Handout 1 - Introduction, Prehistoric Art, Ancient Near Eastern Art, Ancient Egyptian Art
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Paleolithic
Begins about 200,000 BCE; The “old” Stone Age, during which humankind produced the first sculptures and paintings
Neolithic
Begins about 8,000 BCE
Bronze Age
Begins 3,000 BCE
Archaeology
Study of human past through the material remains genetic archaeology, inherited DNA, both in fossils and humans
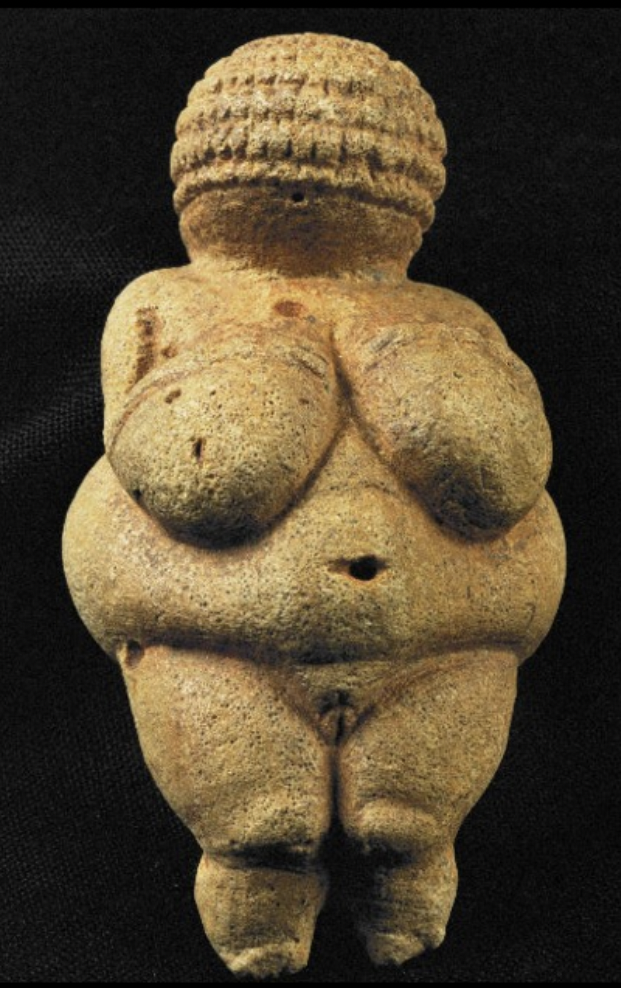

Venus of Willendorf (Austria), ca. 28,000 BCE, limestone with traces of red paint
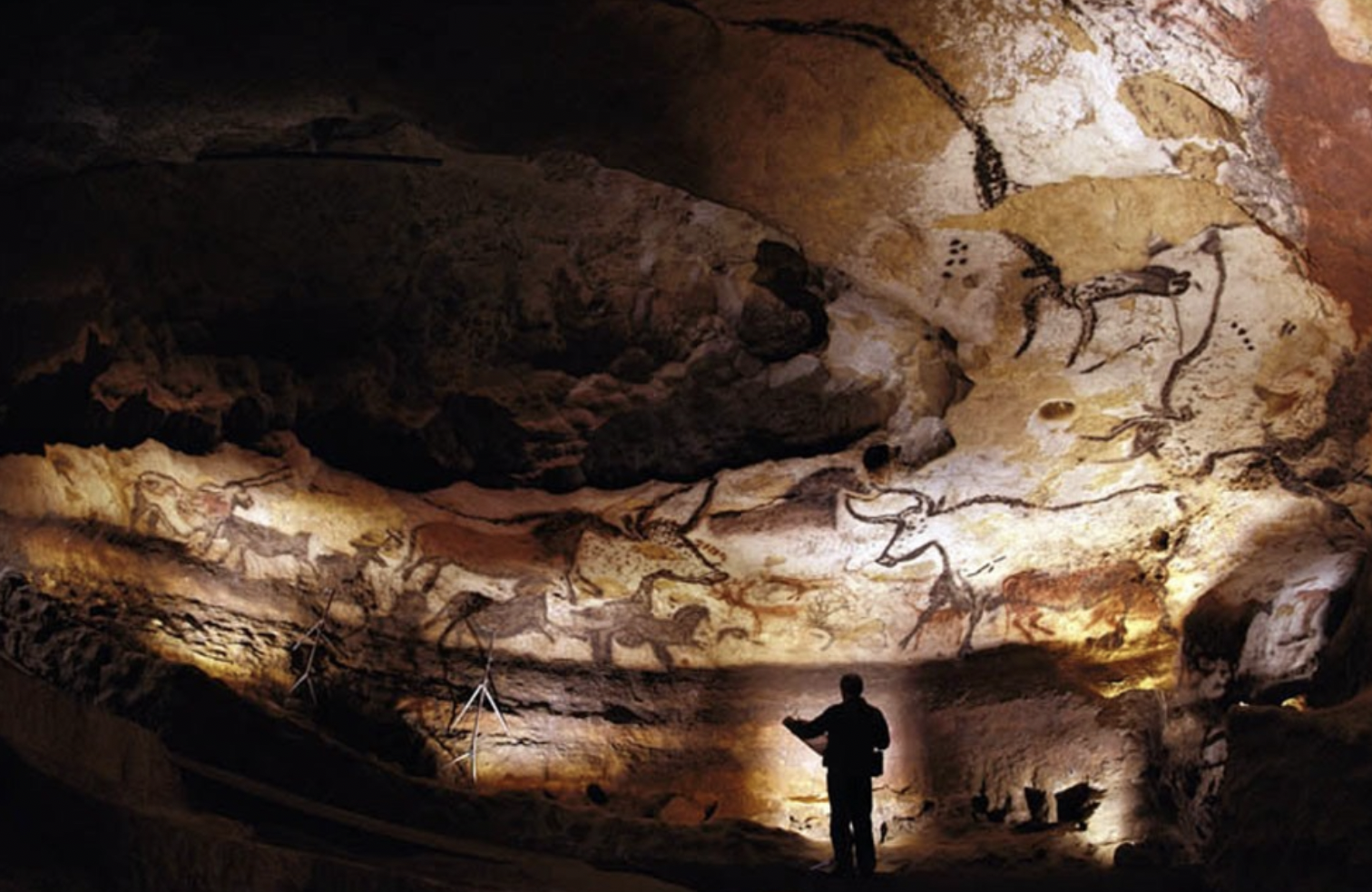

