The Muscular System
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
What does muscle do?
Shortens to create tension
What does muscles organization effect?
Power, range and speed of muscle movement
Fascicles
Muscle cells (Fibers) that are organized
How are skeletal muscles classified?
By fascicles and their relationships to the tendonds
What is the organization of skeletal muscle fibers?
Parallel, Convergent, Pennate and Circular muscle
Parallel muscle
Fibers parallel to the long axis of muscle, ex. Biceps brachii
Convergent muscle
Broad area that converges an attachment site, ex. tendon
Pennate muscle
Attatch slanted and can be in multiple angles1
Unipennate
A type of Pennate muscle, fibers on one side of the tendon, ex extensor digitorium
Bipennate
A type of Pennate muscle, Fibers on both sides of tendon, ex rectus femoris
Multipennate
A type of Pennate muscle, Tendon branches within muscle, ex deltoid
Circular muscles
Open and close to gaurd entrances in the body, ex orbicularis
Skeletal motion
Uses levers (bones), joints/fulcrum (a fixed point) muscle to provide applied force required to overcome loads
What are the three lever classes?
First class, Second class and Third class
First class lever
Like a seesaw, force and load are balanced
Second class lever
Like a wheelbarrow, small force moves a large weight
Third class lever
Most common, greater force moves smaller load, like a catapult
Origins
Fixed points of attachment
Insertion
One moving point of attachment
Actions
Movements produced by muscle contraction
How do the muscles interact?
Work in groups to maximize efficiency
What muscles reach maximum tension first?
Smaller muscles
Agonist
Prime mover, produces particular movement
Antagonist
Opposes movement of agonist
Synergist
Smaller muscle that assists agonist
Muscle opposition
Agonists and antagonists work in pairs
How does aging effect muscles?
Muscle fibers become smaller in diameter, less elastic, increased amount of fibrous tissue, decreased tolerance of exercise and decreased ability to recover
What are the three layers of connective tissue?
Epimysium, perimysium and endomysium
Epimysium
Separates muscle from surrounding tissues
Perimysium
Surrounds muscle fiber bundles (Fasicles)
Endomysium
Surround individual muscle cells (muscle fiber cells)
What do the ends of muscle become?
Tendons
Muscles have extensive v-
vascular systems
Are skeletal muscles voluntary or involuntary?
Voluntary
Sarcolemma
The cell membrane of a muscle fiber cell, a change in transmembrane potential begins contractions
Transverse tubules
Transmit action potential through cell, have same properties as sarcolemma
Myofibrils
Made of bundles of myofilaments
What are the types of myifilaments
Thin (Actin) and Thick (Myosin)
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Membranous structure surrounding myofibrils, transmit action potential to myofibril, forms terminal cisternae attached to T tubules
Triad
T tubule and two terminal cisternae
Sarcomeres
Contractile units of muscle
Thin filaments
F-actin
Tropomyosin
Double strand that prevents actin-myosin interaction
Troponin
Globular protein that binds tropomyosin to G-actin
Initiation of thin filaments
Calcium binds to receptor and troponin molecule, troponin-tropomyosin complex change, exposes active site of F-actin
Thick filament
Contains myosin and titin
Titin
Strands that recoil after they stretch
Skeletal muscle contraction process
Neural stimulation by sarcolemma, muscle fiber contraction and tension is produced
Sarcoplasm
Cytoplasm of muscle fiber(cell)
Cisternae
Release calcium into sarcomeres to begin muscle contraction
Neuromuscular junction
Special intercellular connection of nervous system and skeletal muscle fiber, controls calcium ion release in sarcoplasm
Excitation-contraction coupling
Active site exposure, cross bridge formation, myosin head pivoting, cross bridge detachment, myosin reactivation
Relaxation depends on?
ATP, neural stimulus and number of free calcium ions
Rigor mortis
Fixed muscular contraction, ATP stops, calcium builds in sarcoplasm
Tension depends on
Pivoting cross-bridges, fibers resting length and frequency of stimulation
Twitch
One single contraction
Warmup latent period
Action potential moves through sarcolemma, causing calcium to releaseC
ontraction phase
Calcium ions bind, tension builds to peak
Relaxation phase
Calcium levels fall, active sites are covered and tension falls to resting levels
Tetanus
Maximum strength
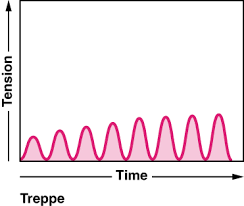
Treppe
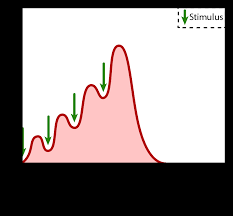
Wave
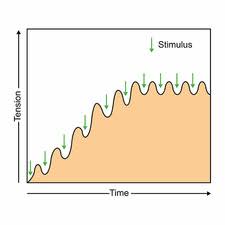
Incomplete tetanus
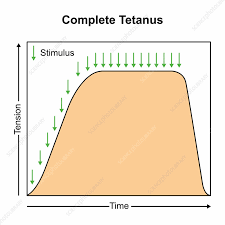
Complete tetanus
Motor units
Bundles of fibers attached to neurons, contract at the same time
Recruitment
Mutiple motor units stimulated
Muscle tone
Normal tension and firmness at rest
What does increased muscle tone increase?
Metabolic energy used even at rest
Elastic forces
The pull of elastic elements, expands the sarcomeres to resting length
Atrophy
Flaccid or weak
ATP
Active energy molecule
Creatine phosphate
Storage molecule for excess ATP energy in resting muscle
Creatine kinase
Enzymes that recharges energy
ATP generation
Produced by aerobic metabolism and anaerobic glycolysis
Aerobic metabolism
Primary energy source of resting muscles, breaks down fatty acids
Anaerobic glycolysis
Primary energy source for peak muscular activity, breaks down glucose from glycogen
Lactic acid
Low pH
Muscle fatigue
When muscles can no longer perform a required activity
Recovery period
The time required after exertion for muscles to return to normal
Oxygen debt/EPOC
After excercise the body needs more oxygen than usual to restabalize
Fatigue
Depletion of metabolic reserves, damage sarcolemma
Slow fibers
Slow to contract and fatigue
Fast fibers
Twitch fast muscle fibers