Geology Test Terms
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Last updated 5:29 AM on 11/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
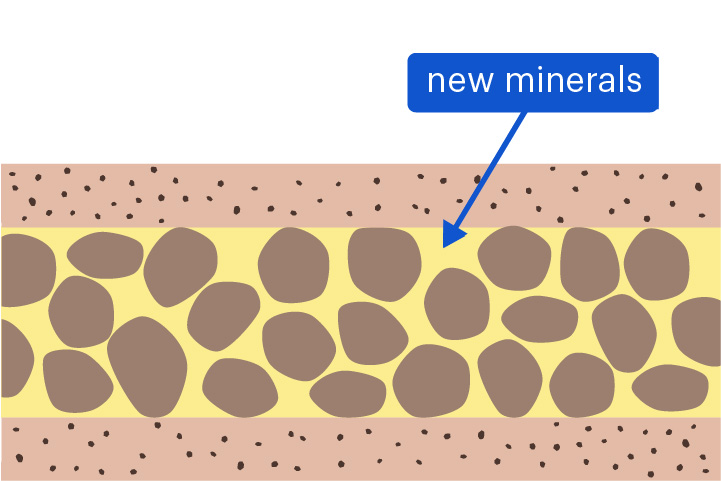
cementation
The gluing together of sediment by new mineral crystals
Cementation can cause sediment grains to stick together, forming sedimentary rock.
2
New cards
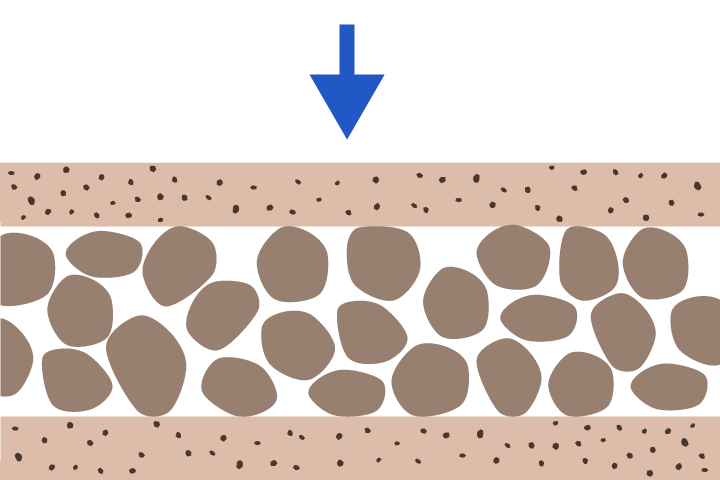
compaction
The squeezing of sediment by the weight of overlying layers
Compaction can cause sediment grains to stick together, forming sedimentary rock.
Compaction can cause sediment grains to stick together, forming sedimentary rock.
3
New cards
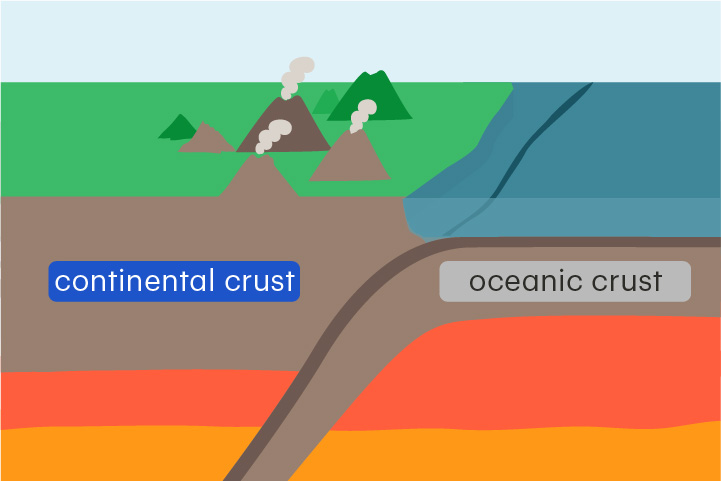
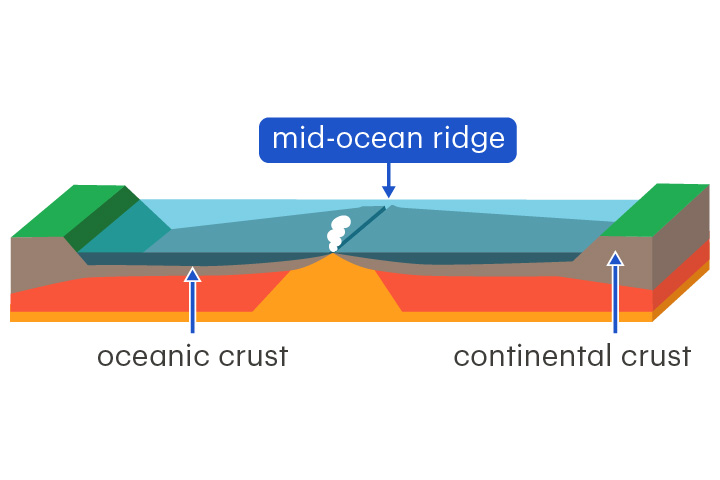
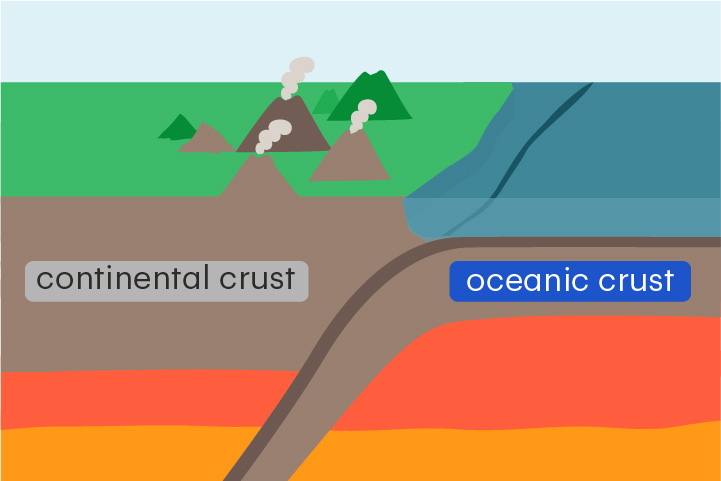
continental crust
Crust that lies beneath a continent
Continental crust is about 25–70 km thick and is less dense than oceanic crust.
Continental crust is about 25–70 km thick and is less dense than oceanic crust.
4
New cards
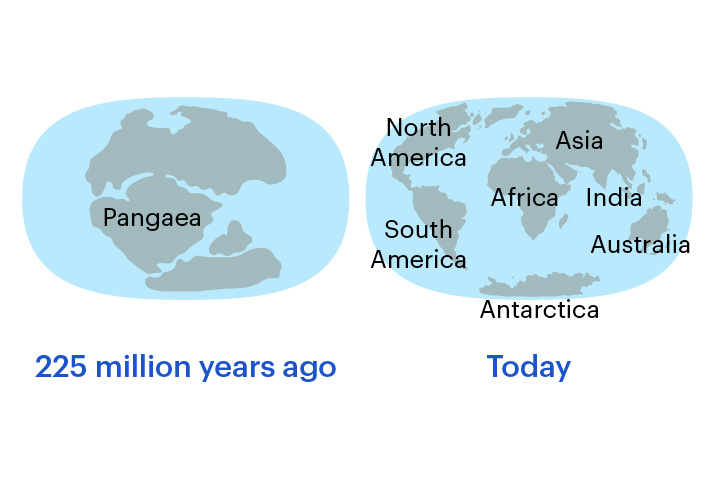
continental drift
The movement of continents around the surface of Earth
Continental drift theory was proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912 but was widely accepted only in the 1960s.
Continental drift theory was proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912 but was widely accepted only in the 1960s.
