Lecture 4 Color Vision Stereopsis
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Photoreceptors allow us to see
Rods – scotopic (dim) conditions Peripheral retina
Cones – photopic (bright) conditions – color
Central retina – macula/fovea
Trichromatic vision – 3 types of cones
Red sensitive Green sensitive Blue sensitive
develop color vision around what age? whats the visible spectrum of light?
Develop around 5 months of age Visible spectrum of light 400nm-700nm
Monochromats – 1 type of cone
Does not see color Rare May also have reduced VA
Dichromats – 2 primary cone types
Protanopia – unable to distinguish red/green hues Brightness of red/orange/yellow is diminished 1/100 males (1%)
Deuteranopia – unable to distinguish red/green hues Does not have the diminished brightness 1/100 males (1%)
(Tritanopia – unable to distinguish blue/yellow hues (0.001%)
Trichromats – 3 primary cone types
Anomalous trichromacy – one or more of the peak sensitivity of the pigments isn’t right Protanomaly (protanomalous) Reduced sensitivity of red Colors shifted towards green 1/100 males (1%) Deuteranomaly (deuteranomalous)* Reduced sensitivity of green Colors are shifted towards red 5/100 males (5%) Tritanomaly Reduced sensitivity to blue © Neiman, Rev Fall 20240.0001%
Anomalous trichromacy –
one or more of the peak sensitivity of the pigments isn’t right

