Maternal Nursing Exam 1 (menstrual cycle, infertility, contraception, fetal development)
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
menstruation
-LMP = first day of last menstrual period (used to determine pregnancy)
-estrogen spike around age 8-11 causes menarche
-become regular and ovulatory after 1 year
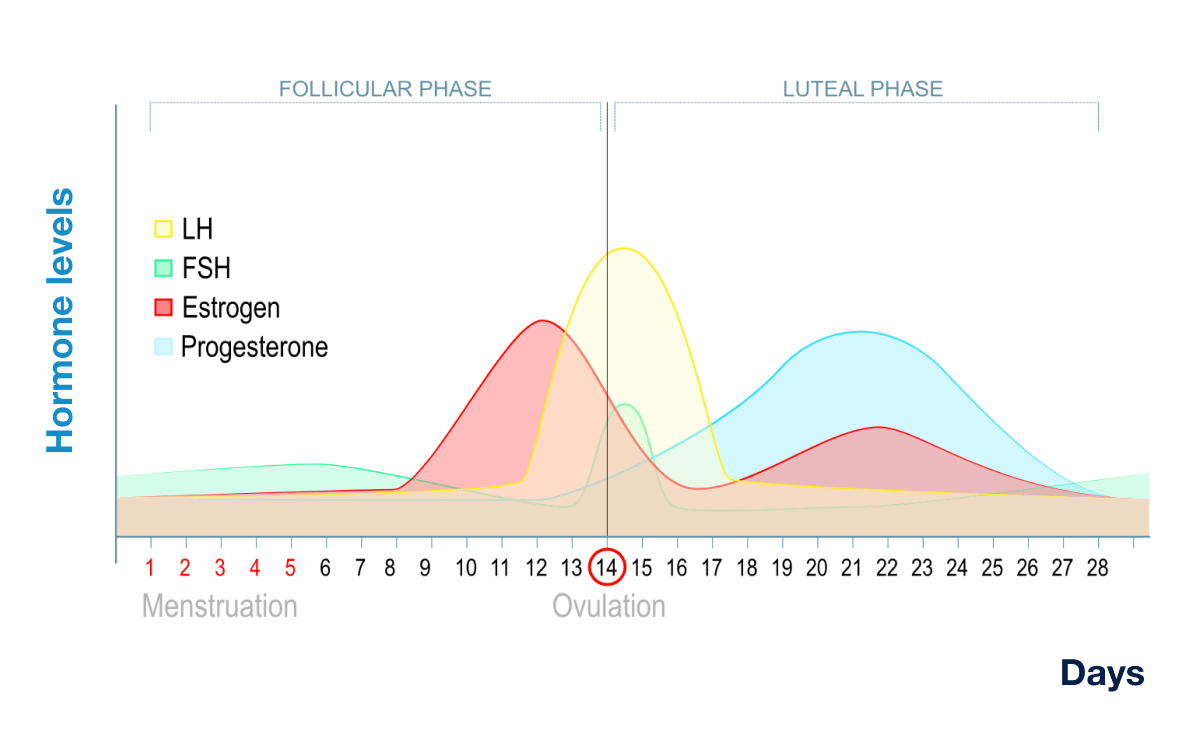
-ovulation occurs, then 14 days later menstruation
-average: cycle = 28 days, bleeding = 3-6 days
endometrial/uterine cycle
1) menstrual phase: shedding of endometrium (except basal layer) via vasoconstriction
2) proliferation: growth of endometrium (lasts from day 5 to ovulation)
3) secretory phase: ovulation to 3 days before menstruation
-progesterone made, endometrium matures and secretes to support ovum
4) ischemic phase: blood supply blocked, endometrium necrotizes to cause bleeding
-E&P drop
hypothalamic/pituitary cycle
-cycle ending causes E&P to drop→hypothalamus makes GnRH→anterior pituitary makes FSH→ovarian follicles develop & make estrogen
-anterior pituitary also is stimulated by GnRH to make LH (day 12)→ovum leaves follicle
-LH peaks around day 13-14 to cause ovulation, then corpus luteum regresses if no zygote is implanted
-E&P drops→menstruation→repeat
ovarian cycle
-FSH causes follicles to mature
-body temp rises, mucus thins & clears, possible pain
-LH causes one follicle & oocyte to mature→ovulation
-empty follicle becomes corpus luteum
—makes E&P, which thicken uterine lining
—peaks 8 days after ovulation
—zygote implants, otherwise corpus luteum is shed
hormones during the cycle
infertility
-unable to conceive after 1 year (6 months if over 35 y.o. or other risk fx)
-increases age 40+
-subfertility = prolonged time to conceive
-primary = never been pregnant; secondary = after having been pregnant before
-fecundity = can carry to term & have a live birth
-40% d/t male, 40% d/t female, 20% unexplained
female infertility
-anovulation
—primary d/t hypothalamus or pituitary gland
—secondary d/t low fat %, thyroid gland, PCOS, etc.