5
New cards
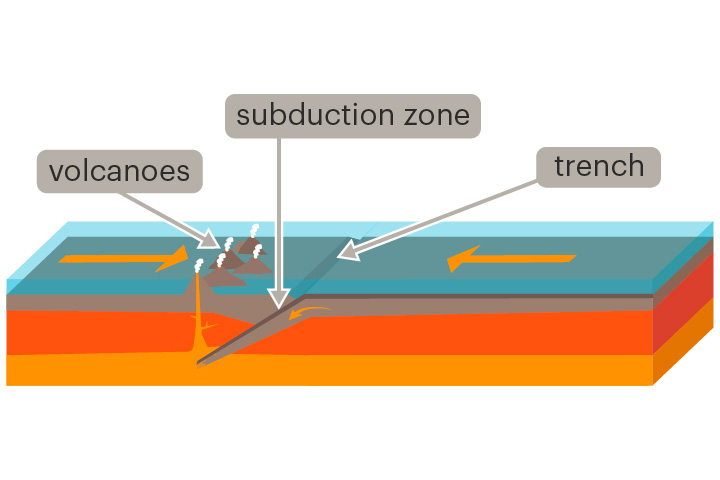
convergent boundary
A place where two tectonic plates move towards each other
At convergent boundaries, mountain ranges, ocean trenches and volcanoes can form.
At convergent boundaries, mountain ranges, ocean trenches and volcanoes can form.
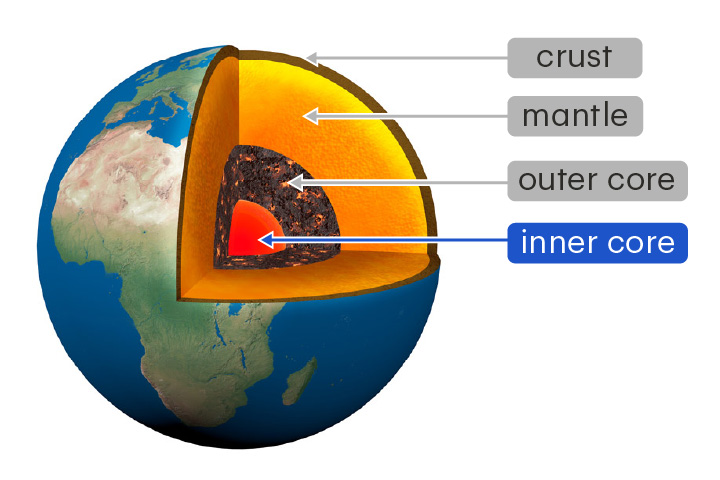
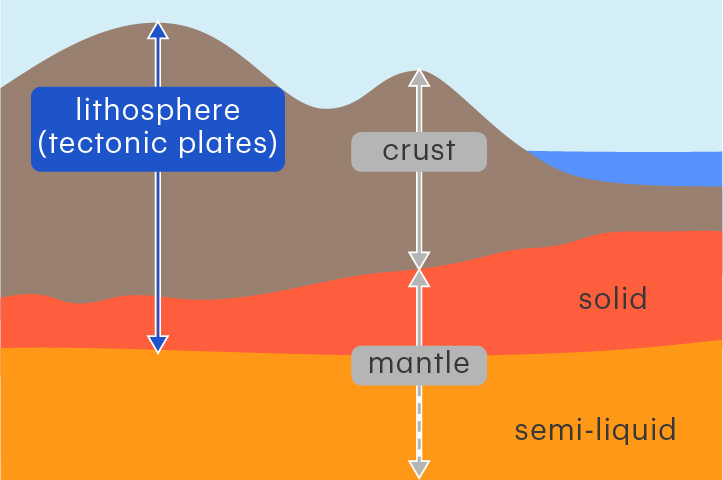
6
New cards
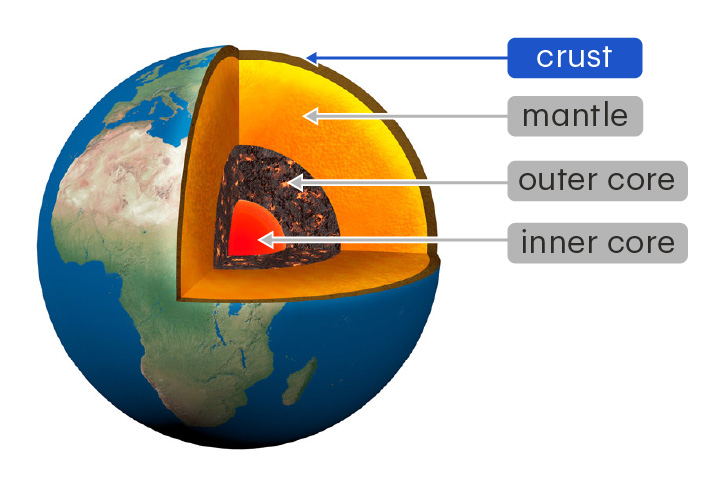
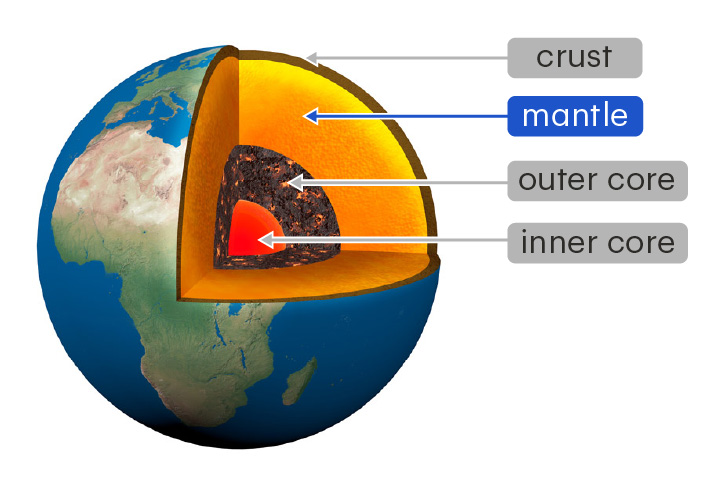
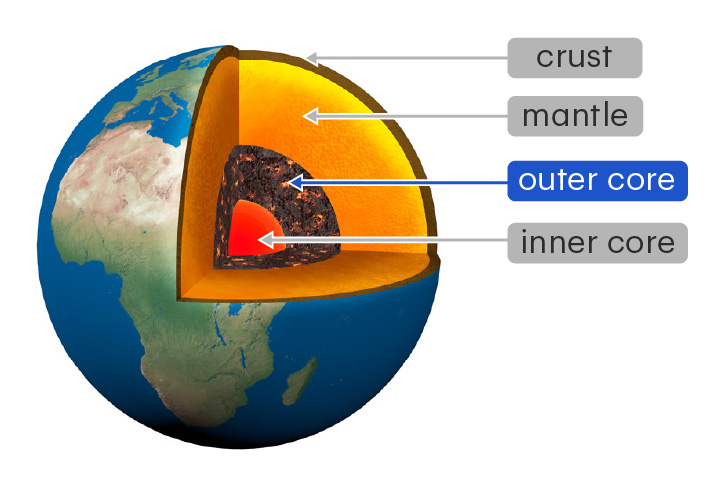
crust
The outermost layer of Earth
The crust is made of solid rock and is 5–70 km thick. It is thickest underneath the continents.
The crust is made of solid rock and is 5–70 km thick. It is thickest underneath the continents.
7
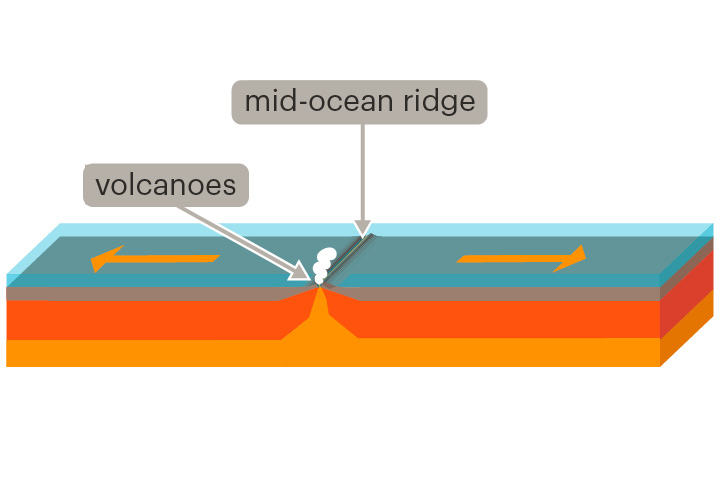
New cards
divergent boundary
A place where two tectonic plates move away from each other
At divergent boundaries, rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges can form.
At divergent boundaries, rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges can form.
8
New cards
earthquake
The sudden shaking of Earth's surface
An earthquake is a natural hazard that occurs when two slabs of rock suddenly slip against each other.
An earthquake is a natural hazard that occurs when two slabs of rock suddenly slip against each other.

