approaches
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Psychosexual phases
Stages of childhood development proposed by Freud, including oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital phases
what is the main idea of the psychodynamic approach
that most of our mind is unconscious
What are defence mechanisms?
Strategies employed by the ego to protect the mind from overwhelming feelings. They are denial, repression and displacement
What is denial?
A complete refusal to acknowledge the occurrence of an event to prevent harm.
what is displacement?
substituting the real target of overwhelming emotions onto a defenceless target
What is repression?
Forcing a distressing memory out of our concous mind
explain the Oedipus complex
A boys sexual desires for his mother and jealousy of his father, identification is the egos' decision to copy traits of father to attract a woman like his mother in later life (electra complex for girls)
What is the role of the ego in the tripartite personality?
The ego mediates between the desires of the Id and what is realistic, acting as the decision-making component.
What is the role of the super ego in the tripartite personality?
Morality principle that developes with parenting
Describe the Id in the context of personality in the tripartite personality
The most selfish part of the personality, present at birth and concerned only with desires so has no sense of morality.
Strengths of the psychodynamic approach
Has good explamitory power fro gender development and OCD
Limitations of the psychodynamic approach
Low scientific status as the ideas are unflasifiable, case study for oedupus complex isn't genrralisable and was biased
What does the Behaviourist approach suggest about children at birth?
Children are born as 'tabulae rasae' (blank slates) and learn through interactions with their environment.
Define classical conditioning.
learning by associating an object that produces a response to a neutral stimulus
explain pavlov’s dogs experiment findings
dogs learnt from a neutral stimulus (the sound of a bell ringing when given food) that they would get food because their body responded to the stimulus by salivating
Define operant conditioning
A form of learning by direct consequences for behaviour, including rewards and punishment leading to positive and negative reinforcement
What is negative reinforcement?
avoiding something negative or unpleasant
What is positive reinforcement?
receiving reward when a behavior is performed
explain skinners box experiment for operant conditioning
showed how animals can learn and respond to stimuli as they realised their behaviour resulted in ether punishment (electric shock) or reward (treat)
Primary reinforcer
A reward in itself
Secondary reinforcer
A token that can be exchanged in for rewards or goods
Real world application of behaviourist approach
Token economies habe been sucessful in instituions, encouraging operant conditioning
Psychic determinism
Behavior is determined by unconscious thoughts in our psyche (psychodynamic)
Environmental determinism
Behaviour is determined by our environment (behaviorists)
strengths of the behaviourist approach
Uses scientific methods of research because the experiments are objective, measurable and observable
limitations of the behavioural approach
Focuses too much on the 'nurture' side of the nature/nurture debate
Ethical issues raised by using animals in experiments
What analogy does the Cognitive approach use to explain the human mind?
The human mind is like a computer, with internal mental processes converting input to output.
What is congruence in psychology?
When a person’s ideal self and actual self are aligned.
What is incongruence in psychology?
When someone’s ideal self and perceived self are very different
Define free will in psychological terms.
The idea that we are in full control of our behaviour and decisions.
What is the core belief of the Humanistic approach?
It is a person-cemtered approach because it sees all humans as individuals
Who are the psychologists for the humanistic approach
Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow
Conditions we need to grow according to Maslow
Empathy, genuineness, acceptance (unconditional love)
Strengths of humanistic approach
Good explanatory power for our needs and narcissists, affirms free will
Limitations of the humanistic approach
Poor scientific status because concepts are unfalsifiable and the approach is idiographic
Real world application of the humanistic approach
Client-centred therapy, assumes people have what they need to reach their full potential if given the right conditions to grow. Includes techniques such as active listening and reflection.
What is identification in social learning theory?
A form of learning where humans learn by observing role models they perceive as similar to themselves.
How does imitation occur according to social learning theory?
People learn through copying the behaviour of a role model with whom they identify.