Dichromats
absolute color deficient
examples of Dichromats
Protanopia – red deficient - 1% males Deuteranopia – green deficient - 1% males Tritanopia – blue deficient - 0.001% males
Trichromats
– Partial color deficient
examples of trichoromats
Protanomaly – red weakness – 1% males Deuteranolmaly - green weakness - 5% males * most common Tritanomaly – blue weakness – 0.0001% males
Red/Green deficiencies
Sex linked – X chromosome Recessive trait Males mostly affected (8%) Females (0.4%)
Congenital Color Vision Defects
Present since birth Stable Bilaterally symmetric Throughout the visual field Patient is asymptomatic
Acquired Color Vision Defects
Present secondary to ocular or visual pathway disease Asymmetric in one or both eyes May affect only a portion of the visual field May progress or regress Highly symptomatic
Once thought: Kollner
Optic Nerve Disease = red/green Retinal disease = blue/yellow
However, too many exceptions: Verriest
Type I = Red/Green with shift in peak spectral sensitivity to shorter wavelengths Type II = Red/Green with preservation of the spectral sensitivity Type III = Blue/Yellow with shift in peak spectral sensitivity to shorter wavelengths Type IV = ill-defined or not classifiable
autorefrac use near infared
out of light we can see
Color Vision – Why test
All new patients Rule out congenital color deficiencies Rule out acquired color deficiencies
Support ocular signs of disease Optic nerve, macula problem…
Color vision necessary for professions Airline pilot Air traffic controller Firefighter Police officer Train conductor Some ranks in the armed forces Some electrical/electronic engineers
Color Vision - Tests
Identify numbers/shapes Ishihara – Red/Green HRR – Red/Green and Blue /Yellow
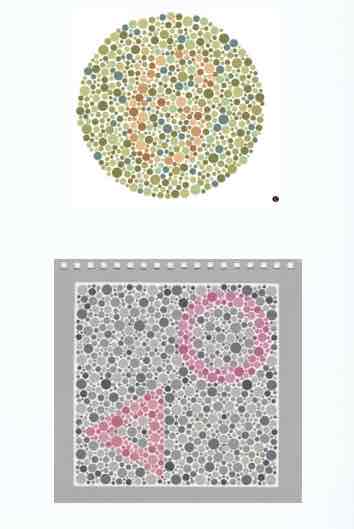
color vision tests
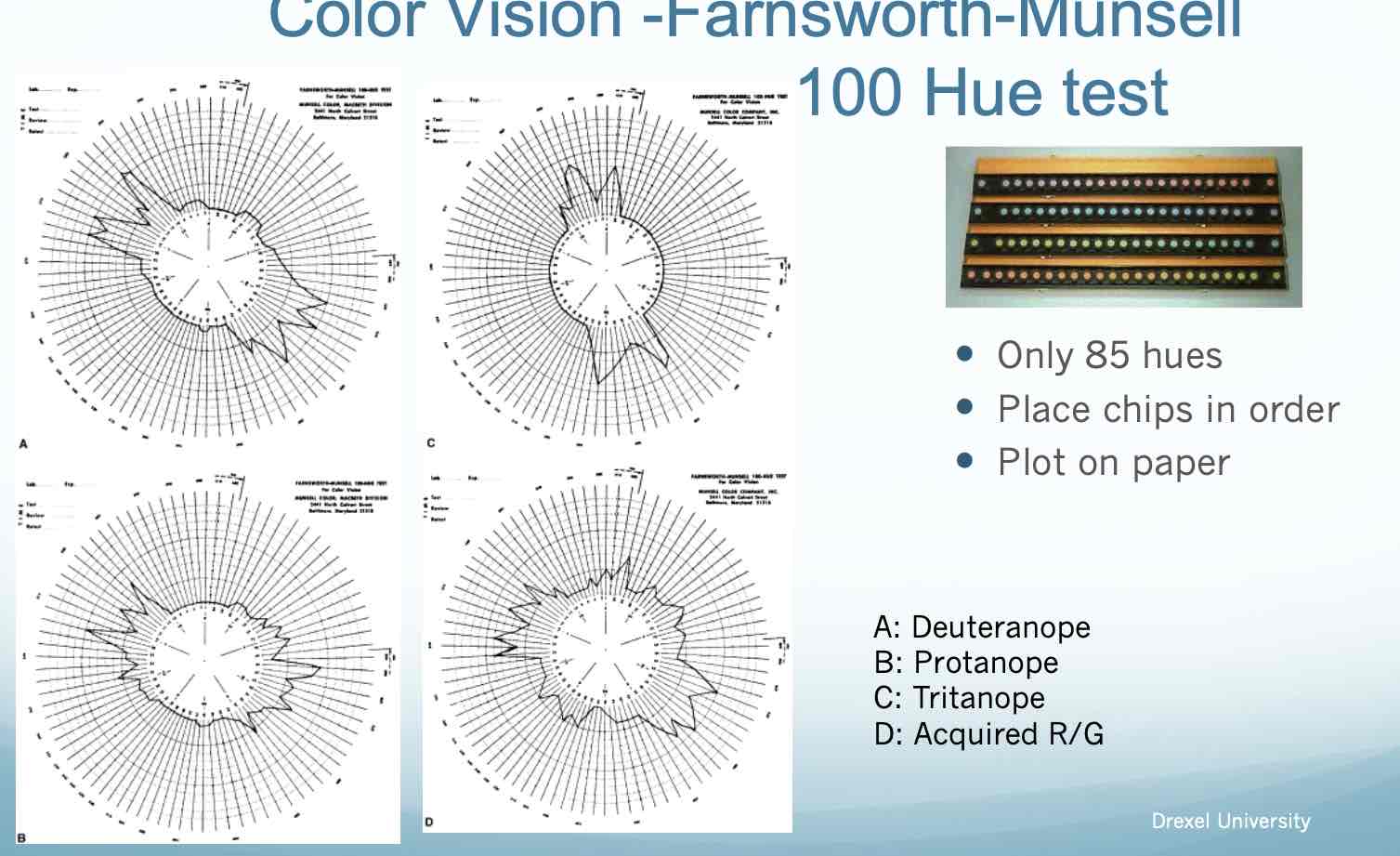
Arrange colors in an orderly spectral sequence D 15 Farnsworth-Munsell 100 Hue test

