bio unit 1 12U
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
how many bonds can carbon form
4
what atoms make up the base of every organic molecule
carbon atoms
hydrocarbon consist of
carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms
shapes of carbon skeleton
linear, branched, or closed ring shape
Carbon Structure: linear
fats
Carbon Structure: ring
carbohydrate
organic
found in living things
organic molecules
large molecules that are found mainly in living things
all organic molecules are composed of mainly
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
monomer
(simplest unit) a molecule that may react chemically to another molecule of the same type to form a larger molecule
polymers
large molecules that are formed when monomers link together chemically in a chain
monosaccharide → polymer name
polysaccharides (carbohydrate)
fatty acids → polymer name
lipids
amino acids → polymer name
protein
nucleotide → polymer name
nucleic acid
amount of bonds that carbon can do
3 different ways producing 3 different shaped bond
functional groups
“additives” that
hydroxyl group increases
polarity
carboxyl groups increase
acidity and polarity of a molecule
amino and sulfhydryl groups are found
primarily in proteins and DNA/RNA
anything that is polar
can dissolve in water
carbohydrates classifications
monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides
carbohydrates purposes
source of energy, “identification flags” on cells and molecules, structural building blocks (ie. cellulose in cell walls of plants)
monosaccharide
simple sugar
composed of C - H - O
a 1:2:1 ratio
anything that ends in “ose”
a sugar
dehydration
anabolic reactions: take water to build bonds
hydrolysis
catabolic reactions: adding water to break bonds
glycosidic bond
only carbohydrates have this bond (creating a disaccharide)
carbohydrates have 2 functional groups
hydroxyl (OH) & carbonyl (carbon double bonded to an oxygen)
monosaccharides & disaccharides polarity
polar, hydrophilic, soluble
sucrose
disaccharide: glucose + fructose
lactose
disaccharide: galactose + glucose
maltose
disaccharide: glucose + glucose
polysaccharide monosaccharide amount
hundreds to thousands linked by glycosidic
polysaccharide polarity
polar, hydrophilic, non-soluble(b/c large size)
cellulose
polysaccharide
glycogen
polysaccharide: energy storage for animals
starch
polysaccharide: energy source for plants
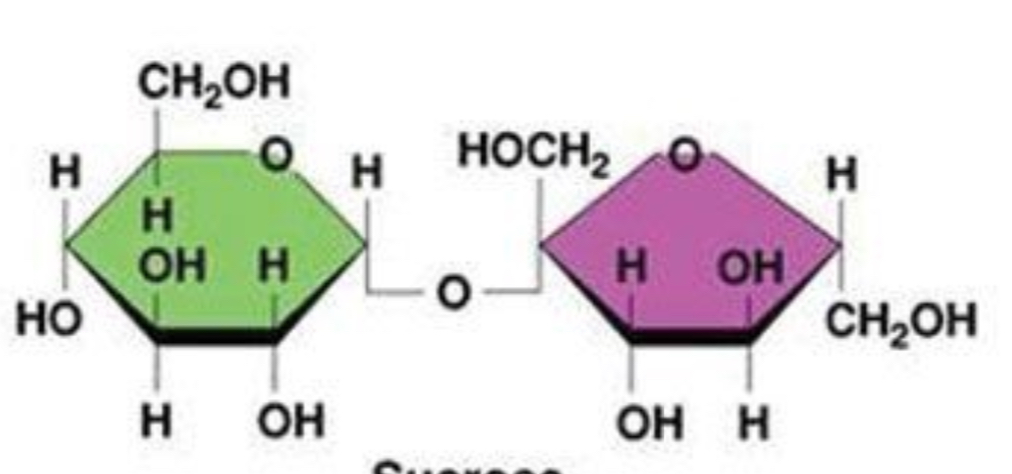
sucrose: alpha glycosidic bond (straight across)
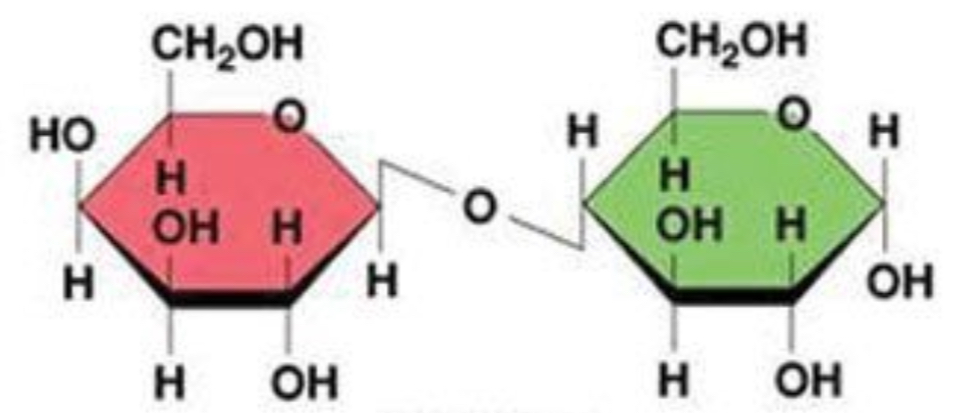
lactose: beta glycosidic bond (slanted)
cellulose bonds
has both alpha and beta glycosidic bonds
maltose bond
alpha glycosidic bond
hydrolysis word meaning
hydro = water, lysis = split
which linkage tends to be tougher
beta linkages
triglyceride composition
3 carbon glycerol molecule attached to 3 long chained fatty acids
all fatty acids have this functional group
carboxyl
ester linkage
when a fat creates a bond
functional group that glycerol has
hydroxyl
lipids (in animals)
main energy stores
animal lipids state
solid at room temp
plant oils state
liquid at room temp
structure of animal fats
single bonds and max amount of hydrogens
structure of plant fats
at least one double or triple bond (can have more) and less hydrogens
saturated fats
animal fats, solid at room temp, long fatty acid tail and single bonds
unsaturated fats
plant fats, liquid at room te mp, shorter fatty acid chains and double or triple bonds “have bends to it”
steroids
