Chapter 16 - Respiratory Emergencies
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
dyspnea
shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
JVD (jugular vein distention)
symptom where the jugular veins in the neck become visibly swollen and bulging due to increased pressure
key sign of various heart and circulatory problems, including heart failure
JVD
DKA (diabetic ketoacidosis)
characterized by hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), elevated ketones, and acidosis,
triggered by insulin deficiency or inadequate insulin intake.
dehydration, fruity breath, and rapid breathing
brainstem
what senses blood carbon dioxide levels
regulates breathing rate and depth
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
disorder in which subsets of patients may have dominant features of chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or asthma
Slow process of dilation and disruption of airways and alveoli
Caused by chronic bronchial obstruction
Tobacco smoke can create chronic bronchitis
pulmonary edema
condition characterized by an abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs, primarily within the air sacs (alveoli)
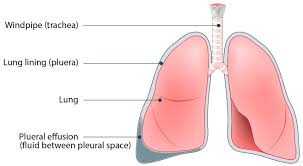
pleural effusion
condition where excessive fluid accumulates in the pleural space, the area between the lungs and chest wall
Upright position eases pain
pleural
hyperventilation syndrome
similar symptoms as panic attack
pnemonia, bronchitis
common lung infectious diseases
croup
Inflammation and swelling of pharynx, larynx, and trachea
Stridor and seal-bark cough
Responds well to humidified oxygen
epiglottitis
Bacterial infection causing inflammation of epiglottis
Children are often found in tripod position and drooling
Position comfortably and provide oxygen
RSV (respiratory syncytial virus)
Common cause of illness in young children
Causes infection in the lungs and passages
Highly contagious
Look for signs of dehydration.
Treat airway and breathing problems.
Humidified oxygen is helpful
bronchiolitis
Viral illness often caused by RSV
Usually affects newborns and toddlers
Bronchioles become inflamed, swell, and fill with mucus.
Provide oxygen therapy and frequently reassess
pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia will come on quickly and result in high fever.
Viral pneumonia presents more gradually and is less severe.
Especially affects people who are chronically ill
Assess temperature and provide airway support and supplemental oxygen
pertussis (whooping cough)
Airborne bacterial infection that mostly affects children younger than 6 years
Patients will be feverish and exhibit a “whoop” sound on inspiration after a coughing attack.
Watch for dehydration and suction as needed
flu
Became pandemic in 2009
Symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, headache, and fatigue.
May lead to pneumonia or dehydration
covid
Similar to the virus that causes the common cold
Preferentially affects the elderly, those living in close quarters with one another, and those with weakened immune systems.
Transmitted by aerosol droplets and airborne particles
Respiratory deterioration may occur rapidly
TB
Bacterial infection that most often affects the lungs
Can remain inactive for years
Patients often complain of fever, coughing, fatigue, night sweats, and weight loss.
Wear gloves, eye protection, and an N-95 respirator (at a minimum).
acute pulmonary edema
Heart muscle cannot circulate blood properly.
Fluid builds up within alveoli and in lung tissue.
Usually result of congestive heart failure
Most patients have a long-standing history of chronic congestive heart failure.
In severe cases, a frothy pink sputum forms at the nose and mouth
emphysema
the most common type of COPD
Loss of elastic material in the lungs
Causes include inflamed airways, smoking
chronic bronchitis, emphysema
what two illnesses are most common elements of patients with COPD
wet
patients with pulmonary edema have "___” lung sounds
dry
patients with COPD will have “____” lung sounds
CHF (congestive heart failure)
Feeling short of breath (like you can't get enough air) when you do things like climbing stairs. ...
Fatigue or weakness even after rest.
Coughing.
Swelling and weight gain from fluid in your ankles, lower legs, or abdomen (belly).
Difficulty sleeping when lying flat
asthma
acute spasm of smaller air passages (bronchioles), associated with excessive mucus production and swelling of the mucus membranes
hay fever
causes cold-like symptoms.
Allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander.
anaphylaxis
can produce severe airway swelling.
Total obstruction is possible.
redness, hives
Treat with epinephrine, oxygen, and antihistamines
pneumothorax
accumulation of air in pleural space.
Most often caused by trauma
May be caused by medical conditions (spontaneous)
Breath sounds may be absent on affected side
pulmonary embolism
blood clot circulates through venous system
circulation cutoff partially or completely
decreases blood flow
can cause sudden death if large enough
purple coloration
can be asymptonatic
hypervetnilation
May be indicator of life-threatening illness
Body may be trying to compensate for acidosis.
Buildup of excess acid in blood or body tissues
May be indicator of life-threatening illness
Body may be trying to compensate for acidosis
acidosis
Buildup of excess acid in blood or body tissues
no nitro
BP under 100
on viagra or other vasodilators