Nursery Terms/Abbreviations
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
ABO Incompatibility
hemolytic disease that occurs when the mother’s blood type is O and the newborn’s blood type is A, B, or AB
Acrocyanosis
Peripheral cyanosis; bluish discoloration of hands and feet in most newborns at birth that is a normal finding for the first 24 hours
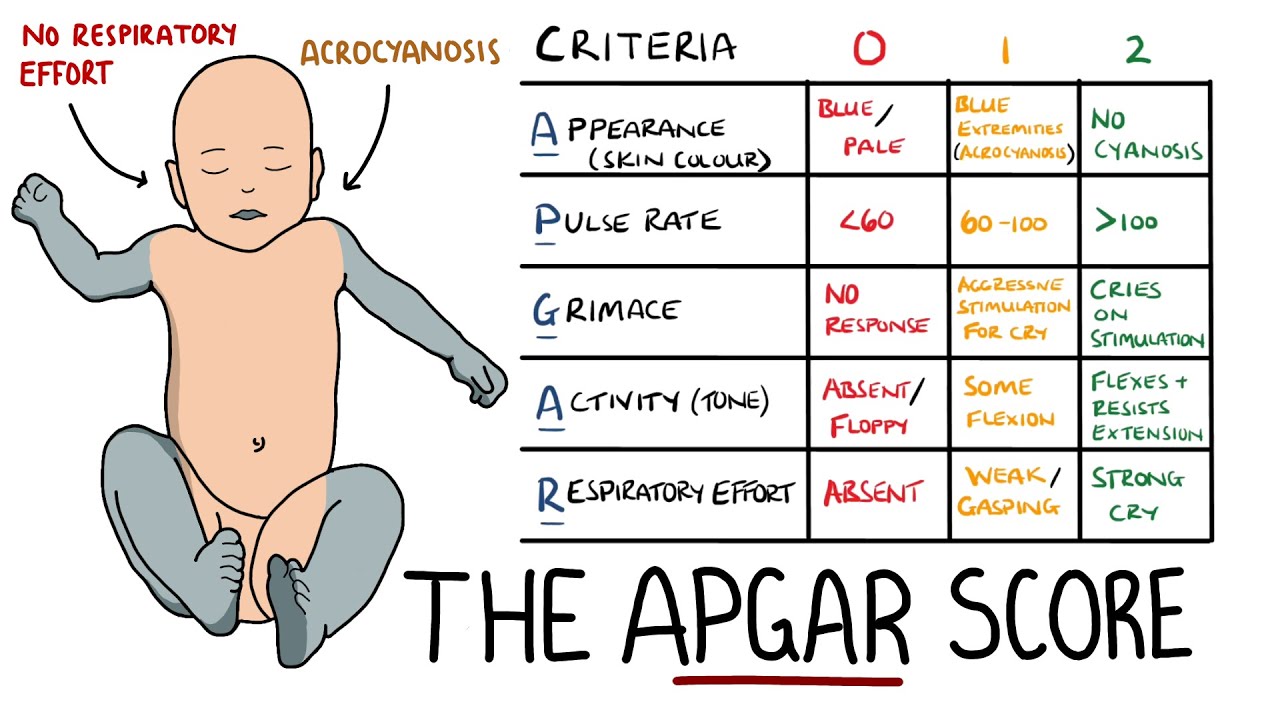
Apgar Score
A test given to newborns soon after birth, it checks baby’s HR, muscle tone, response to stimulation, skin coloration, score of 10 represents best possible condition
Test is usually done twice: 1 min after birth and 5 mins after birth
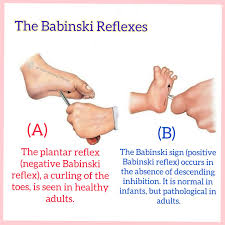
Babinski Reflex
reflex from newborn that disappears as CNS matures
positive response is normal in infants → great toe pointing upward and the other toes fanning out when the sole of the foot is stimulating, usually disappears between 12-24 months
negative respone (or normal response) → downward curling of toes
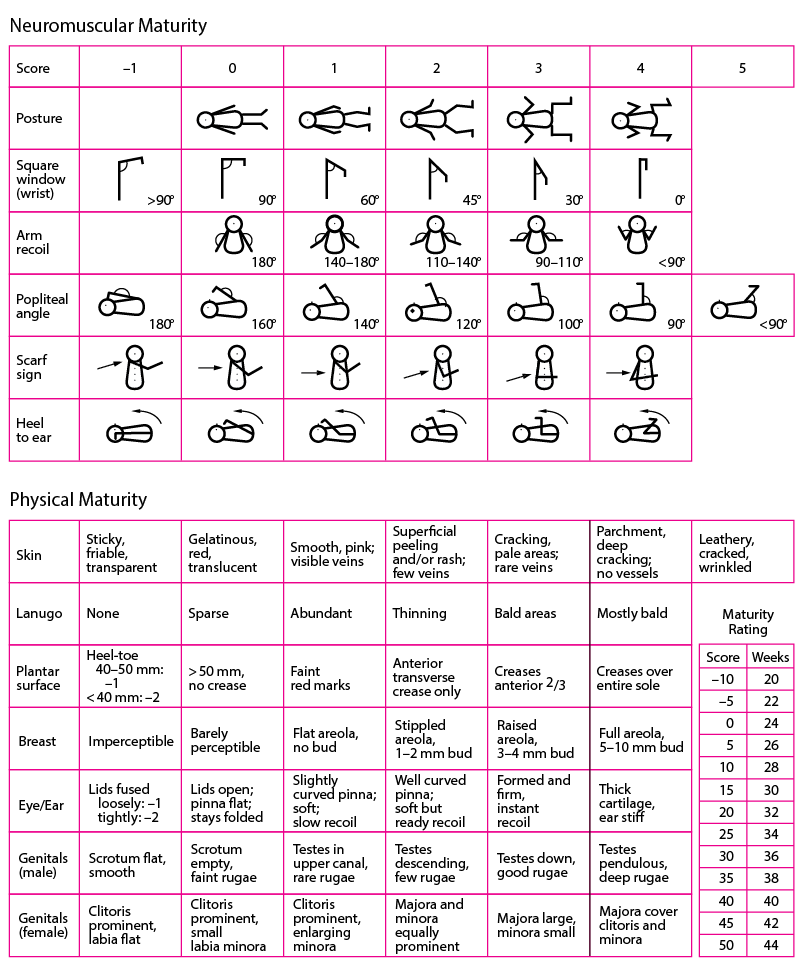
Ballard Score
used to determine gestational age
scores are given 6 physical and 6 nerve and muscle development (neuromuscular) signs of maturity, scores for each range from -1 to 5
premature babies have low scores, babies born late have high scores
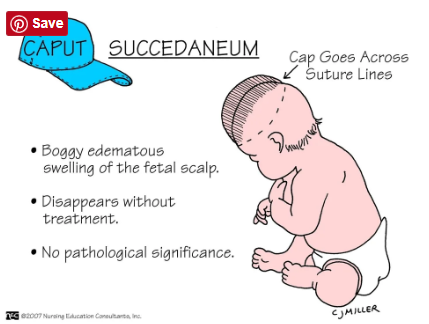
Caput Succedaneum
generalized, easily identifiable edematous area of the scalp, most often on the occiput
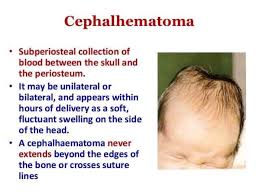
Cephalhematoma
Collection of blood that forms under the periosteum (scalp membrane) of a newborn’s skull, typically caused by pressure and shear forces during a difficult birth, raised bulge that does not cross the cranial suture lines, generally harmless and resolve on their own within weeks to months but some can calcify which would require medical attention
Circumcision
surgical procedure that involves the removal of the foreskin
Coombs Test
Indirect: detmination of Rh-positive antibodies in maternal blood
