Periodic Table/Electron Configuration vocabulary Diagram | Quizlet
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
TERM
Alkali Metals
DEFINITION
Group of elements that have the most reactive metals
TERM
Noble Gases
DEFINITION
Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are filled
TERM
Transition metals
DEFINITION
filling the d sublevel
TERM
inner transition metals
DEFINITION
filling the f sublevel
Cation
positively charged ion (lost electrons)

Anion
negatively charged ion (gained electrons)
Electronegativity
The tendency for the atoms of an element to attract electrons when the atoms are in a compound
ionization energy
the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in its gaseous state
quantum mechanical model
the modern mathematical description of the location and energy electrons in atoms
quanta
The "set" amount of energy required to move an electron from its present energy level to the next higher one
Photon
Packets/bundles of electromagnetic energy
Hertz
SI Unit of measurement for frequency
Hund's Rule
orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin (maximize spin then pair)
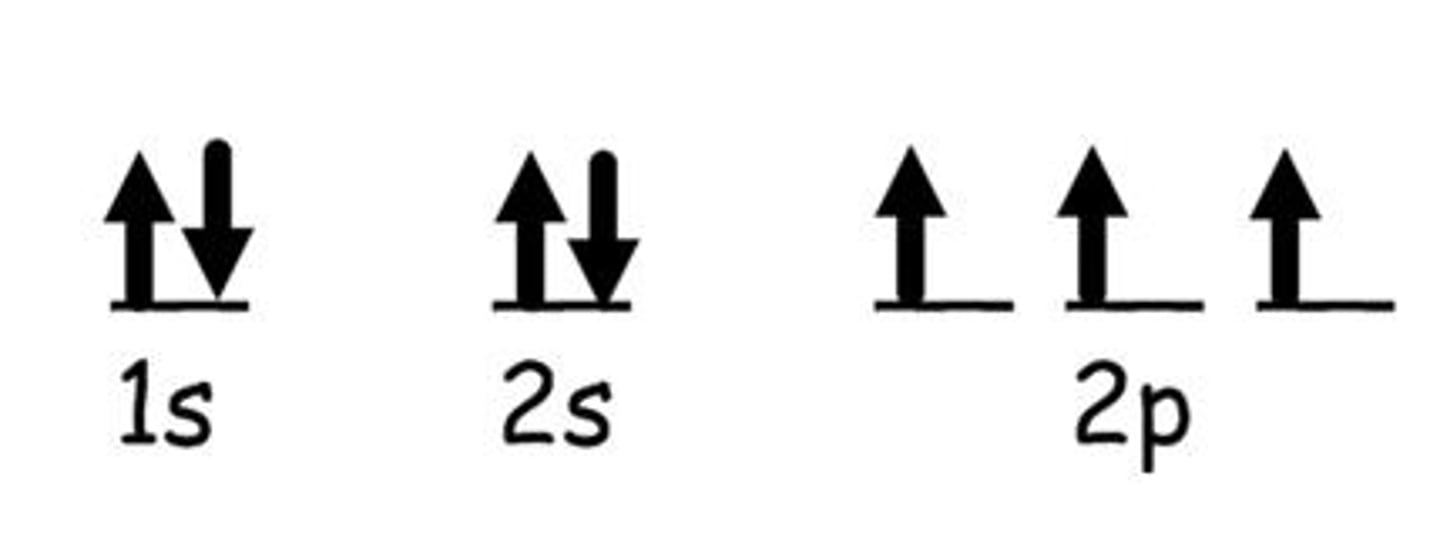
Pauli Exclusion Principle
An atomic orbital may describe at most two electrons, each with opposite spin direction
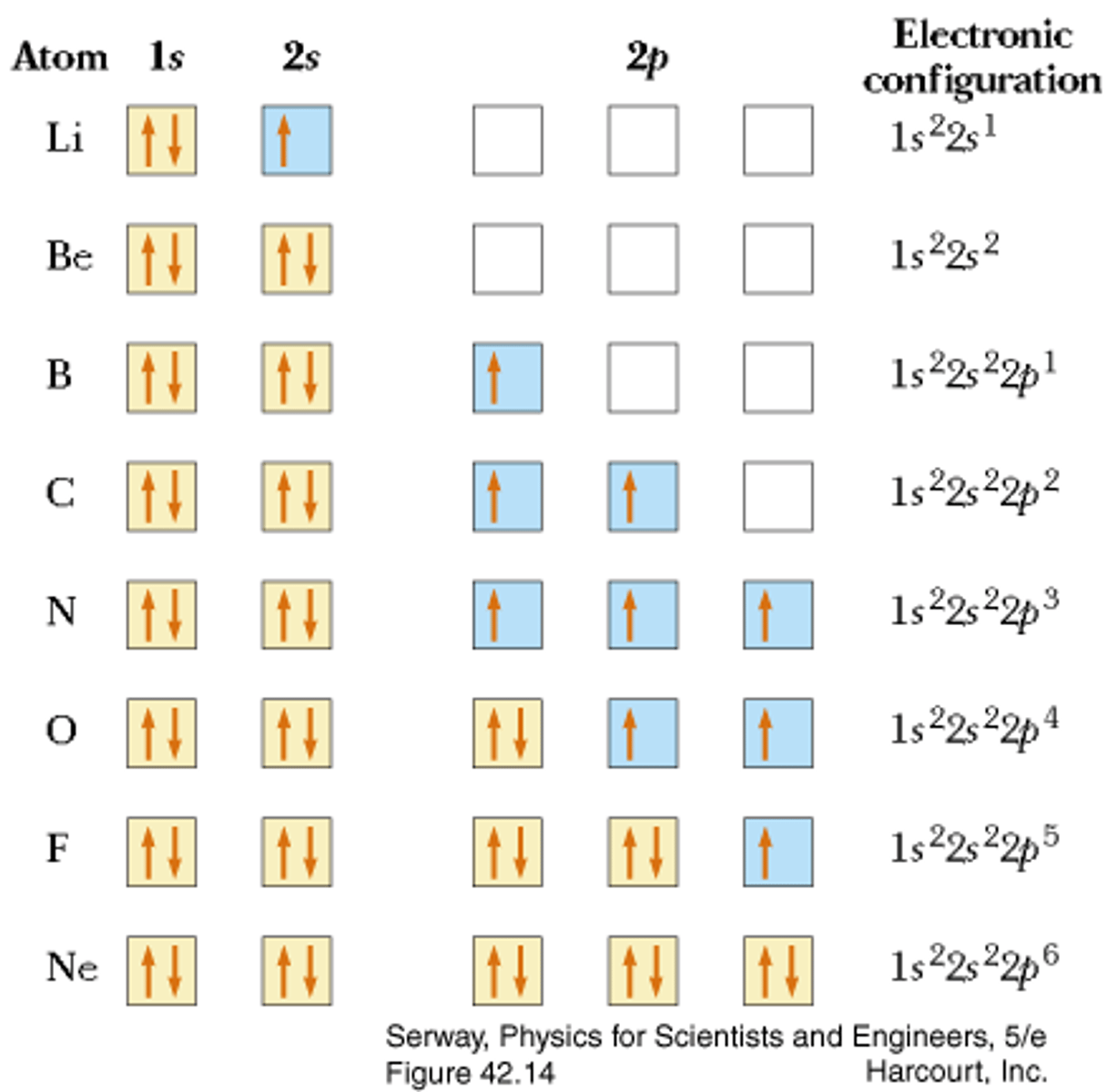
Aufbau Principle
the rule that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first

electron configuration
the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom, detailed list of how electrons fill levels/sublevels/and orbitals about the nucleus
Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge, partly a wave/partly a particle
photoelectric effect
The emission of electrons from a material when light of certain frequencies shines on the surface of the material
purple has higher frequency, red lower so purple ejects electrons, red rarely does