Color Vision – Ishihara
Tests for Red-Green color deficiencies Identify numbers Abbreviated test/full test Plate #1 – demonstration plate Plates #2 – 15 – screening plates Plates #16 – 17 – diagnostic plates Plates # 18 – 24 – illiterate plates
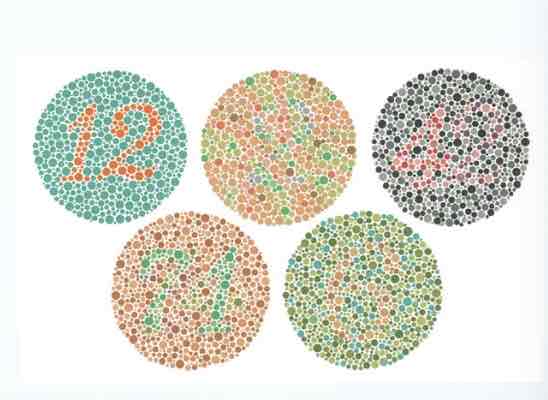
Color Vision - Ishihara requirments
Pt must have 20/200 acuity to test Pt wears their glasses Lighting – C-daylight Bulb vs glasses* Overhead on full Stand light projected toward the plates 75 cm testing distance Demonstration plate – first plate “12” Anyone that has 20/200 acuity or better should see this – malingerer Does not count in your recording
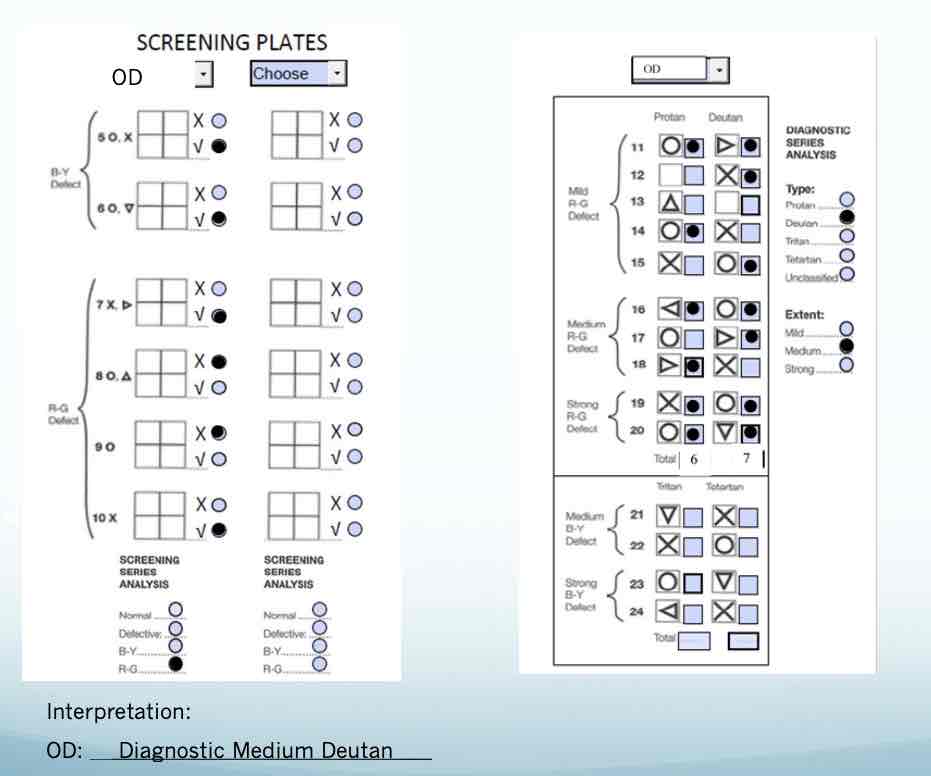
testing for Color Vision - Ishihara

