DYSLIPIDEMIA TREATMENT: PRIMARY PREVENTION
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What nutritional changes are recommended for primary prevention?
•Emphasize vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts, whole grains, and fish
• Replace saturated fat with non-unsaturated/ polyunsaturated fats
• Reduce cholesterol and sodium in diet
• Minimize processed meats, refined carbohydrates, sweetened beverages
• Avoid trans fats
What is recommended for exercise and physical activity for primary prevention?
• Optimize physically active lifestyle
• At least 150 minutes per week of moderate- intensity or 75-minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity
• If unable to meet minimum physical activity requirements, some moderate- or vigorous activity can be beneficial
What is recommended in terms of being overweight and obese for primary prevention?
Weight loss if recommended to improve ASCVD risk factor profile
• Counsel on comprehensive lifestyle intervention
What groups may not benefit from lipid-lowering primary prevention?
Age 0-19 (unless familial hypercholesterolemia)
Age 20-39 (unless family history of premature ASCVD or LDL-C ≥ 160 mg/dL)
Patients over 75 years (unless risk discussion warrants treatment)
What groups may benefit from lipid-lowering primary prevention?
All patients with LDL-C ≥ 190 mg/dL
Patients 40-75 years with diabetes
Patients 40-75 years with LDL-C ≥ 70 - < 190 mg/dL without diabetes (dependent on ASCVD-risk)
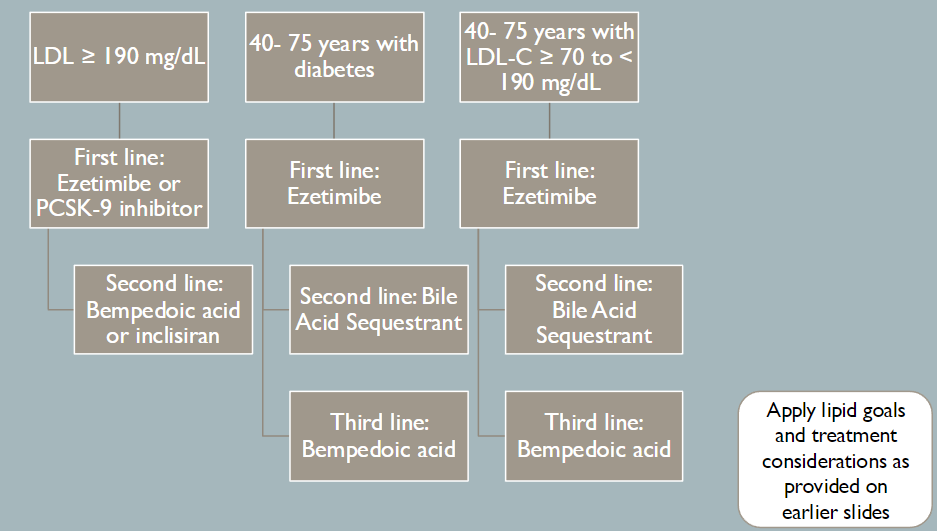
What is the primary prevention treatment for patients LDL-C ≥ 190 mg/dL and the therapeutic goal?
High Intensity Statin
Consider Ezetimibe and/or PCSK-9 inhibitors
May consider bempedoic acid or inclisiran
Goal: Lowers LDL-C by 50% and LDL-C to less than 100 mg/dL and non- HDL-C less than 130 mg/dL
How do you choose between ezetimibe and a PCSK-9 inhibitor for patients LDL-C ≥ 190?
Favors ezetimibe:
• <25% additional LDL-C lowering required
• Cost
• Lack of injection
Favors PCSK-9 inhibitor:
• > 25% additional LDL-C lowering required
• Patient preference
How do you choose between bempedoic acid and inclisiran for patients LDL-C ≥ 190?
Favors bempedoic acid:
• <17% additional LDL-C lowering required
• Lack of injection
Favors inclisiran:
• > 17% additional LDL-C lowering required
• Desire for twice yearly dosing regimen
What should be noted about the treatment of patients with LDL-C ≥ 190?