Hall of Bulls, Lascaux Cave (France), painting, ca. 16,000-13,000 BCE
Twisted Perspective
When a subject is represented from multiple view points at once
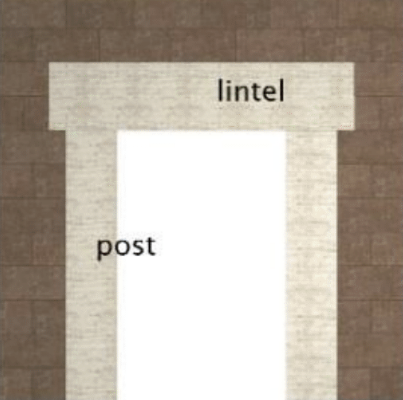
Post and lintel door opening; construction in which two upright elements support a horizontal element
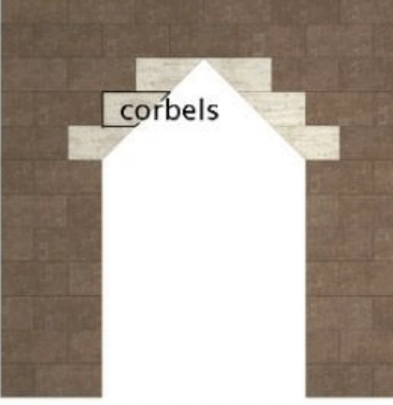
Corbel arch door opening
Megalith
Construction in large stones, corbel vault
Corbel
A projection in a wall that supports a beam or other object above
Corbel Vault
A stone ceiling made of corbels (technically not a vault)

Visual Art
This term refers to the practice of creating works that are primarily visual in nature, including painting, sculpture, photography, and digital art. It focuses on aesthetics, composition, color, and form to convey ideas, emotions, or narratives.
Archaeology
The scientific study of human history and prehistory through the excavation of sites and the analysis of artifacts, structures, and other physical remains. It helps us understand past cultures and societies.
Medium/Media
Material used; The material in which an artist works; also, in painting, the vehicle (usually liquid) that carries the pigment
Ex. Bronze, marble, clay
Pigment
Color ingredient
Support
What was painted on
Mural
A wall painting
Fresco
Painting on lime plaster, either dry or wet. In the latter method, the pigments are mixed with water and become chemically bound to the freshlt laid lime plaster, allowing the colors to bond as the plaster dries. This method is known for its durability and vibrant colors. Often found in historical buildings, churches, and palaces, with notable examples including Michelangelo's Sistine Chapel ceiling.
Carving & Modeling
Carving: Subtractive; created by cutting away; hard material
Modeling: Additive; soft material; created by building up; soft material
Lost Wax Casting
A metal casting process that involves creating a wax model of the desired object, encasing it in a mold, and then melting away the wax to leave a cavity. Molten metal is poured into the mold to create the final product, allowing for intricate designs and precise details.
Relief Sculpture
A type of sculpture where the figures are raised above the background. It can be classified into two main types:
Low Relief (Bas-Relief): The projection from the background is minimal.
High Relief: The figures project significantly from the background, often with parts fully detached.
Relief sculptures are commonly found in architecture and monuments. In low/bas relief, artists cut designs into the surface so that the highest projecting part of the image are no higher than the surface itself.
Sculpture in the Round
Free standing figures, carved or modeled in three dimensions
Architecture
The art of designing buildings (once considered a minor art/decorative art)
Patron
Person/entity (business, church, etc), who employs the artist
Patronage
Refers to the support, encouragement, or financial aid that an organization or individual provides to artists, writers, or other creators. It can also denote the practice of appointing individuals to positions of power or influence, often based on their loyalty or service rather than merit. Patronage has historically played a significant role in the arts and politics.
Visual Analysis
A method of examining art, architecture, or design to understand its communication and functionality. It involves assessing elements like composition, color, form, and context to interpret meaning and impact
Iconography
The study of a work of art’s subject matter or symbolism
What does the picture represent? Does the picture tell a story? Are the images symbolic?
Iconographic categories
Narrative; religious, historical, mythological
Genre paintings; paintings of everyday life
Landscapes (and seascapes and cityscapes)
Still-life paintings; paintings of inanimate objects
Portraits
Do the visuals contribute to the meaning?
Iconology
The study of visual imagery and its symbolism in art and culture. It goes beyond mere description of images to interpret the deeper meanings and cultural contexts behind them; analyze how images reflect societal values, beliefs, and historical contexts.
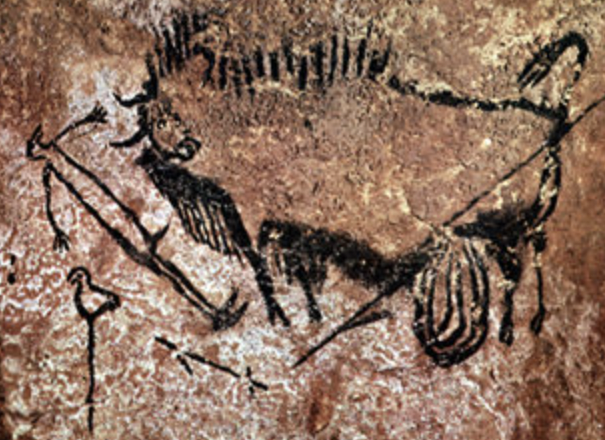

