Reproductive system
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Fundamental purpose of reproductive system is to
create gametes and to form a zygote
Gametes
sex cells that merge to form zygote
male gametes are
sperm cells
female gametes are
oocytes
Fertilization refers to
creation of zygote once a sperm cell and oocyte have merged
reproductive system consists of:
gonads (testes/ovaries) —→ produce gametes and endocrine hormones
reproductive tract
accessory glands
external genitalia
Male reproductive system:
scrotum
testis
epididymis
Ductus deferens
Urethra — transports urine and seminal fluid
glands
seminal gland
prostate gland
bulbo-urethral gland
penis
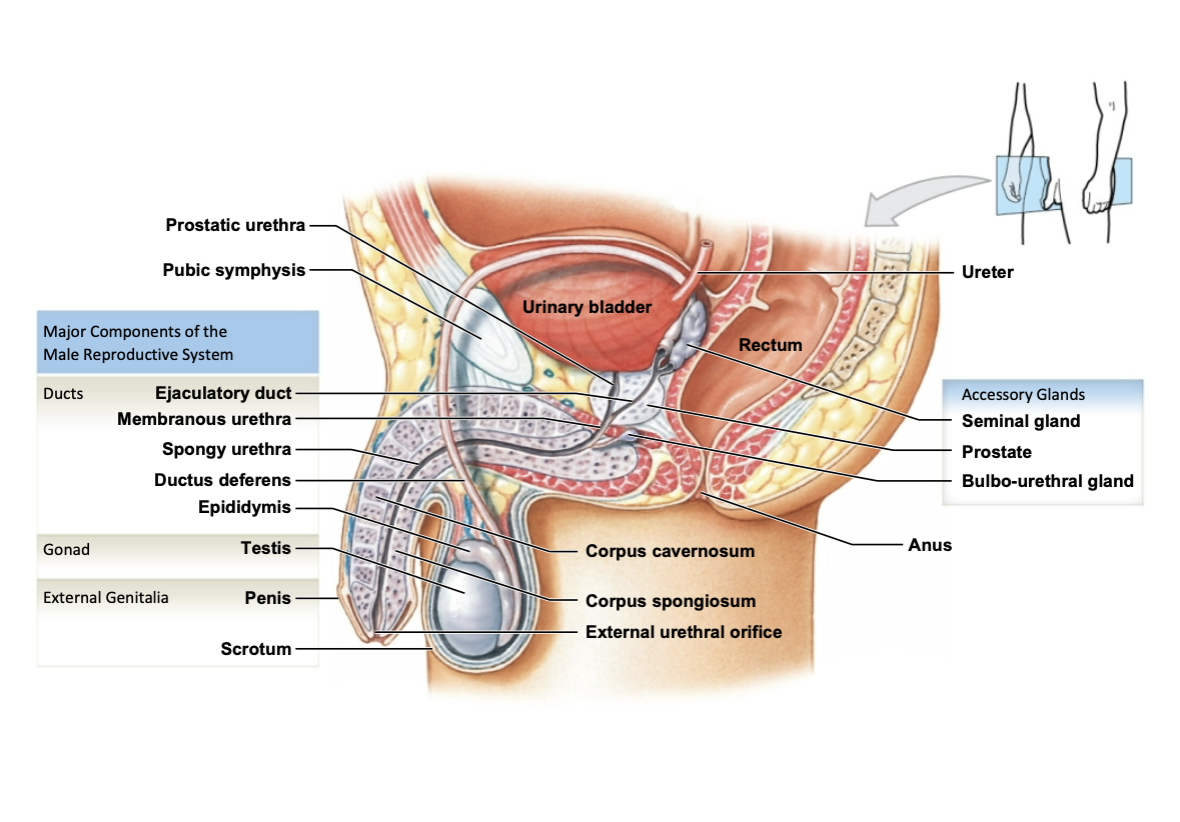
3 parts of male urethra
prostatic
membranous
spongy
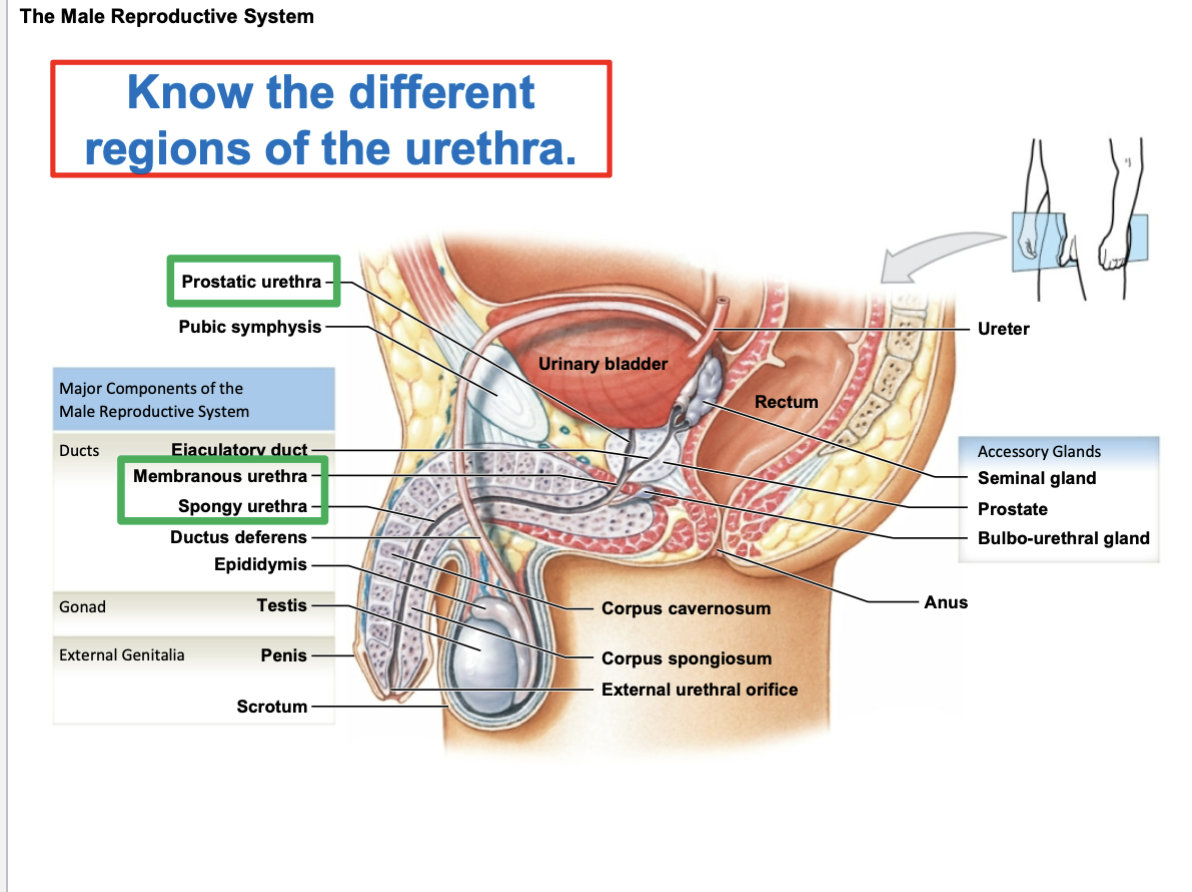
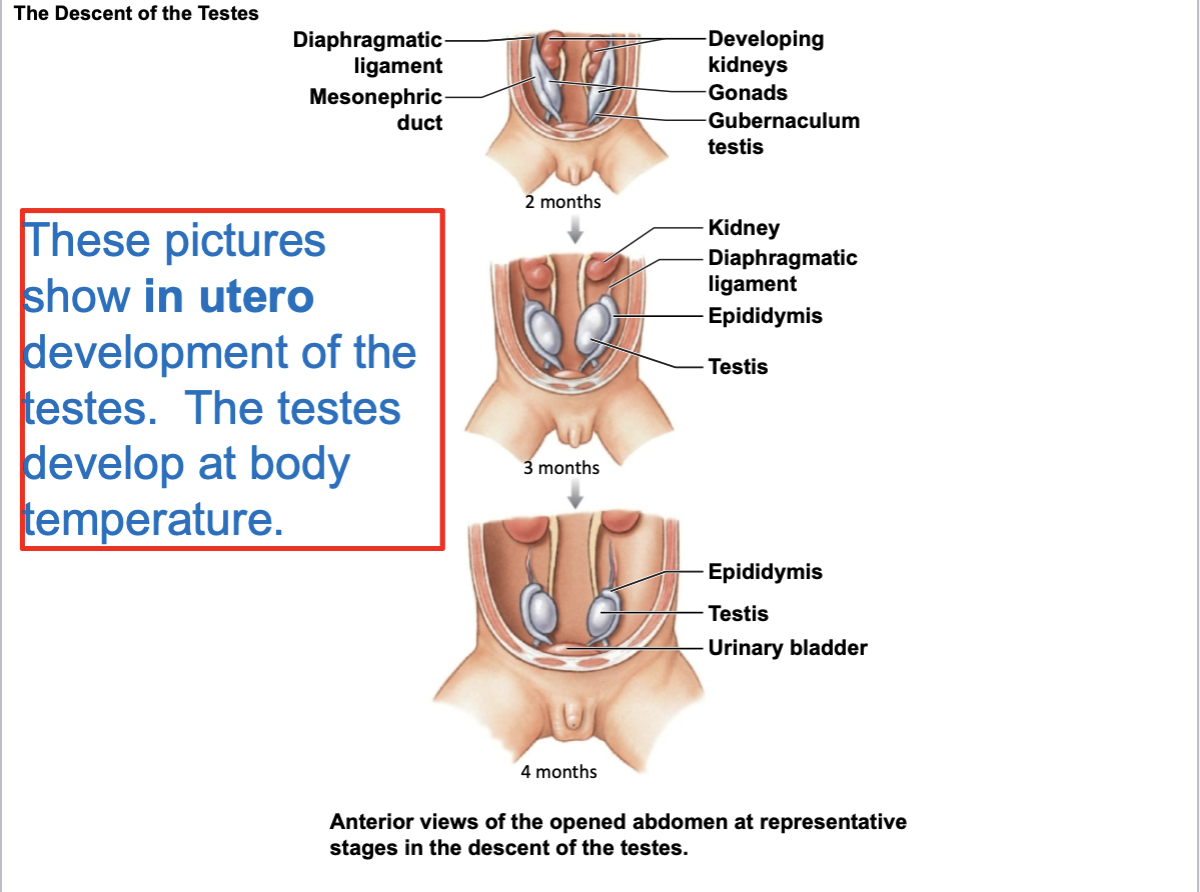
During in ureto development, the testes actually form ____. As in ureto development progresses, the testes slowly drop from ____ and descend into the ____
inside the abdominal cavity ; the abdomen ; scrotal sac
what develop at body temperature
testes
Sperm development takes place at
slightly below body temp (around 93-95F)
Spermatic cord connects directly to _____
testis
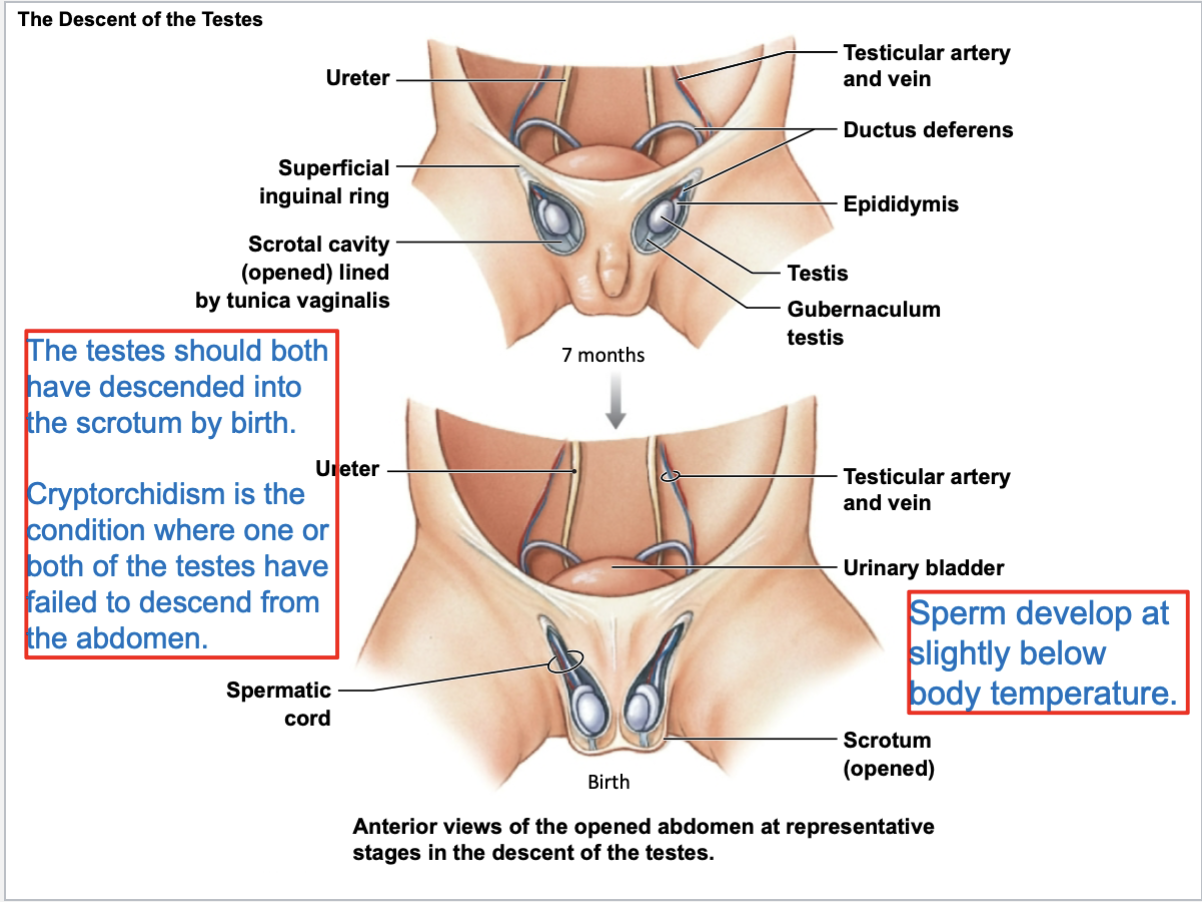