testing for Color Vision - Ishihara pt 2

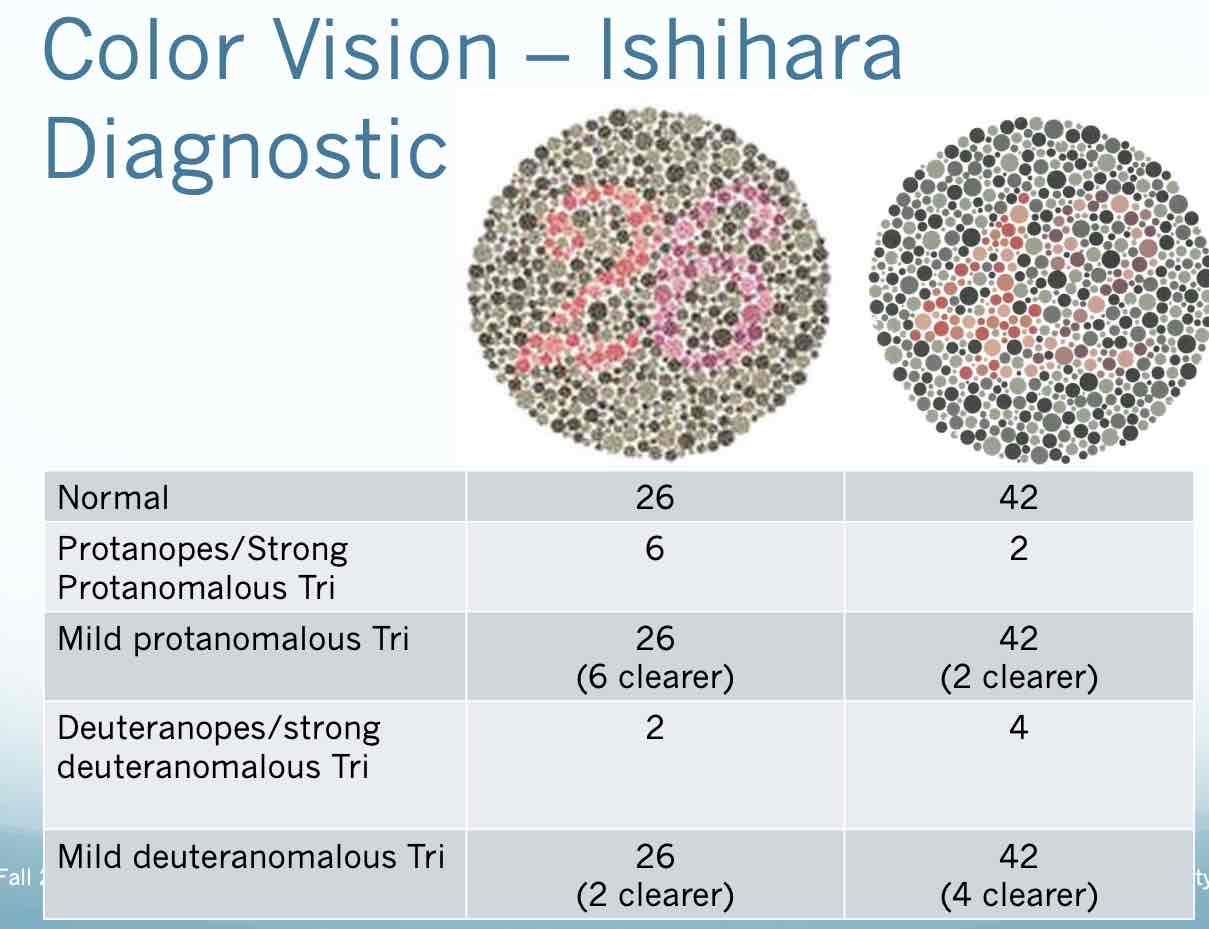
Color Vision - HRR purpose
Tests for Red-Green and Blue-Yellow color deficiencies Identify shapes Plates #1 – 4 – demonstration plates Plates #5 – 10 – screening plates #5-6 blue yellow #7-10 red green Plates #11– 24 – diagnostic plates #11-20 red green #21-24 blue yellow



HRR color vision screening plates

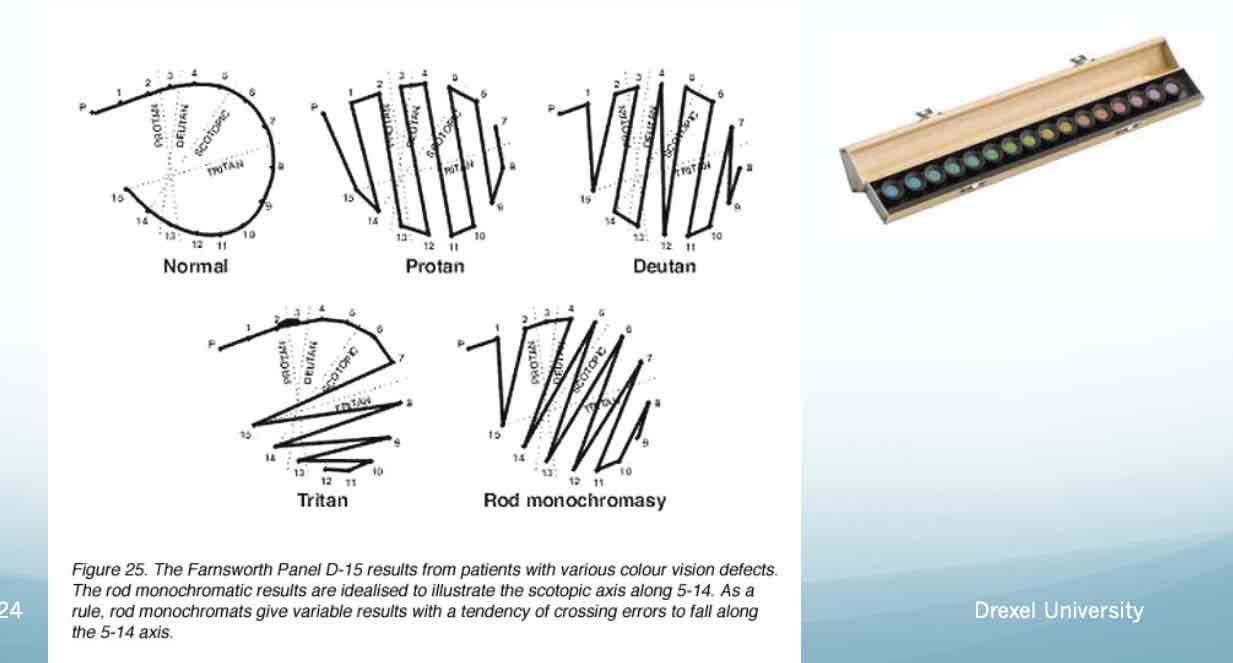
Color Vision – D-15
Place chips of color in order from stationary chip Plot out on paper to determine deficiency
Anomaloscope
An instrument that requires the patient to adjust the knob to match a ‘test’ field Patient adjusts the red/green color until it matches Provides the examiner with type of color vision deficiency depending on the amount of colors used

