chapter 3 enzymes
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
define activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction,
before a reaction takes place, activation energy(an energy barrier) must be overcome
define a catalyst
a substance that increases rate of a chemical reaction but remains unchanged at the end of the reaction
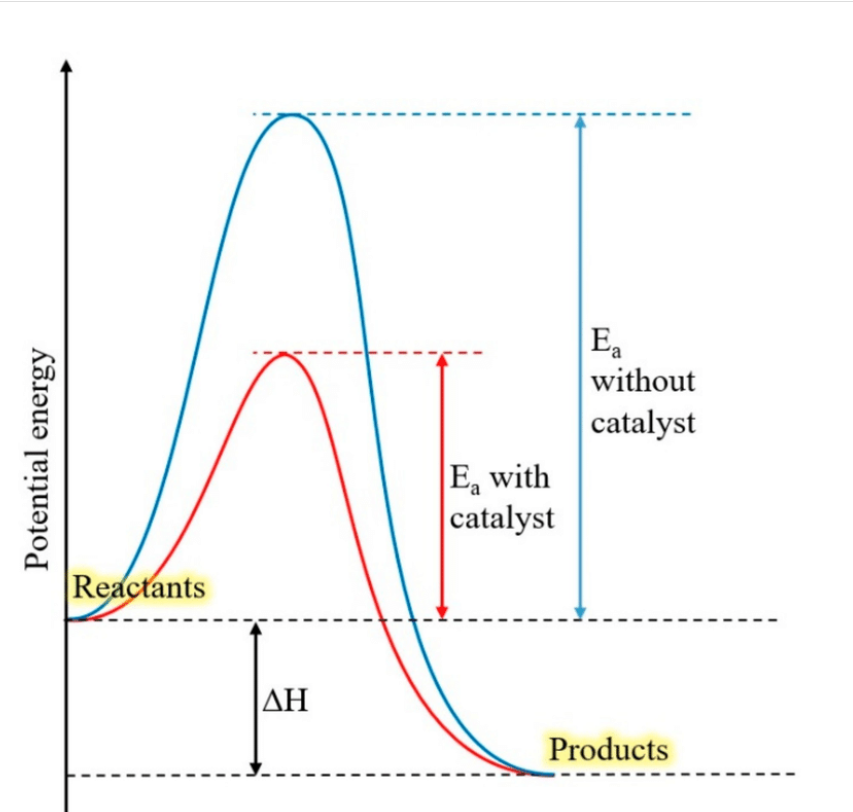
describe the uphill, peak and downhill portion of the energy profile
uphill: initial investment of energy required to start a reaction, the activation energy ea
peak: reactants are in unstable transition state where bonds are being broken or formed
downhill: after bonds formed/broken, new molecules settle into their new bonding arrangement to form the product
define an enzyme
a biological catalyst that speeds up biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy of a reaction
effect of enzyme on a reaction
lowered ea
more reactant molecules can overcome ea to rch transition state to be converted to product molecules
properties of enzymes [6]
enzymes are very efficient(enzyme catalysed reaction is 10^8 faster)
enzymes are needed in minute amts (remain chem unchanged and can be reused)
enzymes hv high degree of specificality (enzymes specific to substrate)
enzymes can be denatured by temperature and pH
enzymes hv optimum pH and temp which they work best in
enzymes can be regulated w activators or inhibitors
what kind of protein are enzymes
globular
how is enzyme denatured
when bonds holding the enzymes in their specific 3d conformation are disrupted
what are the 4 category of amino acids enzymes are made of
catalytic aa: r grp is directly involved in the ctaalytic activity(break/form bond)
binding aa: r grp helps bind w susbtrate to hold in position(non covalent/weak bonds)
structural aa: maintains specific 3d conformation of active site and whole enzyme
non essential aa: no specific function. doesnt matter if they gone
what are cofactors
additional non protein components, enzyme interact w via covalent/weak bonds
what are the three types of cofactors
inorganic metal ions, prosthetic group and coenzymes
describe all three