Female Reproductive system
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Principle organs of the female reproductive system
Ovaries
Uterine tubes (Fallopian)
Uterus
Vagina
Perineum
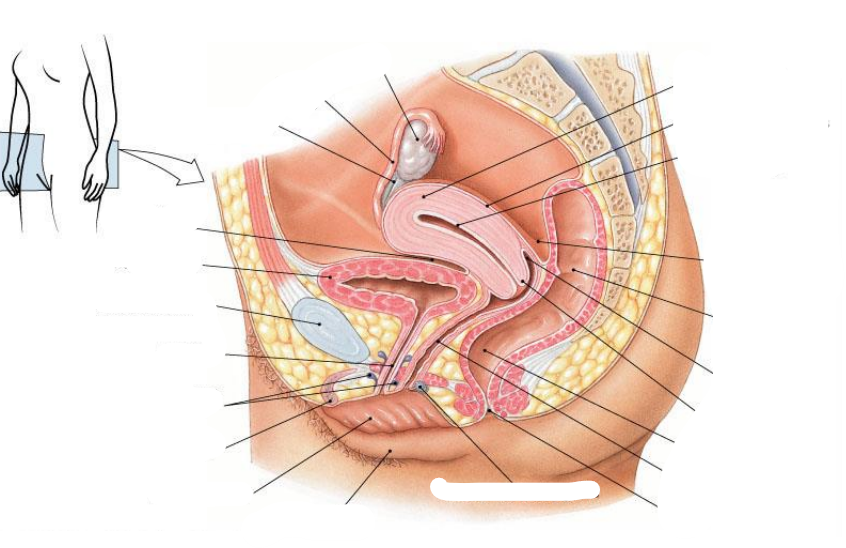
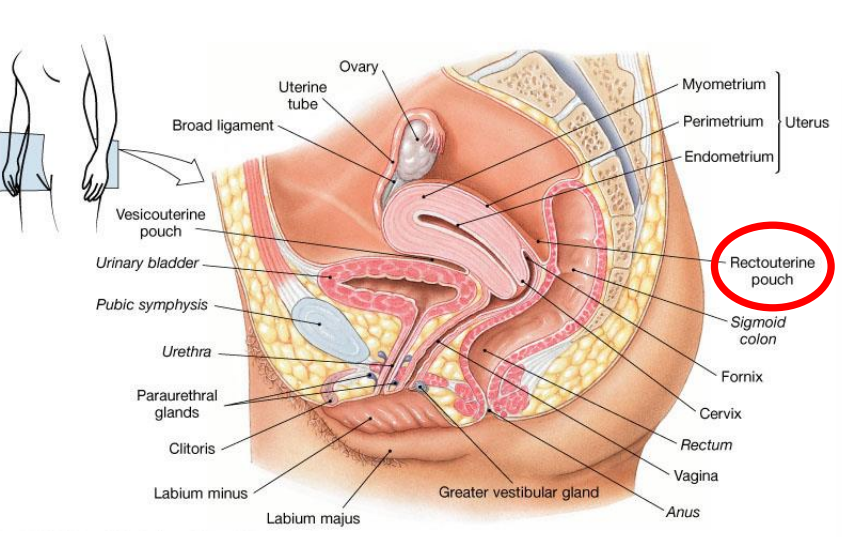
Rectouterine pouch is aka
Pouch of Douglas
What covers the T of female reproductive anatomy
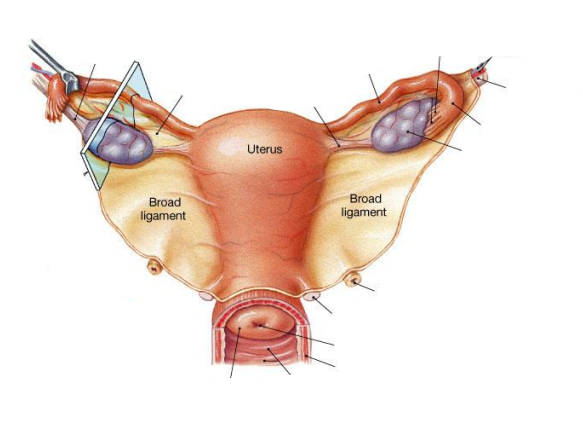
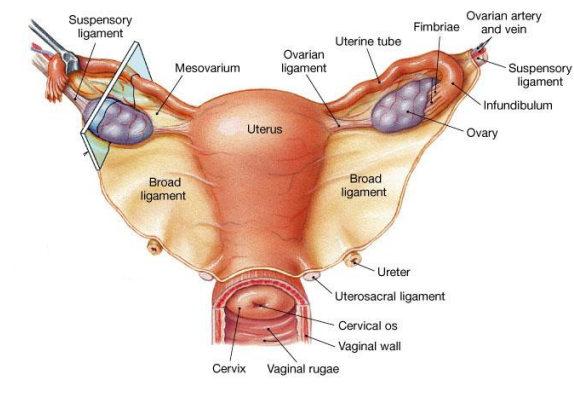
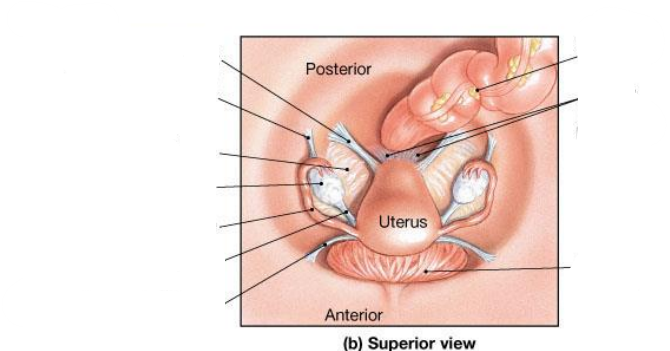
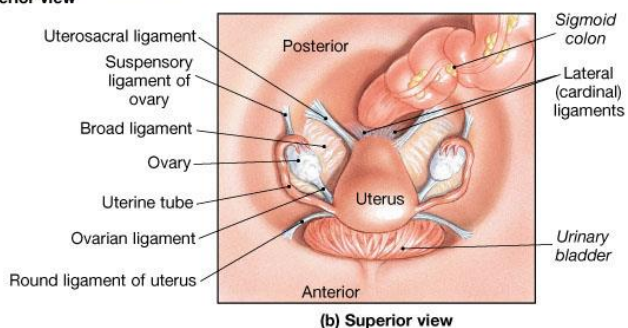
Broad ligament = a fold in the lining of the peritoneal cavity (a double layer of peritoneum that supports the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. It acts like a mesentery for the female reproductive organs)
Name the 3 parts of the broad ligament
Mesometrium: Largest portion of the broad ligament. Extends from the lateral pelvic walls to the uterus (wraps around uterus)
Mesosalpinx: Upper part of the broad ligament, surrounding the uterine (fallopian) tube. (wraps around fallopian tubes)
Mesovarium: Small portion of the broad ligament that attaches to the anterior border of the ovary. Supports & stabilises the ovary (attaches ovaries to the broad ligament)
What happens to the broad ligament at the points where structures pass through it?
