Wk 2 Cement Mortar and Concrete
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What concrete comprised of?
cement
water
aggregates
optional admixtures
What do admixtures do?
they tailor workability, setting and durability (adjusts properties) - usually in liquid or powder form
What are the good qualities of concrete?
mouldability
rapid early gain (quick gain in strength after being placed)
versatility
high long term compressive capacity
What is mortar?
a mix of cement water and sand (with no course aggregate)
What is the use of cement?/ what is cement?
a powder substance used for bonding parts to form a single whole
What are the two types of cement?
Hydraulic cement - consists of inorganic, non-metalic compounds that react with water to set
Portland cement - a type of hydraulic cement that contains Calcium Oxide and silicon dioxide
What are aggregates?
the materials mixed with cement and water to provide bulk and modify the physical properties of the concrete
What type of reaction occurs between cement and water?
hydration
starts of by remaining plastic until it sets and begins to gain strength (hardening)
What is gel porosity?
degree of hydration that governs strength stiffness and permeability
What is essential for continued hydration and densification?
adequate moisture and time
What is fine aggregate and its use?
e.g. sand
improves cohesion
workability
finish
What is the use of coarse aggregate?
provides bulk
reduces shrinkage
What is grading?
the distribution of particles of aggregates amongst various sizes - usually expressed in terms of cumulative percentages of larger or smaller than each other
What is proper grading?
The way we use different sized aggregates in combination to minimise voids and reduces the demand for paste (cement and water mix)
How are aggregates graded?
Using a tower of sieves with successively reducing sizes
aggregate placed inside and vibrated for a specific period
aggregates in each sieve are then weighed
weights are used to provide a profile of the distribution of different particle sizes
can create the aggregate grading curve
What are the properties aggregates should have?
hard
strong
chemically inert
non-porous
durable
good adhesion
good shape (sharp vs rounded)
recycled materials can be used as aggregates
What happens when w/c is so low that it is below critical?
too little water can lead to
incomplete hydration
harsh mixes
poor consolidation (not properly mixed - nonuniform)
What happens when w/c ratio is too high?
increases porosity
reduces strength
What will low w/c cause in general?
increased strength
increased durability
but it still needs to have sufficient water for workability
examples of admixtures and their uses?
air-entrainers (freeze thaw protection)
plasticizers - reduce water demand (makes it more flexible)
accelerators/retarders - speed up or slow down the setting process
What is workability?
the ability to place concrete without segregation of its components
influenced by w/c, aggregates, admixtures
poor workability causes voids, weak bonds to the reinforcements
workable concrete defined as suitable for placing and compacting under site conditions
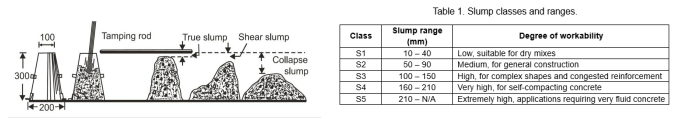
What is the slump test?
fresh concrete placed in a mould (trapezium shaped)
in 3 layers
when each layer is added, the concrete is compacted using a tamping rod 25 times (penetrating the layers below without touching the bottom layer)
the mould is lifted and the concrete settles
the way it settles will measure the consistency (used as quality control)
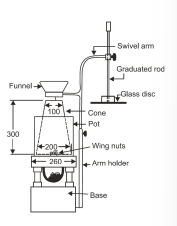
What is the vebe test?
Measures time required for a concrete volume, shaped as a conical frustum, to spread into a cylindrical form under vibration. After the cone is lifted, vibration causes the concrete to spread, and a stopwatch records the time until it fully contacts the glass disc
time known as the vebe degree (VB) measured in seconds
time indicates consistency of concrete
Hand mixing vs machine mixing
Mixing: the combining of the materials to form a uniform and workable mass, ensuring uniform coating of aggregate with paste
Hand mixing
suitable for small scale works
requires thorough mixing
poor mixing can cause segregation and weak zones/inconsistent properties
Machine mixing
used in most construction projects
more efficient and ensures better uniformity
What must we do with transport to ensure that the mixed materials don’t segregate?
transport promptly (can use a pump, bucket, wheelbarrow)
minimise delays
maintain temperature
avoid contamination
What must we do with placing to avoid segregation of materials?
place as close to the final position as possible to ensure bonding and compaction
place in layers
avoid drops of more than 1.5 meters - avoids cold joints (a visible seam that forms when fresh concrete is poured onto hardened concrete due to a delay between pours caused by mixing times)
Purpose of compaction
remove entrapped air
to make the concrete more dense and strong/durable
What happens if the concrete is insufficiently compact?
voids
honey combing
poor bonding to the reinforcement
higher permeability
less strong
air becomes trapped - significantly reduces strength
Methods of compaction?
Manual - rodding tamping or light hammering
Mechanical - interal vibrators, table vibrators, surface vibrators
What can over vibration cause?
bleeding
segregation
ensure the correct vibration frequency, amplitude and time
What is curing?
the maintenance of optimal conditions of temperature (greater than 10 degrees celsius) and humidity to promote the hydration of cement
It plays an important role on strength development and durability of concrete
Methods : water curing (sprinkling/ponding), membrane curing compounds, plastic sheeting and steam curing (precast)
Proper curing reduces permeability, cracking and enhances long-term strength

Strength development of concrete?
most of the strength is developed in the first 3 days (40-50%)
increases to 60-70% after a week
curing beyond 28 days will increase strength and durability
What is durability?
ability to resist environmental/service actions (chlorides, sulfates, freeze– thaw, carbonation) over service life.
How can we achieve durability?
low permeability - low w/c, good compaction, good curing
account for exposure environment (de-icing salts, marine, industrial)
quality control, placing and curing
What can cause durability issues in concrete?
reinforcement corrosion (the steel around it deteriorating/rusting)
freeze thaw damage (we can minimise by air entraining the mixes)
sulfate attack (reduce permeability)
carbonation
alkali-silica reaction
What are the desirable properties of hardened concrete?
strength
water tightness (low permeability)
durability
resistance to cracking
abrasion resistance