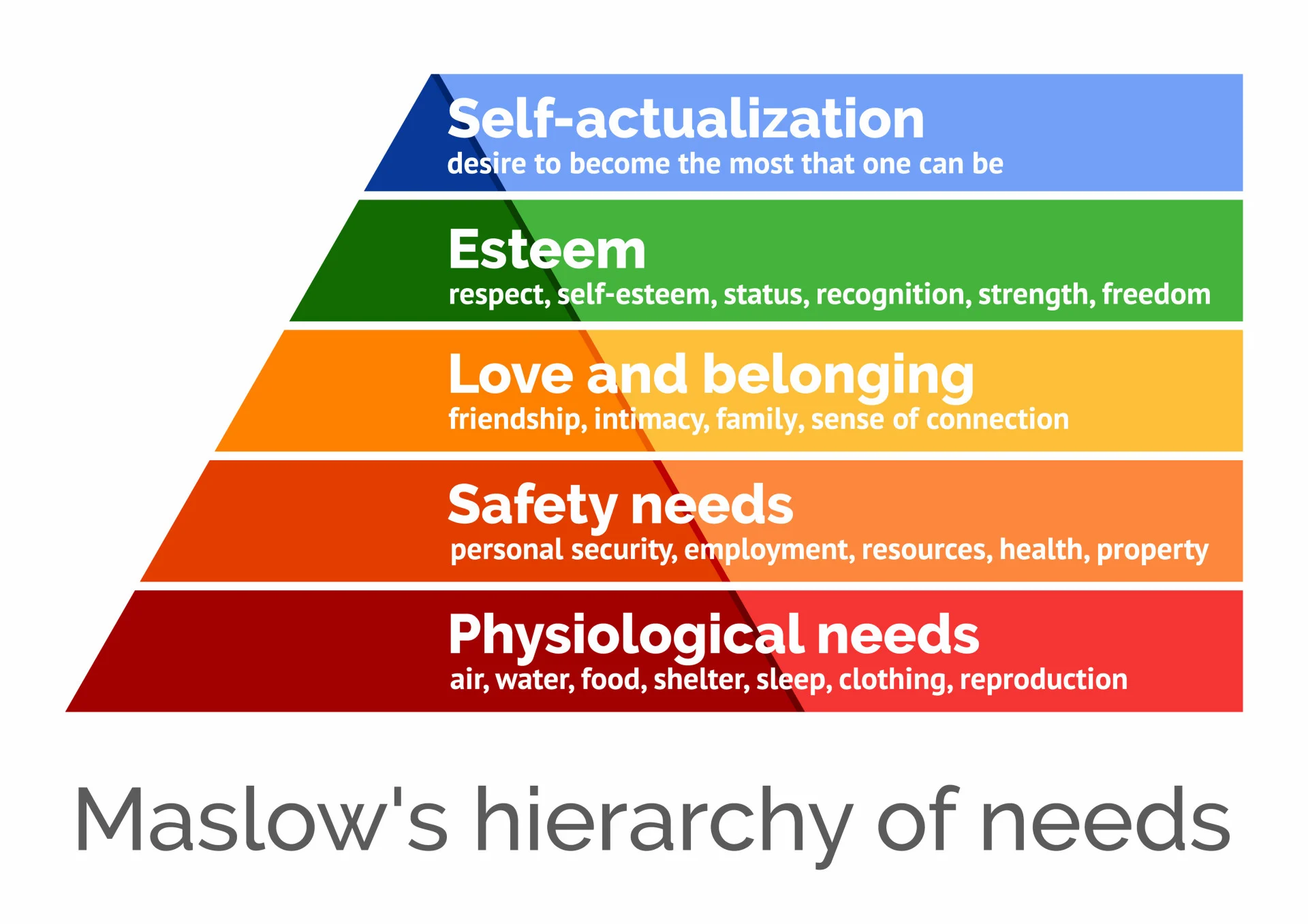
What does Maslow’s hierarchy of needs propose?
Humans have multiple needs that must be achieved in a specific order to fully achieve their potential.
What is modelling in the context of learning?
When a role model enacts behaviour that can be imitated by an observer.
Explain mediational processes in social learning theory.
Internal processes that contribute to producing certain behaviours, acting as 'mediators' between observation and imitation.
What is a schema?
A package of related information on a topic from our experiences
3 types of schema
Role - expected behavior for specific roles
Event - expected events in situations
Self - ideas of the kind of person you are
Pros and cons of schemas
Enables us to process lots of information quickly without getting overwhelmed and helps us in new situations but can distort our perceptions causing us to not remember things correctly
Cognitive neuroscience
The coming together of cognitive psychology and the field of neuroscience. May become the new paradigm in psychology
What does self-actualisation signify?
A person’s full potential, achievable after primary needs have been met.
What does the Social learning theory combine?
The ideas of learning through the environment with cognitive ideas of internal mental processes.
What is vicarious reinforcement?
Indirect encouragement of behaviour through observation of consequences for other people's behaviour.
Strengths of the social learning theory
High control in lab studies, high correlation coefficient, good explanatory power for human behaviour, more comprehensive than behaviorist and the research is done on humans rather than animals
Limitations of the social learning theory
Very young sample of children so not generalisable, artifical task means low ecological validity, exclusively on the nurture side of the debate, limeted understanding of biological factors
Why do cognitive psychologists see humans similar to computers
Human minds have limited processing capacity, is controlled by a central control mechanism and has information flowing through different stores
Real world application of cognitive approach
Cognitive behavioural therapy gets rid of distortions such as utopionism
Strengths of cognitive approch
Good explanatory power for people reacting differently to the same situations and for people with low self esteem
Good scientific status from lab experiments and neuroscience
Limitations of the cognitive approach
Research may lack external validity
Machine reductionism
who is the main psychologist for social learning theory?
Albert Bandura
3 assumptions of the biological approach
humans are evolved animals and purely physical
behaviour is driven by biological structures in our bodies such as DNA, hormones and neurotransmitters
this means that just as physical illnesses have biological causes, so does psychological ones
research methods in the biological approach
twin studies, adoption studies, brain scans
What does genotype refer to?
the genetic makeup of an individual coded in chromosomes
What does phenotype refer to?
the physical manifestation of a persons genotype
monozygotic twins
identical twins, 100% shared genes
dizygotic twins
non-identical twins, 50% shared genes (same as any brother or sister)
concordance rate
the percentage of pairs of twins or other blood relatives who both exhibit a particular trait or disorder
natural selection
Organisms that are more adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and pass on those adapted genes to their offspring
sexual selection
species competing for mates by fighting or looking impressive e.g. peacocks tails
Strengths of biological approach
High scientific status
Good explanatory power for sexual selection and depression
Limitations of biological approach
Reductionist
Biological determinist
Real world application of biological approach
Gene therapy - manipulating genes to fix illnesses
Drug therapy - antidepressants increase seratonin