9
New cards
erosion
The wearing away and removal of rock
Eroded sediment is transported by wind, water or ice.
Eroded sediment is transported by wind, water or ice.

10
New cards
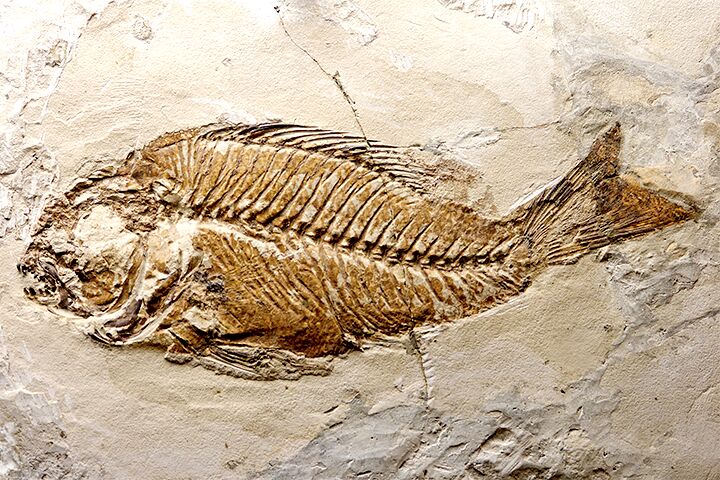
fossil
The remains or traces of an ancient organism preserved in rock
Fossils provide information about how life evolved and how Earth's surface has changed.
Fossils provide information about how life evolved and how Earth's surface has changed.

11
New cards
geologist
A scientist who studies the Earth
Geology is the scientific study of the processes that change the Earth and their history.
Geology is the scientific study of the processes that change the Earth and their history.

12
New cards
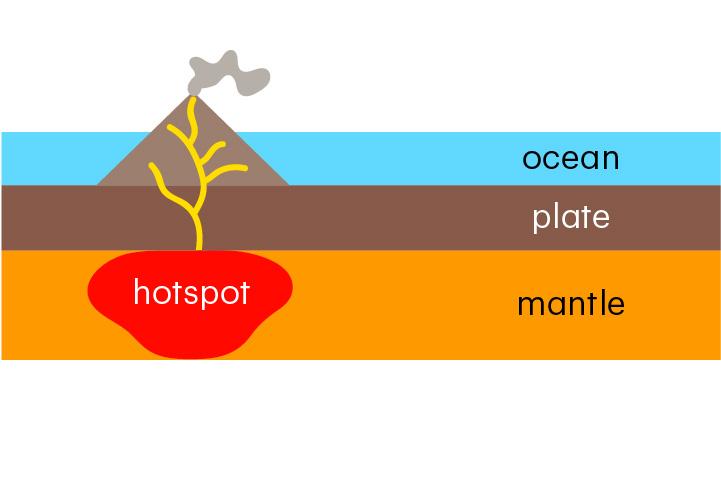
hotspot
An unusually hot part of the mantle where volcanoes can form
At hotspots, magma can rise through the crust to form volcanoes, even away from plate boundaries.
At hotspots, magma can rise through the crust to form volcanoes, even away from plate boundaries.
13
New cards
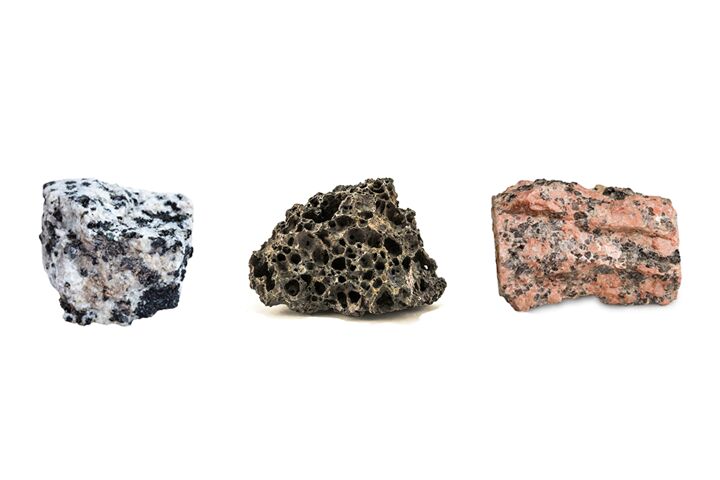
igneous rock
Any rock formed by the cooling of magma or lava
The size of the crystals in an igneous rock indicates the speed at which it cooled.
The size of the crystals in an igneous rock indicates the speed at which it cooled.

