Chemistry Quiz 1
1/154
Earn XP
Description and Tags
f25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
What are some specific conversions?
5280ft = 1mi
2.54cm = 1in
12in = 1ft
1mL =1cm3
60s = 1min
60min = 1hr
24hr = 1 day
365 days = 1yr
What are some metric prefixes?
G = 109
M = 106
K = 103
h = 102
da = 101
base unit
d = 10-1
c = 10-2
m = 10-3
μ = 10-6
n = 10-9
p = 10-12
What is the freezing and boiling point of oF, oC, and K?
K: freezes at 273K, boils at 373k
oF: freezes at 32oF, boils at 212oF
0C: freezes at 0oC, boils at 100oC
What is the temperature conversion equations?
K = oC + 273.15
oF = oC(9/5) + 32
What is density?
The ratio of mass to volume
What is density’s equation?
Density = Mass / Volume
Name 3 materials and their density’s
Osmium metal = 22.6 g/mL
Water = 1.00 g/mL
Hydrogen gas = 8.99 × 105 g/mL
What is precision?
Precision is the number of digits/ how well measurements agree with one another
What is accuracy?
Accuracy is how well measurements agree with the accepted value
What are the sigfig rules?
All none zero numbers are significant, all leading zeros are not significant, all trailing zeros after a decimal are significant, all zeros between two sigfigs are significant, and all exact numbers have infinite sigfigs
What do sigfigs look like when you add or subtract?
You use the least number of decimal places
What do sigfigs look like when you divide and multiply?
You use the least number of sigfigs
Chemistry definition
study of matter and associated changes
Matter definition
everything with mass and volume
Composition definition
substances and their amounts in matter
Pure substance definition
Material with constant composition
Element definition
Pure substance that can’t be broke down further by physical or chemical means
Compound definition
Pure substance with more than one element
Atom definition
smallest particle of element that shares same properties
Molecule definition
substance with two or more atoms connected by chemical bond
Ion definition
charged atom or molecule
Mixture definition
contains multiple substances and can be separated by physical means
Draw a line with the following words: low temp, condensation point, melting point, boiling point, increased temp, freezing point
look in notebook
What is a heterogenous mixture?
varying compositions (think water and oil)
What is a homogenous mixture?
Uniform compositions
What are the phases of matter?
solid, liquid, and gas
Define physical properties
Relates to observable properties such as color, mass, volume, and dimensions
Define chemical properties
Relates to reactions/ processes that alters the identites of substances
What is the law of conservation of mass?
Matter cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be converted from one form to another
What is the law of definite composition?
Compounds always contain a fixed ratio of their elements
What is the scientific method?
Observations —→ hypothesis (predictions) —→ experiment (collect data, only change 1 variable at a time) —→ model (theory, law)
Define theory
Describes causes
Define law
Describes consistent observations (mathematics equation typically)
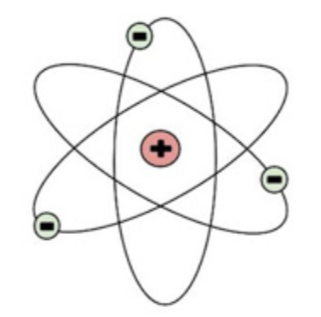
What is this?
It’s the nuclear model of an atom. The red contains neutrons and protons while the green contains only electrons
What is the mass (ama) of a proton?
1.0073 (roughly 1)
What is the mass (ama) of a neutron?
0
What is the mass (ama) of an electron?
roughly zero
Charge of a proton
+1
Charge of a neutron
0
Charge of an electron
-1
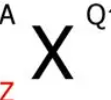
What does each thing stand for?
X is the atomic symbol, A is the mass number, Z is the atomic number, and Q is the charge.
How do you calculate mass number?
Protons + neutrons
How do you determine the atomic number?
The number of protons
How do you determine the charge of an element?
Protons - electrons
Is a negative amount of electrons a thing?
No
What is a group
Elements with similar properties in the same column
What is a period?