special lipids with carbon rings inside of them that are large and heavy, easier to transport through the bloodstream, can pass through fatty portion of CM as well become part of CM
wax
found in plants and some parts of animals, solid at room temp and can soften with increased temp
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
RNA
ribonucleic acid
nucleotide composition
phosphate, pentosugar and nitrogen base
DNA vs RNA
DNA has one less oxygen, one less hydroxyl group
RNA has one more oxygen, one more hydroxyl group
DNA is double stranded
RNA is single stranded
DNA has G, A, C, T
RNA has G, A, C, U
DNA is found in the nucleus and mitochondria
RNA is found attached to rough ER, cytoplasm, and nucleus
DNA is self-replicating
RNA is synthesized utilizing DNA
bond between nitrogenous bases
hydrogen bonds
pyrimidines
single ring (C, T, U)
purines
two rings (A, G)
A & T hydrogen # of bonds
2
C & G hydrogen # of bonds
3
phosphodiester linkage
bond found in nucleic acids, occurs at carbon 3
5 prime nucleotide
has phosphate group
3 prime nucleotide
does not have phosphate group
proteins
form necessary structures for all types of tissues, serve as chemical signallers, subunits are amino acids
amino acid composition
a central carbon, an amino functional group, a hydrogen, a carboxyl functional group, and an R-group that varies
peptide bond
formed between the amino group & carboxyl group of two amino acids
N terminus
first amino acid
C terminus
last amino acid, can only add amino acids through this end
polypeptide
several (50+ usually) amino acids strung together by peptide bonds
dipeptide
2 amino acids with a peptide bond
4 levels of protein organization
primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure
primary structure
a unique linear sequence of amino acids, 50 or more a.a. strung together by peptide bonds, known as a polypeptide
2 forms of secondary structure
Beta pleated sheet: forms a side-by-side alignment
or
A helix: hydrogen bonds between every 4th amino acid
how secondary structures are created
created as the protein begins to fold in on itself - atoms on the protein molecule begin interacting with other parts of the chain to create 3D shapes
tertiary structure creation
created by the side chains (R-group to R-group interactions) interacting with each other. This creates further folding → functional 3D structure, one can see multiple secondary structures within
quaternary structure creation
created when multiple tertiary structures come together to form a protein
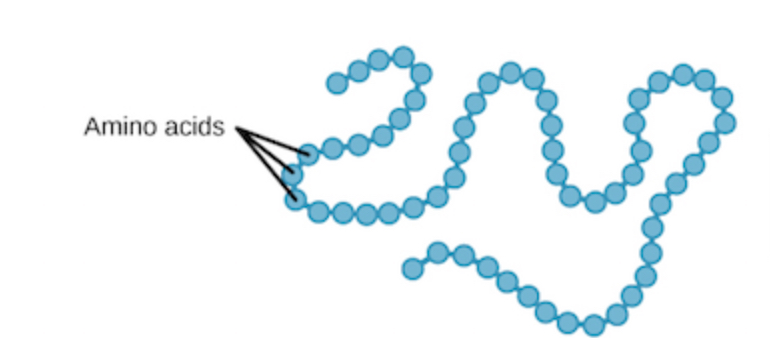
primary structure
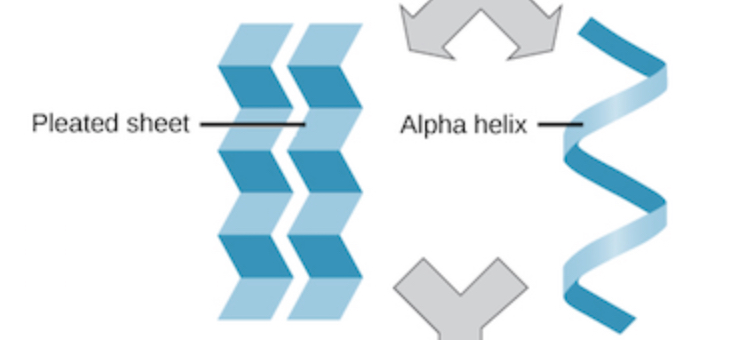
secondary structure
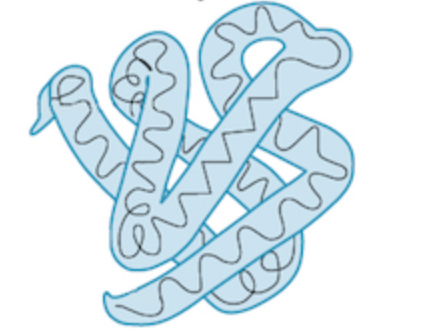
tertiary structure

quaternary structure
hydrophobic interactions (protein bonds)
amino acids orient themselves towards the centre of the polypeptide to avoid the water
disulphide bridge (protein bonds)
amino acid cysteine forms a bond with another cysteine forms a bond with another cysteine through its R group
hydrogen bonds (protein bonds)
Polar “R” groups on the amino acids form bonds with other Polar “R” groups
hydrophilic interactions (protein bonds)
these amino acids orient themselves outward to be close to the water
ionic bonds (protein bonds)
positively charged R group
codon
a structure that has 3 nitrogenous bases that codes for one amino acid
start codon
A U G and it’s methionine
stop codons
UAA, UAG, UGA
DNA and RNA process
DNA replication → RNA transcription → RNA processing → mRNA transport → protein translation