SYSTEMATICS LEC GROUP 1 FINALS TERM
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
181 Terms
Perennials
Plants that live for more than 2 years
Woody plants
These types of plants supports an immense share of the Earth’s terrestrial biodiversity, providing food and habitats for innumerable microorganisms, epiphytes and invertebrate and vertebrate species
400 million years ago
When did the first woody trees evolved in earth?
419.2 million to 358.9 million years
What year was the Devonian period?
Devonian period
During this period, terrestrial plants were generally small (an inch or so tall) and did not have roots, seeds, leaves, or woody tissue. Plant height during this period was also restricted because the organisms did not have tissues capable of dealing with the stresses associated with extensive vertical growth
100 feet (30 meters)
Towards the end of the Devonian period, how tall did the first forests grew?
Seeds, leaves, woody tissues
Due to the evolution of these 3 factors, it enabled further growth, efficient food production, and resilience
354 million to 290 million years
What year did the Carboniferous period started?
Carboniferous Period
During this period, vascular land plants dominated the area, ranging from small, shrubby growths to trees exceeding heights of 100 feet (30 meters)
Lycopods, sphenopsids, cordaites, seed ferns, true ferns
Five important groups in the Carboniferous period
Lycopods
includes tall trees with dense, spirally arranged leaves; reproduction is either cones or spore-bearing organs on the leaves
Sphenopsids
trees and shrubs with a jointed stem and leaves arranged in spirals from those joints
Cordaites
extinct members of the gymnosperms; precursor to the conifers; favored upland environments, where they grew tall and possessed tiny scalelike leaves and cones similar to modern conifers
Cretaceous period
During this period, the first appearance and initial diversification of flowering plants occured
Angiosperms
Flowering plants are also called?
New food sources
Insects and other organisms evolve to take advantage of the what?
Figs, magnolias, poplars, willows, sycamores, herbaceous plants
Groups that belong to Angiosperm
Montsechia vidalli
This is the oldest known fossil of angiosperm
130 million years to 125 million years
How old is Montsechia vidalli?
Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
The two major groups of woody plants
Gymnosperms
Although since the cretaceous period, this type of woody plants have been gradually displaced by the more recently evolved angiosperms, they are still successful in many parts of the world and occupy large areas of Earth’s surface.
Gymnosperms
This type of woody plant includes the tallest, the most massive, and the longest-living individual plants on earth
Colder and Arctic regions
Gymnosperms form a dominant vegetation in what regions?
Gymnosperms
Pines, spruce, yews, are an example of what type of woody plant?
Angiosperms
This kind of woody plant have the most numerous of all the divisions in the plant kingdom
Woody or herbaceous
Angiosperms can be ________ or _________
Woody plants
This includes trees and some shrubs
Herbaceous plants
lack woody stems; classified as annuals (live for one year or season), biennials (live for two years), and perennials (come back year after year for many years)
Angiosperms
Oak tree, Maple tree, Dogwood tree are examples of?
3.04 trillion
How many wood plants or trees are there worldwide?
43%
Percentage on how many trees grow in tropical and subtropical forests
24%
Percentage on how many trees grow in boreal region?
22%
Percentage on how many trees grow in the temperate regions?
550 gigatons of carbon
The overall biomass composition of the biosphere was estimated at?
Plants
What makes up the majority of the biosphere?
Stems, trunks of trees
What represents the 70% of plant biomass?
Trees
What makes up 60% of the total biomass of our biosphere?
2 gigatons of carbon
All animals and humans taken together make up merely how much gigatons of carbon?
Vascular tissues, root systems, leaf adaptations, seed dispersal
What are the key features that made plants to thrive across diverse ecosystems?
Vascular tissue
This contains xylem and phloem, it also enables vertical growth and transports water, nutrients, and provide structural support
Pith, Heartwood, Phloem, Cambium, Xylem, Outer bark
Identify the parts
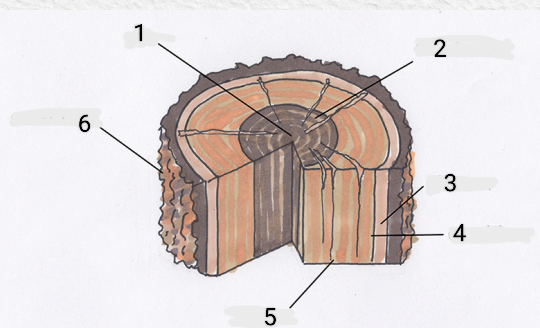
Root systems
These are the anchorages and resources access, it also secures plants in the soil and facilitates access to water and minerals, even in harsh conditions
Fungi
What organism does the root system have a symbiosis with?
Conifers, Deciduous trees
Different types of leaf adaptations
Conifers
These are needle-like leaves, and they minimize water loss, and is suited for cold or arid climates
Deciduous trees
These are broad leaves and optimize photosynthesis in warm, wet climates
Seed development and seed dispersal
Seed adaptations, enable reproduction over long distances. Increase resilience to environmental stress. Diverse Dispersal Mechanisms and help spread species to new habitats
Ancient mosses
What were the earliest land plants related to?