Contents of spermatic cord:
blood vessels, ductus deferens, nerves
Cremaster muscle
wraps around the spermatic cord and testis to which the cord is connected.
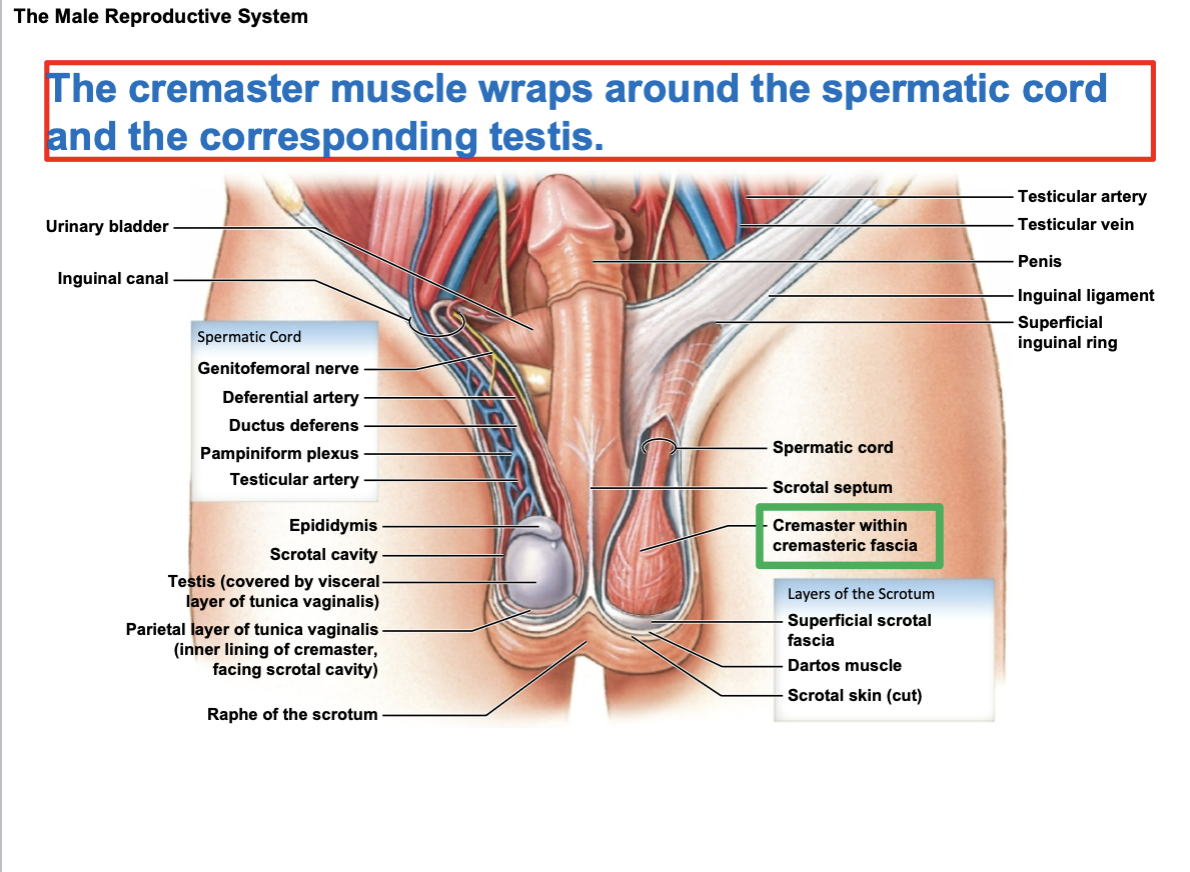
Cremasteric reflex
involves rubbing the skin of the inner thigh and seeing a reflexive elevation of the ipsilateral testis
the seminiferous tubules are:
the coils found within the testes. Sperm are created in the tubules
In between the seminiferous tubules are
special endocrine cells that produce testosterone
Another key structure of the male reproductive tract is the
epididymis
It has a comma shape and it sits on a testis.
