Exam 1: Pulgar-CCBs
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is the difference in Ca ions from ECF to ICF?
ECF=2mM; ICF=100nM
Calcium ions are important in muscle contractions and _____?
neurotransmitter release
In cardiac muscle which calcium channels are of most interest?
L-type and T-type
Why are the L-type channels of so much interest in terms of activation and conduction?
they are in cardiac, smooth and skeletal; high voltage of activation; large single channel conduction; slow inactivation; regulated by signals; inhibited by specific drugs
What are the 5 calcium subunits and their location?
alpha-1, alpha-2, beta, delta, gamma;
alpha-1, gamma, and delta are transmembrane;
beta is intracellular;
alpha-2 is extracellular and connected to delta;
How are calcium channels regulated?
in straited muscle: PKA phosphorylates alpha 1 and beta to increase channel opening time;
PKC phosphorylates the N-terminus of alpha subunit and activates channel;
inhibition-Ca/CaM binds to Cterminus of the alpha subunit
Why are the alpha 1 and 2 the most important of the calcium subunits?
alpha 1 - forms the pore for the Ca to move through, can sense changes in voltage due to aa variations; alpha 2 - binds the Ca/CaM complex and inhibits the Ca channel
Why are B adrenergic receptors able to produce a lot of contractility in heart?
B adrenergic receptors are abundant in the cardiac muscle and are coupled to cAMP and activate PKA and increase Ca channels
What two Ca channels command the currents and control HR?
L and T type channels
What are the roles of calcium channels in CV regulation?
reg. of SA node by Ltype Ca channels to control HR;
reg. of myocardial and vascular contractility by L type channels'
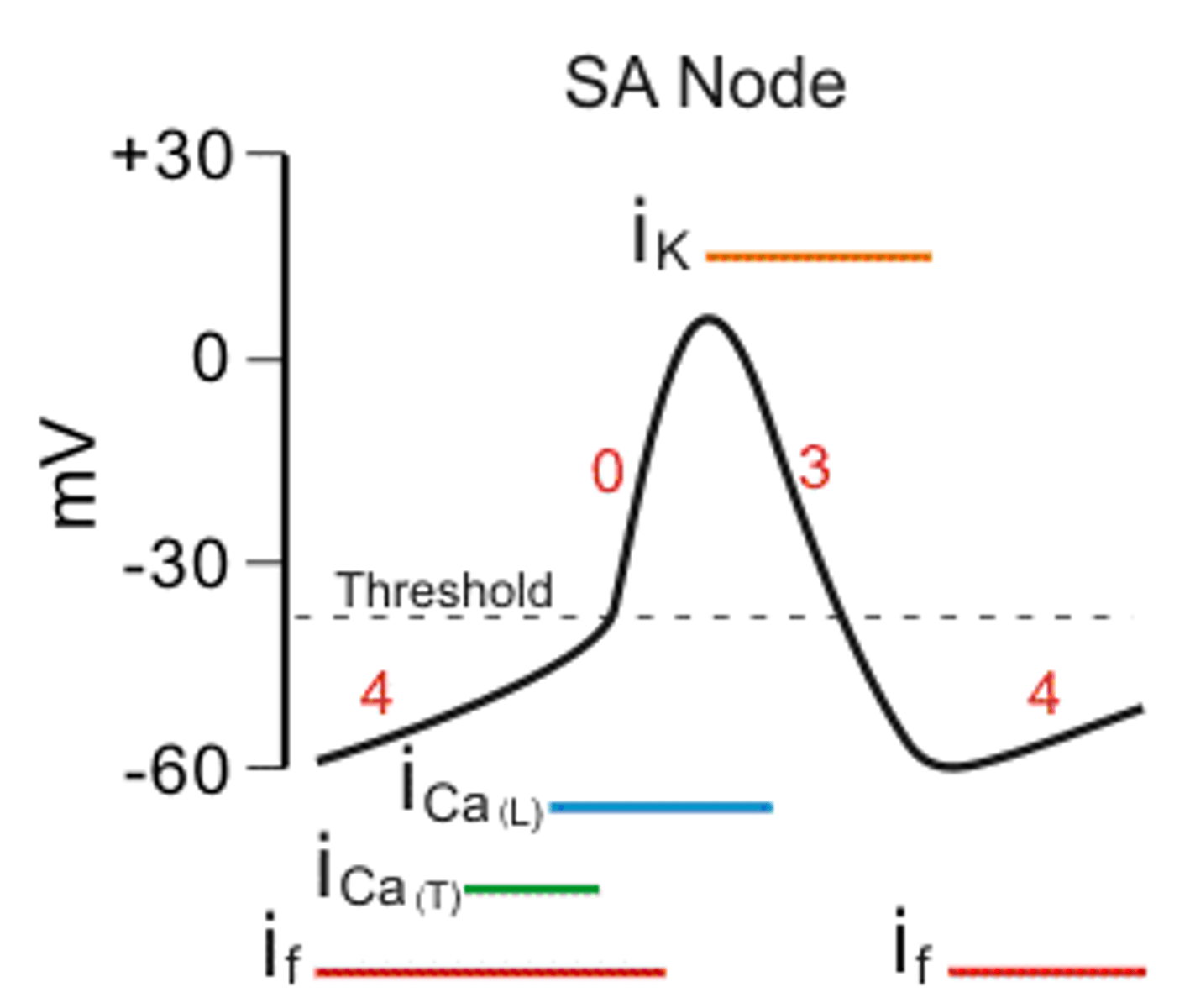
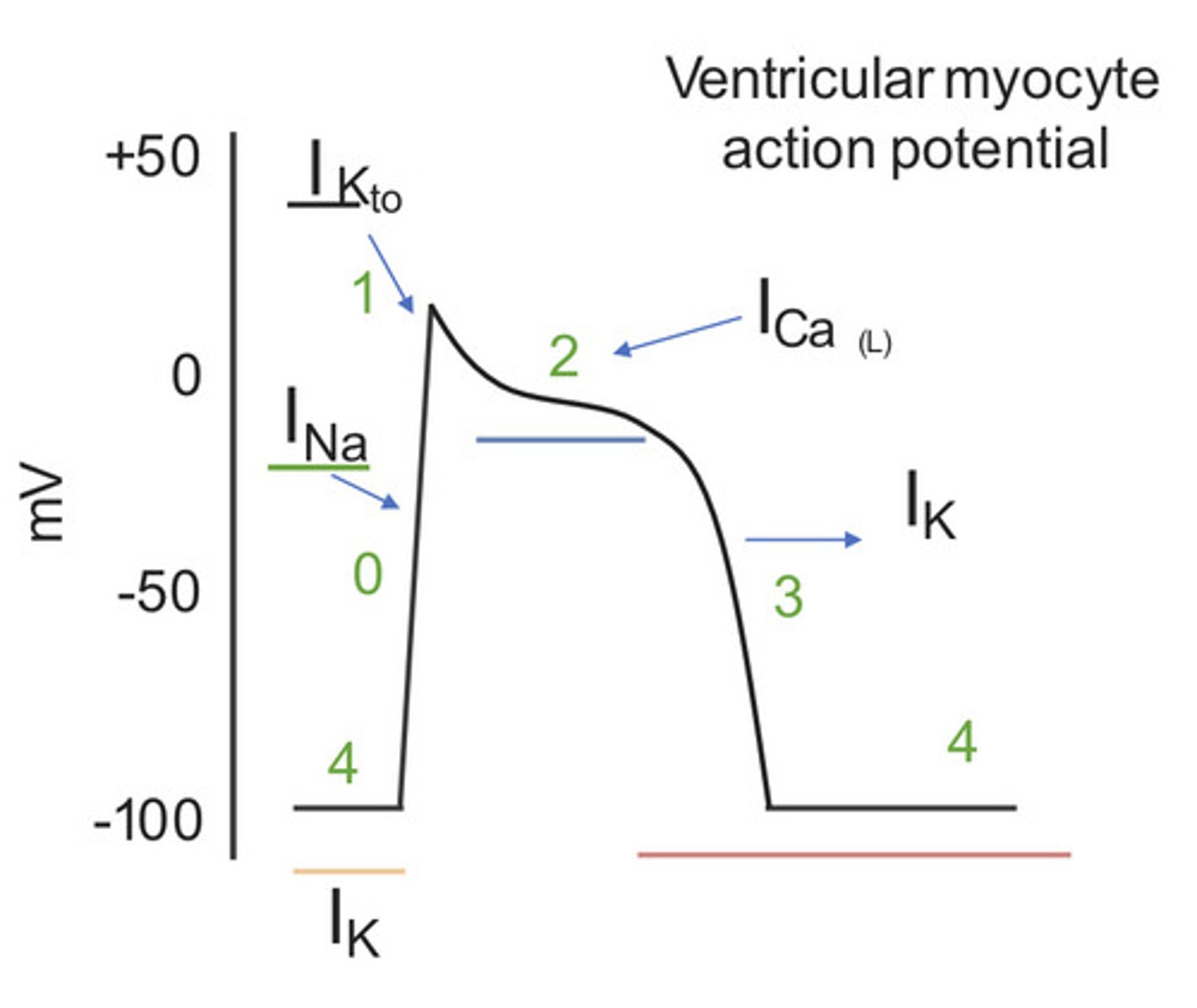
What are the differences in AP in SA node vs. cardiac muscle?