At these points, the broad ligament thickens and becomes fibrous, forming ligaments such as the round ligament of the uterus.
What is the round ligament of the uterus, and where does it pass?
Origin: Uterine horn
Path: Passes through the inguinal canal
Insertion: Labia majora
Function: Maintains anteversion of the uterus
The gubernaculum is an embryonic structure that guides the descent of the gonads during development. What does the gubernaculum become in females?
Upper part → Ovarian ligament (ovary to uterus)
Lower part → Round ligament of the uterus (uterus through inguinal canal to labia majora)
What happens if the uterus doesn’t mature properly
Ovary doesn’t stop and herniates into the inguinal canal - presents as an inguinal hernia
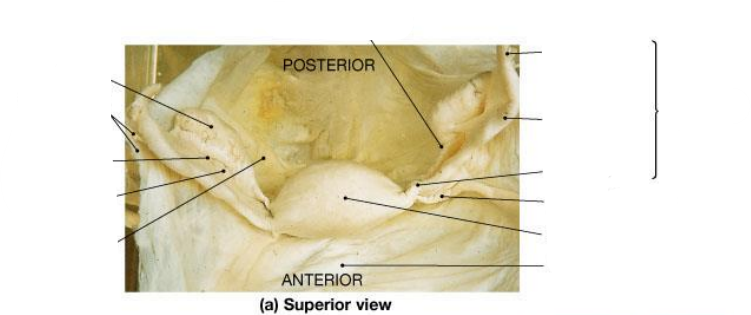
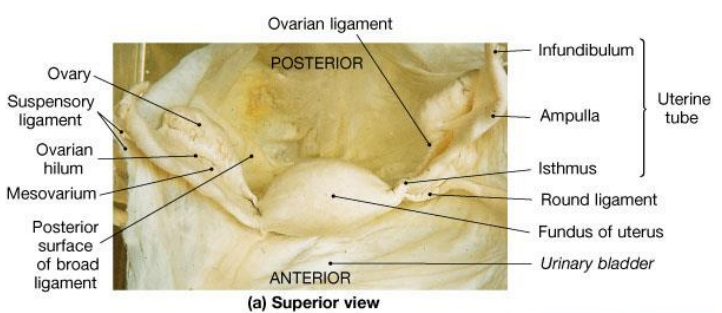
Where do blood vessels enter the ovary
At the ovarian hilus
Which ligaments help support the ovary?
The ovarian ligament and the suspensory ligament.
Suspensory ligament contains what
Suspensory ligament contains ovarian artery
Which part of the ovary contains ovarian follicles?
The germ cell–rich cortex.
If you cut the ovary in half it would show 2 parts - what are the 2 parts
Medulla - rich in blood vessels
Cortex - rich in germ cells
What is oogenesis?
The (monthly) process of ovum (egg) production.
Oogenesis is part of which larger cycle?
The ovarian cycle.
What are the two main phases of the ovarian cycle?
The follicular (preovulatory) phase and the luteal (postovulatory) phase.
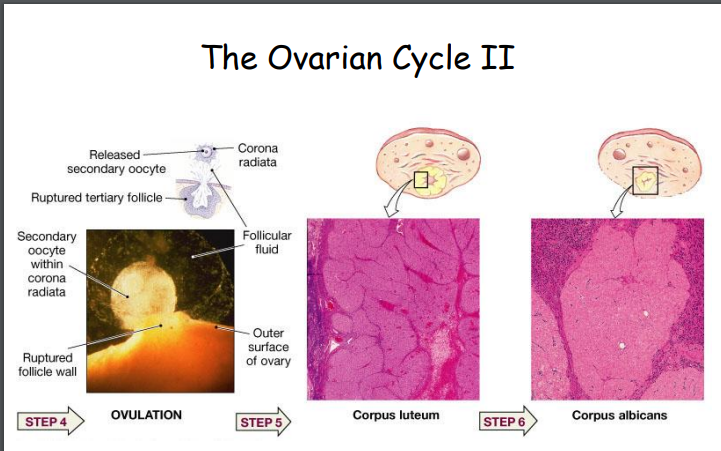
What are the 4 main steps in the ovarian cycle
Formation of primary, secondary, and tertiary follicles
Ovulation
Formation and degeneration of the corpus luteum
Degradation of the corpus luteum
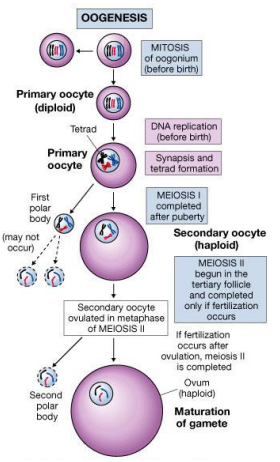
Explain the process of oogenesis
Describe ovarian follicles appearance
Balls of cells
Role of oestrogen
Makes a woman look like a woman - secondary sexual characteristics
Role of progesterone
To prepare and maintain the endometrium for implantation of a fertilized egg.
