Lesson 1 - Isotopes, Radioactive Decay, and Nuclear Equations
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Isotope
element that has the same atomic number, but a different atomic mass due to differing numbers of neutrons.
Standard notation
is a way to represent isotopes using the element's symbol, atomic number, and mass number

What is the mass number of carbon - 14
14
What are the 3 types of radiation?
Alpha (αα - energized particle), beta (ββ - energized particle), gamma (γ - energy)
Describe alpha radiation
positively charged, largest of the 3, made of 2 protons and 2 neutrons, piece of paper can stop them

Describe beta radiation
size of electron, moves faster than an alpha particle, neutron changes into a proton and an electron (electron has a charge of -1 so it “gains” another proton, changing into the next element on the periodic table) can penetrate paper, stopped by aluminium
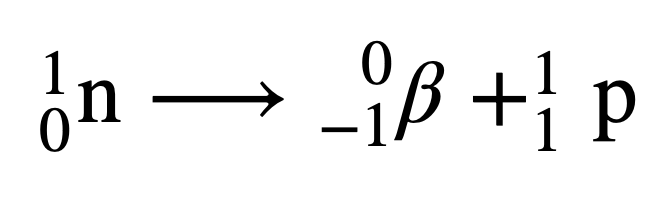
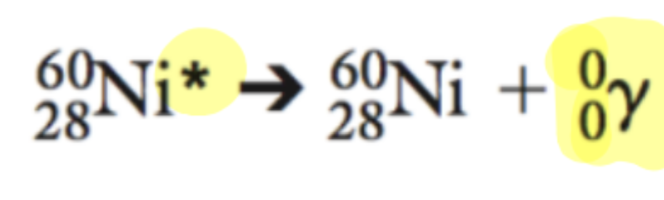
Describe gamma radiation
not particle, high frequency, high energy, short wavelength of the electromagnetic spectrum, can penetrate most materials, requires lead or thick concrete to stop, does not change the mass/atomic number of the atom