Direct: detmination of maternal Rh-positive antibodies in fetal cord blood
positive test result indicates the presence of antibodies, which can be attached to baby’s RBCs, potentially causing anemia or jaundice
important to check if the mother’s immune system has created antibodies that could harm the baby’s red blood cells, esp if the mother is Rh-negative and the baby is Rh-positive
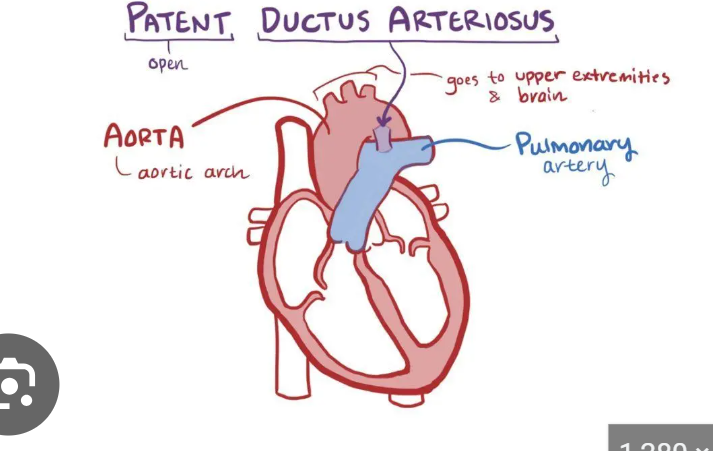
Ductus Arteriosus
aka DA, a temporary blood vessel that connects the aorta to the pulmonary artery, during fetal development the DA allows blood to bypass the non-functional lungs (fetus recieves oxygen from placenta)
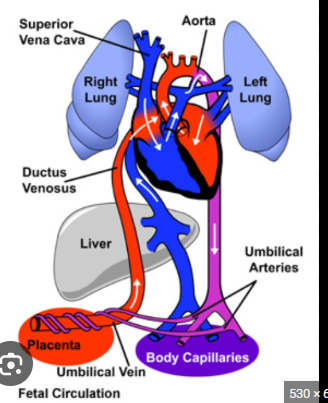
Ductus Venous
temporary blood vessel present in fetus that connect the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava → allowing oxygenated blood from the placenta to bypass the liver and directy into the fetal heart, ensuring proper oxygenation
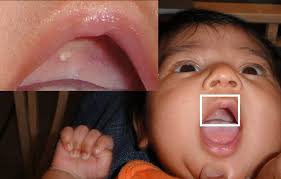
Epstein Pearls
small, white bumps that commonly appear in newborns mouths
Fontanel
space between bones of the skull in an infant where ossification is not complete and the futures are not fully formed, commonally known as the “soft spot”
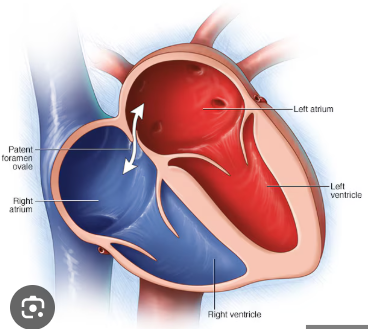
Foramen Ovale
small opening in the septum (wall), between the upper chambers of the heart (atria) that is present in all fetuses during pregnancy
Hyperbilirubinemia
condiition where high levels of bilirubin build up blood, causing jaundice
Hypothermia
condition where body’s core temperature drops below 97.7f (for newborns)
Jaundice
conditioning characterized by the yellowing of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes
Lanugo
downy, fine hair characteristic of the fetus between 20 weeks of gestation and birth that is most noticeable over the shoulders, forehead, and eyebrows
Meconium
first stool of infant → viscid, sticky, dark greenish brown, almost black, odorless
Milia
