Kins 714: Exertional Hyponatremia
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
physiological hyponatremia
sodium deficiency in which plasma sodium concentration is at least less than 135 mEq and may or may not be accompanied by symptoms of hyponatremia
symptomatic exertional hyponatremia
sodium deficiency that involves a plasma sodium concentration of less than 130 mEq and is accompanied with typical symptoms.
hypervolemic hyponatremia
an excess of total body water (fluid overload) with an expanded extracellular fluid volume and increased whole0body sodium
common sign of this condition is extremity edema
hypovolemic hyponatremia
a reduced extracellular volume with deficits of total body sodium and water
etiology
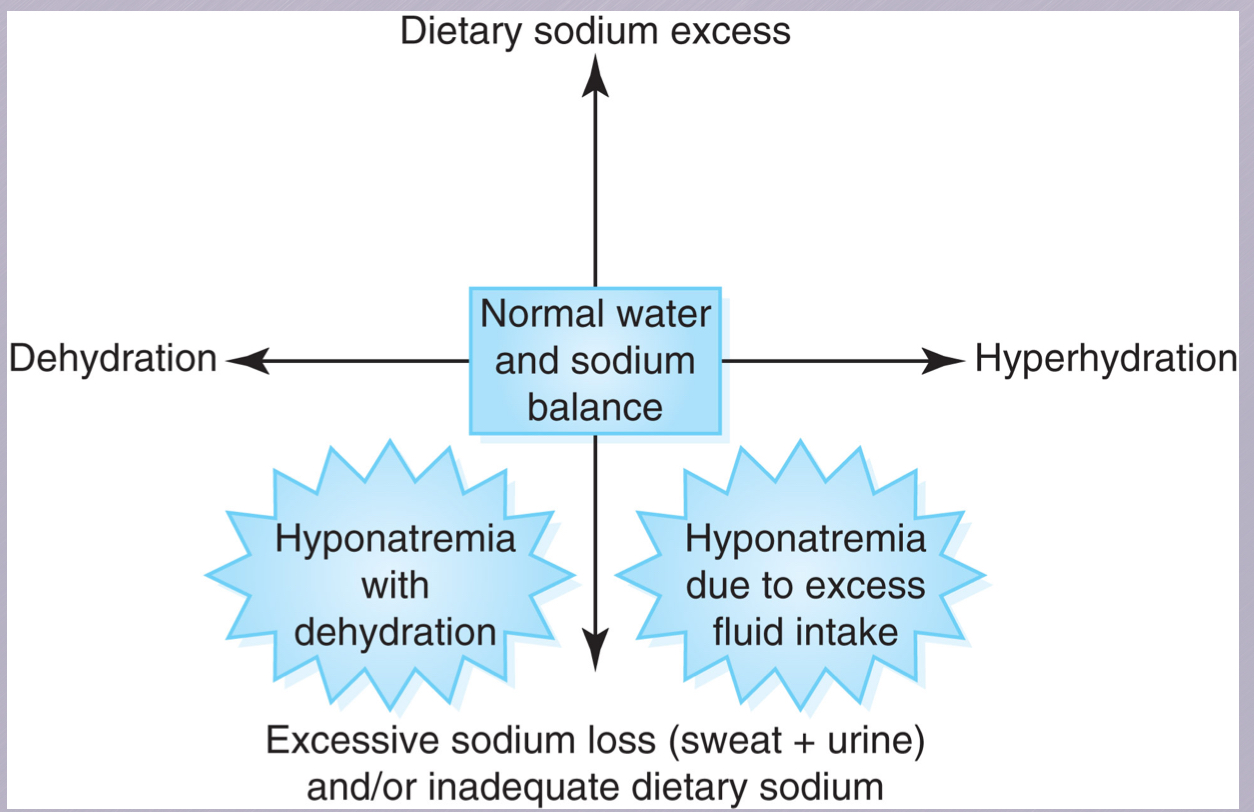
pathophysiology
when a large volume of hypotonic fluid is consumed, the extracellular fluid becomes dilute because the fluid moves from the intestine directly into the blood
as extracellular tonicity falls, water flows into cells and they swell
brain edema usually accompanies severe EHs
predisposing factors
a large volume of hypotonic fluid is consumed within a few hours
sodium losses in sweat and urine not replaced
absence of heat acclimatization
exercise duration
premeditate drinking large volumes of water pre exercise
genetic tendency for high sweat concentration
female hikers and marathon runners were more likely than males
prevention
consume fluids during exercises to not exceed weight loss over 2%
consume ample dietary Na when training in hot environment and as a part of daily meals
acclimatize to heat
consume salty foods with water during long duration events, and avoid overconsumption
educate athletes of risk of extertional hyponatremia
do not gain weight during exercising by overhydrating
recognition
key differential is blood Na assessment which should be measured in collapsed athletes in medical tent
clinical symptoms combined with blood Na concentration warrant diagnosis
medical emergency
complications of correcting hyponatremia
normal saline administration does not correct fluid overload and is contraindicated for EH (need 3% hypertonic saline)
central pontine myelinolysis (CPM): brain dysfunction caused by destruction of the myelin sheath of nerve cells within the brain stem. this occurs most often when low blood sodium levels are corrected too quickly via hypertonic intravenous saline.
recovery
when treated appropriately with IV hypertonic saline EH spontaneously resolves without complications
chronic morbidity is rare
rapid recognition and appropriate treatment reduce the risk of encephalopathy or CN damage