Which structure mainly produces progesterone after ovulation
The corpus luteum
How long does the corpus luteum last
If you don’t become pregnant, the corpus luteum lasts 7 days
Fallopian tubes are aka…….. (2)
Uterine tubes
Oviducts
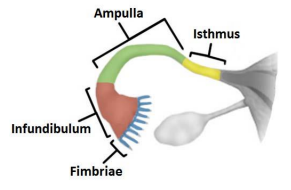
What and where are the 3 main parts of the fallopian tubes
Infundibulum: End closest to the ovary with numerous fimbriae (finger-like projections that help sweep the ovulated ovum into the tube)
Ampulla: The middle, widest portion. Fertilization occurs in ampulla of the uterine tube, generally 12-24 hours after ovulation
Isthmus: The narrow segment that connects the tube to the uterine wall.
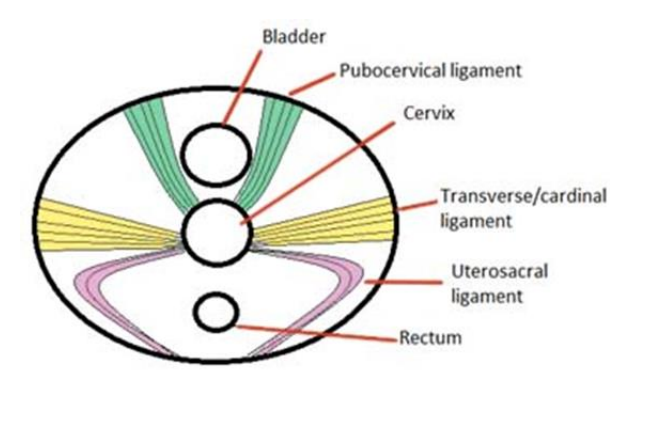
The uterus is supported by what 4 things
Broad ligament & 3 pairs of suspensory ligaments
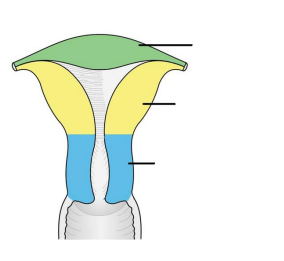
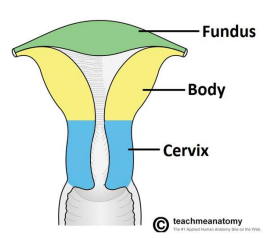
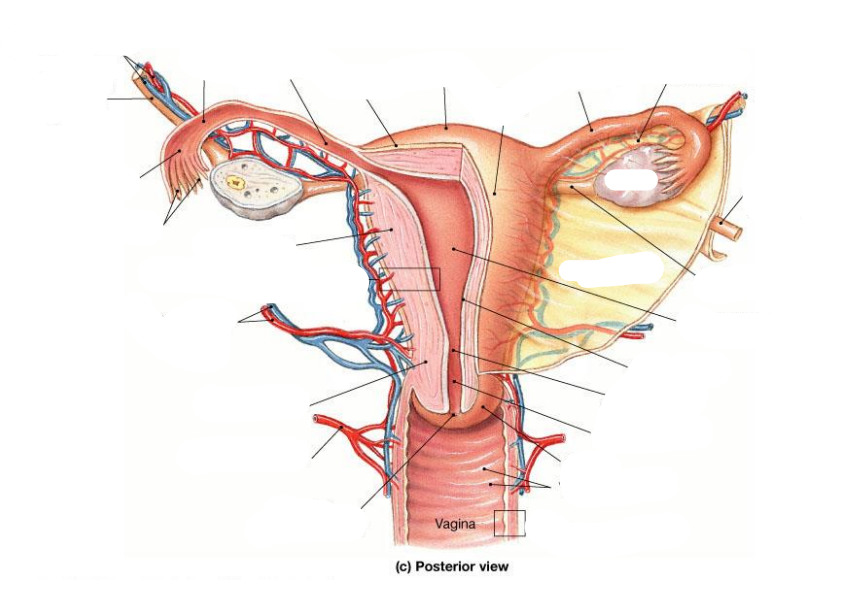
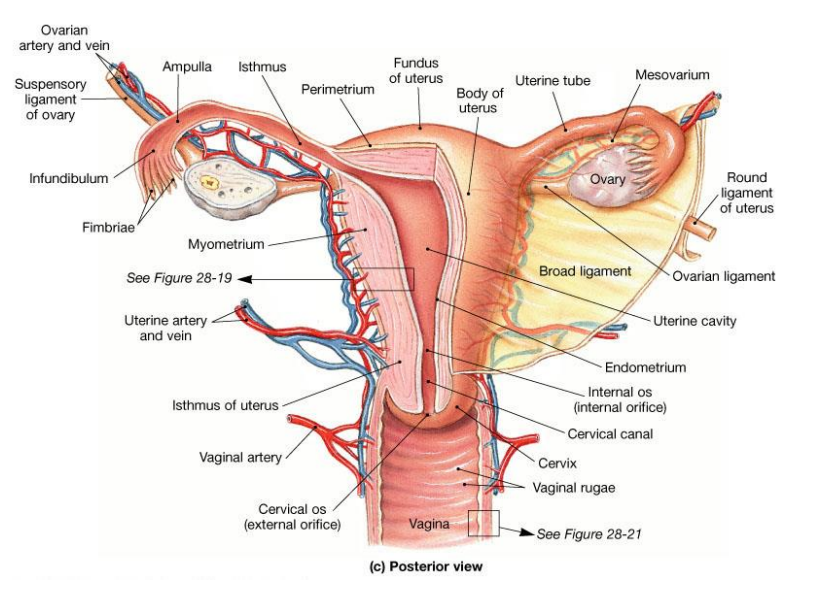
Structure of the uterine wall
Myometrium: outer muscular layer
Endometrium:a thin, inner, glandular mucosa
Perimetrium: incomplete serosa
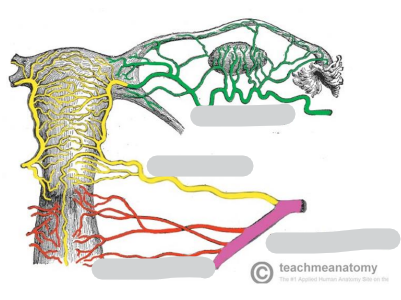