Lascaux Cave(France), ca.16,000-13,000 BCE, Wounded Man
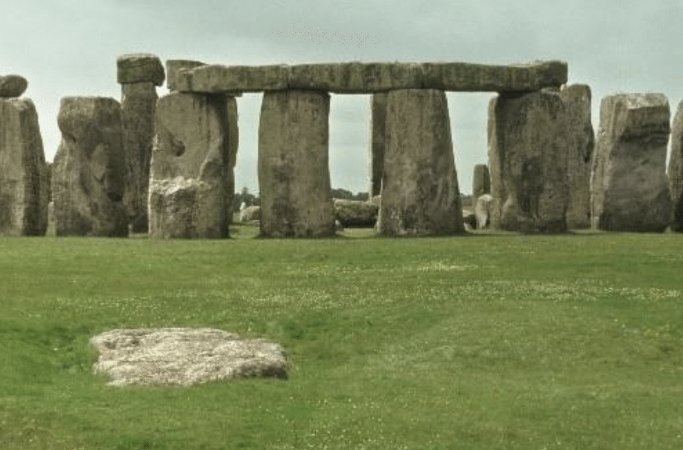

Stonehenge, Salisbury Plain (England), ca.2550-1600 BCE, stone (megaliths)
Ziggurat
Temple raised on a high platform
Cella
Innermost room of a temple
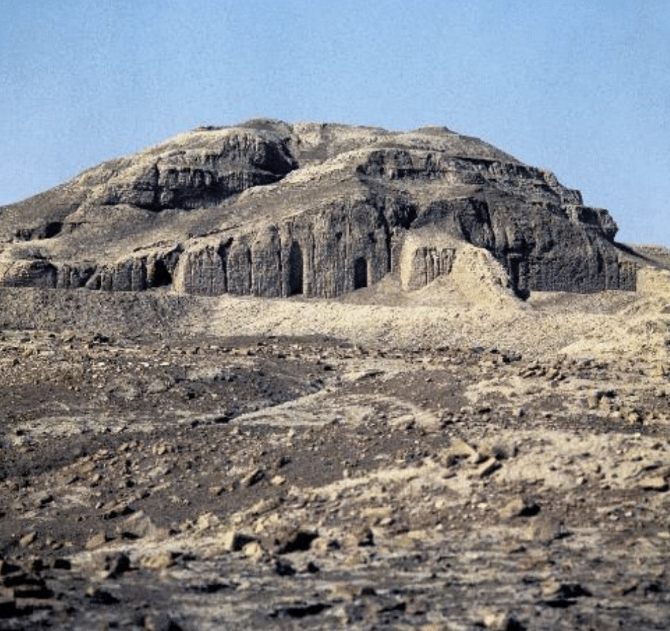