A key process that occurs in the epididymis is
the maturation of sperm cells — a process called capacitation.
Spermatozoa must be biochemically modified here so that they are eventually able to penetrate an oocyte.
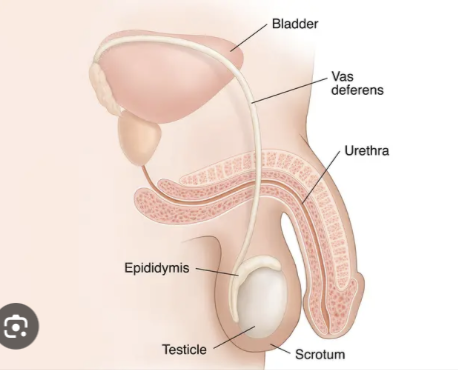
Male reproductive tract:
epididymis
capacitation
ductus deferens (vas deferens)
urethra
Structures that contribute to composition of seminal fluid
seminal vesicles, prostate gland, bulbo-urethral gland, epididymis
Semen is comprised of
sperm cells, seminal fluid and enzymes
Internal structure of penile tissue :
Two posterior corpora cavernosa
One anterior corpus spongiosum
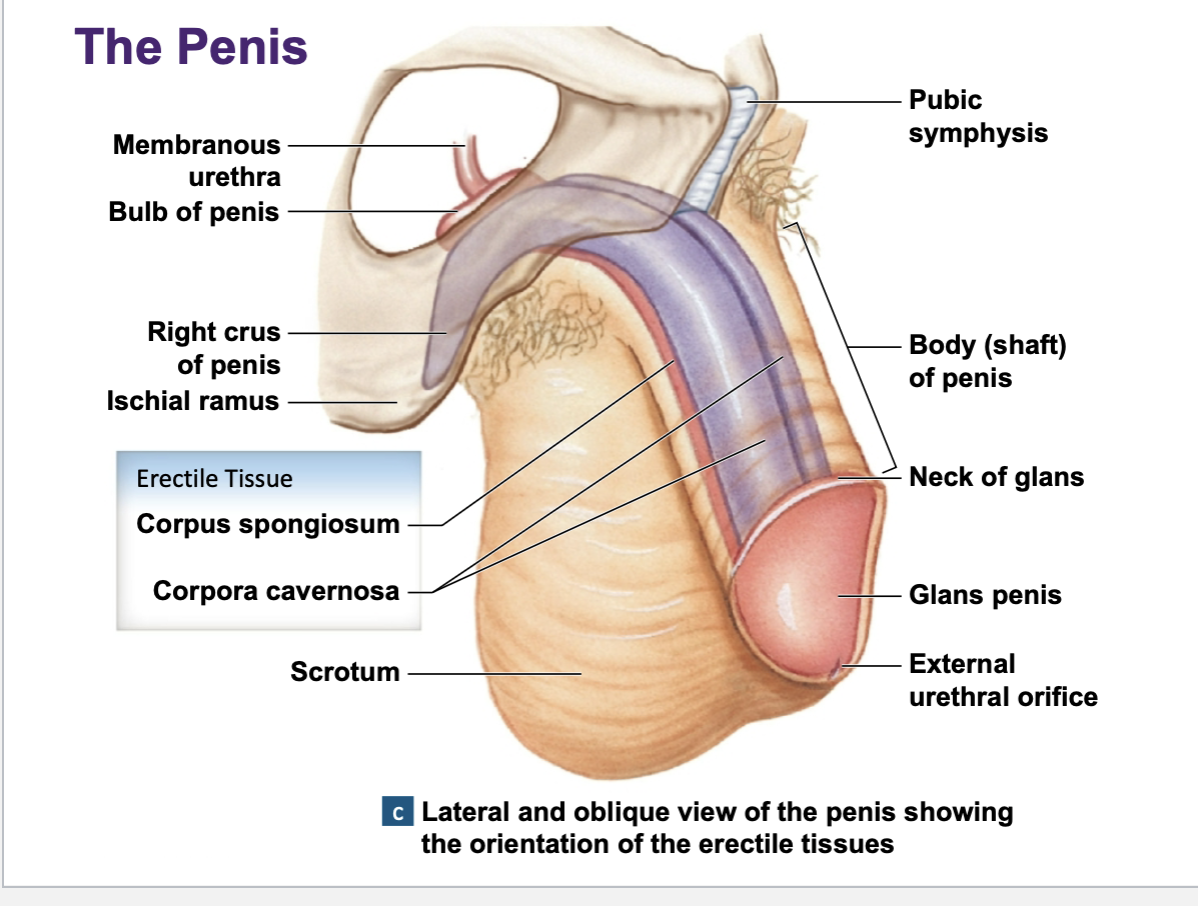
parasympathetic & sympathetic nerves act upon on penile tissue
Erection of penis -
parasympathetic nerves are activated
Smooth muscles in the arterial walls relax
Arterial vessels and within the corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum become engorged w blood
erection occurs
Semen release and ejaculation
sympathetic activity
emission
Ejaculation
contractions of ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus
Main female reproductive structures
ovaries
uterine tubes (fallopian tubes)
fimbriae
Uterus
cervix
vagina
external genitalia
labia minora/majora, clitoris
breasts
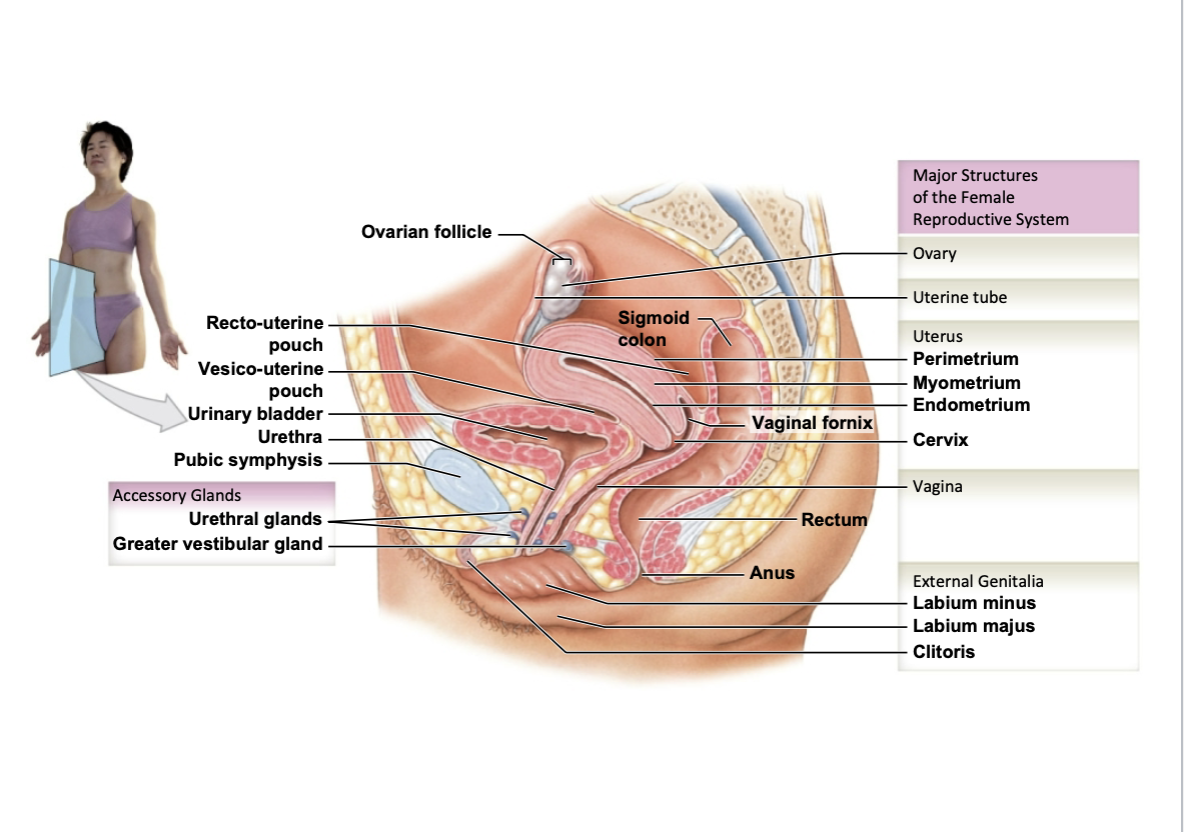
