DNA probes
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
what is a DNA probe? what are DNA probes used for?
piece of ssDNA with bases complementary to gene of interest, chemical attached to a radioactive/fluorescent dye
used to locate specific alleles of genes and to screen patients for heritable conditions, drug responses or health risks
why are DNA probes labelled? what are they usually labelled with?
for identification/detection
radioactive/fluorescent dye
how are DNA probes produced?
target allele’s base sequence identified using DNA sequencing
complementary probe made using gene machine
sequence replicated using PCR
describe the process of screening DNA for a specific allele using a DNA probe:
individual’s DNA strands extracted and heated, causing them to separate into 2 ssDNA
DNA sample digested into fragments using restriction enzymes and separated using electrophoresis
add fluorescently/radioactively labelled DNA probes
hybridisation occurs - DNA probes bind w/ target gene
DNA washed so any XS unbound DNA probes washed away
visualise any DNA probe which has been hydrolysed to DNA fragments using UV light/radiography (respectively)
the presence of the radioactive/fluorescent label indicates that the allele of interest is present in the DNA sample
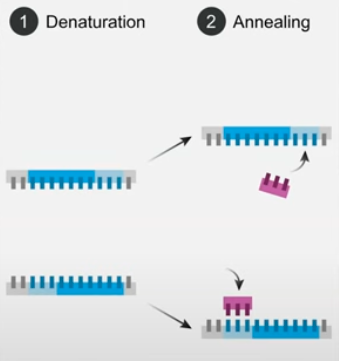
describe the DNA hybridisation stage:
DNA sample heated, causing it to denature so H bonds between bases break and becomes ssDNA
the ssDNA sample is mixed w/ the DNA probe and cooled so any complementary sequences can align and anneal, forming H bonds
some of the patient’s DNA samples will anneal back together, but some will anneal w/ DNA probe
give one advantage of having your DNA screened:
acts as personalised medicine - e.g. certain drugs may be more/less effective based on genotype
so allows best dose to be determined - increases effectiveness/safety and helps save money
what is genetic counselling?
form of social work in which people have their family history researched to consider the likelihood of them carrying any alleles linked to diseases/disorders
e.g. if you find you are likely to carry an allele relating to a certain cancer, you can opt for more regular tumour screenings