no phase 2 in AP of SA node bc no stable AP as in cardiac muscle; it is always going to depolarization due to leaky Ca channels; called slow response;
then SA node AP is sent to myocyte, stimulates rel of Ca stores; the cardiac muscle has large spike then plateau of Ca to prolong repolarization
Draw action potential of SA node.
Draw action potential of cardiac myocyte.
How does Ca effect vascular contractility?
influx of Ca from ECF to ICF form the Ca/CaM complex and activates MLCK and it phosphorylates myosin so it can bind to actin and myosin;
the Ca/CaM complex can act as a neg. feedback also to inactivate the channel
CCBs appear to bind to ___________
L type Ca channel and prevent their opening causing depolarization of cardiac muscles and pacemaker
CCB-DHPs are preferential to the___________?
arteries and arterioles over veins and venules and blocks vascular L-type channels at lower conc than cardiac channels; decr BP and is dose dependent; incre HR and force a little as well
What are the AE of CCB DHPs?
bc of excessive vasodilation: dizziness, hypotension, HA, flushing and nausea
True/False: in patients with heart disease DHPs are preferred?
False
Specifically which drug should not be used in pts with myocardial ischemia, angina or post-MI?
Nifedipine
Grape juice will do what if taken with DHPs?
increase the level of DHPs due to inhibition of CYP enzyme
Which CCB is a nonHDP and a benzothiazopine
Diltiazem
Describe the availability of Diltiazem.
good oral absorption, but first pass effect so reduced bioavailability, high plasma protein binding
MOA of Diltiazem
decr Ca influx --> decr smooth muscle contraction, decr cardiac contractility; has similar potency for both cardiac and vasculature so the reflex of symp ns is not shown; therefore neg chronotropic and ionotropic effect with diliatazem
AE of Diltiazem
bradycardia, heart block, transient sinus arrest, hypotension, flushing, dizziness, headache and constipation
What CCB is a non-DHP and also a phenylalkylamine?
Verapamil
Availability of Verapamil?
good oral absorption, high first pass effect so lower bioavailability, high plasma protein binding
MOA of Verapamil?
inhibits L type Ca channels and decreases smooth muscle contractility
Which CCB is metabolized by N-demethylation?
Verapamil
What is different about the binding of the various CCBs to the Ca channel?
Verapamil appears to bind directly to the pore "active site"; amlodipine and nifedepine binds to the side of the channel and diltiazem bind to open and inactive forms of the channel
Is Verapamil more effective than other CCBs?
yes since it binds directly to the channel and produces a bigger negative chronotropic and ionotropic effect; but AE are more severs such ad bradycardia, heart block, sinus arrest, hypotension, flushing, dizziness, HA and constipation
Which CCB has no effect on conduction at the AV node?
Amlodipine since it does not bind to the Ca channel but rather binds at allosteric site on the channel protein
How is Verapamil useful in treating cancer patients?
it blocks the action of the P170 transporter glycoprotein (that usually pumps out multiple drugs); the cancer drugs can stay in longer to have greater effect
What drugs to Verapamil interact and enhance cardiac depression?
Beta blockers
Name some DHP CCBs
Amlodipine (Norvasc)
Nifedepine (Procardia)
Name a Benzoothiazepine CCB
Diltiazem (Cardizem)
Name a Phenylalkylamine CCB
Verapamil (Calan, Isoptin)
The calcium gradient in cells is used in ________ and _________?
neaurotransmitters, muscle contraction
What are the main two types of channels in heart conduction?
T and L type
How do L type calcium channels work?
high voltage activation, large single conductance, skow inactivation