week2 it
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
What are the key components of the program development cycle?
The steps involved include problem-solving, algorithm development, and systematic design of software solutions.
What is a computer system?
A combination of all components required to process and store data using a computer, including hardware and software.
What is hardware in the context of a computer system?
The physical devices associated with a computer, such as keyboards, mice, speakers, and printers.
What is software?
Computer instructions that tell the hardware what to do, including programs written by programmers.
What are the two broad types of software?
Application software and system software.
What is application software?
Programs applied to a task, such as word processing, spreadsheets, and games.
What is system software?
Programs used to manage a computer, including operating systems like Windows, Linux, and mobile OS such as Android and iOS.
three major operations accomplished by computer hardware and software?
Input, processing, and output.
What does the input operation in a computer system involve?
Data items entering the computer system and being placed in memory for processing.
What is the role of the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer system?
To process data items by organizing, sorting, checking for accuracy, or performing calculations.
pseudocode
A high-level description of a computer program's logic, written in a way that resembles programming language.
What is the purpose of using a sentinel value in programming?
To signify the end of a program or a loop.
What does the term 'programming' refer to?
The process of writing software instructions.
What are flowchart symbols used for?
To visually represent the flow of a program or algorithm.
What is the significance of logical thinking in programming?
It helps in creating effective and efficient software solutions.
How can software be classified?
Into application software and system software.
What is an example of input hardware?
Keyboards and mice.
What types of data can be processed by a computer?
Text, numbers, images, sounds, and user interactions.
What is the evolution of programming models?
The historical development and changes in programming paradigms and methodologies.
What are some examples of application software?
Word processing programs, spreadsheets, payroll programs, and games.
What is the importance of the programming process?
It focuses on the systematic approach to developing software solutions.
What is the difference between data and information in programming?
Data refers to input items, while information refers to data items that have been processed and output.
What are common output devices for processed information?
Printers, monitors, or storage devices like hard drives and cloud-based devices.
What is the purpose of storage devices in programming?
They hold information for later retrieval and can be used as input for another program.
What is a programming language?
A formal language used to write computer instructions, such as Visual Basic, C#, C++, or Java.
What is program code?
The instructions written using a programming language.
What are syntax errors?
Mistakes in a programming language's usage that violate its rules of word usage and punctuation.
What is RAM and its role in programming?
Random Access Memory (RAM) is volatile internal storage used for quick access to running programs and data.
What is the difference between volatile and nonvolatile storage?
Volatile storage (like RAM) loses its contents when power is off, while nonvolatile storage retains its contents.
What is source code?
The program instructions written in a programming language before being translated to machine language.
What is object code?
The translated machine language statements that represent the source code.
What software is used to translate source code into machine language?
A compiler or an interpreter.
What is machine language also known as?
Binary language, represented as a series of 0s and 1s.
How do compilers or interpreters assist programmers?
They translate code and highlight syntax errors, providing error messages for corrections.
What happens when a program runs?
It accepts input, processes it, and produces output.
What is the program development cycle?
The process involving writing, testing, and refining a program, which does not start with immediate typing.
What is the role of a programmer in the development cycle?
To write, test, and refine code, ensuring it functions correctly.
What is the significance of permanent storage devices?
They retain data even when power is lost, allowing for recovery of work.
What is the purpose of translating source code?
To convert it into machine language that the computer can execute.
What does it mean to code a program?
To write instructions in a programming language.
What is the typical flow of a computer program?
Input is accepted, processing occurs, and results are output.
How does a programmer know if there are mistakes in their code?
The compiler or interpreter displays error messages when incorrect components are used.
What is the importance of syntax in programming languages?
Syntax governs the rules for word usage and punctuation, essential for correct code execution.
What happens to the contents of RAM when the computer is turned off?
The contents are lost, as RAM is volatile memory.
What is the purpose of saving work at regular intervals?
To ensure that work is not lost during power outages or system failures.
What are the seven steps of the program development cycle?
1. Understand the problem. 2. Plan the logic. 3. Code the program. 4. Use software to translate the program into machine language. 5. Test the program. 6. Put the program into production. 7. Maintain the program.
What is the purpose of documentation in programming?
Documentation provides supporting paperwork for a program, including original requests from users, sample output, and descriptions of data items available for input.
What is the significance of planning the program's logic?