White Temple and ziggurat, Uruk (modern Warka, Iraq), ca. 3200–3000 BCE
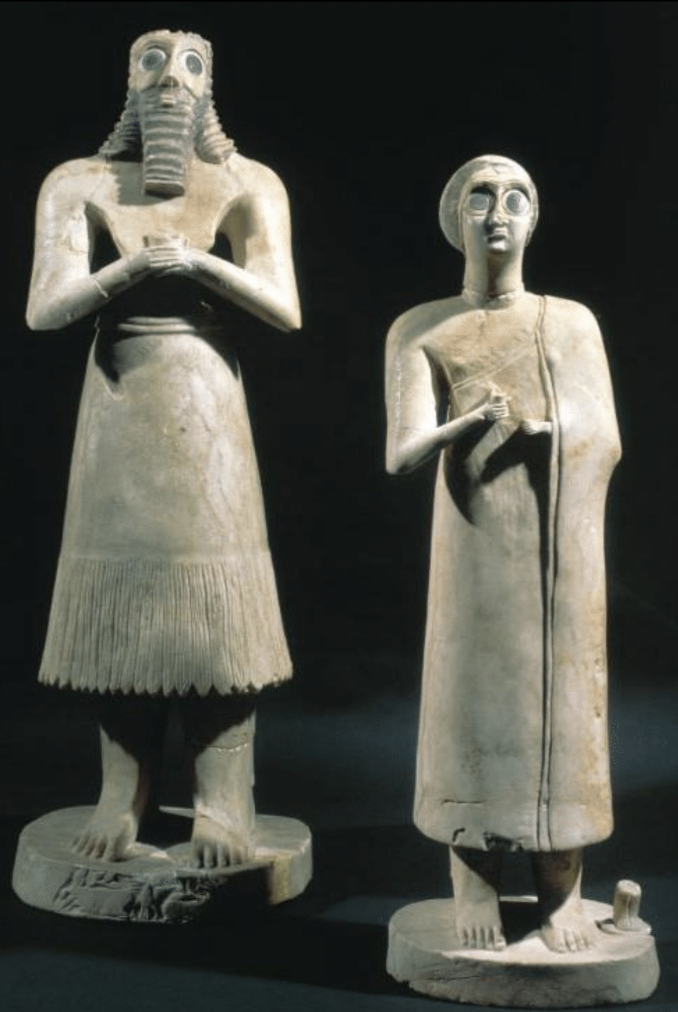

Statues of worshippers, ca. 2700 BCE, gypsum, shell, black limestone
Pharaoh
A ruler/king in Ancient Egypt
Hierarchical Scale
An artistic technique that uses unnatural proportions to emphasize the importance of certain figures or objects in a work of art. In this technique, figures of higher importance are depicted as larger than those of lesser importance
Pharaohs and other important figures were depicted as much larger than other figures in paintings and sculptures.
Ka
Spirit of life or force
Mastaba
Standard tomb in Ancient Egypt
Pyramid
Monument structures to house the tombs of the pharaohs
Sarcophagus
Stone coffin
Papyrus
A material and plant invented by the Egyptians around 3000 B.C. as a writing surface and was used for writing, art, transportation, and construction
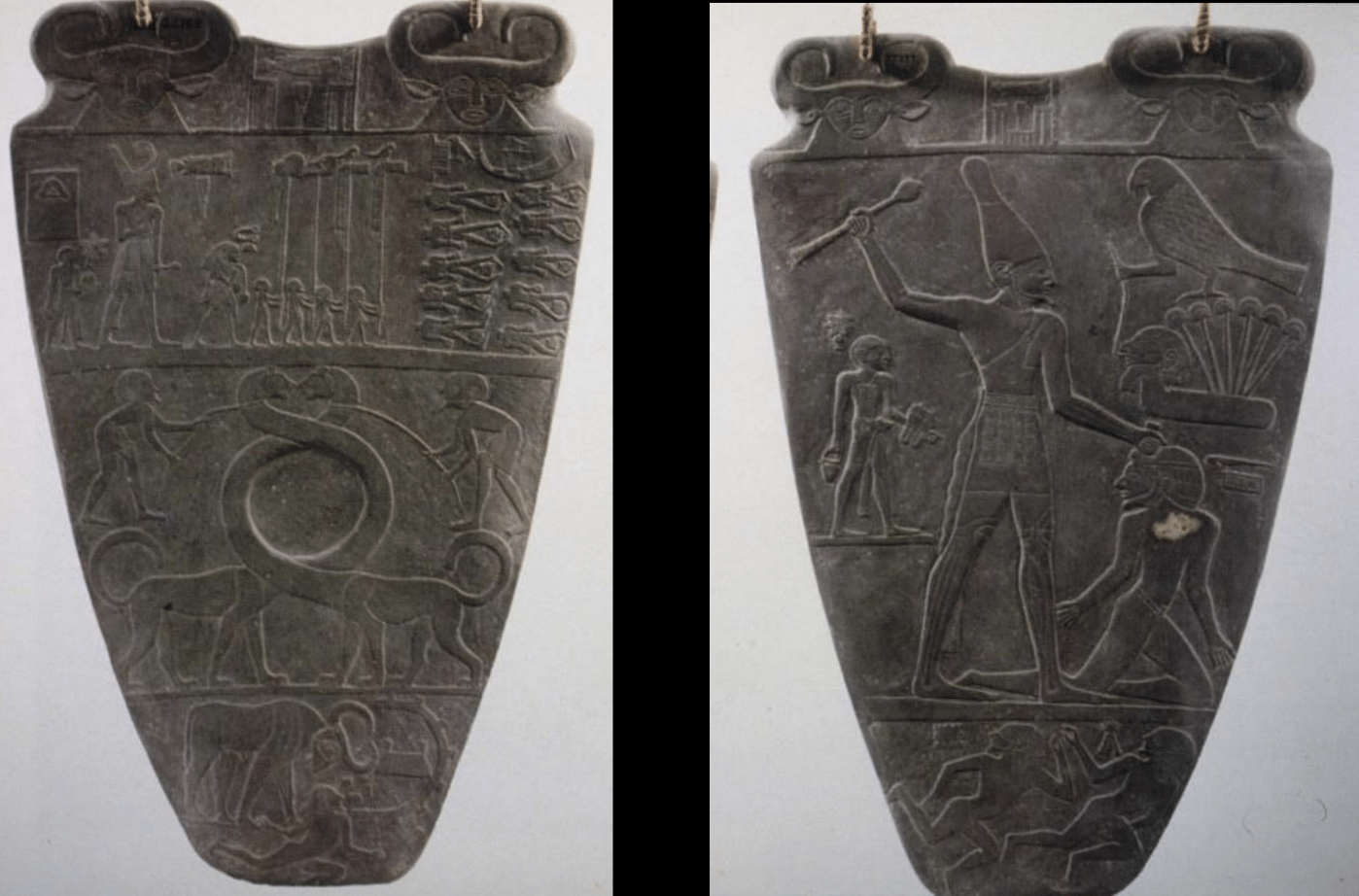

