Instrumentation and Patient/Operator Positioning (POHS I)
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
Adaption
relationship between the working end and tooth surface
Angulation
angle formed by the working end with tooth surface
Stroke
motion from an instrument, unbroken during assessment or debridement
Terminal shank
working end to first bend
Functional shank
working end to last bend
blade
working end of an instrument
curet
curved, rounded instruments (universal or area specific)
lateral pressure
pressure with an instrument
scaling
method in removing calculus and biofilm
Neutral work position
position in which the normal curve of the spine is maintained; muscles and joints are naturally aligned
Ergonomics
study of human performance and workplace design to maximize health, comfort, and effciency
supine
flat position; for maxillary arch; chin is UP
semi-supine
raised 15 from supine; mandibular arch
trendelenberg
modified supine where head is lower than heart
postural hypotension
low-blood pressure from lying down; lightheadedness and fainting
modified pen grasp
method for holding periodontal instruments; three-finger combo
handle
part of instrument used for holding
shank
metal between handle and working end
working end
carries out function of the instrument
fulcrum
provides stability during instrumentation; ring finger
indirection vision
use of dental mirror to see teeth that cannot be directly seen
retraction
use of mirror head to hold cheek, lip or tongue out of the way
indirect illumination
use of mirror surface to reflect light onto tooth in dark areas
transillumination
directing light off of the mirror and through the teeth
Why do we do neutral working position?
decrease risk of musculoskeletal injuries
efficacy and endurance of performance
Eyes are _-_ away from oral cavity
15-22
can tilt head forward to _
15 degrees
can raise elbows to __
20
dont raise elbows above
60
semi-upright position
reclined 45; for pt with congestive heart failure, vertigo, emphysema, asthma and pregancy
light is angled _ to _ in supine position
60 to 90
light is angled _ to _ in semi-supine position
90
position of trendelenburg
back extra 10-15
positioning sequence
me
patient
equipment
non-dominant hand
dominant hand
clock positions for right-handed
8-12 o clock
clock positions left-handed
12-4 o clock
divide dentition into _ sextants
6
section and are anterior sextants
2 and 5
sections _,_,_, and _ are posterior sextants
1,3,4, and 6
anterior sextants are for __surfaces
facial and lingual
posterior sextants are for __ aspects
buccal and lingual
8-9 o clock (and 3-4) are ___ surfaces ___
anterior surfaces towards
12 o clock are surfaces __
anterior surfaces away
9 o clock (and 3 o clock) are ___ surfaces __
posterior surfaces towards
10-11 o clock (1-2 o clock) are surfaces _
posterior surfaces away
mirror types
front, concave, and plane
front surface
most common, reflects surface on front of glass
concave
reflects surface on front of mirror; distorted
flat surface
reflects surface to back of mirror; double-image
4 functions of dental mirror
indirect vision, retraction, and indirect illumination and transillumination
3 types of fulcrums
intraoral → max fulcrum; palms are up
extraoral → mand fulcrum; palms are down
alternative → finger on finger or non-dominant hand
intraoral fulcrum is used for ___ arch
maxillary; palms are up
extraoral fulcrum is used for __arch
mandibular; palms are down
two types of Instrument strokes
Assessment stroke
scaling or working stroke
assessment stroke
light, use with all explorers, use with curets and scalers when looking for calc
purpose of scaling or working stroke
used for calculus removal
instrument stroke characteristics
grasp →light for calc, firm for removal
hand stability → pivots on fulcrum
motion → action of shoulder, arm, wrist and hand
length → 2-3mm
vertical stroke
up and down
all anterior surfaces, posterior mesial and distal surfaces
oblique stroke
diagonal (like this /)
posterior buccal and lingual surfaces
horizontal strokes
side to side
anterior facial/lingual surfaces and posterior around line angles, deep pockets and furcations
common musculoskeletal disorders
carpal tunnel syndrome
ulnar nerve entrapment
tenosynovitis
tendinitis
3 instrument design components
handle, shank, and working end
properties of handle
thickness → 10mm
weight → <15.0g
texture → ribbed
others → design name, number, and manufacturer
shank connects _ to _
working end to handle
two types of shanks
function or terminal shank
type of shank SHAPE
simple or complex
simple shank shape
anterior teeth
complex shank shape
posterior teeth/universal
single-ended instrument has ___
one working end and shank (mirror)
double-ended instrument are __
mirrored on both sides of handle (11/12 exp)
unpaired instruments are __
different on each side (TU17/23)
What instruments are single-ended?
mirrors, pliers, UNC12 probe
What instruments are double-ended?
11/12 exp, nabers, 204SD, L3/4 and gracey
what instruments are unpaired?
Tu17/23 and nevi1/H33 (anterior sickle)
_and _ are assessment instruments
explorers and probes
example of explorer
TU17/23 and Exp 11/12
example of probes
NUC 12 probe and naber probe
_, _, and _ are debridement instruments
sickle scalers, universal curets, and area-specific curets
example of sickle scalers
anterior sickle Nevi1/H33 and posterior sickle 204 SD
examples of universal curtes
barnhart 5/6 and langer 3/4
example of area-specific instruments
graceys 1/2, 11/12, 13/14 and 15/16
Assessments are used for _
detect changes from tactile sense (calc, caries, defective restorations)
Characteristics of explorers
thin and adapt 1-2mm
Design of explorers
stepherd hook (23 end)
Pigtal cowhorn
Orban-type
11/12 type
stepherd hook (23 end)
crown only
caries detection
pigtail and cowhorn
limited cal detection
caries detection
orban-type (17 end)
tip bend 90 to the shank
simple shank
anterior shank/calculus detection
11/12 type
tip bent 90
complex shank
uni calc detection
Debridement instrument is used for _
removal of hard/soft depositis (calc, materia alba, biolfim, and staining)
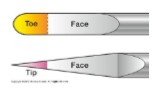
Debridement instruments has what types of working ends?
tip or toe
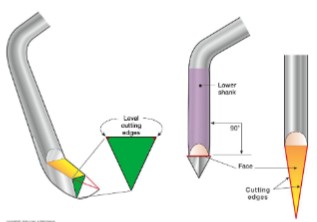
Sickle scaler has what kind of working end?
tip, two cutting edges, triangular, 90 degrees
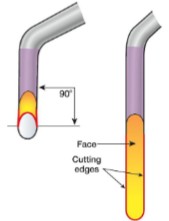
universal curets have what kind of working end?
toe, two cutting-edge, semi-circular, 90 degrees
area-specific curets have what kind of working end?
toe, ONE cutting edge per working end, semi-circular, 70 degrees
gracey ½ is used on ___ teeth
anterior
gracey 11/12 and gracey 15/16 are used on ___ teeth
posterior, medial
gracey 13/14 is used on __ teeth
posterior, distal
type and function of instrument TU-17
assessment; explore for calculus
type and function of instrument 23
assessment; caries detection
type and function of instrument UNC12 Probe
assessment; measurement
type and function of instrument nabers probe
assessment; measurement