Planning the program's logic is crucial as it involves deciding the steps to include and their order, which can be done using tools like flowcharts and pseudocode.
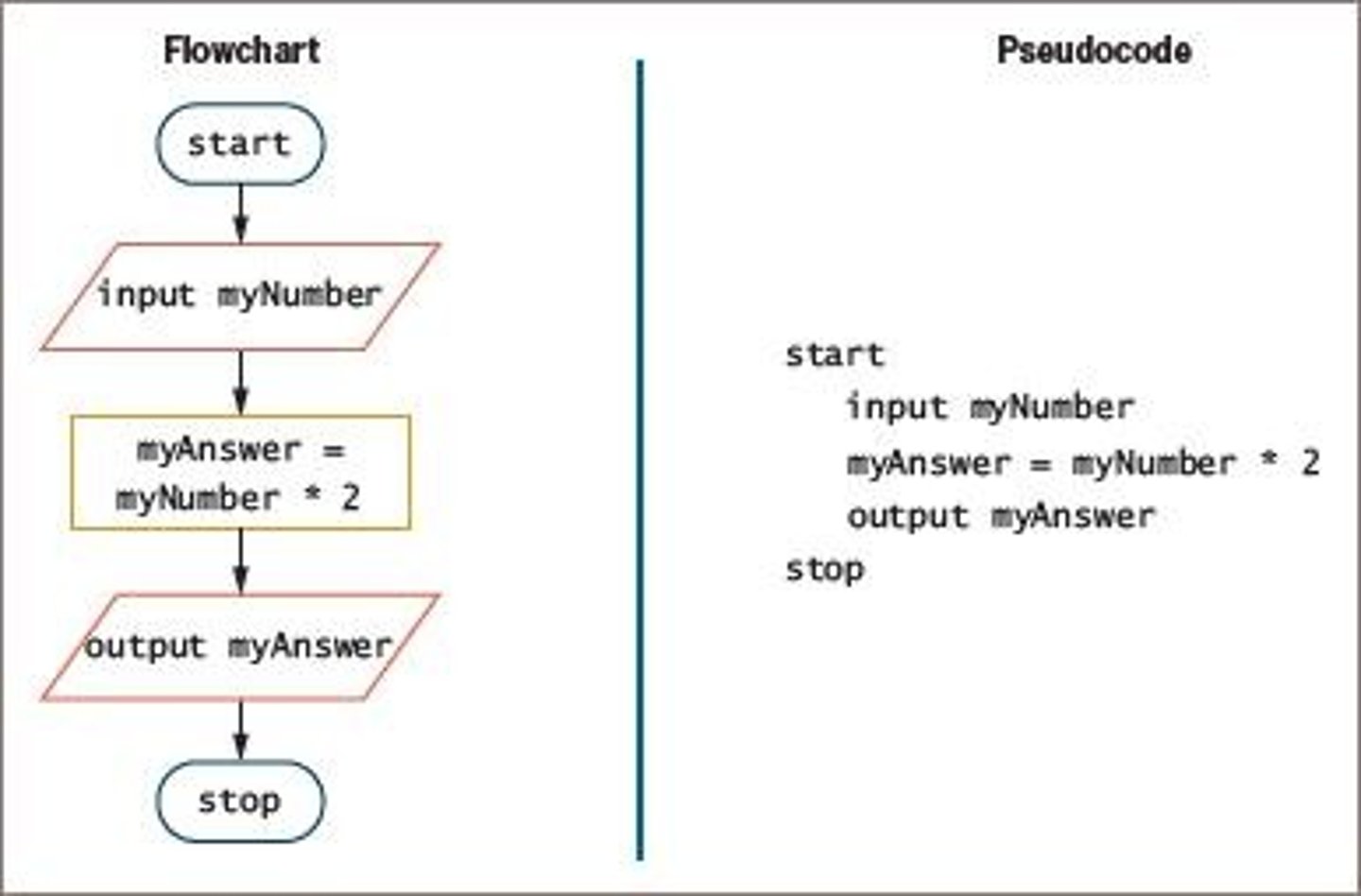
What are flowcharts and pseudocode used for in programming?
They are planning tools that help programmers outline the steps of a program in a structured way.
What is an algorithm in programming?
An algorithm is the sequence of steps or rules followed to solve a problem.
What does desk-checking refer to in programming?