-meds (OCPs, antidepressants, steroids, chemo)
-tubal inflammation, decreased motility, adhesions
-uterine tumors
-decreased cervical mucus
-sperm antibodies
-obesity
-thyroid
male infertility
-gland tumor or trauma
-increased androgens/estrogen/cortisol
-obesity
-testicular disorder
-sperm antibodies
-decreased libido, impotence, ED
infertility treatment
-counsel pt to have intercourse 2-3x/wk, especially day before and day of ovulation
-should wait 2 years after birth to get pregnant again to decrease PP hemorrhage
-tests:
—female: HSG, Chlamydia, laparoscopy, sonography, progesterone, cervical mucus, BBT, hormone analysis, ovulation tests
—male: semen, sperm penetration assay, FSH, testicular biopsy
-Rx: lifestyle, diet, exercise, weight loss, good BGM
—men: loose clothes, lower temp water
—also: meds, ART (IVF, insemination, IUI)
coitus interruptus
failure rate = 96%
fertility awareness
-fertility is the 5-7 days around ovulation
-NFP = avoiding intercourse around 4 days before & after ovulation by tracing menstruation, mucus, BBT (abstain from day one of menstruation until day 3 of temp rise)
—must measure BBT before moving in morning
-calendar rhythm = track cycle length; must track period for 6 mo before
-standard days = fixed number of days; use bracelet
-breastfeeding (LAM) = feeding q4h during day and q6h at night
barrier method
-spermicide (may increase HIV or cause lesions)
—apply 1 hr before
—must contact cervix
—best if used with another method
-condoms (help decrease STIs)
-diaphragm (reusable)
-cervical cap (has spermicide)
—woman must be comfortable touching her cervix
-sponge
OCPs
-decrease flow, reduce anemia, alleviate PMS & dysmenorrhea
-decreases FSH & LH to stop ovulation, thins uterine lining, thickens mucus, may prevent implantation
-contraindicated: thromboembolic issues, CAD, breast CA, tumors, pregnancy (till 6 wk after birth), liver/gallbladder problems, smoking, HTN, migraines w/ aura, DM, MI, CVA
-decreased fertility for 3-12 months after
-actions decreased by antiseizure meds, antifungals, anti-TB, anti-HIV, antibiotics
-can be given in emergency w/in 72 hr
effects of the pill
-increased progesterone may stop menstruation and cause weight gain
-dangerous AEs: Abdominal (liver) pain, Chest pain (DVT→PE), Headache, Eye problems, Severe leg pain (DVT)
-at first increased estrogen causes nausea, breast tenderness, chloasma
-increased progesterone makes body think estrogen has dropped, causing early spotting, hypomenorrhea, vaginitis, painful sex
—also increased appetite, fatigue, depression, vaginal yeast infections, oily skin, hirsutism, amenorrhea
-low progesterone will cause heavy/irregular bleeding
other hormonal birth control
-patch (3 wks on, 1 wk off)
-vaginal ring
-IM progesterone q3mo (Depo-provera)
-implant (Nexplanon), lasts 2-3 years
IUD
-copper (spermicide, lasts 10 years) or Mirena (progesterone, lasts 5 years)
—also thins endometrium
-may cause PID, uterine perforation, ectopic pregnancy, vaginosis
-string stays behind cervix
-may be inserted right after birth or in emergency (w/in 5 days)
sterilization
-female = tubal ligation = occlusion
—reconstruction sometimes possible, but considered permanent
—Medicaid requires consent to be signed 30 days before procedure
-male = vasectomy
induced abortion
-need ultrasound and Rh Ig before
-defined as pregnancy ending before 20 weeks
-elective = pt request
-therapeutic = b/c of maternal/fetal health
-1st trimester = surgical (aspiration)
—local anesthesia
—suction cannula used
—heavy period-like bleeding after