Name the arteries
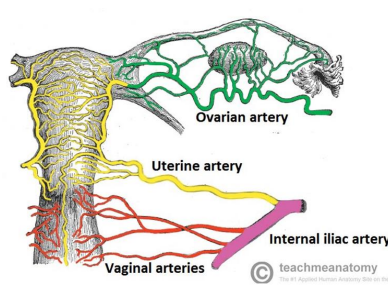
Micro-artery supply
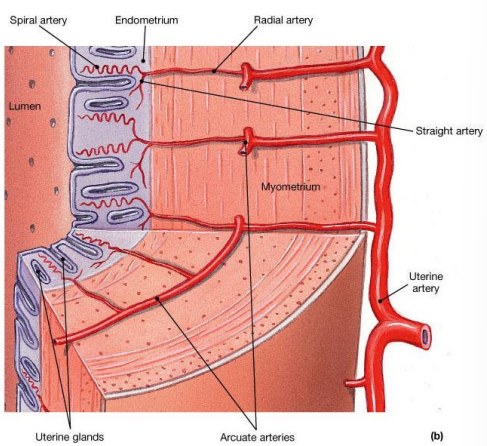
Menstrual cycle is aka…
uterine cycle
Menstrual cycle continues from what to what
Continues from menarche to menopause
3 main phases of menstrual cycle
Menses: Degeneration of the endometrium
Proliferative phase: Restoration of the endometrium
Secretory phase: Endometrial glands enlarge and accelerate their rates of secretion
Fill int he hormones
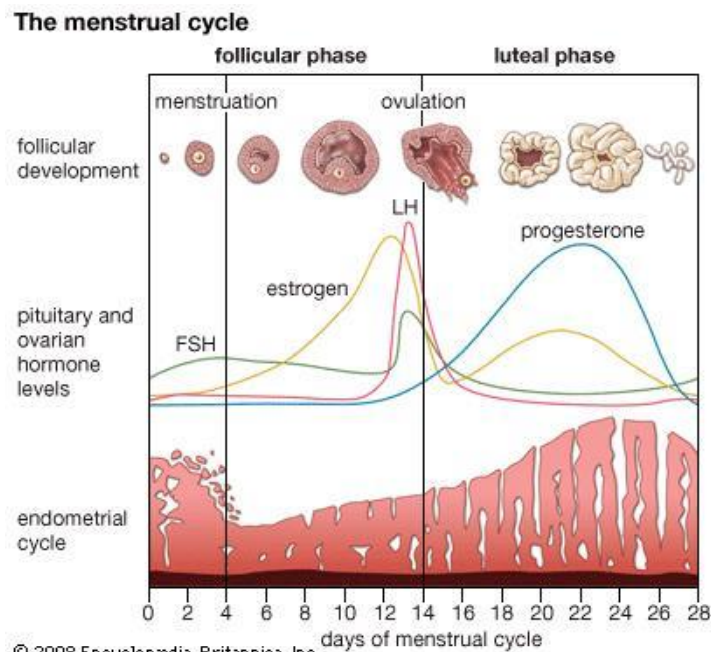
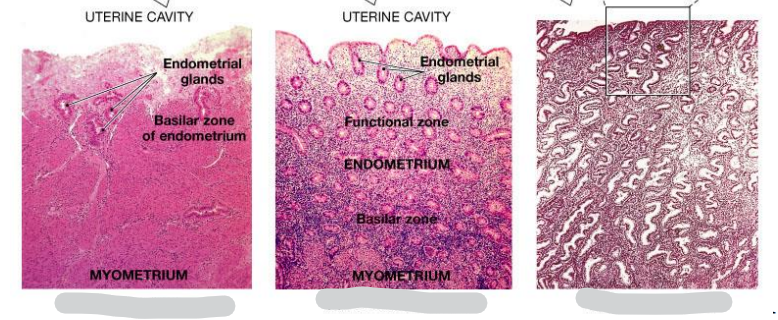
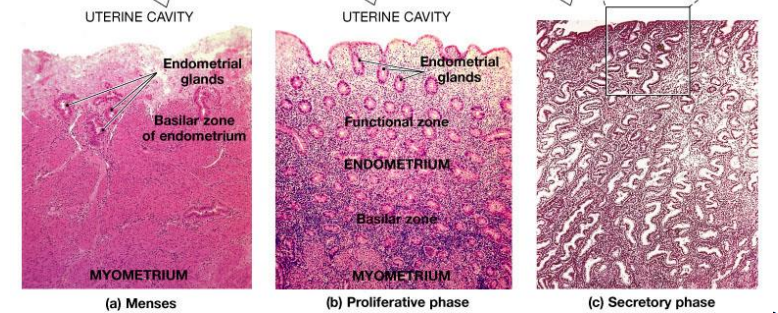
Name the phase represented by each one
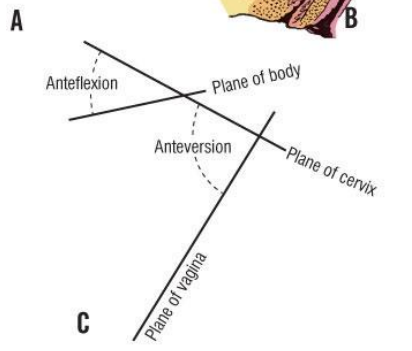
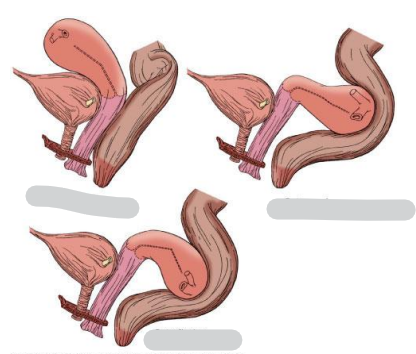
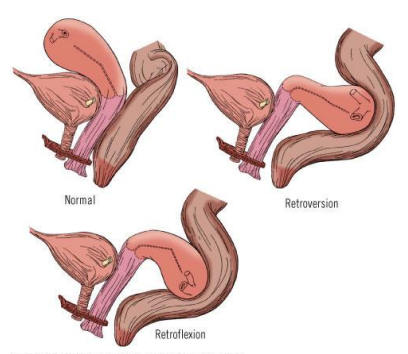
The position of the uterus is normally described as what
anteversion anteflexion
Anteversion – the uterus tilts forward relative to the vagina.
Anteflexion – the body of the uterus bends forward relative to the cervix.
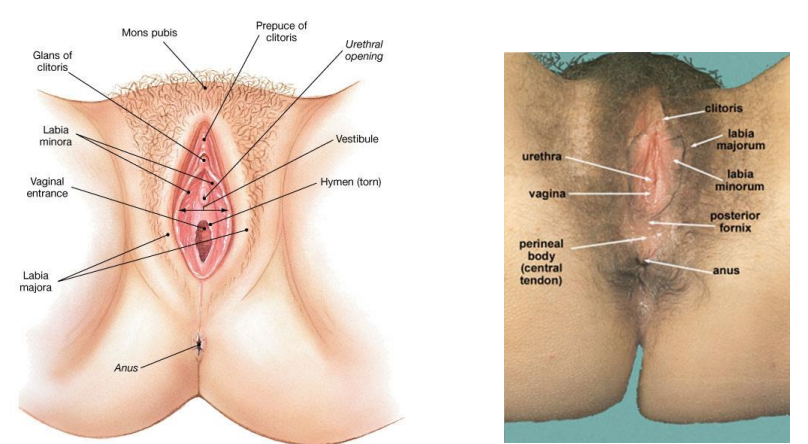
Vagina major functions
Passageway for elimination of menstrual fluids
Receives the penis during sexual intercourse