Bryophytes
What is the scientific name of Ancient moss?
500 million years
How many years were the earliest land plants were related to ancient moss?
Liverworts and early vascular plants
What followed after bryophytes?
Pterophytes
Example of early vascular plants
Ferns
Pterophytes are the ancestors of what organisms?
Bryophytes, Pterophytes
Both of these organisms rely on water for reproduction (male gametophytes release swimming sperm)
Dominant sporophyte stage
Seed plants evolved into this stage, reducing gametophyte reliance
Heterospory
It is a two spore type, and in early plants (e.g., Selaginella) paved the way for seed plants
Seeds and pollen
Seed plants developed these two in order to reproduce without water, aiding survival in dry areas
Angiosperms
What thrived, and became the most diverse groups of plants by the cretaceous period?
Megaspores, Microspores, Selaginella
Seed plants are heterosporous, producing?
Megaspore
The female gametophytes (egg-producing)
Microspores
Male gametophytes (sperm-producing)
Selaginella
These are ancestral heterosporous plant and has both male and female sporangia in one strobilus, with distinct spore functions
Pollen
protects male gametophytes, enabling wide dispersal without water
Seeds
provide embryos with protection, nourishment, and dormancy, supporting survival in diverse environments.
Bryophytes and ancestors
Land colonization was aided by adaptations of what?
350 million years ago
When did the earliest seed plants appear?
319 million years ago
When were gymnosperms first recorded?
Pennsylvanian period
In what period was gymnosperm recorded around 319 million years ago?
Progymnosperms
Gymnosperms evolved from what?
380 million years
Gymnosperms evolved from progymnosperms around how many millions of years ago?
Conifers, spores
Progymnosperms resembled what? and also reproduced through?
Triassic
In what period where gymnosperms became dominant?
240 million years
How many million years ago was the Triassic period?
Cretaceous
Angiosperms overtook gymnosperms in diversity during what period?
Elkinsia Polymorpha
This is a seed fern around 400 million years ago and is the earliest known seed plant, with seeds in protective capsules
Seed ferns
These types of seed became abundant in the Carboniferous coal swamps
Progymnosperms
Early gymnosperms that originated 390 million years ago in the middle of the Devonian period
Seed plants
During the permian period, the drier climate favored
Ginkgoales and Gingko Biloba
They appeared in the Jurrasic, marking the early gymnosperm diversity
Mesozoic era
In what era did gymnosperms peaked?
Taiga, Alpine forests
In what ecosystems do gymnosperms dominate?
Bryophyte, Fern Spores
These are single haploid cells needing moisture to grow into gametophyte
Diploid zygote
In seed plants, the female gametophyte has a few cells, including the egg and endosperm-producing cells. After fertilization, the ________ ___________ develops into an embryo within a protective seed coat
Seed advantages
Storage tissue nourishes the embryo.
Protective coat prevents desiccation, enabling dormancy until favorable conditions.
Seeds disperse widely by wind, water, or animals, reducing competition with the parent.
Pollen grains (male gametophytes) are adapted for dispersal without water, using wind, water, or animal pollinators .
In most seed plants, sperm lack flagella, but motile sperm with flagella persist in cycads, Ginkgo, and some gymnosperms
Angiosperm radiation
This provided the foundation for today’s diversity and richness in flowering plants.
Flowering plants
These plants remain integral to shaping and sustaining life on earth
Archaefructus
One of the oldest angiosperm fossils is named?
Northeastern China
Archaefructus was disovered in?
Archaefructus
Had primitive flower-like structures and is often cited as one of the earliest angiosperms, giving scientists insights into what early flowering plants may have looked like
Rapid Diversification
This is due to several adaptation traits such as their flowers and fruits facilitated cross-pollination as well as seed dispersal. Their vascular system was also efficient in rapidly growing and adapting to very diverse environments.
Magnoliids, Eudicots, Monocots
What are the major groups that emerged?
Magnoliids
characterized by broad leaves and simple flowers
Eudicots
largest group; mainly characterized by having two seed leaves upon germination.
Monocots
characterized with one seed leaf, but parallel-veined leaves, grass and grass-like flowering plants,
Desert
Adaptation: Succulence and Spines
Benefit: Maximizes water conservation, allowing the plant to flourish in extreme drought conditions.
Desert
Cacti in Arid regions is an example of an ecological niche called
Tropical Rainforest
Adaptation: Water-holding Rosettes
Benefit: Provides access to water in a humid yet competitive environment where soil contact for water absorption is limited
Tropical Rainforest
Epiphytic Bromeliads is an example of an ecological niche called
Temperate Forests
Adaptation: Seasonal Leaf Shedding
Benefit: Aids in resource conservation and protection during cold seasons with reduced sunlight and water availability.
Temperate forests
Deciduous trees is an example of an ecological niche called?