14
New cards
inner core
The innermost layer of Earth
The inner core is a solid mixture of iron and nickel at extreme pressures and temperatures.
The inner core is a solid mixture of iron and nickel at extreme pressures and temperatures.
15
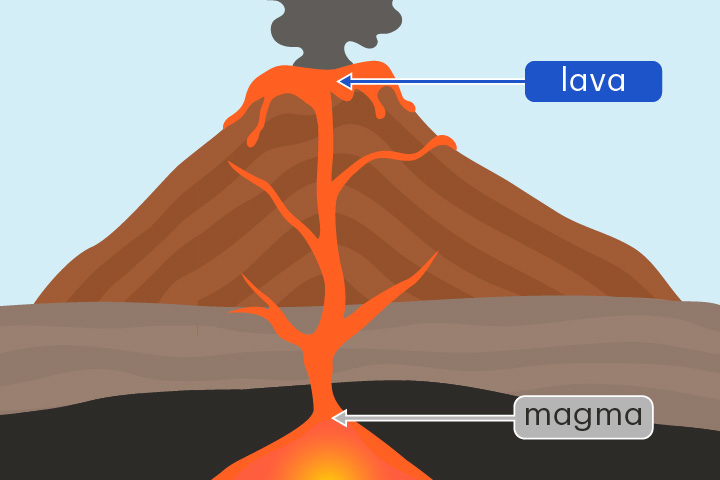
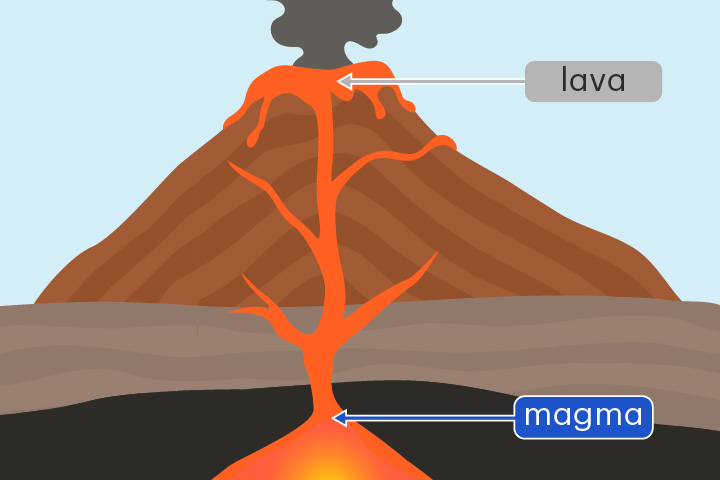
New cards
lava
Hot liquid rock located above the Earth's surface
When magma rises up from underground and flows on the surface it is called lava.
When magma rises up from underground and flows on the surface it is called lava.
16
New cards
lithosphere
The rigid outer part of Earth, made of the crust and upper mantle
The lithosphere is divided into slow-moving tectonic plates.
The lithosphere is divided into slow-moving tectonic plates.
17
New cards
magma
Hot liquid rock located below the Earth's surface
Magma can rise to the surface to form volcanoes.
Magma can rise to the surface to form volcanoes.
18
New cards
mantle
The thickest layer of Earth, between the core and the crust
The mantle is made of solid and partially melted rock. It can flow over very long timescales.
The mantle is made of solid and partially melted rock. It can flow over very long timescales.
19
New cards
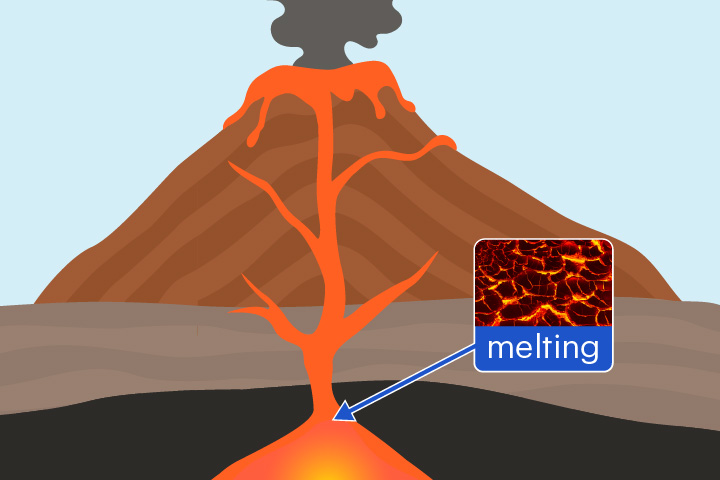
melting
A change of state from solid to liquid
When rock is heated deep underground, it melts to form magma.
When rock is heated deep underground, it melts to form magma.
20
New cards
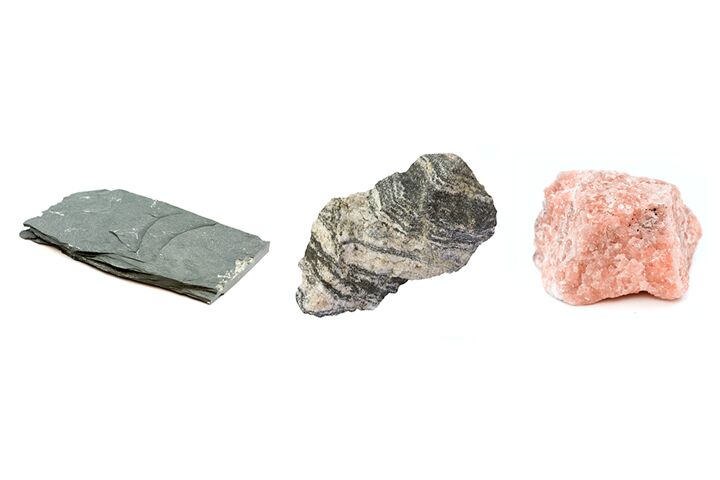
metamorphic rock
Any rock that has been changed by intense heat and pressure
Heat and pressure can change the types of minerals and the size and shape of the crystals.
Heat and pressure can change the types of minerals and the size and shape of the crystals.