Forms the inferior portion of the birth canal
Vagina epithelium
Stratified Squamous non-keratinised epithelium
Vaginal epithelial cells are rich in what
Glycogen
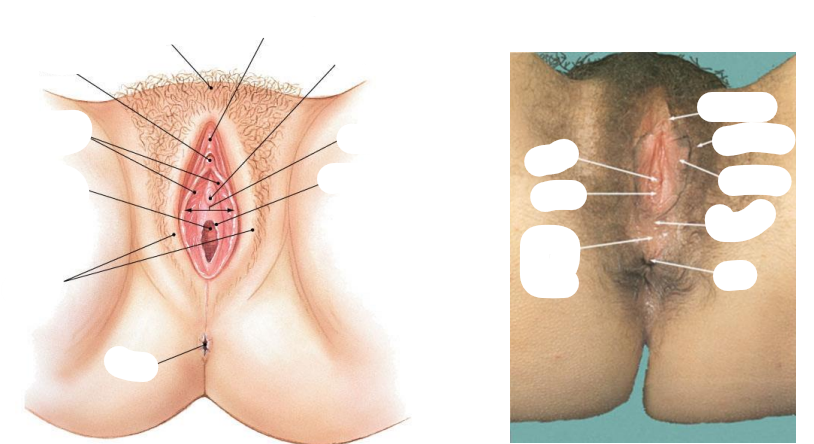
Female external genitalia (vulva) consists of what
Vestibule
Labia minora and majora
Paraurethral glands
Clitoris
Lesser and greater vestibular glands
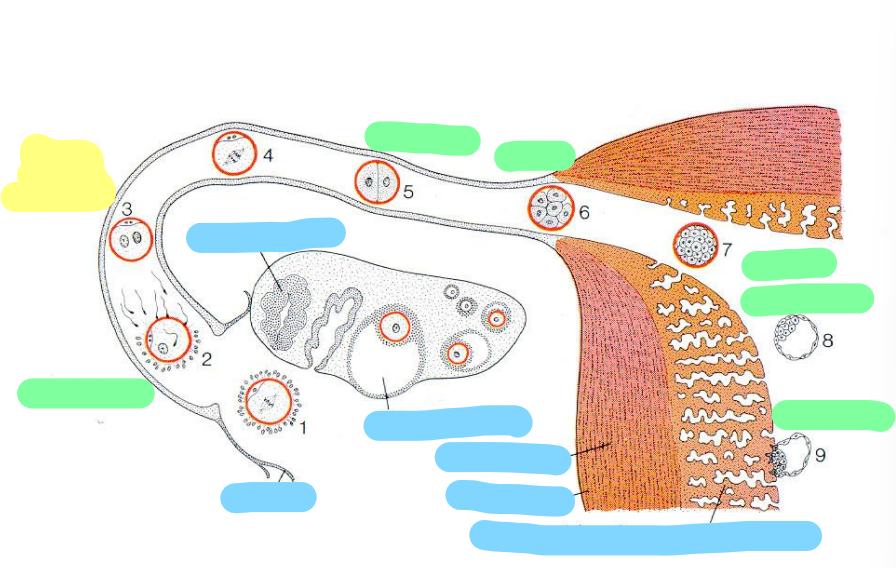
Blue: what is this
Green: how many days does this represent
Yellow: what’s happening here
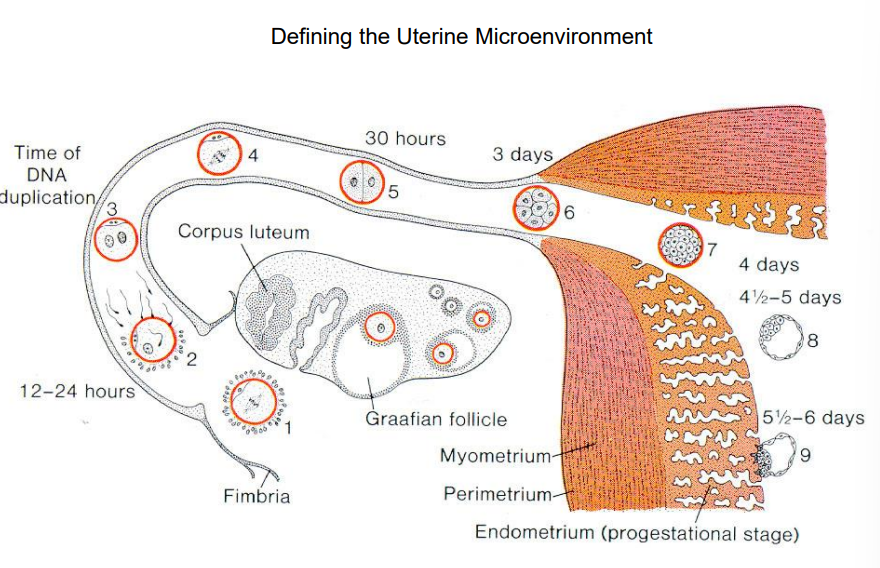
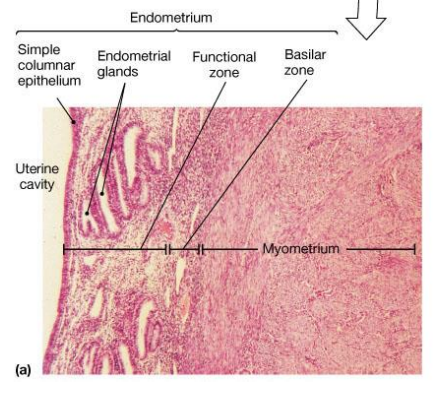
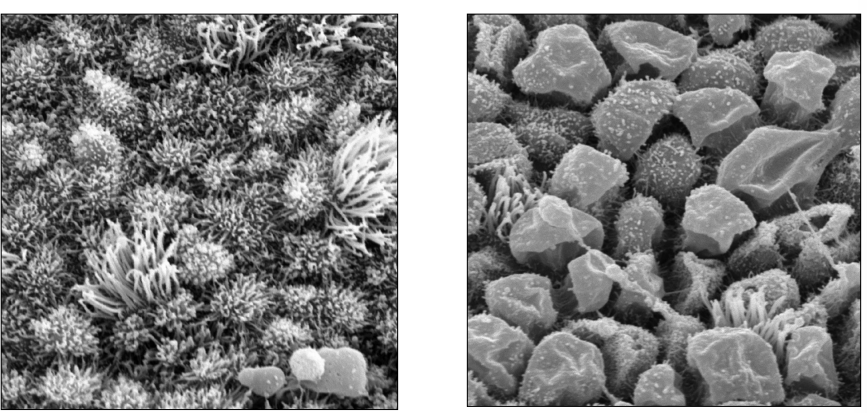
Where is this epithelium
Luminal epithelium
Where is this epithelium
Glandular epitehlium
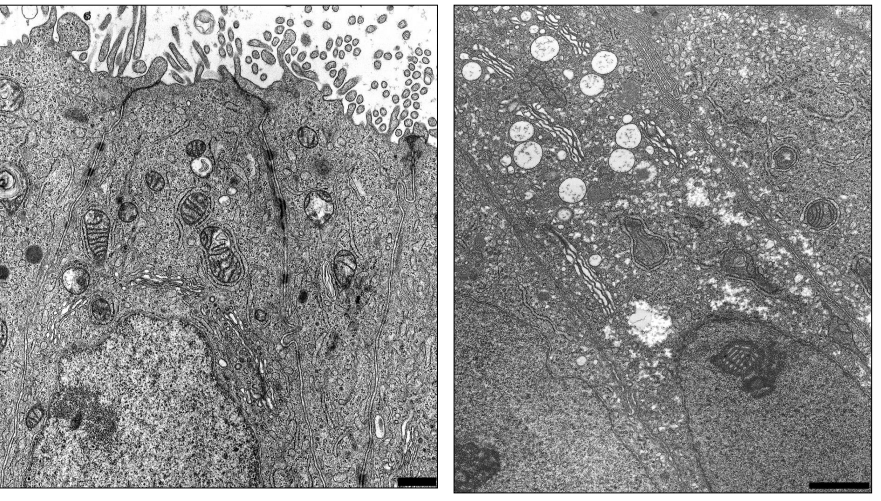
Where is this epithelium
Endometrium
Where is this epithelium
Endometrial stroma
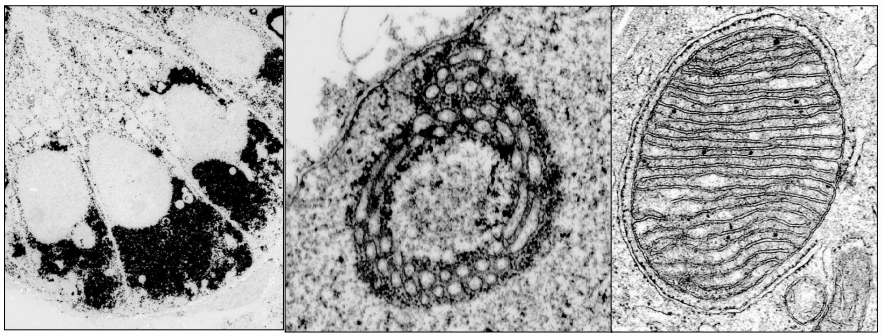
Where is this epithelium
Endometrial vasculature
Where is this epithelium
Myometrium
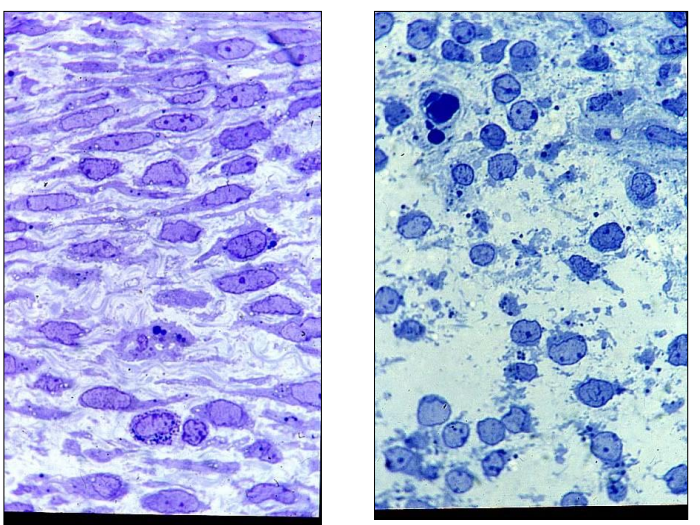
Where is this epithelium
Myometrium
Where do we get the first evidence that vessel elongation is a major angiogenic mechanism