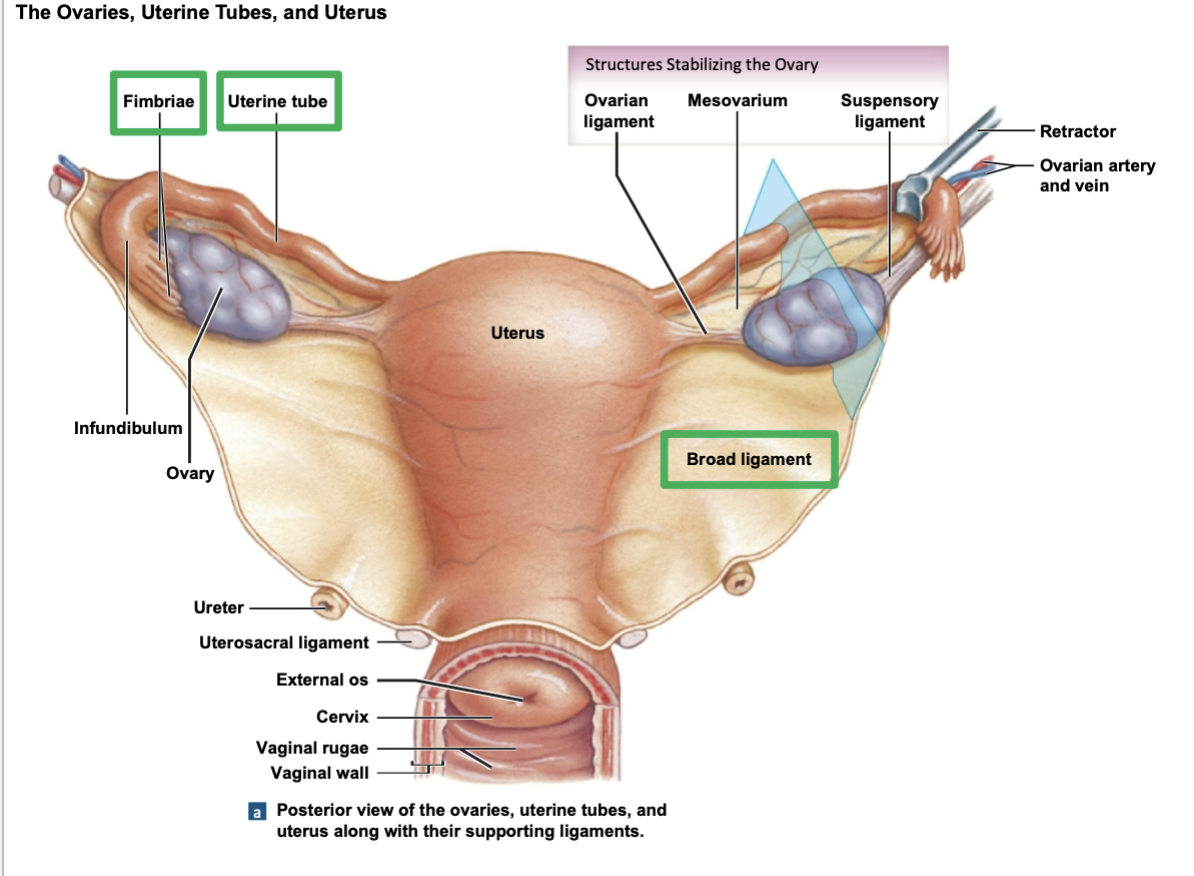
Broad ligament
attaches to lateral edges of the uterus
ligament is an important stabilizing structure for the uterus, especially during the expansion of uterus during pregnancy
Fimbriae are adjacent to, but not attached to, the ovary
3 processes occurring in female reproductive tract
oogenesis (creation of oocytes)
ovarian cycle
uterine cycle
Ovulation occurs when
oocyte is released by the ovary
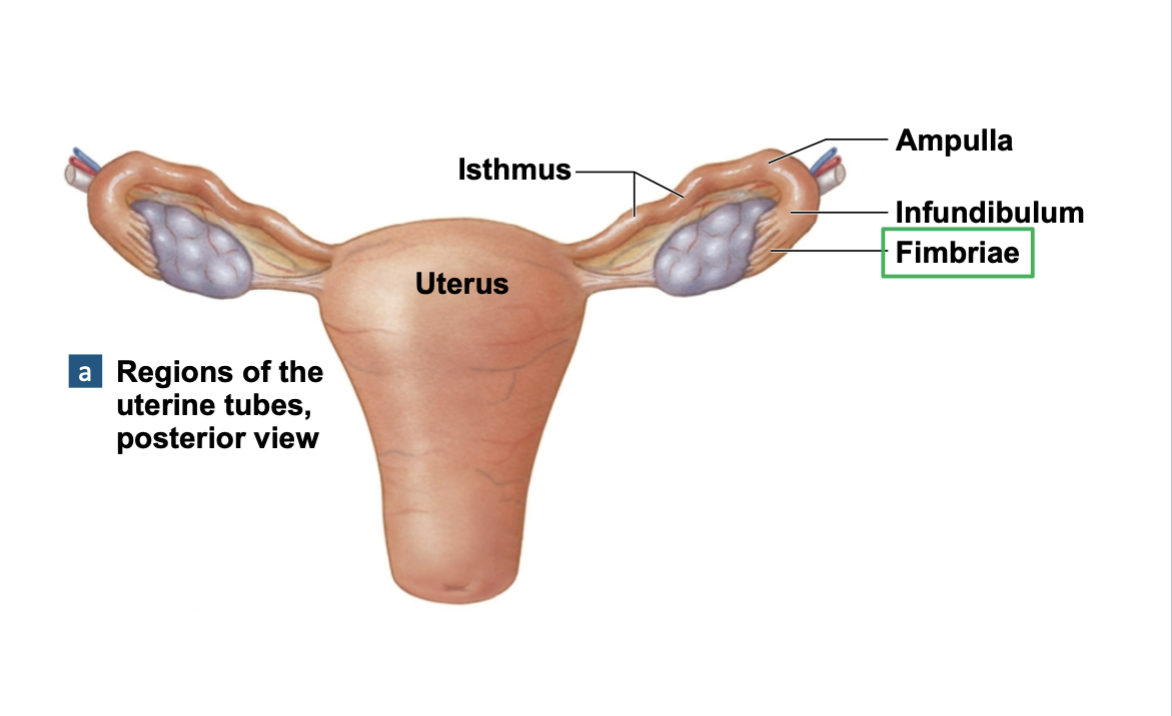
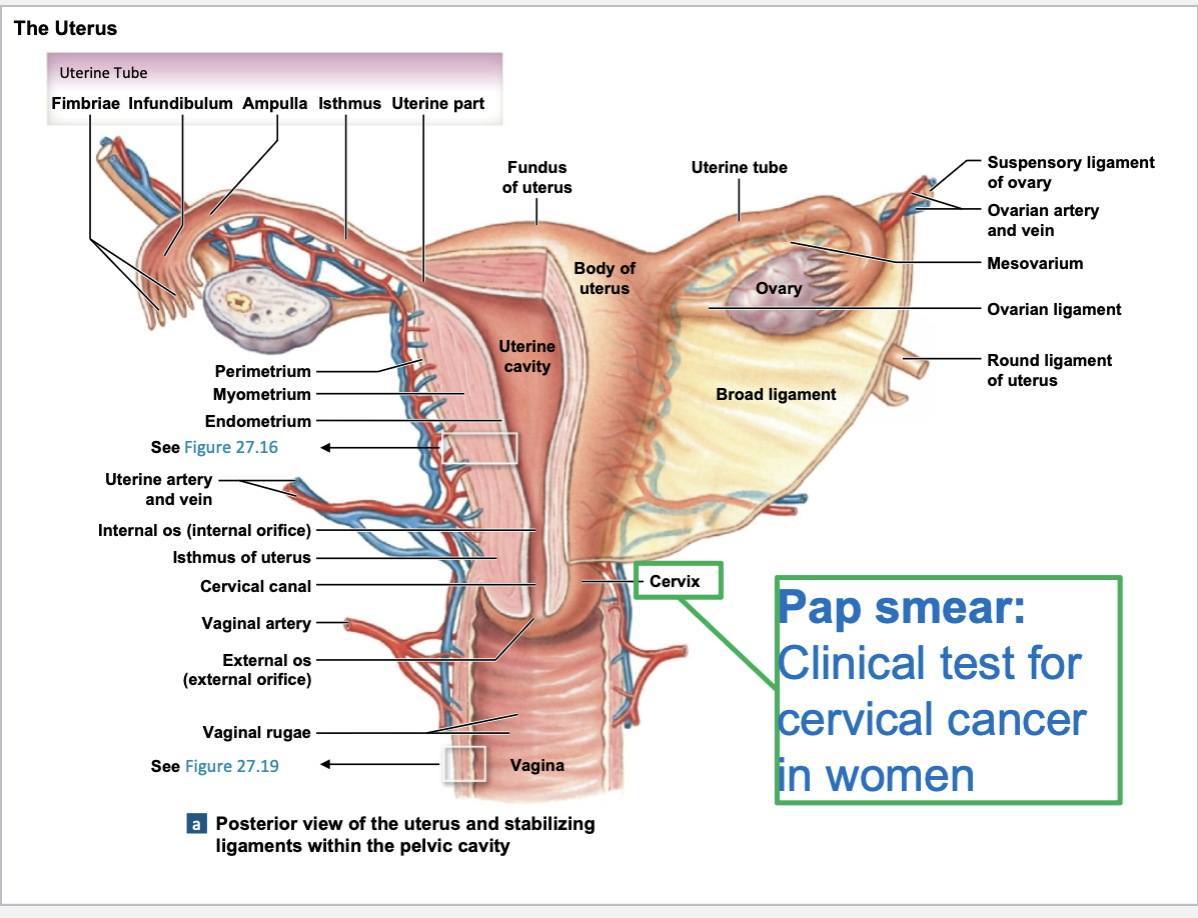
uterus consists of
body
fundus
uterine cavity
isthmus
internal os
cervix
cervical canal
External os
Menstrual cycle
