordinately expressed and regulated genes in bacteria.
Structural gene
A gene that codes for a protein or RNA molecule.
(s) =group & same function
RNA polymerase
The enzyme responsible for synthesizing RNA from a DNA template.
Operator
A segment of DNA that a repressor binds to, blocking transcription.
Repressor
A protein that inhibits gene transcription by binding to the operator.
Inducible operons
Operons that must be activated by inducers to initiate transcription. (lactose operon)
Repressible operons
Operons that are continuously transcribed until deactivated by repressors. (arginine operon)