mid-late proliferative phase human endometrium (existing vessels mainly elongate to support tissue growth, rather than forming lots of new branches)
When does oogenesis begin and what happens after birth?
Oogenesis begins before birth with the formation of primary oocytes. After birth, the oocytes are arrested in prophase I of meiosis. During puberty, maturation accelerates, but they remain suspended until ovulation.
What happens to the primary oocyte in the ovary?
The primary oocyte becomes surrounded by ovarian cells, forming a follicle (a small ball of cells). It remains in this suspended state until it is released during ovulation, which occurs monthly from around age 13 to ~50.
Why is there a greater incidence of genetic abnormalities in older women?
Because the primary oocyte remains arrested in prophase I for years, its genetic material is vulnerable, increasing the risk of abnormalities with maternal age.
What happens during the first meiotic division of the primary oocyte?
The primary oocyte undergoes meiosis I and divides into:
A large secondary oocyte (retains most cytoplasm)
A small polar body (contains less cytoplasm and less cytoplasmic material)
The polar body usually degenerates.
When does the secondary oocyte complete meiosis?
The secondary oocyte arrests at metaphase II and only completes meiosis II if fertilization occurs.
The primary oocyte undergoes meiosis I and divides into:
A large secondary oocyte (retains most cytoplasm)
A small polar body (contains less cytoplasm and less cytoplasmic material)
The polar body usually degenerates.
When does the secondary oocyte complete meiosis?
The secondary oocyte arrests at metaphase II and only completes meiosis II if fertilization occurs.
First text you ever send your mother is
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
hCG is produced by the placenta after implantation.
Its main function is to maintain the corpus luteum in early pregnancy so it continues secreting progesterone to support the endometrium
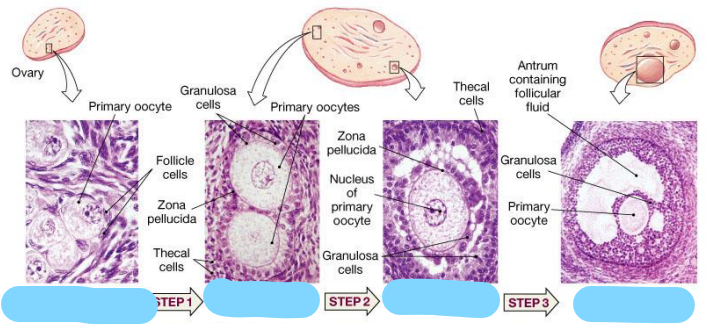
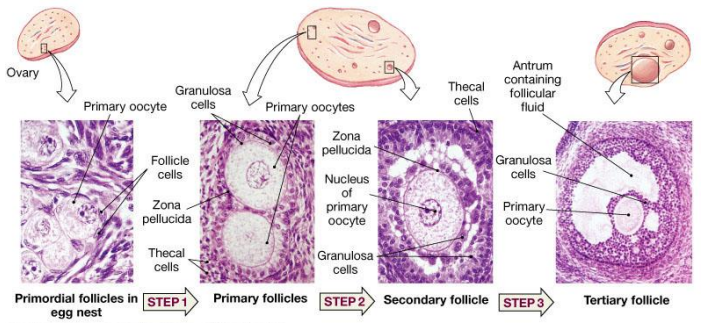
What surrounds primary oocytes in the ovary
Primary oocytes are surrounded by small, flat follicle cells
How many eggs does a woman typically release in her lifetime?