unopened sebaceous glands appearing as tiny, white bumps on forehead, nose, cheeks, and chin of neonate → dissapear in a few days/weeks
Molding
shaping of fetal head by overlapping cranial bones to facilitate movement through birth canal during labor
Mongolian Spots
benign blue/gray birthmark found on lower back or butt of newborns
Moro Reflex
involuntary response in infants where they extend arms and legs as response to being startled and/or feeling like they are falling
Nasal Flaring
the widening of nostrils with each breath → sign of difficulty breathing or respiratory distress
Ortolani Manuever
a test used to detect dislocation of hip that can be reduced (put back into place)
Phototherapy
light therapy to reduce serum bilirubin levels by oxidating bilirubin into water-soluble compounds to process in liver and excrete into bile and urine
Retractions
a sign of working hard to breathe → areas below ribs, between ribs, and in neck sink in with each attempt to inhale
RH isoimmunization
occurs when Rh-neg pregnant woman develops antibodies against Rh-positive fetal blood cells → may cross placenta and destroy baby’s circulating RBCs
Rooting Reflex
normal response of newborn to move toward whatever touches area around the mouth and attempt to suck
Sleep Wake cycle
variations in the state of consciousness of infants; infants have shorter sleep cycles and transition between REM and nonREM more frequently
Thermoregulation
maintenance of balance between heat loss and heat production
Vernix
protective gray-white fatty substance of chessy consistency covering fetal skin
Wharton’s jelly
main connective tissue found within the umbilical cord that protects the umbilical vein and arteries from compression and kinking, ensuring proper blood flow between fetus and placenta
SGA
smalll for gestational age → below 10th percentile
LGA
large for gestational age → above 90th percentile
IUGR
intrauterine growth restriction → fetus grows slower than expected rate in uterus resulting in SGA fetus