• Ezetimibe and/or PCSK-9 should be ADDED to maximally tolerated statin therapy
• Bempedoic acid can be ADDED to regimen
• Inclisiran can be ADDED to regimen, but should NOT be used with PCSK-9 inhibitor
What is the cutoff for patients considered to be a high risk for PATIENTS 40- 75 YEARS WITH DIABETES
Patients are high-risk if:
10-year ASCVD Risk Score ≥ 7.5% or Diabetes-Specific Risk Enhancers
What is the treatment for 40- 75 YEARS WITH DIABETES not at high risk and therapy goal?
Moderate Intensity Statin
High Intensity Statin
Add Ezetimibe
Therapy goal: Lowers LDL-C greater than or equal to 30-49% and LDL-C less than 100 mg/dL and non-HDL-C less than 130 mg/dL on at least moderate intensity statin
What is the treatment for 40- 75 YEARS WITH DIABETES at high risk and therapy goal?
High intensity statin
Ezetimibe
Therapy goal:
if 10-year ASCVD < 20%:
Lowers LDL-C ≥ 50% and LDL-C < 100 mg/dL and non-HDL-C < 130 mg/dL
10-year ASCVD ≥ 20%:
Lowers LDL-C ≥ 50% and LCL-C < 70 mg/dL and non- HDL-C < 100 mg/dL
How is PATIENT S 40- 75 YEAR S WITH LDL-C ≥ 70 TO < 190 MG/DL grouped/assessed?
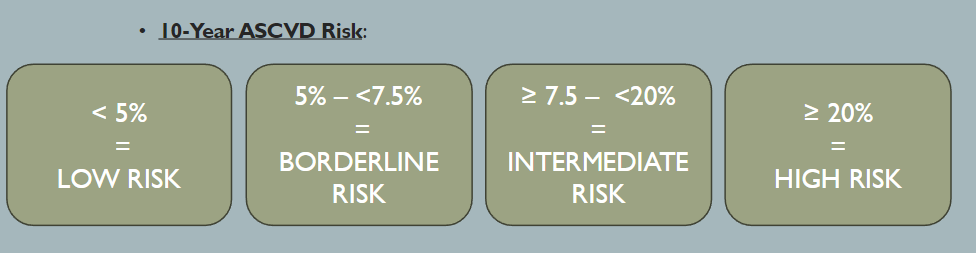
What is the primary treatment with PATI ENT S 40- 75 YEARS WITH LDL-C ≥ 70 TO < 190 MG/DL at a low risk and the therapeutic goal?
If Risk enhancers present, moderate statin
High Intensity Statin
Therapy goal:
Lowers LDL-C ≥ 30-49% and LDL-C < 100 mg/dL and non-HDL-C < 130 mg/dL on at least moderate intensity statin
What is the primary treatment with PATI ENTS 40- 75 YEARS WITH LDL-C ≥ 70 TO < 190 MG/DL at intermediate/borderline risk and the therapeutic goal?
If risk enhancers present, moderate statin
high intensity statin
Therapy goal:
Lowers LDL-C ≥ 30-49% and LDL-C < 100 mg/dL and non-HDL-C < 130 mg/dL on at least moderate intensity statin
What is the primary treatment with PATI ENTS 40- 75 YEARS WITH LDL-C ≥ 70 TO < 190 MG/DL at a high risk and the therapeutic goal?
High Intensity Statin
Ezetimibe
Therapy goal: Lowers LDL-C ≥ 50% and LCL-C < 70 mg/dL and non-HDL-C < 100 mg/dL
What is recommended for patients that cant tolerate statins?
What are the recommendations for Aspirin for Adults aged 40 to 59 years with a 10% or greater 10-year cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk?
Small benefit
What are the recommendations for Aspirin for Adults 60 and older?
Not recommended
How to manage statin side effects
1.Discontinue statin therapy until symptoms are relieved
2. Rechallenge with statin therapy to determine if symptoms recur
3. If pain still exists, use statins that are metabolized by different pathways and that have different lipo/hydrophilicity
4. Attempt lowest approved dose and alternative dosing
True statin intolerance
Unacceptable muscle-related symptoms that resolve with
discontinuation of therapy and recur with rechallenge on at
least 2 (preferably 3) statins that are metabolized by
different pathways, have different lipo/hydrophilicity, and at
the lowest approved dose