process that occurs in female body to prepare body for potential pregnancy. inner lining of uterus is built up. in case a release oocyte is not fertilized, the inner lining of uterus is shed (period)
Process of menstruation is regulated by
hormones
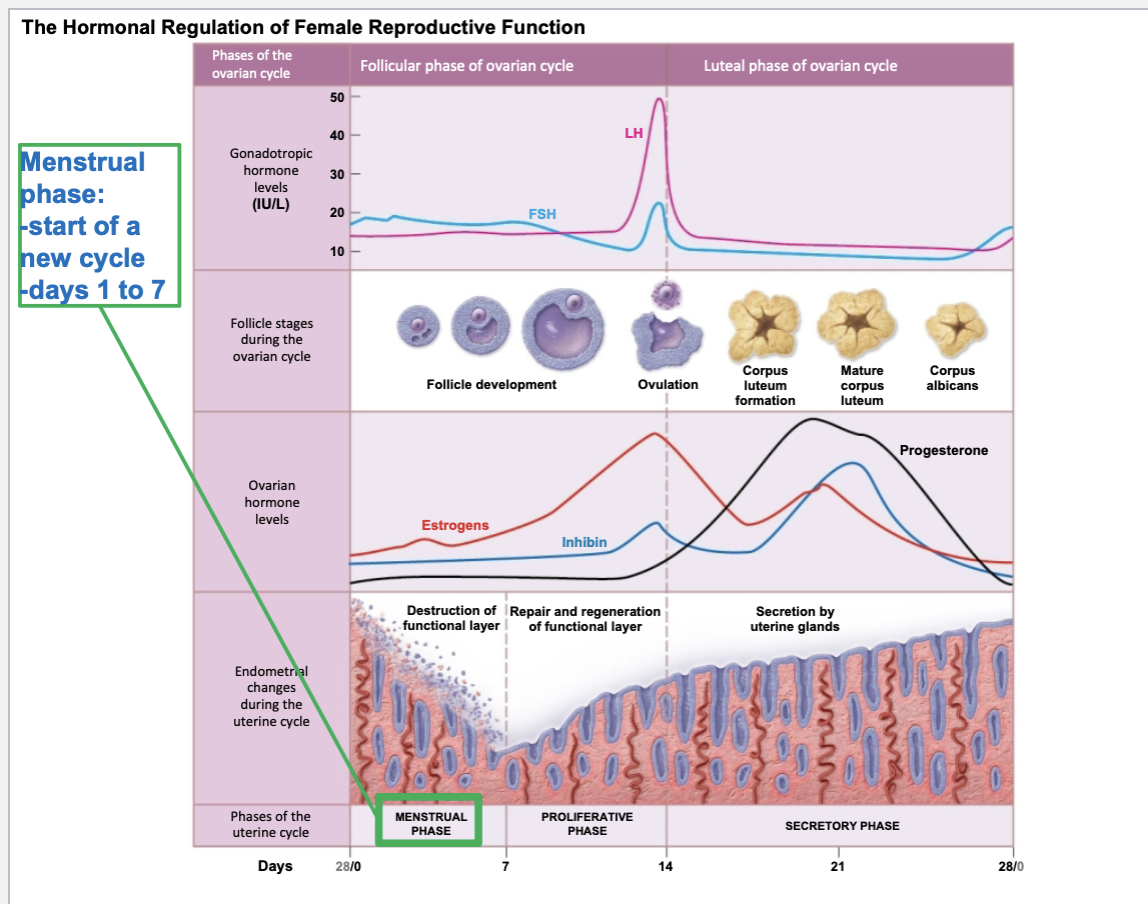
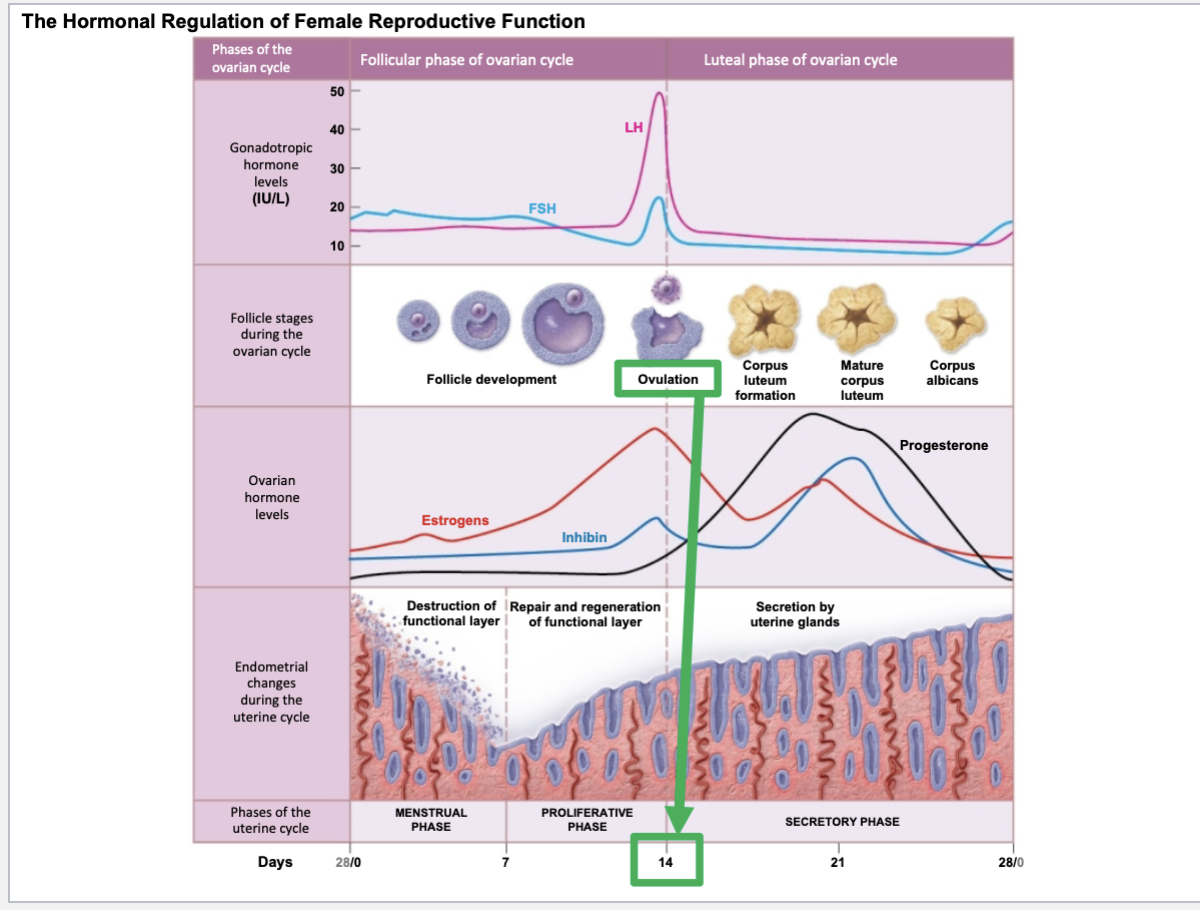
Ovulation occurs at day 14
A surge of luteinizing hormone stimulates this event
On avg, menstrual cycle takes place over course of 28 days
3 phases of menstrual cycle: in the order they are:
menstrual phase
proliferative phase
secretory phase
Uterine lining is shed during these first 7 days
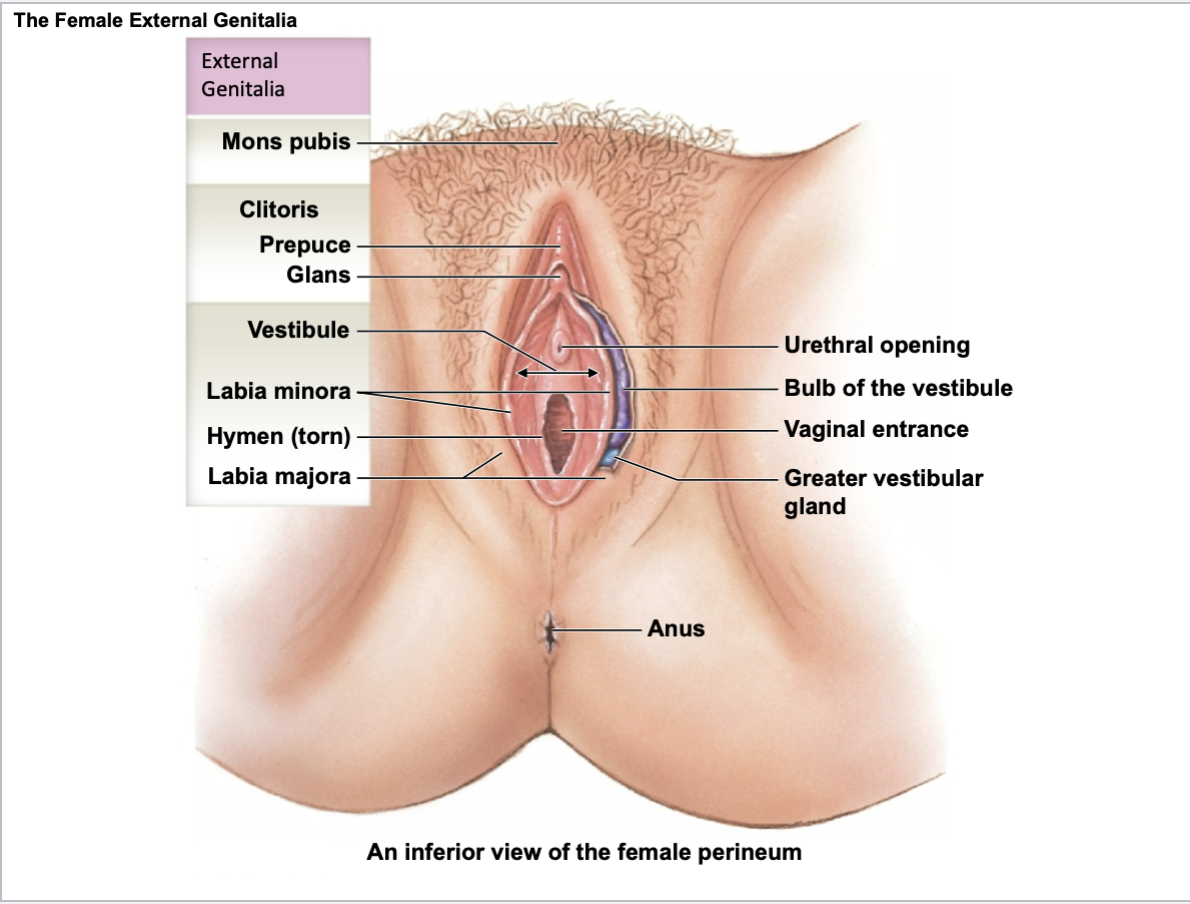
External genitalia
mons pubis
clitoris
cestibule
labia minora
hymen
labia majora
Breast tissue is part of female reproductive system
Which hormone stimulates milk ejection from breast
oxytocin (released by pituitary gland)
Female climacteric (menopause)
decline in estrogen levels results in:
reduced size of uterus
reduced size of breasts
thinning of vaginal walls
weakening of supportive tissues of reproductive organs
osteoporosis
hot flashes
Typically occurs at age 45-55
Male Climacteric
testosterone levels begin to decline (not as rapidly as estrogen however)
occurs gradually between ages 50-60
reduction in sexual activity