Desk-checking is the process of walking through a program's logic on paper before actually writing the program.
What must a programmer do after developing the logic for a program?
The programmer can then write the source code for the program.
Why do programmers choose specific programming languages?
Programmers choose languages based on built-in capabilities that make them more efficient for certain types of operations.
What basic capabilities do most programming languages share?
Most programming languages can handle input operations, arithmetic processing, output operations, and other standard functions.
What is the role of a compiler or interpreter in programming?
A compiler or interpreter translates high-level programming languages into low-level machine language that the computer understands.
What happens to the commands after they are translated into machine language?
The commands are saved as a machine language program that can be run multiple times without needing to repeat the translation step.
What is required for a program to be considered executable?
A program is executable only when the code is free of syntax errors.
What is the difference between syntax errors and logical errors?
Syntax errors occur when the code violates the rules of the programming language, while logical errors occur when a syntactically correct statement is used incorrectly in context.
What is meant by maintaining a program?
Maintaining a program involves making updates and fixes after it has been put into production.
What is the first step in the program development cycle?
Understanding the problem.
What is the last step in the program development cycle?
Maintaining the program.
What might a programmer need to do if they make changes to the source code?
They need to retranslate the code into machine language.
How can logical errors affect a program?
Logical errors can lead to incorrect results even if the program runs without syntax errors.
What is the significance of testing a program?
Testing ensures that the program is functioning correctly and is free of logical errors.
What is the relationship between source code and machine language?
Source code is written in a high-level programming language and must be translated into machine language for the computer to execute it.
What is the role of the end user in the programming process?
The end user is the person whose needs the program is designed to satisfy.
What does it mean to put a program into production?
Putting a program into production means deploying it for use by end users.
What is the purpose of testing a program after it is free of syntax errors?
To execute it with sample data and verify whether the results are logically correct.
What is involved in putting a program into production?
It may involve running the program, training data-entry personnel, training users, or converting existing data to a new format.
What does the term 'conversion' refer to in programming?
The entire set of actions an organization must take to switch over to using a new program or set of programs.
What is maintenance in the context of programming?
Making necessary changes to a program after it has been put into production.
What are some reasons maintenance might be required for a program?
Changes in tax rates, alterations in input file formats, or user requests for additional information.
the first step when maintaining previously written programs?
Understanding the changes that need to be made.
What tools do programmers often use to plan the logic for a programming solution?
Pseudocode or flowcharts
What is a flowchart?
A pictorial representation of the logical steps to solve a problem.
What is the typical structure of pseudocode?
It begins with a 'start' statement and ends with a 'stop' statement, with indented steps in between.
What are some standards for writing pseudocode?
Programs begin with 'start' and end with 'stop', module names are followed by parentheses, and program statements are indented.
How should program statements be formatted in pseudocode?
Each statement should perform one action, be indented, and appear on a single line if possible.
What is the capitalization rule for program statements in pseudocode?
Program statements begin with lowercase letters.
What punctuation is used in pseudocode statements?
No punctuation is used to end statements.
What happens if a program requires a substantial number of changes?
The original program might be retired, and a new program development cycle might be started.
What is the significance of clear code and documentation in programming?
It helps maintain programs effectively, especially when changes are required.
What is the role of training in putting a program into production?
Training is necessary for users to understand the output and for data-entry personnel to prepare input.
What does 'debugging' refer to in programming?
The process of identifying and fixing errors in a program.
Why is selecting test data considered an art?
Because it requires careful consideration to ensure it effectively tests the program's logic.
What might be a consequence of not maintaining a program?
It may become outdated or fail to meet user requirements.
What is the relationship between maintenance and the development cycle?
When maintaining programs, you repeat the development cycle: understand, plan, code, translate, and test.
What geometric shapes are used in flowcharts to represent individual statements?
Geometric shapes such as parallelograms for input/output and rectangles for processing.
What does a parallelogram represent in a flowchart?
An input or output operation, often referred to as the I/O symbol.