Palette of King Narmer, ca.3000-2920 BCE, slate
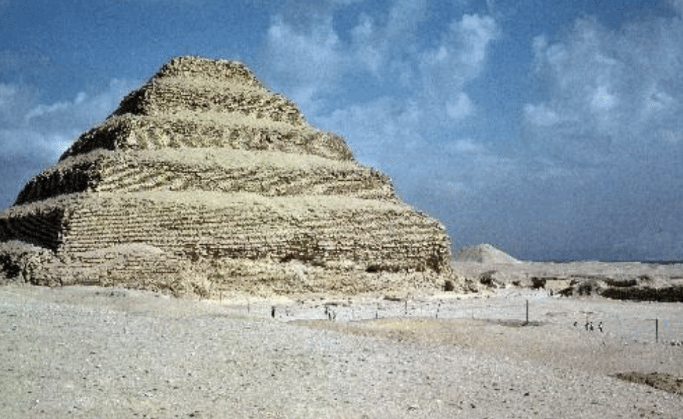

Imhotep, Stepped pyramid and mortuary precinct for Pharaoh Djoser, Saqqara (Egypt),2630-2611 BCE
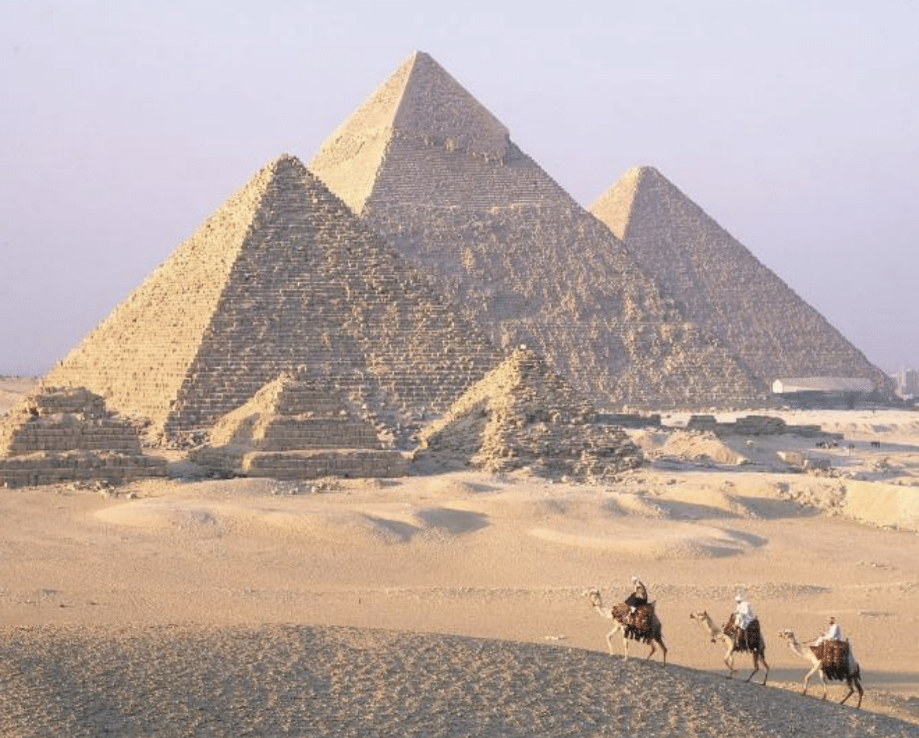