21
New cards
mid-ocean ridge
An underwater mountain system where new oceanic crust forms
Mid-ocean ridges form at divergent boundaries. New oceanic crust is formed from cooling lava.
Mid-ocean ridges form at divergent boundaries. New oceanic crust is formed from cooling lava.
22
New cards
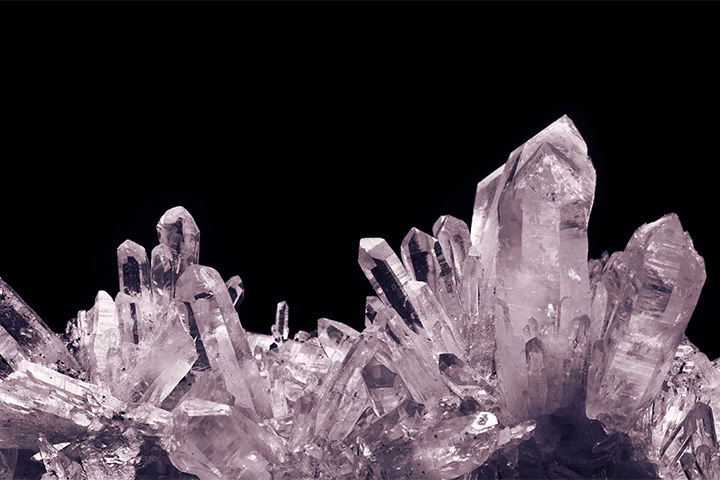
mineral
A natural substance usually found as crystals in rocks
Minerals are the building blocks of rocks. Quartz is a common rock-forming mineral.
Minerals are the building blocks of rocks. Quartz is a common rock-forming mineral.

23
New cards
mitigation
An action that decreases the harmfulness of an event
An emergency evacuation plan is one way to mitigate the damage from natural disasters.
An emergency evacuation plan is one way to mitigate the damage from natural disasters.

24
New cards
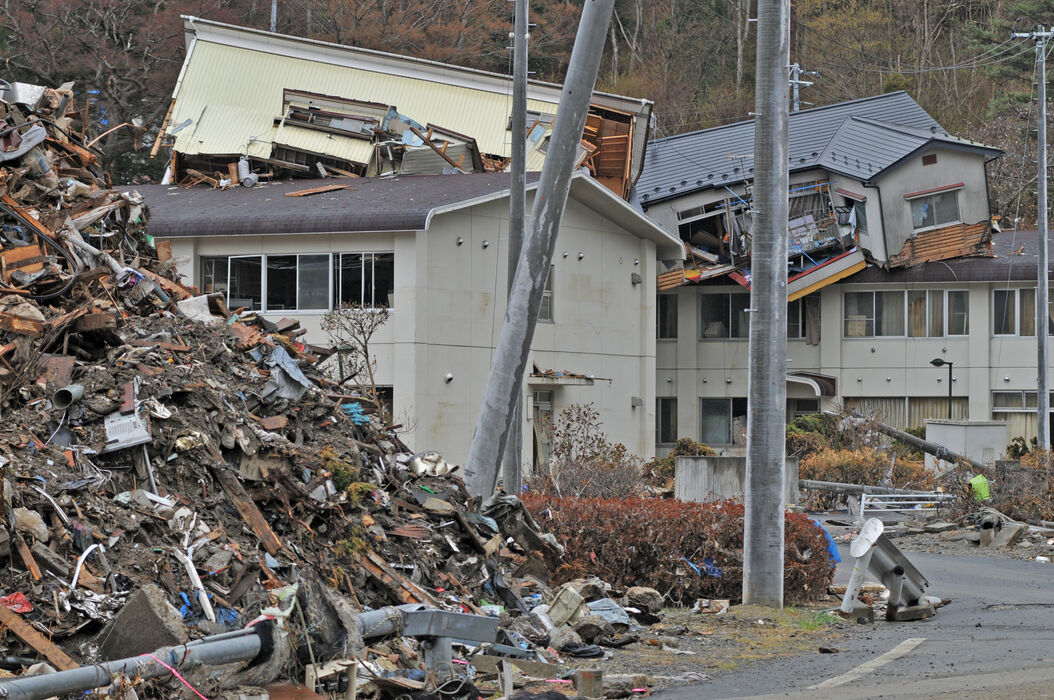
natural disaster
An event in the natural world that causes death and destruction
Natural disasters cause injuries, deaths and damage to buildings, roads and towns.
Natural disasters cause injuries, deaths and damage to buildings, roads and towns.

25
New cards
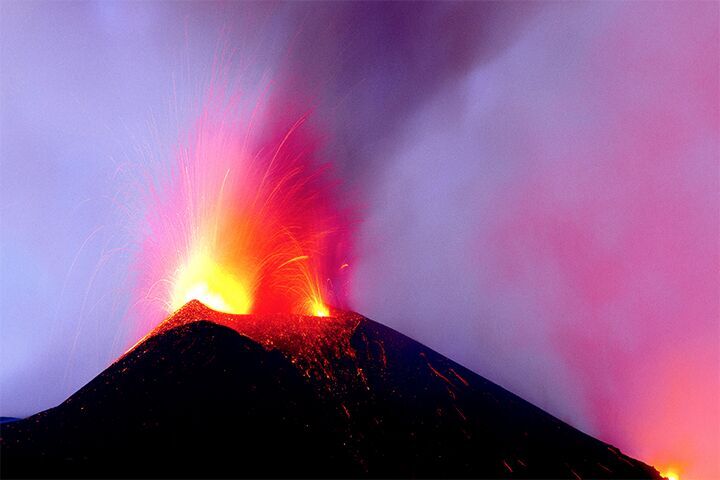
natural hazard
An event in the natural world that endangers living things
Natural hazards include volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and tsunamis.
Natural hazards include volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and tsunamis.