Stereopsis
The perception of nearness or farness of object points obtainable from disparate, but fusible, retinal images Due to binocular horizontal retinal disparity Lateral displacement of our eyes – different views of the same object.
Important indicator for the binocularity of your patient
simultaneous perception
1-3 months
flat fusiion
3 months
stereopsis
3-5 months
1-3 months – simultaneous perception
Determine presence/absence or degree of stereopsis Look for suppression Screen for constant strabismus/microstrabismus Requirement for professions Aid in prognosis/treatment of vision therapy
Reduced Stereopsis
Constant strabismus – does NOT have binocularity, unable to appreciate stereopsis Intermittent strabismus – will have binocularity and appreciate stereopsis but may be reduced Reduced acuity in one or both eyes Small central suppression scotoma Unequal refractive errors – changes image size on the retina – may reduce stereopsis
Monocular Clues for Depth
Relative Size Interposition Linear perspective Aerial Perspective Light and Shade Monocular movement - parallax
relative size
perceive smaller objects as further away – size constancy
interposition
an object that is behind is further away
linear perspective
Parallel lines that converge as move away from you
aeriel perspective
objects in the distance have less contrast and less saturated color
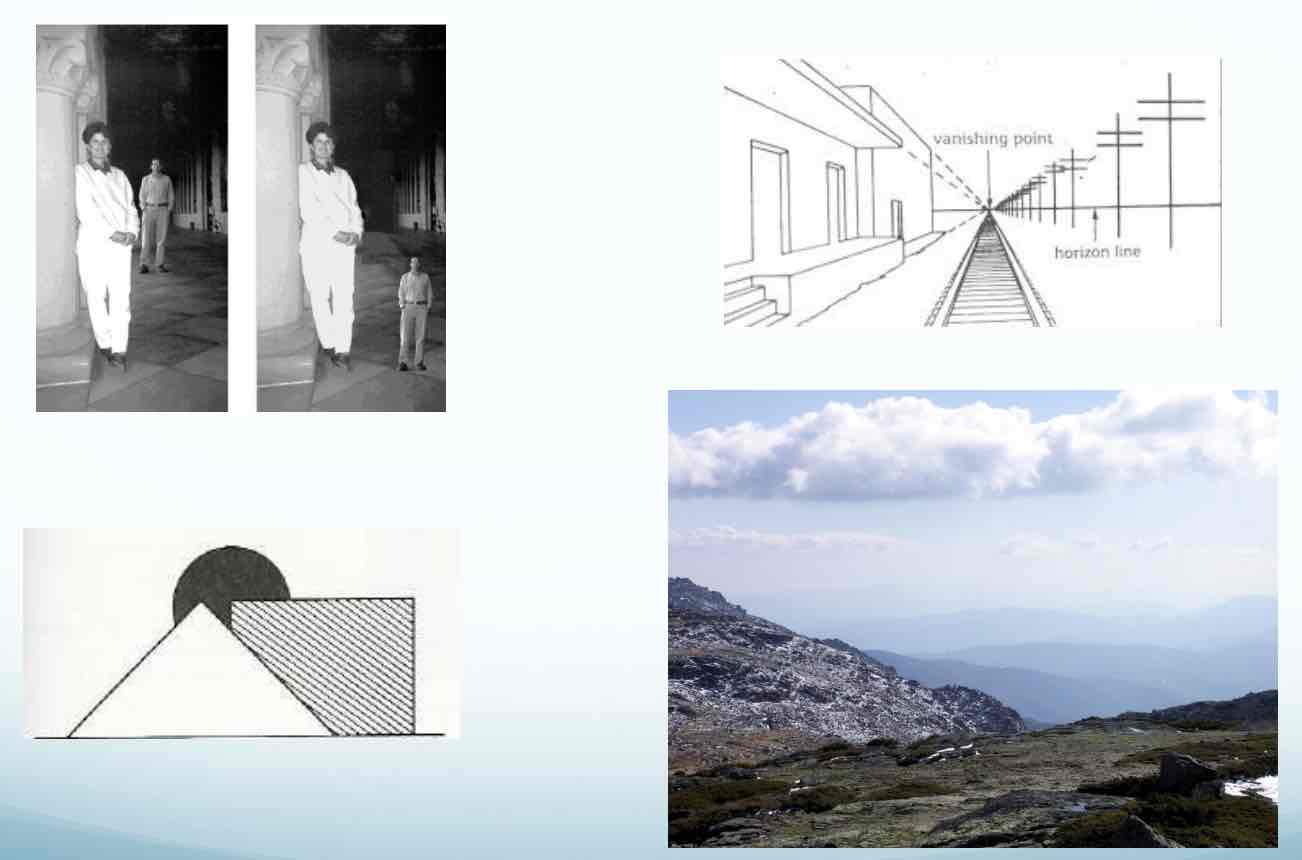
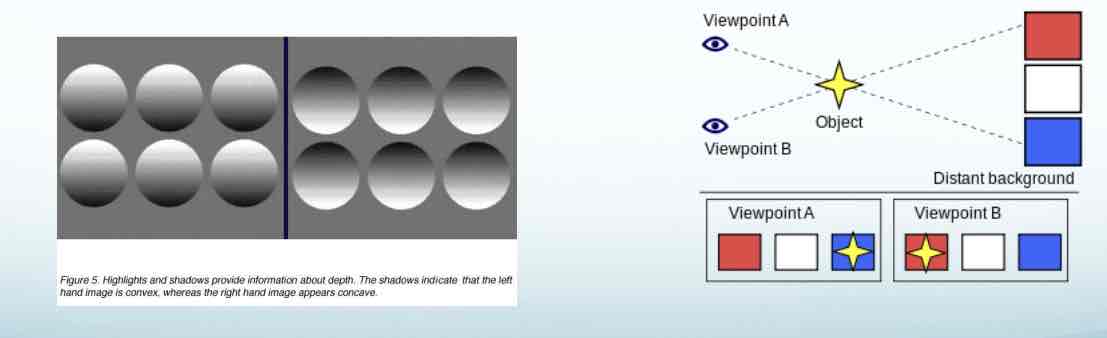
Monocular Clues Light and shade
can provide info about depth
monocular clues Monocular Movement Parallax
hold up your fingers Close objects move ‘against’ Far objects move ‘with’
Randot Stereotest
Randot circles – local stereopsis/contour targets Two similar targets that are laterally displaced The finer the stereoacuity (secs of arc), the smaller the lateral displacement (localization acuity) Monocular clues are present that may help your pt. Stereo-acuity – finer measurement Seconds of arc