Great Pyramids of Pharaohs Khufu (Grandfather), Khafre (Father), and Menkaure(Son), Gizeh (Egypt), ca. 2528-2490 BCE
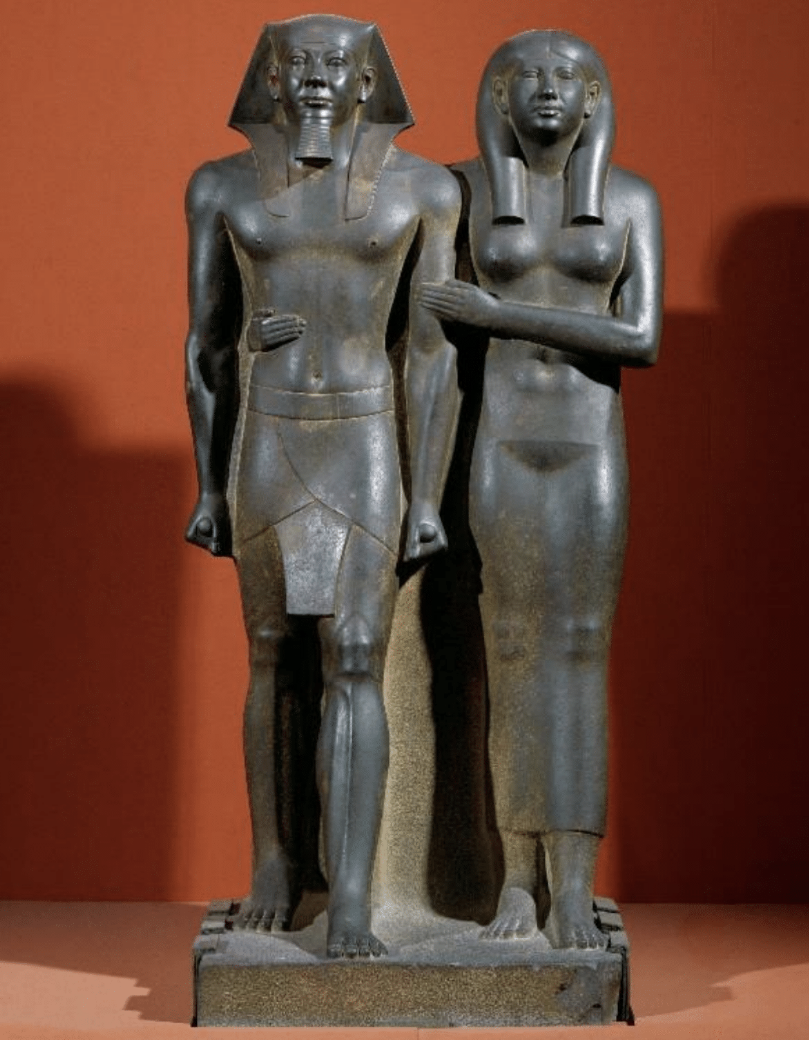

Pharaoh Menkaure and Queen, ca.2490-2472 BCE, graywacke
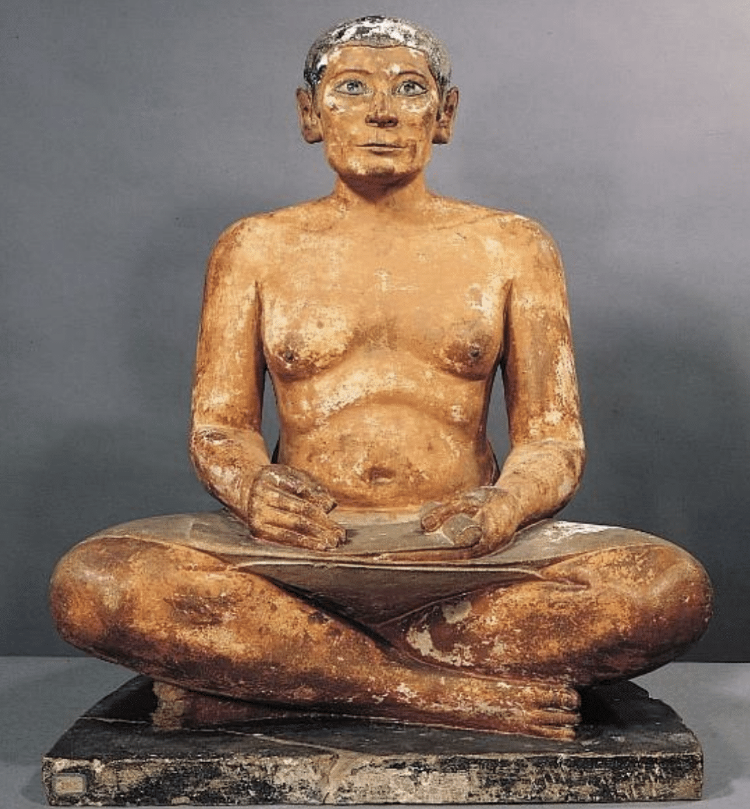