26
New cards
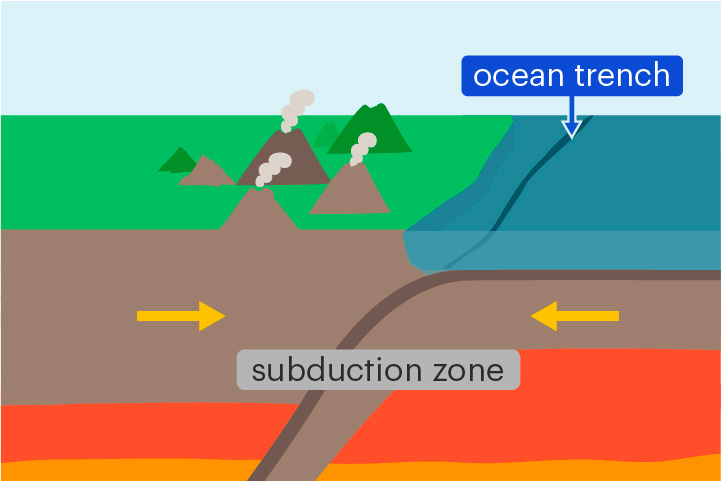
ocean trench
A deep valley in the ocean floor formed at a convergent boundary
Ocean trenches form where one plate subducts beneath another.
Ocean trenches form where one plate subducts beneath another.
27
New cards
oceanic crust
Crust that lies beneath an ocean
Oceanic crust is about 5–10 km thick and is made up of basalt, a dense volcanic rock.
Oceanic crust is about 5–10 km thick and is made up of basalt, a dense volcanic rock.
28
New cards
outer core
The layer of Earth that lies between the mantle and inner core
The outer core is a liquid mixture of iron and nickel. Its flow generates Earth's magnetic field.
The outer core is a liquid mixture of iron and nickel. Its flow generates Earth's magnetic field.
29
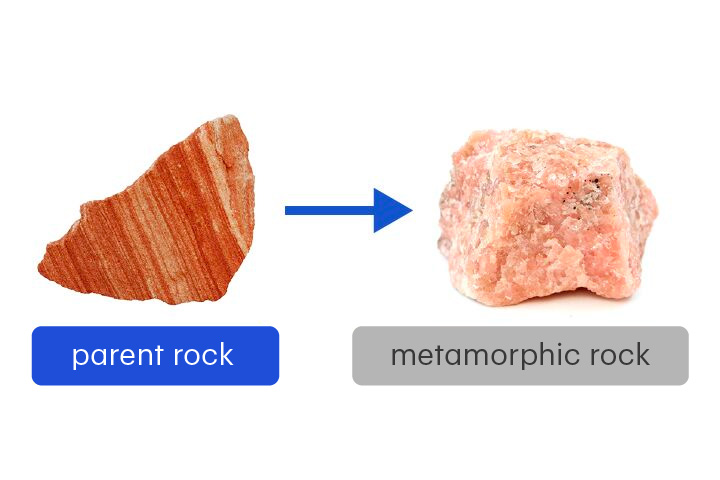
New cards
parent rock
The original rock from which a metamorphic rock formed
Parent rocks may be sedimentary, igneous or metamorphic.
Parent rocks may be sedimentary, igneous or metamorphic.
30
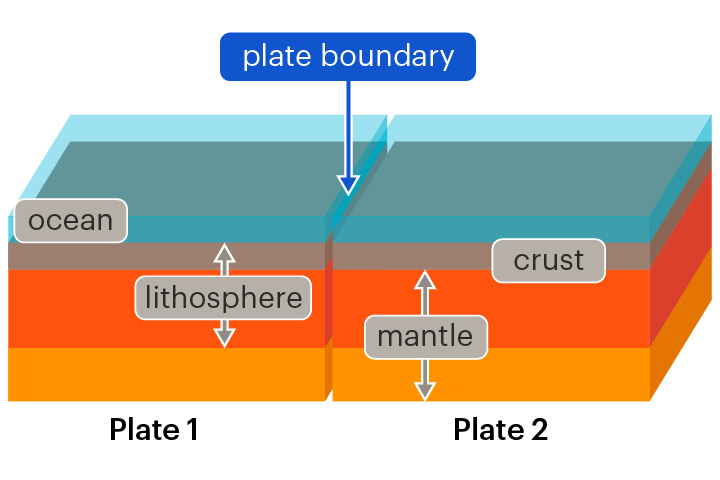
New cards
plate boundary
A border between two neighbouring tectonic plates
Tectonic plates interact at plate boundaries. This can cause earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Tectonic plates interact at plate boundaries. This can cause earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
31
New cards
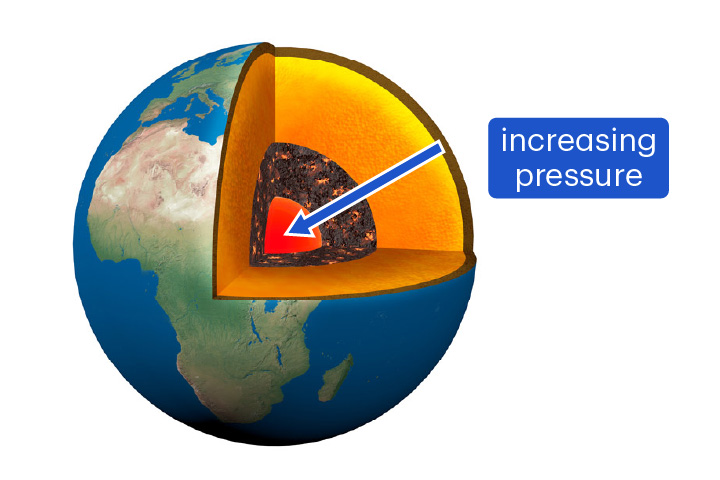
pressure
The amount of force applied over a certain area
Pressure can be measured in the units pascal (Pa) and gigapascal (GPa).
Pressure can be measured in the units pascal (Pa) and gigapascal (GPa).
32
New cards
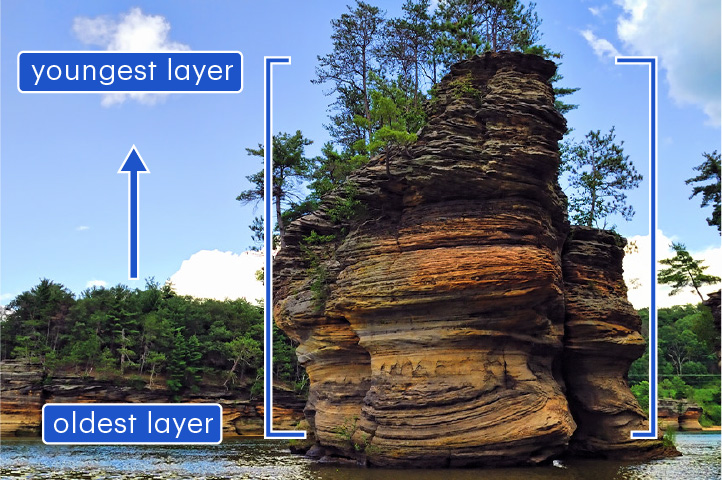
relative dating
A method to determine if one rock layer is older or younger than another layer
In a sequence of sedimentary rocks, the lowest layer has the oldest relative age.
In a sequence of sedimentary rocks, the lowest layer has the oldest relative age.
33
New cards
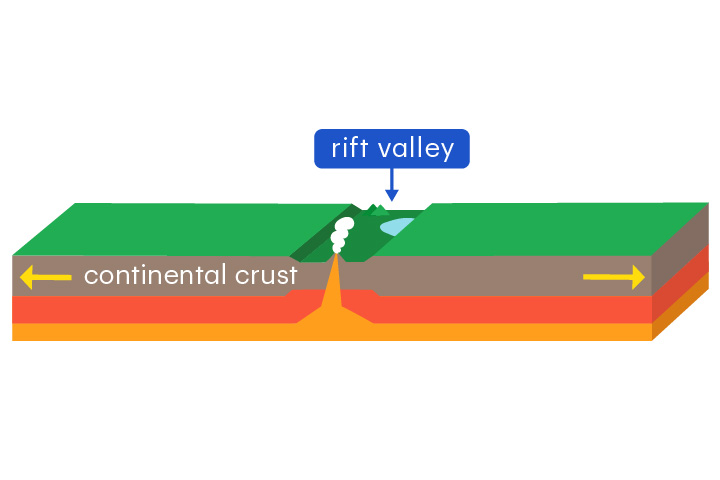
rift valley
A long depression formed when a continent is pulled apart
Rift valleys form at divergent boundaries in continental crust.
Rift valleys form at divergent boundaries in continental crust.
34
New cards
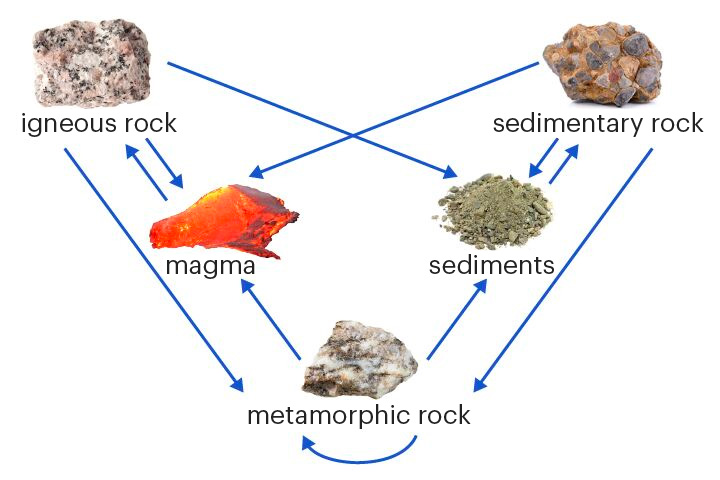
rock cycle
The set of changes that turn one rock type into another
Rocks can change between igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic types over millions of years.
35
New cards
seafloor spreading
The formation of new oceanic crust at a mid-ocean ridge
The discovery of seafloor spreading provided new evidence for continental drift theory.
The discovery of seafloor spreading provided new evidence for continental drift theory.
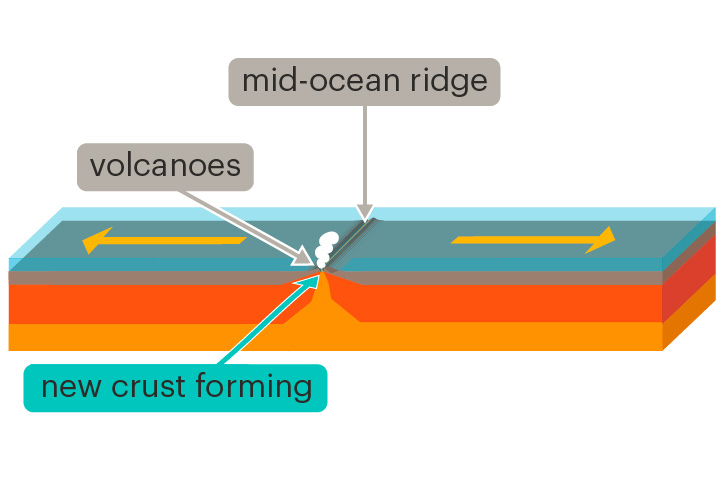
36
New cards
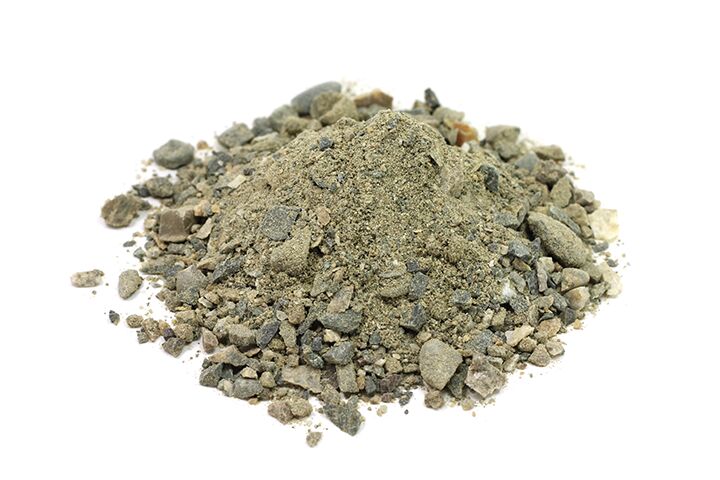
sediment
Small rock fragments such as mud, sand or gravel
Sediments form when rock is exposed to weathering and erosion.
Sediments form when rock is exposed to weathering and erosion.