Rows on the periodic table
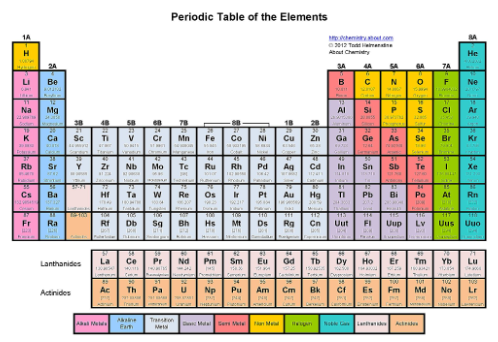
Where are the alkali metals?
The first column
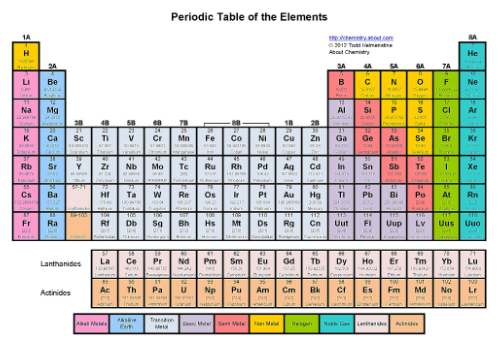
Where are the alkaline earth metals?
The second column
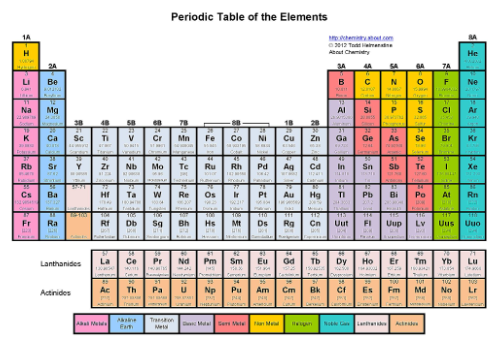
Where are the icosagones?
The third tallest column
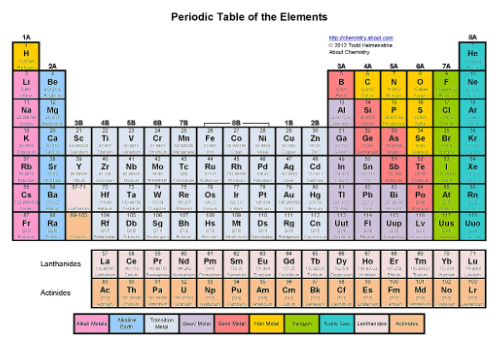
Where are the crystallogens?
The fourth tallest column
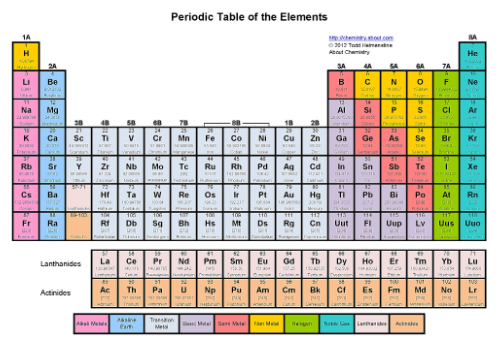
Where are the pnictogens?
The fifth tallest column
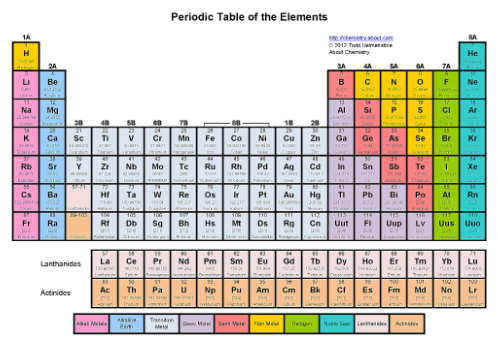
Where are the chalcogens?
The sixth tallest column
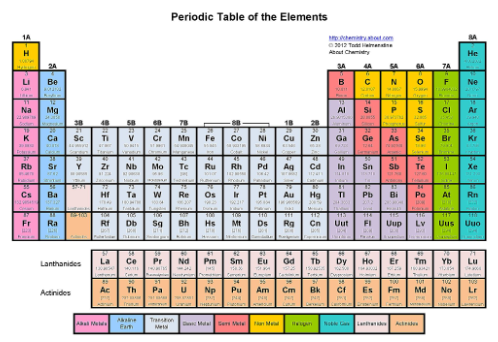
Where are the halogens?