Seated Scribe,c. 2500 BCE, painted limestone
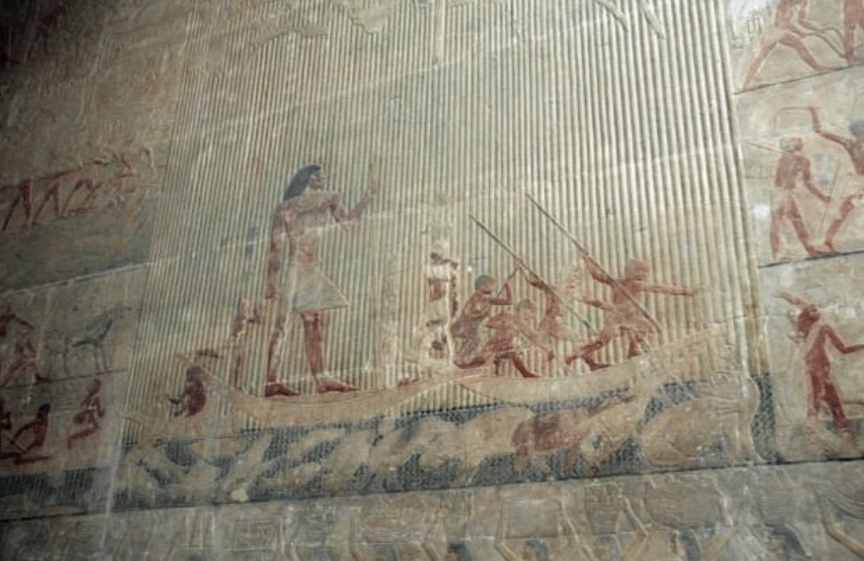

Ti watching a hippopotamus hunt,mastaba at Saqqara (Egypt), ca.2450-2350 BCE,painted limestone relief
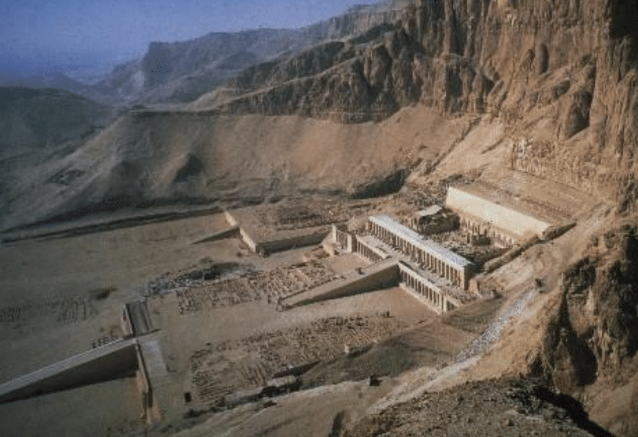

Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut, Deir el-Bahri (Egypt), ca. 1473–1458 BCE
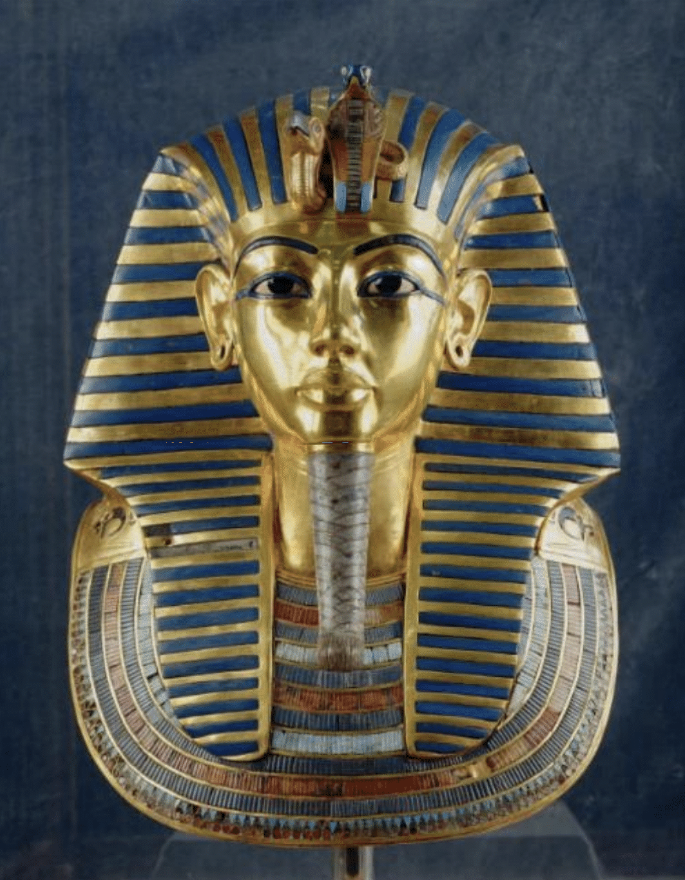

