Topic 8 Cell Cycle & DNA Replication Review
1/47
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
purpose of cell division?
growth, repair, and reproduction.
interphase
longest phase of the cell cycle, consisting of three stages: G1, S, and G2
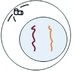
G1 - Cell increases in size, preparation for DNA replication, and new organelles/proteins are made
What is G0
Cells exit the active cell cycle and temporarily stop dividing/cells that don’t do mitosis (nerve cells)
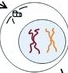
S - the cell duplicates its entire genome, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material.
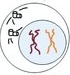
G2 - Growth and prep for mitosis. Organelles replicated (especially centrioles in animal cells)
Cyclins
A protein manages cell cycle checkpoints
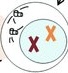
Prophase - Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, spindle fibers form and attach to centromeres, centrioles move to opposite poles, nuclear envelope disappears
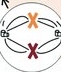
Metaphase - chromosomes are moved to metaphase plate. Checkpoint: are spindles attached to all centromeres.
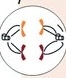
Anaphase - spindles pull sister chromatids to opposite poles and cell becomes longer
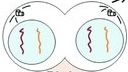
Telophase - spindle breaks down, cytoplasm cleaves (cleavage furrow), nuclear membrane reforms, chromosomes decondense into chromatin
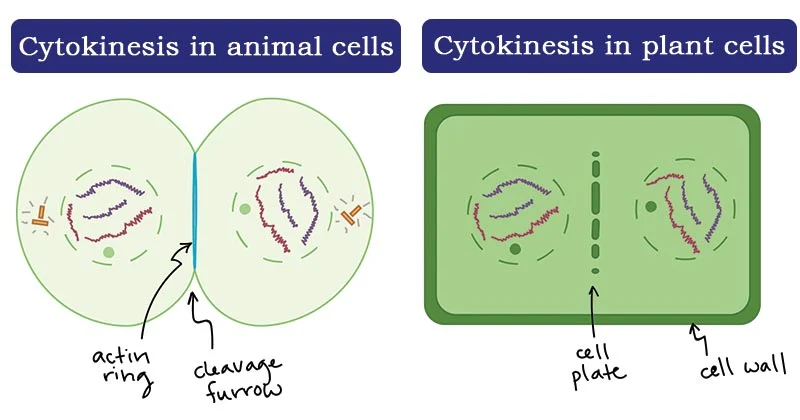
cytokinesis phase
Division of cytoplasm and cell membrane resulting in two daughter cells. Animal cells, a cleavage furrow forms and pinches the cell into two. Plant cells, a cell plate forms between the daughter nuclei and develops into a new cell wall.
purpose of mitosis
Repair tissue, replace cells, growth, asexual reproduction
chromatin
A mixture of DNA and proteins will form the chromosomes during mitosis
chromosomes
Chromatin that is condensed intro structures to be used during cell division
chromatid
One of two identical halves of a chromosome; sister chromatids are identical
sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome, connected by a centromere.
centromere
Region where sister chromatids are joined.
centriole
Organelle involved in spindle fiber formation.
Spindle fibers
Microtubules that separate sister chromatids during cell division.
Mitotic Index (not formula)
Measure of the percentage of cells in a population undergoing mitosis
formula for mitotic index
(number of cells/total number of cells)100
cancer
Abnormal/uncontrolled cell growth
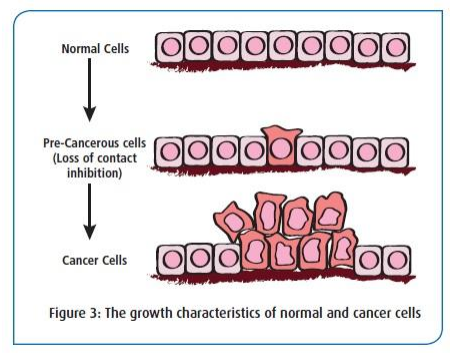
characteristics of cancer cells
Grow uncontrollably, invade nearby tissues, and spread to other parts of the body. They ignore signals that regulate normal cell division and often carry genetic mutations.
P53 gene
Tumor suppressor gene involved in regulating cell division and preventing mutations.
tumor
Abnormal mass of cells.
contact inhibition
Normal cells stop dividing when they come into contact with other cells, but cancer cells continue to divide uncontrollably.
DNA
Genetic information in all living organisms
structure of DNA
Double helix composed of nucleotides.
base pairing of DNA
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G)
antiparallel
The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions.
nucleotide structure
Phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose 5’ and 3’), and a nitrogenous base.
DNA replication
Process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA (S phase, nucleus)
exanucleases
Removes mismatched DNA nucleotides replaces w/ correct ones
DNA helicase
Unwinds DNA by breaking H-bonds making replication fork
topoisomerase
Relieves tension from helicase by preventing super-coiling
single stranded binding proteins (ssbp)
Prevents DNA from reforming after H bonds are broken by helicase
DNA primase
Builds short sequence of RNA primer on parent strand for DNA polymerase III to bond
DNA polymerase III
Adds new DNA nucleotides in 5’ to 3’ direction
nucleoside triphosphates
Nucleotide w/3 phosphastes to provide energy to DNA poly III
leading strand
New strand built continuously toward replication fork
lagging strand
New strand built discontinuously in fragments away from replication fork
DNA polymerase I
Replaces the RNA primer w/DNA nucleotides (one on leading, multiple on lagging)
DNA ligase
Joins sections of DNA (Okazaki fragments) by forming phosphodiester bonds.
direction of DNA synthesis
5’ to 3’ direction
where does DNA polymerase attach
Attaches to the 3’ end of the primer
Why does DNA elongate in the 5’-->3’ direction?
Due to the structure of the DNA molecule and the directionality of DNA polymerase.
okazaki fragments
Short segments of DNA that are synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during DNA replication.