The seventh tallest column
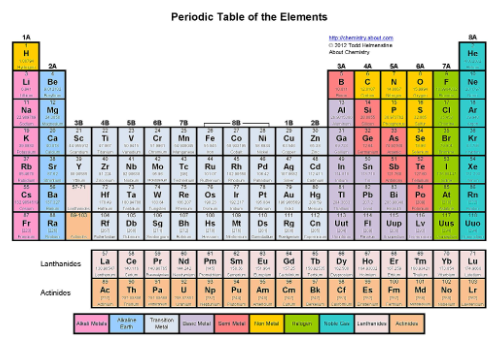
Where are the noble gases?
The last column
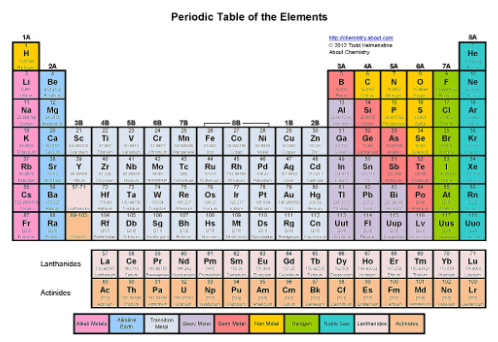
Where are the rare Earth metals?
The two periods at the bottom (rows called periods)
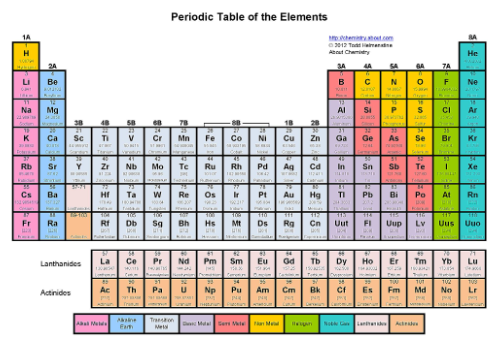
Where are the metals, metalloids, and nonmetals?
Metals on the left side, metalloids are the staircase ( the reds) and the nonmetals are above the staircase
What are some metal traits?
Generally solid at room temperature, good conductors, form cations, malleable, and ductile(can be made into wires)
What are some nonmetal traits?
They vary between solids, gases, and liquids due to being brittle. They form anions and are poor conductors
What is something special about carbon?
It has multiple isotopes in nature (same p+ different n0)
What is average atomic mass?
A weighted average
What few elements exist alone in nature?
Noble gases, diatonic molecules, and coinage metals
Since few elements exist by themselves in nature, how do other atoms exist?
As compounds. Metals in ores typically
How can you identify if something is ionic?
Metals and nonmetals, typically ions [charged], they’re represented as a formula unit. They have HIGH melting/ boiling points, and they separate into ions in water
How can you identify if something is covalent (molecular)?
Typically just a nonmetal, neutral atoms, represented as molecule, have LOW melting/ boiling points and separate into neutral molecules in water
What does it mean for something to be ionic?
They transfer electrons
What does it mean for something to be covalent (molecular)?
They share electrons
What are the rules for the name and formulas of ionic compounds?
Write the name of metal first, nonmetal second but change the ending to “-ide”. For transition metals and late metals write the charge after metal in parenthesis using roman numerals (EXCEPT FOR Al, Zn, Ag), and polyatomic ions keep their suffix
What is a polyatomic ion?
An ion that has covalent bonding between the parts
What are the three transition metals that you don’t need to list their charges?
Aluminum, zinc, and silver
Hg22+
Mercury(I)
NH4+
Ammonium
H3O+
Hydronium
OH-
Hydroxide
O22-
Peroxide
CN-
Cyanide
SCN-
Thiocyanate
C2O42-
Oxalate
C2H3O2-
Acetate
N3-
Azide
NO3-
Nitrate
NO2-
Nitrite
CO32-
Carbonate
HCO3-
Bicarbonate
ClO-
Hypochlorite
ClO2-
Chlorite
ClO3-
Chlorate
ClO4-
Perchlorate
BrO3-
Bromate
IO3-
Iodate
CrO42-
Chromate
Cr2O72-
Dichromate
PO43-
Phosphate
HPO42-
Hydrogen phosphate
H2PO4-
Dihydrogen phosphate
SO42-
Sulfate
HSO4-
Bisulfate
SO32-
Sulfite
S2O32-
Thiosulfate
MnO4-
Permanganate