Approximately 400 eggs are released over a lifetime.
How many oocytes grow each month, and how many usually mature fully?
Each month, 20–30 oocytes start to grow, but usually only 1 becomes fully mature and is ovulated.
What types of cells surround the developing oocyte, and what do they produce?
The oocyte is surrounded by granulosa cells and follicular cells.
They produce estrogen during the follicular phase and progesterone after ovulation.
What is the zona pellucida?
The zona pellucida is a glycoprotein-rich shell that wraps around the oocyte and protects it, also important for sperm binding during fertilization.
What is a Graafian follicle?
A Graafian follicle is the mature, large ovarian follicle ready to release an oocyte during ovulation. It has a fluid-filled cavity called the antrum, and the oocyte is surrounded by granulosa cells (cumulus oophorus).
Where does fertilization usually occur
Fertilization usually occurs in the ampulla of the Fallopian tube.
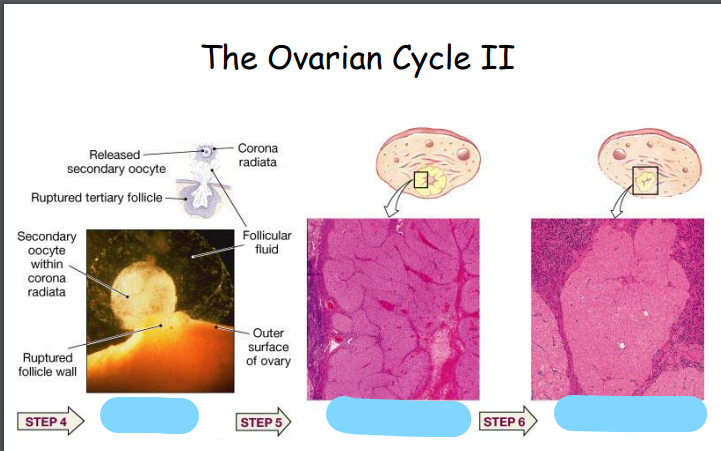
What happens to the follicle after the oocyte is released?
The rest of the follicle collapses on itself and forms the corpus luteum.
What does the corpus luteum produce?
The corpus luteum produces estrogen and progesterone, which support the endometrium and early pregnancy.
What happens to the corpus luteum if pregnancy does not occur?
If there is no pregnancy, the corpus luteum degenerates into the corpus albicans (white body) because the mother does not receive hCG from an implanting embryo.
What hormone maintains the corpus luteum during early pregnancy?
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) from the embryo maintains the corpus luteum, allowing it to continue producing progesterone.
Fallopian (uterine) tubes are lined with a ______ epithelium.
ciliated
Main structural support for the uterus
Bones of the pelvis
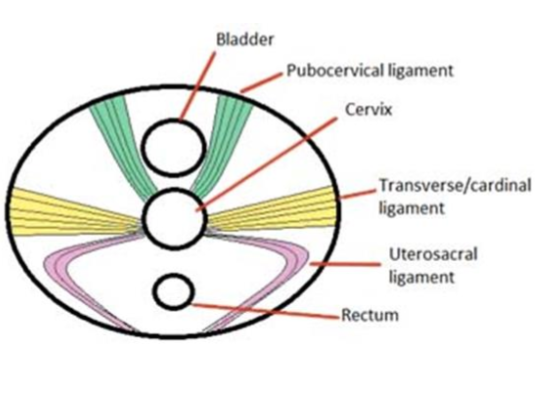
If these ligaments are disrupted (e.g. during childbirth/trauma) what can happen to the uterus, bladder & rectum
- Uterus can fall out - uterine prolapse
- Bladder can descend - urinary incontinence
- Rectum - faecal incontinence
Implantation should occur in what section of the uterus
Body/Fundus
Myometrium = thin/thick, smooth/skeletal muscle
Myometrium = thick, smooth muscle
Endometrium is about _ mm thick at its thickest - during menstruation it goes down to __mm thick
3
1
Uterine artery & vaginal artery are terminal branches of what artery
Internal iliac
What hormone from the pituitary stimulates the ovarian follicles during the proliferative phase?
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH).
What effect does FSH have on the ovarian follicles?
It stimulates the follicles to produce oestrogen.
What is the effect of oestrogen on the endometrium during the proliferative phase?
Oestrogen thickens the endometrial lining and stimulates the cells to divide, causing glands to grow longer.
What is the name of the phase in which the endometrium thickens under the influence of oestrogen?
The proliferative phase.
Which hormone signals the endometrial glands to produce “uterine milk” to support a potential embryo?
Progesterone.
What is the shape of the cervical opening (os) in women who have never given birth vs who have?
It is a round hole in women who have never given birth vs a slit in those who have
What is a colposcopy?
It is a procedure where a sample or smear is taken from the surface of the cervix for examination.
What effect does bacteria feeding on glycogen have in the cervix?
It lowers the pH by producing lactic acid.
Lactobacilli (the “good bacteria”) thrive in this acidic environment?