37
New cards
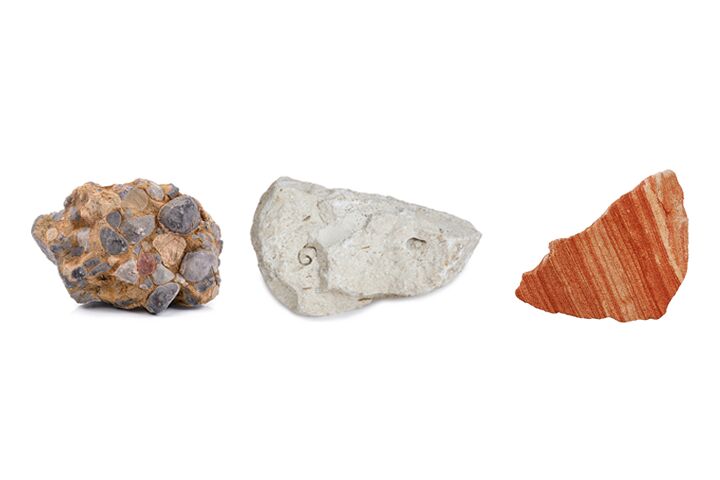
sedimentary rock
Any rock formed when sediment is compacted or cemented
Sedimentary rocks can also form from the remains of living things.
Sedimentary rocks can also form from the remains of living things.

