19.8 short- term regulation: Neutral Controls
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
MAP is maintained by
altering blood vessel diameter, which alters resistance
Ex: If blood volume drops, all vessels constrict (except those to heart and brain)
Can alter blood distribution to organs in response to specific demands
Neural controls operate via reflex arcs that involve:
Cardiovascular center of medulla
Baroreceptors
Chemoreceptors
Higher brain centers
Cardiovascular center:
composed of clusters of sympathetic neurons in medulla
Cardiovascular center consits of;
Cardiac centers: cardioinhibitory and cardioacceleratory centers
vasomotor center
sends steady impulses via sympathetic efferents called Vasomotor fibers to blood vessels
baroreceptor reflexes located in
carotid sinuses, aortic arch, and walls of large arteries of neck and thorax
If MAP is high…?
Increased blood pressure stimulates baroreceptors to increase input to vasomotor center
Inhibits vasomotor and cardioacceleratory centers
Stimulates cardioinhibitory center
Results in decreased blood pressure
Vasodilation
decreased output from vasomotor center causes dilation
Arteriolar vasodilation
reduces peripheral resistance, decreasing venous return and CO
Decreased cardiac output
Impulses to cardiac centers inhibit sympathetic activity and stimulate parasympathetic
Reduces heart rate and contractility; CO decrease causes decrease in MAP
If MAP ia low-
Reflex vasoconstriction is initiated that increases CO and blood pressure
Example: upon standing, BP falls and triggers:
Cartoid sinus reflex
baroreceptors that monitor BP to ensure enough blood to brain
aortic reflex
maintains BP in systemic circuit
Baroreceptors are ineffective if altered blood pressure is sustained
chemoreceptor reflexes
Aortic arch and large arteries of neck detect increase in CO2, or drop in pH or O2
Cause increased blood pressure by:
Signaling cardioacceleratory center to increase CO
Signaling vasomotor center to increase vasoconstriction
Influence of higher brain centers
Reflexes that regulate BP are found in medulla
Hypothalamus and cerebral cortex can modify arterial pressure via relays to medulla
Hypothalamus increases blood pressure during stress
Hypothalamus mediates redistribution of blood flow during exercise and changes in body temperature
Hormones regulate BP in short term via changes in
peripheral resistance or long term via changes in blood volume
Adrenal medulla hormones