Death Mask of Tutankhamen, ca. 1323, gold with semiprecious stones
Vault
An arched roof or ceiling that is usually made of stone, brick, or concrete
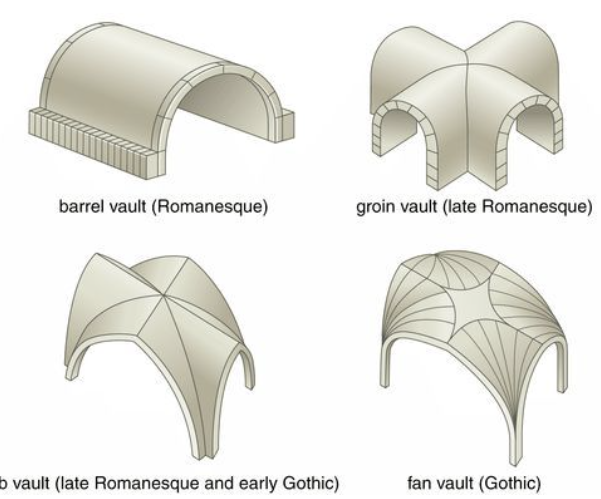
True Arch
Has a continuous line from one end to the other, almost dome-like
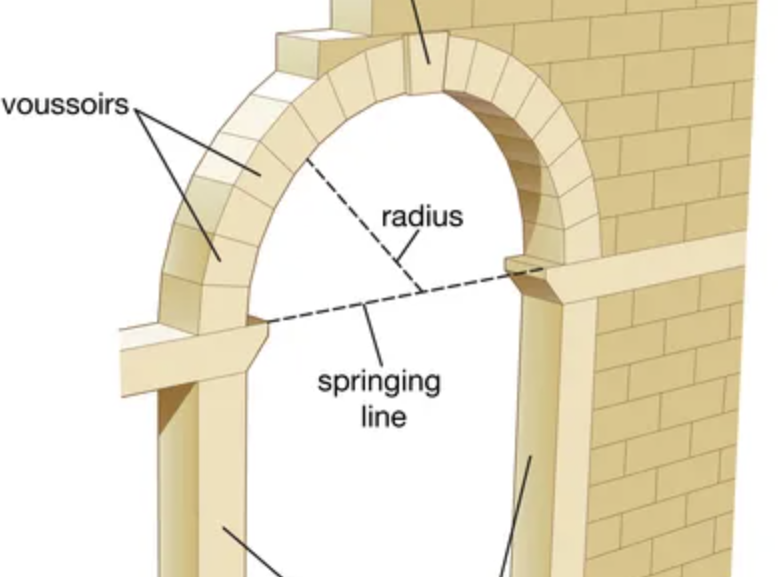
Façade
The “face” of a building, especially the principal front that looks onto a street or open space
Hypostyle Hall
An architectural space with a roof supported by columns
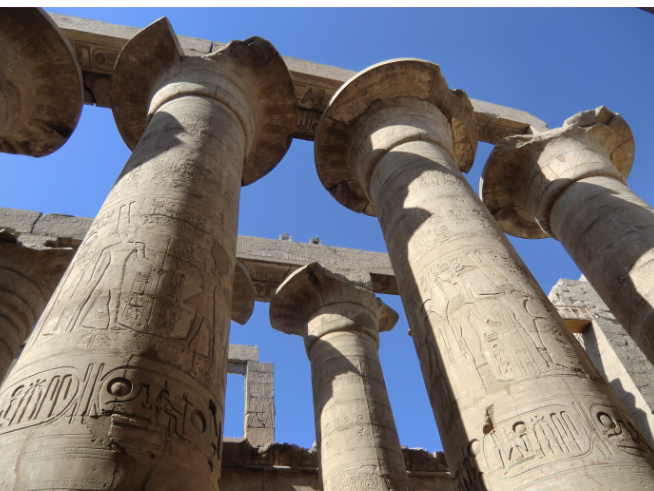

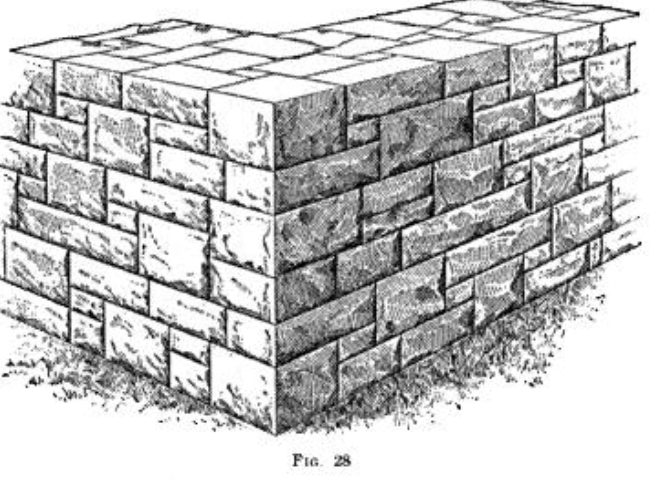
Ashlar
A finely cut and squared stone block, or the masonry built of such stone
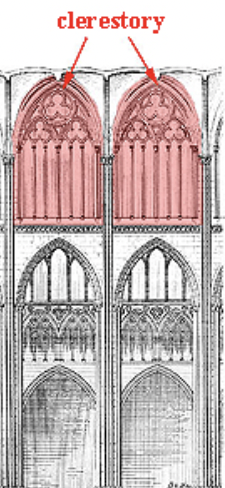
Clerestory
The upper section of a wall in a building, typically in a church, that contains windows placed high above eye level, allowing light to penetrate the interior space by rising above the roofline of the surrounding aisles