Chapter 2: Atoms and Elements
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
H
Hydrogen
He
Helium
Li
Lithium
Be
Beryllium
B
Boron, metalloid
C
Carbon
N
Nitrogen
O
Oxygen
F
Fluorine
Ne
Neon
Na
Sodium
Mg
Magnesium
Al
Aluminum
Si
Silicon, metalloid
P
Phosphorus
S
Sulfur
Cl
Chlorine
Ar
Argon
K
Potassium
Ca
Calcium
Sc
Scandium
Ti
Titanium
V
Vanadium
Cr
Chromium
Mn
Manganese
Fe
Iron
Co
Cobalt
Ni
Nickel
Cu
Copper
Zn
Zinc
Ga
Gallium
Ge
Germanium, metalloid
As
Arsenic, metalloid
Se
Selenium
Br
Bromine
Kr
Krypton
Rb
Rubidium
Sr
Strontium
Cs
Cesium
Ba
Barium
Mo
Molybdenum
Ag
Silver
Sn
Tin
Sb
Antimony, metalloid
Te
Tellurium, metalloid
Xe
Xenon
Rn
Radon
At
Astatine, metalloid
W
Tungsten
Pd
Palladium
Pt
Platinum
Au
Gold
Hg
Mercury
Pb
Lead
Bi
Bismuth
Po
Polonium
Cm
Curium
U
Uranium
Law of Conservation of Mass
In a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed.
Law of Definite Proportions
Also called the Law of Constant Composition. It says that all samples of a given compound, regardless of their source or how they were prepared, have the same proportions of their constituent elements.
Law of Multiple Proportions
When two elements (call them A and B) form two different compounds, the masses of element B that combine with 1 g of element A can be expressed as a ratio of small whole numbers.
John Dalton's Atomic Theory (4 Points)
1. Each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms.
2. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from the atoms of other elements.
3. Atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds.
4. Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. In a chemical reaction, atoms only change the way that they are bound together with other atoms.
Cathode Rays
A stream of electrons produced when a high electrical voltage is applied between two electrodes within a partially evacuated tube.
J.J. Thomson
used the cathode ray tube to discover electrons
electron
a negatively charged, low mass particle present within all atoms
Robert Millikan
Performed the "oil-drop" experiment in which he deduced the charge of a single electron
Plum-pudding Model
J.J. Thomson's model of an atom, in which he thought electrons were randomly distributed within a positively charged sphere.
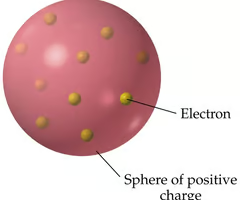
Radioactivity
the emission of small energetic particles from the core of certain unstable atoms; discovered by Becquerel and Curie
Three types of radioactivity
1. alpha particles
2. beta particles
3. gamma rays
Alpha particles are positively charged and they are by far the most massive of the three.
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment
Alpha-particles were directed at a thin sheet of gold foil; most passed through the foil, but a few were deflected. This disproved Thomson's Plum-pudding model and led to the discovery of a small, dense, positively charged nucleus.

Rutherford's Nuclear Theory (3 Parts)
1. Most of the atom's mass and all of its positive charge are contained in a small core called the nucleus.
2. Most of the volume of the atom is empty space, throughout which tiny, negatively charged electrons are dispersed.
3. There are as many negatively charged electrons outside the nucleus as there are positively charged protons within the nucleus, so the atom is electrically neutral.
proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom. The mass of a neutron is similar to that of a proton.
atomic mass unit (amu)
Defined as 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom, which contains 6 protons and 6 neutrons.
atomic number (Z)
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Chemical symbol
A unique one- or two-letter abbreviation listed directly below its atomic number on the periodic table. The first letter is always capitalized. The second letter is never capitalized.
isotope
Atoms with the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons.
natural abundance of isotopes
the relative amount of each different isotope in a naturally occurring sample of a given element
mass number (A)
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
Isotope notation 1
The representation of a specific isotope. The atomic number is listed below the symbol, the mass number above.
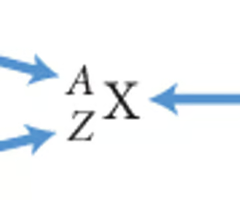
Isotope notation 2
the chemical symbol or chemical name followed by a dash and the mass number of the isotope
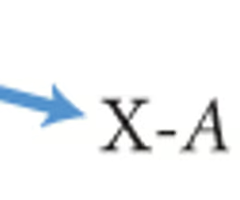
ions
positively and negatively charged atoms
Mendeleev's Periodic Law
When elements are arranged in order of increasing mass, certain sets of properties recur periodically.
Metals
Metals lie on the lower left side and middle of the periodic table and share some common properties: they are good conductors of heat and electricity, they can be pounded into flat sheets (malleability), they can be drawn into wires (ductility), they are shiny, they lose electrons
ductility
The ability to be pulled into thin wires
malleability
the ability of a substance to be hammered or beaten into thin sheets
nonmetals
Nonmetals lie on the upper right side of the periodic table. They are poor conductors of heat and electricity, and they gain electrons when they undergo chemical changes.
metalloids
elements that lie along the zigzag diagonal line that divides metals and nonmetals. They exhibit mixed properties. Examples of metalloids include B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, At
semiconductors
Several metalloids are classified as semiconductors, because of their intermediate (and temperature dependent) electrical conductivity.
main-group elements
elements whose properties tend to be largely predictable based on their position in the periodic table
transition elements
elements whose properties tend to be less predictable based simply on their position in the periodic table.
Family or Group of elements
is a vertical column in the periodic table of the chemical elements.
Period of elements
A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table
Noble Gases
Group 8A or 18 - Unreactive or inert gases.
Alkali Metals
Group 1A - All reactive metals.
Alkaline Earth Metals
Group 2A - Fairly reactive metals, although not as reactive as alkali metals.
Halogens
Group 7A or 17 - Very reactive nonmetals.
Cation
A positively charged ion that forms when a metal loses electrons.
Anion
A negatively charged ion that forms when a nonmetal gains electrons.
Atomic Mass
The average mass of all the isotopes of an element.