Epinephrine and norepinephrine from adrenal gland increase CO and vasoconstriction
angiotensin II
stimulates vasoconstriction
ADH -
high levels can cause vasoconstriction
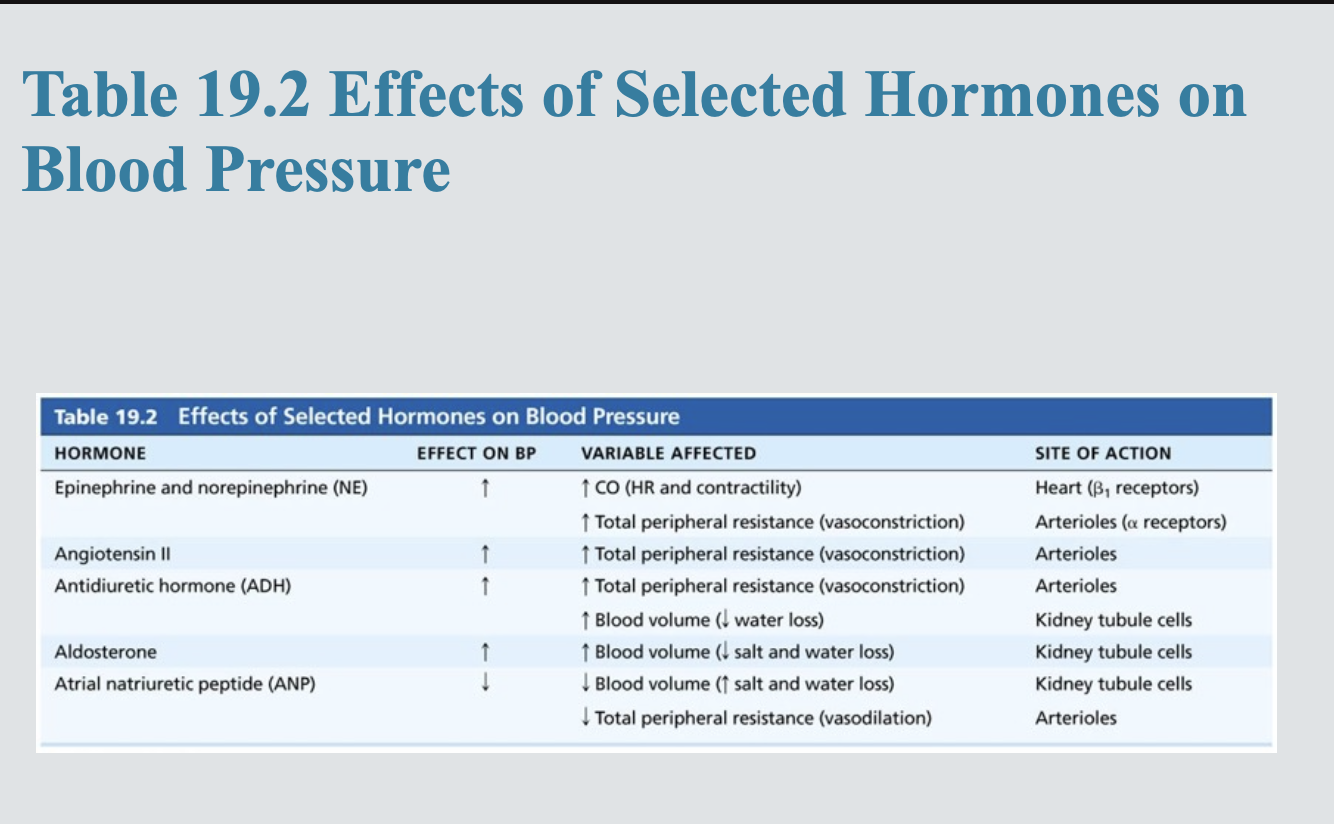
atrial natriuretic peptide
decreases BP by antagonizing aldosterone, causing decreased blood volume
Baroreceptors quickly adapt to
chronic high or low BP so are ineffective for long-term regulation
kidney regulate arterial blood pressure by
Direct renal mechanism
Indirect renal mechanism (renin-angiotensin-aldosterone)
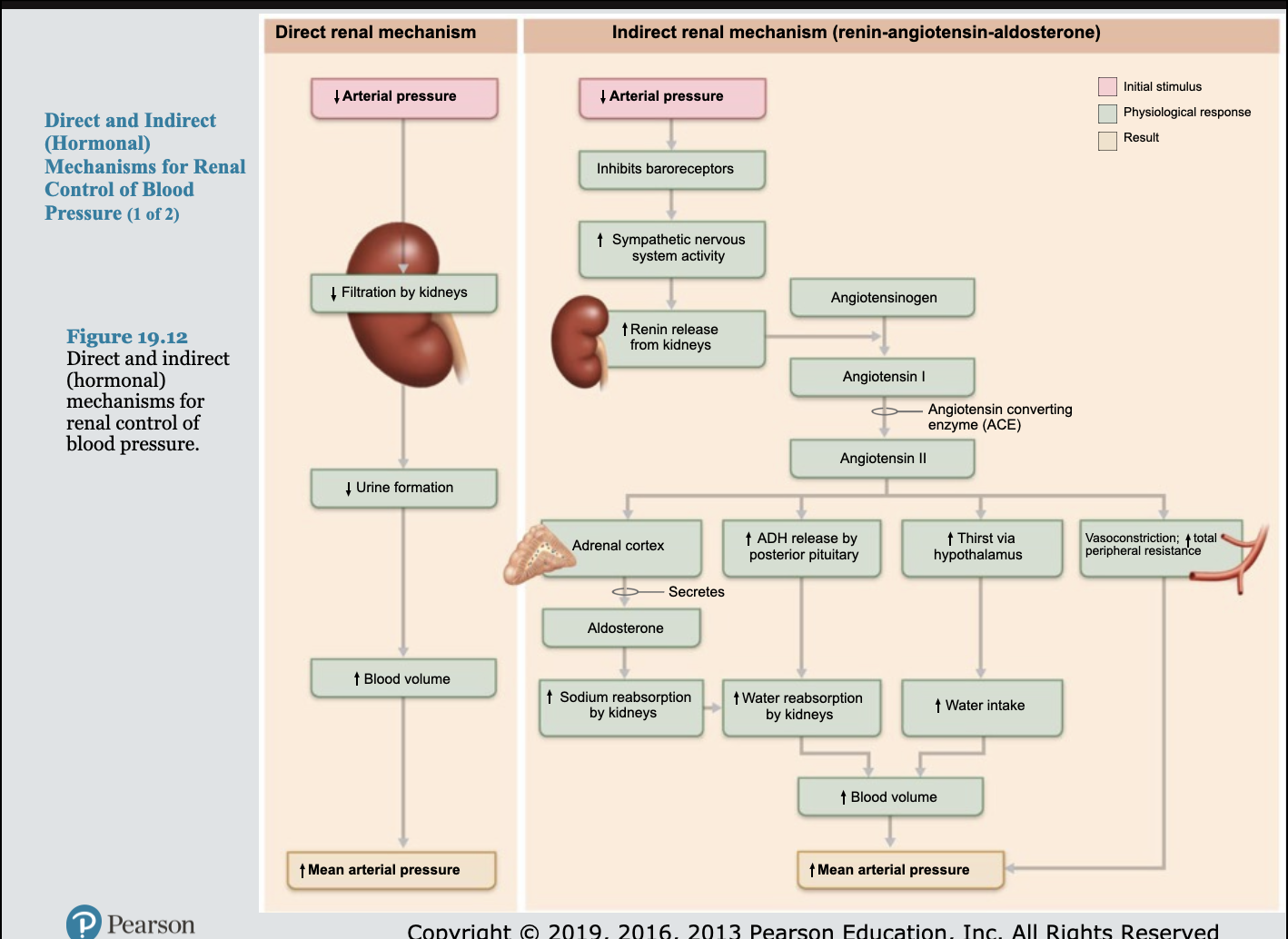
Direct renal mechanism
Alters blood volume independently of hormones
Increased BP or blood volume causes elimination of more urine, thus reducing BP
Decreased BP or blood volume causes kidneys to conserve water, and BP rises
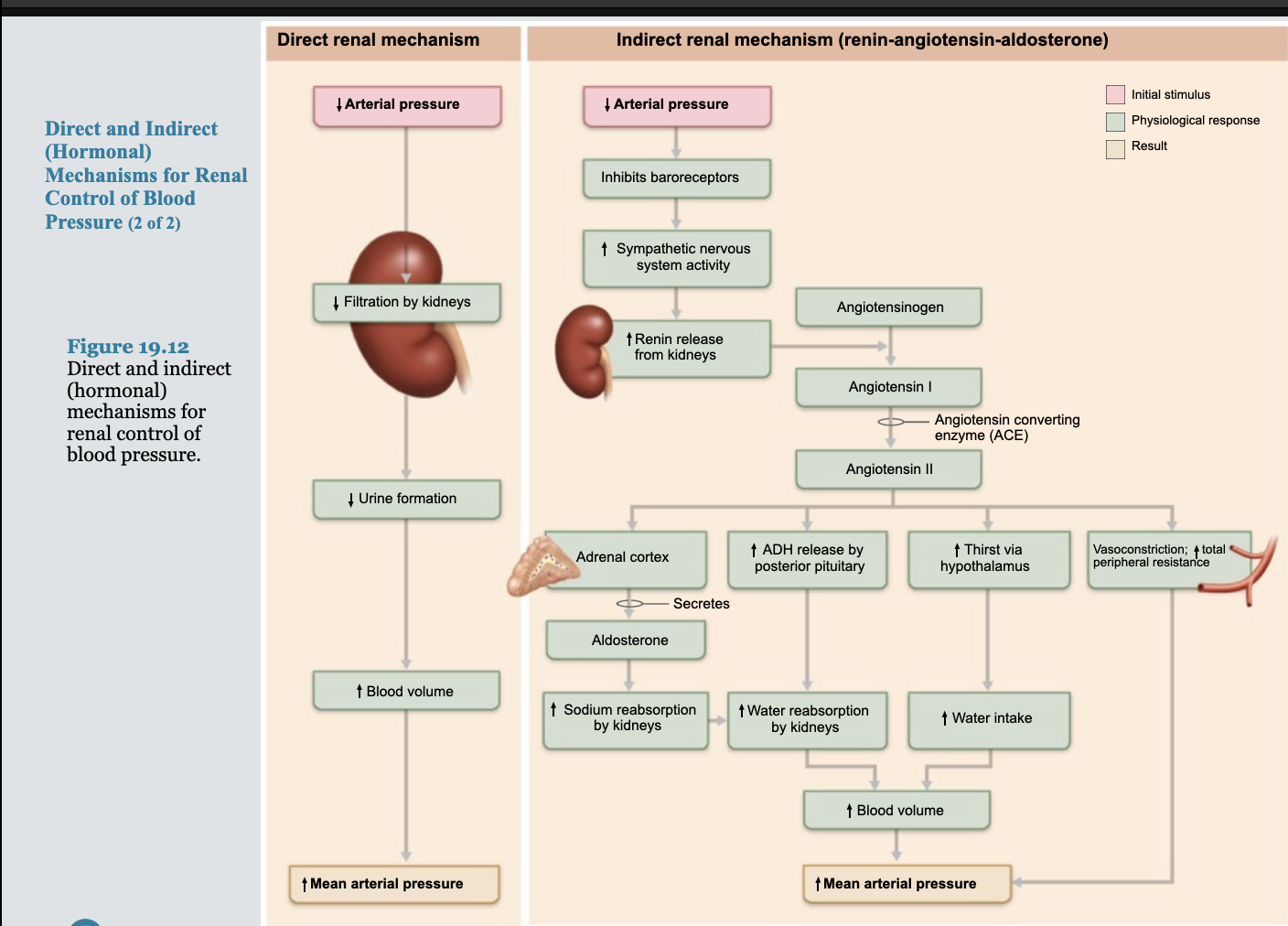
Indirect mechanism
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS):
Decreased arterial blood pressure causes release of renin from kidneys
Renin enters blood and catalyzes conversion of angiotensinogen from liver to angiotensin I
Angiotensin-converting enzyme, especially from lungs, converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II
Stimulates aldosterone secretion