38
New cards
solidification
A change of state from liquid to solid
When magma cools quickly, it solidifies to form a rock with small crystals.
When magma cools quickly, it solidifies to form a rock with small crystals.

39
New cards
subduction
The sinking of one tectonic plate beneath another
Subduction occurs at convergent boundaries. Denser crust sinks beneath less dense crust.
Subduction occurs at convergent boundaries. Denser crust sinks beneath less dense crust.
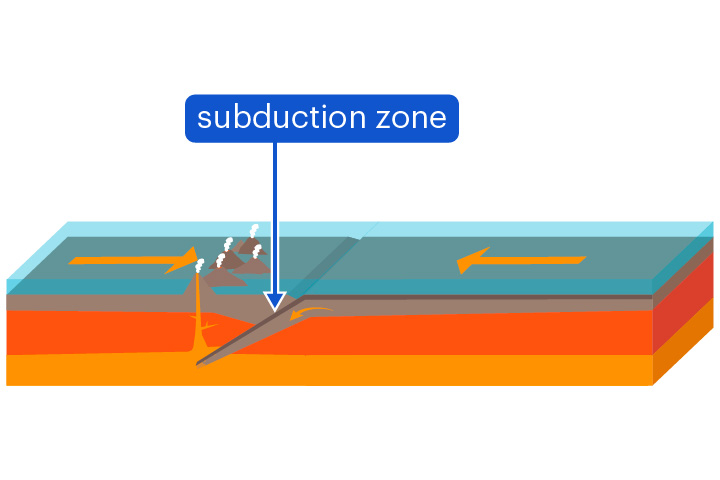
40
New cards
supercontinent
A single landmass made of smaller continents joined together
There have been many supercontinents in Earth's history. Pangaea existed 280 million years ago.
There have been many supercontinents in Earth's history. Pangaea existed 280 million years ago.

41
New cards
tectonic plate
A section of the crust and upper mantle
The movements of tectonic plates cause most earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
The movements of tectonic plates cause most earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
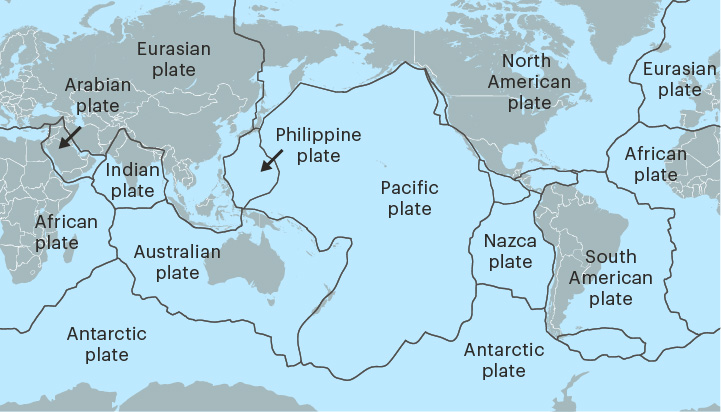
42
New cards
transform boundary
A place where two tectonic plates slide past each other
At transform boundaries, earthquakes often occur as pressure along faults is suddenly released.
At transform boundaries, earthquakes often occur as pressure along faults is suddenly released.
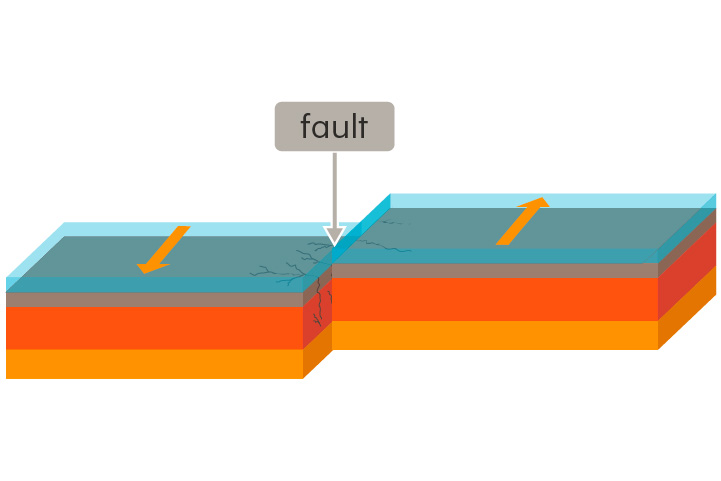
43
New cards
tsunami
A large ocean wave caused by an earthquake or coastal landslide
A tsunami is a natural hazard that can cause widespread damage to coastal towns and cities.
A tsunami is a natural hazard that can cause widespread damage to coastal towns and cities.
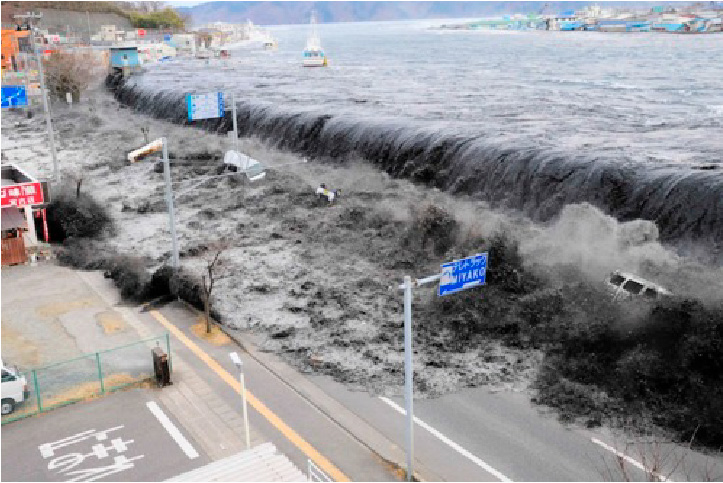

44
New cards
volcanic eruption
A release of magma at the Earth's surface
The eruption of hot liquid rock forms natural hazards such as lava flows and ash clouds.
The eruption of hot liquid rock forms natural hazards such as lava flows and ash clouds.

45
New cards
weathering
The breakdown of rocks into small grains or soil
Rocks at the surface are weathered by wind, flowing water, heat and other processes.
Rocks at the surface are weathered by wind, flowing water, heat and other processes.