-abnormal S/S: fever, chills, excess bleeding, smelly discharge, abdominal pain
-meds used 1st or 2nd trimester
—mifepristone blocks progesterone
—misoprostol stimulates contraction
—methotrexate
-2nd trimester = D&E or D&C, or induced delivery
—very risky
chromosomal abnormalities
-may lead to miscarriage, congenital issue, or gynecologic disorder
-occurs during meiosis or mitosis
-autosomal = of a chromosome number
genetic disorders
-usually multifactorial (e.g. cleft palate, congenital heart disease, neural tube defects, pyloric stenosis)
-risk
—occurrence = known to be at risk for having kids w/ disease
—recurrence = once child w/ disease has been born
-maternal & fetal blood never actually mix; nutrient transfer via chorionic villi
prenatal stages of development
(fertilization)→
zygote→
morula→
blastocyst→
(implantation)→
embryo→
fetus
prenatal layers
-endoderm becomes GI, liver, pancreas, inner lung
-mesoderm becomes CVS, epithelial lung tissue, skeleton, muscles
-ectoderm becomes hair, nails, skin, CNS
conception
-meiosis produces ovum & sperm
-estrogen increases uterine tube movement so cilia propel ovum
—fertile for 24 hours
—2 layers: inner = zona pellucida; outer = corona radiata
-hundreds of millions of sperm per mL (3.5 mL each time)
—average of 4-6 hours to reach tubes
—viable inside female for 2-3 days
—enzymes break down coating of ovum
fertilization
-in ampulla of tube (outer third)
-afterwards, membrane becomes impermeable to more sperm (zonal reaction)
-chromosomes & nuclei combin
-mitosis starts in 30 hours, blastocyst forms
-zygote stays in tube for 24 hrs; propelled to uterus w/in 3-4 days
-blastomeres form morula (16 cells in 3 days)
-forms trophoblast (future placenta) & embryoblast (→ blastocyst w/ cavity)
implantation
-on day 6-10
-may have bleeding at time of first missed period
-chorionic villi develop (vascular processes to transfer nutrients/waste between mom & baby)
-endometrium becomes decidua basalis
hormones during pregnancy
-progesterone maintains endometrium, decreases contractility of uterus, stimulates maternal metabolism, develops breast alveoli
-estrogen stimulates uterine growth & blood flow, proliferated breast glands, stimulates myometrial contractility
stages of pregnancy
-lasts from LMP to birth
-fetus is technically 38 weeks old at birth
-stages
1) ovum/pre-embryonic: till day 14
2) embryo: day 15 to 8 weeks
*most vulnerable to teratogens
3) fetus: 9 weeks to birth
*viability at 22-25 weeks, weight 350-500 g
fetal membranes
chorionic (by placenta) & amnion (by fetus)
amniotic fluid
functions:
-maintains temperature
-nourishes fetus
-teaches fetus to swallow
-takes waste & urine
-allows movement
-prevents cord wrapping
should be between 300 mL and 2 L
fetus breathes it in & out towards the end
yolk sac
-transfers nutrients till placenta can
-becomes primitive GI system till wk 5-6
umbilical cord
-develops week 14
-2 arteries & 1 vein, Wharton’s jelly surrounds & protects
-may wrap around neck = nuchal cord
-inserts on placenta:
—centric
—eccentric
—battledore/margin (edge)
—velamentous (membrane) (dangerous, may cause bleeding)
placenta
-Duncan side by mom, Schultz by baby
-chorionic villi forms 3 layers & divides into cotyledons; complete by 12 weeks
-circulation established by day 17 (heartbeat)
-metabolic exchange/storage
placenta functions
endocrine
-makes hCG (preserves corpus luteum to ensure E&P)
—peaks day 60-70, drops 100-130 days
-makes hCS/hPL (like GH)
—increases insulin resistance in mom to increase free glucose for baby
—transports glucose