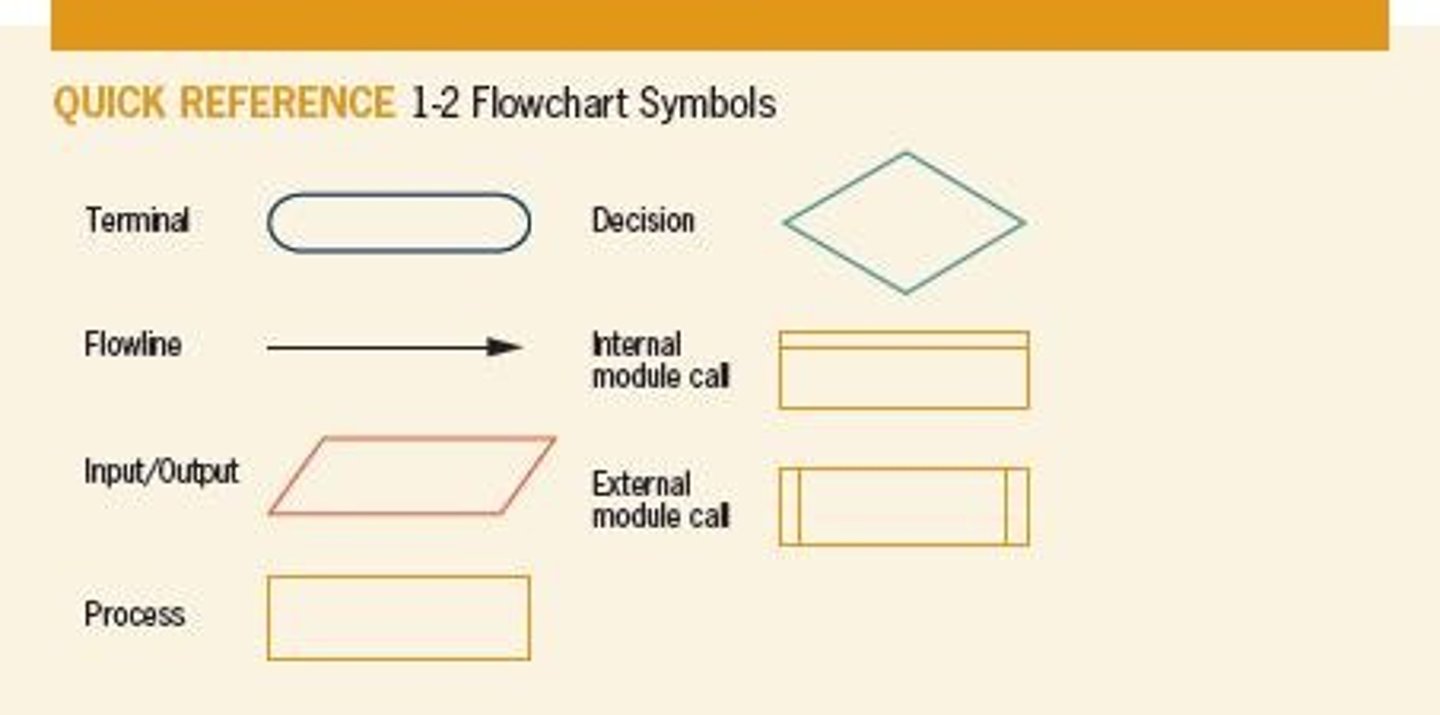
What shape is used in flowcharts to represent processing statements?
A rectangle.
How should the flow of a flowchart be organized?
Most of a flowchart should read from top to bottom or from left to right.
What symbols are used to indicate the start and end of a flowchart?
Terminal symbols or start/stop symbols, often labeled 'start' or 'end'.
What is the purpose of arrows in a flowchart?
To connect the steps and show the correct sequence of statements.
What are the steps a programmer needs to follow after developing a flowchart or pseudocode?
1. Buy a computer, 2. Buy a language compiler, 3. Learn a programming language, 4. Code the program, 5. Attempt to compile it, 6. Fix syntax errors, 7. Compile again, 8. Test with data, 9. Put into production.
What is a loop in programming?
The repetition of a series of steps, allowing the computer to execute the same instructions multiple times.
What is the benefit of using a loop instead of writing repetitive code?
It saves time and effort by allowing the computer to execute the same set of instructions repeatedly.
What is the first step a programmer should take after developing a flowchart?
Buy a computer.
What does the term 'syntax errors' refer to in programming?
Mistakes in the code that violate the rules of the programming language.
What is the final step in the programming process outlined in the notes?
Put the program into production.
What is the purpose of using flowchart symbols?
To visually represent the logic and flow of a program.