Random-dot stereotargets (gross forms) –
global stereopsis
Geometric shapes made from dots that are laterally displaced Minimal monocular clues Higher order form of stereo Can only be achieved with bi-foveal fixation
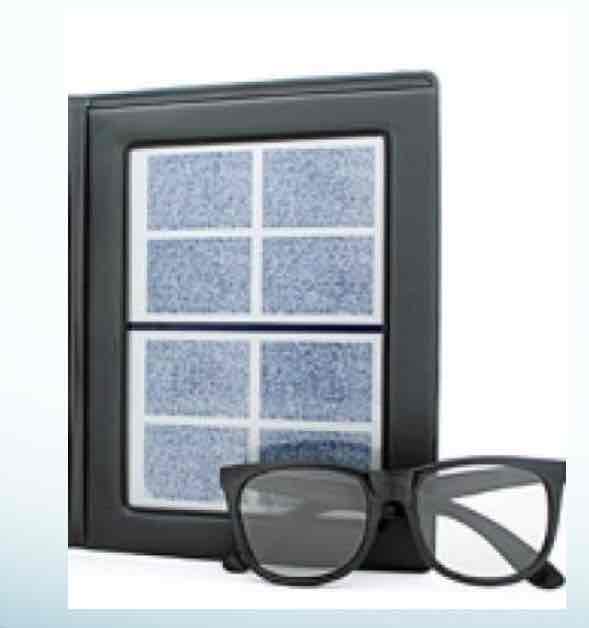


randot stereotest precedure


randot stereotest/interpretation and recording

interpretation of randoty stereo