—stimulates breast development
-makes E&P
circulation
-stores blood during contractions
-*mom cannot lay on back (blocks blood return and causes hTN
-*excess exercise & Braxton Hicks may block blood
fetal CVS
-blood starts forming wk 3, heart beats
-heart complete by 9 weeks
-special circle bypasses lungs (ductus arteriosus)
-Hgb carries 20-30% more O2 & is 50% more concentrated
-HR = 110-160 BPM
-hematopoeisis starts in yolk sac week 3; in liver week 6
-RBCs live 90 days
fetal GI
-upper forms week 5-6
-fetus swallows starting 5 mo or 20 wk
-produces meconium that is passed after birth
—passed before d/t stress; concerned about inhaling
-mature by 36 weeks
hepatic/renal fetal development
-bile at 12 wks
-glycogen storage wk 9-10
-lacking certain coagulation factors
—d/t no vitamin K synthesis (no normal flora)
-less gluconyl transferase enzyme (breaks down bilirubin)
-renal function at 9 weeks
—urine volume depends on renal function (decreased function will lead to oligohydramnios)
—GFR is low
fetal neural development
-neural tube at 4 weeks
-3 folds → forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
-nerves at 8 weeks
-sound response at 24 weeks
-response to light at 24-26 weeks
-taste at 16 weeks
order of fetal circulation
-placenta vein is high pressure and O2-rich (goes from mom to baby)
-bypasses liver mostly (ductus venosus)
-inferior vena cava
-blood moves between atrium via foramen ovale
-bypasses lungs mostly (via ductus arteriosus)
-descending aorta → placenta via 2 arteries (low pressure, low-O2)
fetal endocrine development
-fetus makes own thyroxine at 8 weeks
-adrenals at 6 weeks, cortisol increases closer to term
-insulin at week 20 (does not cross placenta)
—mom w/ DM → fetal hypoglycemia → pancreas islet cell hyperplasia → macrosomia, neonatal hypoglycemia (they make insulin but aren’t getting glucose from placenta)
—also, fetal hyperglycemia → insulin spike → immature lungs
fetal reproductive development
-gender characteristics at week 9-12
-testes descend at week 28
-oogenesis at week 16
fetal musculoskeletal development
-by week 4
-skull sutures still have CT
—2+ bones meet = fontanel (anterior = diamond, posterior = triangle)
-movement by week 11-12
—perceived by mom week 16-20
fetal integument development
-epidermis at week 4
—1 layer mixes with sebaceous gland secretions to make vernix caseosa for protection
-lanugo at week 12-20
fetal immune development
-IgG crosses placenta
-fetus makes IgM by end of 1st trimester
-IgA from breastmilk
twins
-dizygotic
—increased FSH→multiple ova released→2 fertilized
—fraternal
-monozygotic
—1 fertilized ovum divides after 4-8 days
—shared placenta
—earlier split→more shared materials→higher danger
—“identical”
—monochorionic & monoamniotic twins will need to be induced early
Depo-provera
-synthetic progesterone
-converts proliferative phase to secretory, inhibits FSH & LH
-150 mg IM q3mo
-AEs: depression, fluid retention, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, anorexia, jaundice
-teach: report ACHES S/S, vomiting, dizziness, etc
Nexplanon
-implantable
-progestin
-works for 3 years
-minor surgical procedure requiring local anesthesia
-AEs: irregular menstruation, HA, nervousness, skin changes, vertigo
drospirenone/estetrol
-synthetic progestin
-also used for acne & PMDD
-prevents fluid retention
-higher risk of blood clots
-check K+ levels before
diuretics during pregnancy
-not usually used
-may be needed for kidney failure, liver failure, or HTN
-may cause F&E imbalance
-if used: check I&O, daily weight
-give early in the day