Bio - Module 11 (Animal Evolution)
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
characteristics of animal and fungi
eukaryotic, multicellular, and heterotrophic
difference between animals and fungi
fungi have cell walls
animal clade
metazoa
what classification is based on
embryology, morphology, and genetics
animal body planes
asymmetrical, radial, bilateral
asymmetrical
irregular in shape

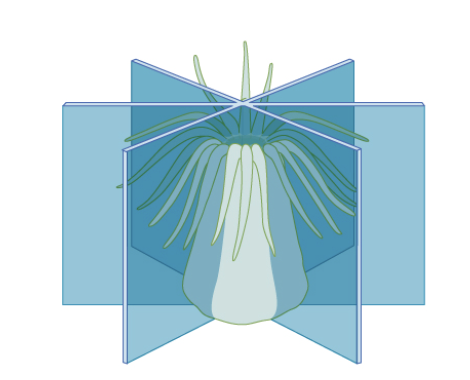
radial
central body axis and thus many planes that divide the animal into mirror image halves
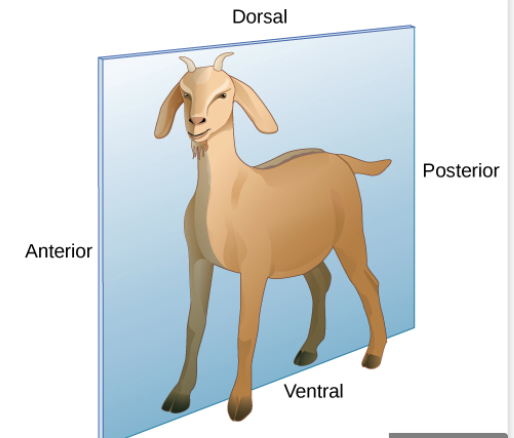
bilateral
have an anterior-to-posterior body axis that divides the animal into mirror image halves
male sex cells
motile
female sex cells
non-motile
haploid
one set of chromosomes
fertilization
union of a sperm and an egg to form a new cell called a zygote
diploid
2 sets of chromosomes
zygote
diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum
germ layers
give rise to specialized tissue and organ systems
endoderm
inner lining of digestive tract
ectoderm
covers exterior of the animal + forms nervous system
mesoderm
various structures like muscles, bones, + some visceral organs
blastopore
first opening to develop in the embryo
protosomes
animals that form mouth first
deuterostome
animals that form anus first
Hox genes
“master control genes”, they turn off and on many other genes involved in animal development
duplication of Hox genes function
allows for greater morphological complexity in more recently evolved animals
representative taxa of the metazoan clade
sponges
derived characteristics of the metzoans
absence of cell walls, multicellular, heterotrophic
eumetazoans representative taxa
comb jellies
eumetazoans derived characteristics
endoderm + ectoderm, specialized tissue
bilaterians representative taxa
8 animal phyla
bilaterians derived characteristics
Mesoderm, bilateral symmetry
deuterosomes representative taxa
sea star
deuterosomes derived characters
Anus develops before mouth from blastopore
chordates representative taxa
lancelets
chordates derived character
Notochord; dorsal hallow nerve cord; pharyngeal slits, post-anal tail
craniate representative taxa
hagfishes
craniates derived characters
Skull protecting a brain and sense organs, pharyngeal GILL slits, 2-chambered heart, duplication of Hox genes
vertebrates representative taxa
lampreys
vertebrates derived characters
Vertebral column, improvements in skeleton and gills
gnathostomes representative taxa
cartilaginous fishes
gnathostomes derived characters
Jaws with teeth, paired fins, lateral line, 2nd duplication of Hox genes
bony “fishes” representative taxa
ray finned fishes (lung becomes swim bladder)
bony “fishes” derived characters
lungs
lobe-finned fishes representative taxa
lungfish
lobe-finned fishes derived characters
Paired fins with strong support of bone + muscle; basal bone of front (pectoral) fin is the humerus, 3CH
tetrapods representative taxa (1)
amphibians
tetrapods derived character (1)
four limbs with toes
tetrapods representative taxa (2)
amniotes
tetrapods derived character (2)
amniotic egg; rib cage ventilation; dry, impermeable skin
comb jellies
rotational symmetry
jelly fish
radial symmetry
derived character between comb jellies and jelly fish
one set of hox genes
debate about comb jellies
we are unsure their placement compared to sponges - genetically makes sense if comb jellies being first, but that would be that sponges lost layers and tissues
large reason for derived characters of the bilaterians
improves ability of prey capture and predator avoidance
deuterosomes show ___________ symmetry in the larval stage, but _________ symmetry in the adult stage
bilateral, radial
pentaradial
5 arms around central axis
special feature about the derived characters of chordates
they all are either present in the embryo or adult stage
this depends on the species
characteristic of craniate
they are more active hunters
lateral line
row of sensory structures to detect movement and vibrations in the water
why there are quotations around fishes in bony “fishes”
they are not all fish, some are tetrapods
swim bladder
organ of buoyancy that evolved from lung
increases or decreases buoyancy, allowing them to not need to keep swimming
benefits of 3 chambered heart
can have one circut to the lungs and another to the rest of the body
keeps blood pressure high
characters
traits that unite the entire clade
cause of the change in body planes between jelly fish and comb jellies
occurrence of Hox genes
animal studied to discover Hox genes
fruit flies
use of the vertebral column
makes them more flexible and helps with muscle attachment and propulsion
shared derived character of reptiles
scales
reptiles representative taxa
turtles, lizards, crocodilians
dinosaurs representative taxa
other dinosaur group, feathered dinosaurs (we write these as T.Rex and Velociraptor)
birds representative taxa
archeopteryx and modern birds
mammals representative taxa
monotremes, marsupials
eutherians representative taxa
other eutherian groups, primates
lizards derived character
scales
crocodilians derived character
4CH
other dinosaur groups derived character
grasping hands, bipedal
T. Rex and Velociraptor derived character
endothermic, feathers
archeopteryx derived characters
wings
modern birds derived character
loss of tail, teeth, and grasping hands
mammals derived character
mammary glands, hair, 4CH, endothermic
marsupials derived characters
placenta type 1 allows only partial development in uterus
other eutherian groups derived characters
placenta type 2 allows complete embryonic development within uterus
primates derived character
grasping hands and feet
fun fact about tetrapods
we knew about them for a while, but didn’t see them alive until a man brough one up, a woman recognized it and put it in a museum
difference between amniotes and amphibians
amniotic egg - the amniotic fluid allows the amniote to lay eggs in a drier environment/move around more freely
amniotes
really dependent on lungs
amniote egg - allowed them to venture
evolved hinges in ribs to allow for better ventilation
pulls in air, not just absorbed
sister clade of all other mammals
monotremes
sister clade of marsupials
eutherians